- Occludin
-
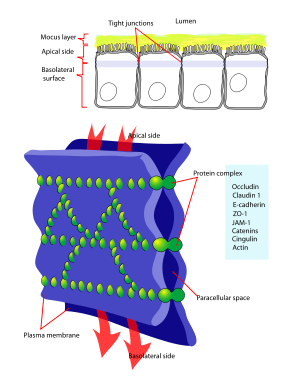
Occludin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OCLN gene.[1][2] Occludin is a 65-kDa (522-amino acid polypeptide -human) integral plasma-membrane protein located at the tight junctions, described for the first time in 1993 by Shoichiro Tsukita.[3] Together with the Claudin group of proteins, it is the main component of the tight junctions.
Contents
Structure
According to its overall hydrophilicity, occludin appears to span the plasma membrane four times, forming two extracellular loops and exposing its NH2 and COOH terminus to the cytosol. Interaction of occludin with several cytoplasmic proteins of the junctional plaque has been found to occur via its COOH terminus, while the extracellular loops are thought to be involved in the regulation of paracellular permeability and cell adhesion. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation plays a major role in regulation of occludin and tight junctions.
Disease linkage
Disruption of occludin regulation is an important aspect of a number of diseases. Strategies to prevent and/or reverse occludin downregulation may be an important therapeutic target.
Interactions
Occludin has been shown to interact with Tight junction protein 2,[4][5][6] YES1[7] and Tight junction protein 1.[8][9]
References
- ^ Ando-Akatsuka Y, Saitou M, Hirase T, Kishi M, Sakakibara A, Itoh M, Yonemura S, Furuse M, Tsukita S (May 1996). "Interspecies diversity of the occludin sequence: cDNA cloning of human, mouse, dog, and rat-kangaroo homologues". J Cell Biol 133 (1): 43–47. doi:10.1083/jcb.133.1.43. PMC 2120780. PMID 8601611. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2120780.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: OCLN occludin". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4950.
- ^ Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993). "Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions". J. Cell Biol. 123 (6 Pt 2): 1777–1788. doi:10.1083/jcb.123.6.1777. PMC 2290891. PMID 8276896. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2290891.
- ^ Peng, Bi-Hung; Lee J Ching, Campbell Gerald A (Dec. 2003). "In vitro protein complex formation with cytoskeleton-anchoring domain of occludin identified by limited proteolysis". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (49): 49644–49651. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302782200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 14512431.
- ^ Itoh, M; Morita K, Tsukita S (Feb. 1999). "Characterization of ZO-2 as a MAGUK family member associated with tight as well as adherens junctions with a binding affinity to occludin and alpha catenin". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 274 (9): 5981–5986. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.9.5981. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10026224.
- ^ Wittchen, E S; Haskins J, Stevenson B R (Dec. 1999). "Protein interactions at the tight junction. Actin has multiple binding partners, and ZO-1 forms independent complexes with ZO-2 and ZO-3". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 274 (49): 35179–35185. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.49.35179. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10575001.
- ^ Chen, Yan-Hua; Lu Qun, Goodenough Daniel A, Jeansonne Beverly (Apr. 2002). "Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase c-Yes interacts with occludin during tight junction formation in canine kidney epithelial cells". Mol. Biol. Cell (United States) 13 (4): 1227–1237. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-08-0423. ISSN 1059-1524. PMC 102264. PMID 11950934. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=102264.
- ^ Fanning, A S; Jameson B J, Jesaitis L A, Anderson J M (Nov. 1998). "The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 273 (45): 29745–29753. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.45.29745. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9792688.
- ^ Rao, Radhakrishna K; Basuroy Shyamali, Rao Vijay U, Karnaky Jr Karl J, Gupta Akshay (Dec. 2002). "Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress". Biochem. J. (England) 368 (Pt 2): 471–81. doi:10.1042/BJ20011804. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1222996. PMID 12169098. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1222996.
Further reading
- Furuse M, Itoh M, Hirase T et al. (1994). "Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions". J. Cell Biol. 127 (6 Pt 1): 1617–1626. doi:10.1083/jcb.127.6.1617. PMC 2120300. PMID 7798316. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2120300.
- Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (1997). "Occludin confers adhesiveness when expressed in fibroblasts". J. Cell. Sci. 110 ( Pt 9): 1113–21. PMID 9175707.
- Kimura Y, Shiozaki H, Hirao M et al. (1997). "Expression of occludin, tight-junction-associated protein, in human digestive tract". Am. J. Pathol. 151 (1): 45–54. PMC 1857944. PMID 9212730. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1857944.
- Saitou M, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Itoh M et al. (1997). "Mammalian occludin in epithelial cells: its expression and subcellular distribution". Eur. J. Cell Biol. 73 (3): 222–31. PMID 9243183.
- Haskins J, Gu L, Wittchen ES et al. (1998). "ZO-3, a novel member of the MAGUK protein family found at the tight junction, interacts with ZO-1 and occludin". J. Cell Biol. 141 (1): 199–208. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.1.199. PMC 2132714. PMID 9531559. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2132714.
- Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA, Anderson JM (1998). "The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (45): 29745–29753. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.45.29745. PMID 9792688.
- Itoh M, Morita K, Tsukita S (1999). "Characterization of ZO-2 as a MAGUK family member associated with tight as well as adherens junctions with a binding affinity to occludin and alpha catenin". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (9): 5981–5986. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.9.5981. PMID 10026224.
- Jiang WG, Martin TA, Matsumoto K et al. (1999). "Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor decreases the expression of occludin and transendothelial resistance (TER) and increases paracellular permeability in human vascular endothelial cells". J. Cell. Physiol. 181 (2): 319–329. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199911)181:2<319::AID-JCP14>3.0.CO;2-S. PMID 10497311.
- Wittchen ES, Haskins J, Stevenson BR (2000). "Protein interactions at the tight junction. Actin has multiple binding partners, and ZO-1 forms independent complexes with ZO-2 and ZO-3". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (49): 35179–35185. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.49.35179. PMID 10575001.
- Kojima T, Sawada N, Chiba H et al. (2000). "Induction of tight junctions in human connexin 32 (hCx32)-transfected mouse hepatocytes: connexin 32 interacts with occludin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 266 (1): 222–229. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1778. PMID 10581193.
- Burns AR, Bowden RA, MacDonell SD et al. (2000). "Analysis of tight junctions during neutrophil transendothelial migration". J. Cell. Sci. 113 ( Pt 1): 45–57. PMID 10591624.
- Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K et al. (2000). "Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins". J. Cell Biol. 147 (6): 1351–1363. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.6.1351. PMC 2168087. PMID 10601346. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2168087.
- Singh U, Van Itallie CM, Mitic LL et al. (2000). "CaCo-2 cells treated with Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin form multiple large complex species, one of which contains the tight junction protein occludin". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (24): 18407–18417. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001530200. PMID 10749869.
- Marzioni D, Banita M, Felici A et al. (2001). "Expression of ZO-1 and occludin in normal human placenta and in hydatidiform moles". Mol. Hum. Reprod. 7 (3): 279–285. doi:10.1093/molehr/7.3.279. PMID 11228248.
- Andreeva AY, Krause E, Müller EC et al. (2001). "Protein kinase C regulates the phosphorylation and cellular localization of occludin". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (42): 38480–38486. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104923200. PMID 11502742.
- Papadopoulos MC, Saadoun S, Woodrow CJ et al. (2001). "Occludin expression in microvessels of neoplastic and non-neoplastic human brain". Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 27 (5): 384–395. doi:10.1046/j.0305-1846.2001.00341.x. PMID 11679090.
- Schmidt A, Utepbergenov DI, Krause G, Blasig IE (2001). "Use of surface plasmon resonance for real-time analysis of the interaction of ZO-1 and occludin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 288 (5): 1194–1199. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5914. PMID 11700038.
- Pummi K, Malminen M, Aho H et al. (2001). "Epidermal tight junctions: ZO-1 and occludin are expressed in mature, developing, and affected skin and in vitro differentiating keratinocytes". J. Invest. Dermatol. 117 (5): 1050–1058. doi:10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01493.x. PMID 11710912.
- Traweger A, Fang D, Liu YC et al. (2002). "The tight junction-specific protein occludin is a functional target of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase itch". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (12): 10201–10208. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111384200. PMID 11782481.
PDB gallery External links
- Vivian Tang. "OCCLUDIN in Focus". www.Zonapse.Net. http://www.zonapse.net/occludin. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- Vivian Tang. "Tight Junction Overview". www.Zonapse.Net. http://www.zonapse.net/tight_junction. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
Histology: Epithelial proteins (TH H1.00.01.1) Lateral/cell-cell Cell adhesion molecules: Adherens junction (Cadherin) · Desmosome (Desmoglein)
Ion channels: Gap junction/Connexon (Connexin)
Cytoskeleton: Desmosome (Desmoplakin, Plakoglobin, Tonofibril)
other membrane proteins: Tight junction (Claudin, Occludin, MARVELD2)Basal/cell-matrix Apical Categories:- Human proteins
- Membrane protein stubs
- Cell biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.