- Lymphedema
-
Lymphedema Classification and external resources ICD-10 I89.0, I97.2, Q82.0 ICD-9 457.0, 457.1, 757.0 OMIM 153100 DiseasesDB 7679 eMedicine derm/958 MeSH D008209 Lymphedema (lymphoedema in British English), also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system.
The lymphatic system returns the interstitial fluid to the thoracic duct and then to the bloodstream, where it is recirculated back to the tissues.
Tissues with lymphedema are at risk of infection.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include severe fatigue, a heavy swollen limb or localized fluid accumulation in other body areas, including the head or neck, discoloration of the skin overlying the lymphedema, and eventually deformity (elephantiasis).
Lymphedema should not be confused with edema arising from venous insufficiency, which is not lymphedema. However, untreated venous insufficiency can progress into a combined venous/lymphatic disorder which is treated the same way as lymphedema.
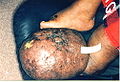
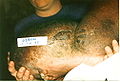
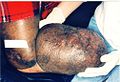
Presented here is an extreme case of severe unilateral hereditary lymphedema which had been present for 25 years without treatment:
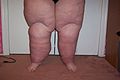
Presented here is a severe case of combined primary lymphedema and lipedema (Stage 3) before and after treatments:[1]
Causes
Lymphedema may be inherited (primary) or caused by injury to the lymphatic vessels (secondary). It is most frequently seen after lymph node dissection, surgery and/or radiation therapy, in which damage to the lymphatic system is caused during the treatment of cancer, most notably breast cancer. In many patients with cancer, this condition does not develop until months or even years after therapy has concluded. Lymphedema may also be associated with accidents or certain diseases or problems that may inhibit the lymphatic system from functioning properly. In tropical areas of the world, a common cause of secondary lymphedema is filariasis, a parasitic infection. It can also be caused by a compromising of the lymphatic system resulting from cellulitis.
While the exact cause of primary lymphedema is still unknown, it generally occurs due to poorly developed or missing lymph nodes and/or channels in the body. Lymphedema may be present at birth, develop at the onset of puberty (praecox), or not become apparent for many years into adulthood (tarda). In men, lower-limb primary lymphedema is most common, occurring in one or both legs. Some cases of lymphedema may be associated with other vascular abnormalities.
Secondary lymphedema affects both men and women. In women, it is most prevalent in the upper limbs after breast cancer surgery and lymph node dissection, occurring in the arm on the side of the body in which the surgery is performed. Head and neck lymphedema can be caused by surgery or radiation therapy for tongue or throat cancer. It may also occur in the lower limbs or groin after surgery for colon, ovarian or uterine cancer, in which removal of lymph nodes or radiation therapy is required. Surgery or treatment for prostate, colon and testicular cancers may result in secondary lymphedema, particularly when lymph nodes have been removed or damaged.
The onset of secondary lymphedema in patients who have had cancer surgery has also been linked to aircraft flight (likely due to decreased cabin pressure). For cancer survivors, therefore, wearing a prescribed and properly fitted compression garment may help decrease swelling during air travel.
Some cases of lower-limb lymphedema have been associated with the use of tamoxifen, due to the blood clots and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) that can be caused by this medication. Resolution of the blood clots or DVT is needed before lymphedema treatment can be initiated.
Pathophysiology
The flow of lymph from the legs towards the heart is the result of the soleus muscle also known as the calf pump. As a person walks, the soleus contracts, squeezing lymph out of the leg via the lymphatic vessels. When the muscle relaxes, valves in the vessels shut preventing the fluid from returning to the lower extremities.[2] The lymph from the legs is filtered through the inguinal nodes in the groin area on its way to the thoracic duct. Blockage of the inguinal nodes can contribute to swelling in the legs. From the thoracic duct, the lymph is returned to the venous circulation through the left subclavian vein.[3]
Diagnosis
Assessment of the lower extremities begins with a visual inspection of the legs. Color, presence of hair, visible veins, size of the legs and any sores or ulcerations should be noted. Lack of hair may indicate an arterial circulation problem.[2] If swelling is observed, the calf circumference should be measured with a tape measure. This measurement can be compared to future measurements to see if the swelling is getting better. Determine if elevating the legs makes the swelling go away. Pressure should be applied with the fingertips over the ankle to determine the degree of swelling. The assessment should also include a check of the popliteal, femoral, posterior tibial, and dorsalis pedis pulses. When checking the femoral pulse, feel for the inguinal nodes and determine if they are enlarged. Enlargement of the nodes lasting more than three weeks may indicate infection or some other disease process requiring further medical attention.[4]
The diagnosis or early detection of lymphedema is difficult. The first signs may be subjective observations such as "my arm feels heavy" or "I have difficulty these days getting rings on and off my fingers". These may be symptomatic of early stage of lymphoedema where accumulation of lymph is mild and not detectable by any difference in arm volume or circumference. As lymphedema develops further, definitive diagnosis is commonly based upon an objective measurement of difference between the affected or at-risk limb at the opposite unaffected limb, e.g. in volume or circumference. Unfortunately, there is no generally accepted worldwide criterion of difference definitively diagnostic, although a volume difference of 200 ml between limbs or a 4 cm (at a single measurement site or set intervals along the limb) is often used. Recently, the technique of bioimpedance measurement (which measures the amount of fluid in a limb) has been shown to have greater sensitivity than these existing methods, and holds promise as a simple diagnostic and screening tool.[5] Impedance analysers specifically designed for this purpose are now commercially available.
Stages
Whether primary or secondary, lymphedema develops in stages, from mild to severe. Methods of staging are numerous and inconsistent. They ranged from three to as many as eight stages.
The most common method of staging was defined by the Fifth WHO Expert Committee on Filariasis:[6][7]
- Stage 0 (latent): The lymphatic vessels have sustained some damage which is not yet apparent. Transport capacity is still sufficient for the amount of lymph being removed. Lymphedema is not present.
- Stage 1 (spontaneously reversible): Tissue is still at the "non- pitting" stage: when pressed by the fingertips, the tissue bounces back without any indentation. Usually upon waking in the morning, the limb or affected area is normal or almost normal in size.
- Stage 2 (spontaneously irreversible): The tissue now has a spongy consistency and is considered "pitting": when pressed by the fingertips, the affected area indents and holds the indentation. Fibrosis found in Stage 2 lymphedema marks the beginning of the hardening of the limbs and increasing size.
- Stage 3 (lymphostatic elephantiasis): At this stage, the swelling is irreversible and usually the limb(s) or affected area is very large. The tissue is hard (fibrotic) and unresponsive; some patients consider undergoing reconstructive surgery, called "debulking". This remains controversial, however, since the risks may outweigh the benefits, and the further damage done to the lymphatic system may in fact make the lymphedema worse.
A new staging system has been set forth by Lee, Morgan and Bergan[8] and endorsed by the American Society of Lymphology.[citation needed] This provides a clear technique which can be employed by clinical and laboratory assessments to more accurately diagnose and prescribe therapy for lymphedema. In this improved version, four stages are identified (I-IV). Physicians and researchers can use additional laboratory assessments, such as bioimpedance, MRI, or CT, to build on the findings of a clinical assessment (physical evaluation). From this, results of therapy can be accurately be determined and reported in documentation, as well as research.
Risk is another measurement altogether. Current research using bioimpedance to measure risk of lymphedema is very promising.
Grades
Lymphedema can also be categorized by its severity (usually referenced to a healthy extremity):[citation needed]
- Grade 1 (mild edema): Lymphedema involves the distal parts such as a forearm and hand or a lower leg and foot. The difference in circumference is less than 4 centimeters, and other tissue changes are not yet present.
- Grade 2 (moderate edema): Lymphedema involves an entire limb or corresponding quadrant of the trunk. Difference in circumference is more than 4 but less than 6 centimeters. Tissue changes, such as pitting, are apparent. The patient may experience erysipelas.
- Grade 3a (severe edema): Lymphedema is present in one limb and its associated trunk quadrant. The difference in circumference is greater than 6 centimeters. Significant skin alterations, such as cornification or keratosis, cysts and/or fistulae, are present. Additionally, the patient may experience repeated attacks of erysipelas.
- Grade 3b (massive edema): The same symptoms as grade 3a, except two or more extremities are affected.
- Grade 4 (gigantic edema): Also known as elephantiasis, in this stage of lymphedema, the affected extremities are huge due to almost complete blockage of the lymph channels. Elephantiasis may also affect the head and face.
Treatment
Treatment for lymphedema varies depending on the severity of the edema and the degree of fibrosis of the affected limb. Most people with lymphedema follow a daily regimen of treatment as suggested by their physician or certified lymphedema therapist. The most common treatments for lymphedema are a combination of manual compression lymphatic massage, compression garments or bandaging. Complex decongestive physiotherapy is an empiric system of lymphatic massage, skin care, and compressive garments. Although a combination treatment program may be ideal, any of the treatments can be done individually.
Compression
Garments
Elastic compression garments are worn by persons with lymphedema on the affected limb following complete decongestive therapy to maintain edema reduction. Depending on the therapist's discretion, a compression garment may be custom-fit or purchased in over-the-counter, standard sizes. Compression garments are meant to be worn every day to maintain edema reduction and must be replaced on a regular basis. Support garments may be the only Garment of Choice for patients with Scrotal edema.
Bandaging or wrapping
Compression bandaging, also called wrapping, is the application of several layers of padding and short-stretch bandages to the involved areas. Short-stretch bandages are preferred over long-stretch bandages (such as those normally used to treat sprains), as the long-stretch bandages cannot produce the proper therapeutic tension necessary to safely reduce lymphedema and may in fact end up producing a tourniquet effect. During activity, whether exercise or daily activities, the short-stretch bandages enhance the pumping action of the lymph vessels by providing increased resistance for them to push against. This encourages lymphatic flow and helps to soften fluid-swollen areas.
Sequential gradient pump therapy
Compression pump technology utilizes a multi-chambered pneumatic sleeve with overlapping cells to promote movement of lymph fluid. Pump therapy may be used in addition to other treatments such as compression bandaging and manual lymph drainage. In many cases, pump therapy may help soften fibrotic tissue and therefore potentially enable more efficient lymphatic drainage. Sequential pump therapy may also be used as a home treatment method, usually as part of a regimen also involving compression garments or wrapping.
A Stanford University medical study showed that patients receiving the combined modalities of MLD/CDT and pneumatic pumping had a greater overall reduction in limb volume than patients receiving only MLD/CDT.[9] However, some therapists have begun to raise concern that compression pumps can cause genital swelling when used on persons with leg lymphedema.
Complete decongestive therapy or manual lymph drainage
Complete decongestive therapy (CDT) is a primary tool in lymphedema management consisting of manual manipulation of the lymphatic ducts,[10] short stretch compression bandaging, therapeutic exercise, and skin care. The technique was pioneered by Emil Vodder in the 1930s for the treatment of chronic sinusitis and other immune disorders. Initially, CDT involves frequent visits to a certified therapist with a doctor's prescription. Once the lymphedema is reduced, increased patient participation is required for ongoing care, along with the use of elastic compression garments and non-elastic directional flow foam garments.
Manual manipulation of the lymphatic ducts consists of gentle, rhythmic massaging of the skin to stimulate the flow of lymph and its return to the blood circulation system. In the blood’s passage through the kidneys, the excess fluid is filtered out and eliminated from the body through urination. The treatment is very gentle and a typical session will involve drainage of the neck, trunk, and involved extremity (in that order), lasting approximately 40 to 60 minutes. CDT is generally effective on non-fibrotic lymphedema and less effective on more fibrotic legs, although it has been shown to help break up fibrotic tissue.
Surgical techniques
Surgical techniques for correcting lymphedema may be excisional or physiological. However, surgery for lymphedema does not cure the disease or eliminate the need for decongestive treatment. Surgical treatment is used only in extreme cases in order to reduce the weight of the affected limb, to help minimize the frequency of inflammatory attacks, to improve cosmesis, and to potentially reduce the risk of secondary angiosarcoma.[10] Although surgery has shown to reduce edema in the short-term, there is a lack of evidence to suggest that it is beneficial in the long-term. Excisional techniques include:
- Circumferential excision of the lymphedematous tissue followed by skin grafting (Charles technique); longitudinal removal of the affected segment of skin and subcutaneous tissue and primary closure (Homans technique); excision of subcutaneous tissue and tunneling of a dermal flap through the fascia into a muscular compartment of the leg (Thompson technique).
- Lympholymphatic anastomosis (autologous lymphatic grafts to bridge obstructed lymphatic segments); lymphovenous shunt (anastomosis of lymphatic channels to veins); lymphangioplasty enteromesenteric flap omental transfer (pedicled portion of omentum transposed to the affected limb).
- Modified liposuction has been developed in Sweden in recent years to remove adipose tissue associated with longstanding lymphedema, primarily in the upper region. This technique is meant to reduce the volume of a limb and does not cure lymphedema. Compression garments and compression bandages must still be worn after the operation.
Low level laser therapy
Low level laser therapy (LLLT) has been cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of lymphedema in November 2006.[11]
According to the US National Cancer Institute,
Studies suggest that low-level laser therapy may be effective in reducing lymphedema in a clinically meaningful way for some women. Two cycles of laser treatment were found to be effective in reducing the volume of the affected arm, extracellular fluid, and tissue hardness in approximately one-third of patients with postmastectomy lymphedema at 3 months posttreatment. Suggested rationales for laser therapy include a potential decrease in fibrosis, stimulation of macrophages and the immune system, and a possible role in encouraging lymphangiogenesis.[12][13]
Early prevention and disease regression in breast cancer
In 2008 an NIH study revealed that early diagnosis of lymphedema in breast cancer patients (called stage 0 in the article) associated with an early intervention, a compression sleeve and gauntlet for 1 month, led to a return to preoperative baseline status. In a 5-year followup patients remained at their preoperative baseline, suggesting that preclinical detection of lymphedema can halt if not reverse its progression.
Complications
When the lymphatic impairment becomes so great that the lymph fluid exceeds the lymphatic system's ability to transport it, an abnormal amount of protein-rich fluid collects in the tissues of the affected area. Left untreated, this stagnant, protein-rich fluid causes tissue channels to increase in size and number, reducing the availability of oxygen. This interferes with wound healing and provides a rich culture medium for bacterial growth that can result in infections: cellulitis, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, and in severe cases, skin ulcers. It is vital for lymphedema patients to be aware of the symptoms of infection and to seek treatment at the first signs, since recurrent infections or cellulitis, in addition to their inherent danger, further damage the lymphatic system and set up a vicious circle.
In rare cases, lymphedema can lead to a form of cancer called lymphangiosarcoma, although the mechanism of carcinogenesis is not understood. Lymphedema-associated lymphangiosarcoma is called Stewart-Treves syndrome. Lymphangiosarcoma most frequently occurs in cases of long-standing lymphedema. The incidence of angiosarcoma is estimated to be 0.45% in patients living 5 years after radical mastectomy.[14][15] Lymphedema is also associated with a low grade form of cancer called retiform hemangioendothelioma (a low grade angiosarcoma).[16]
Since lymphedema is disfiguring, causes difficulties in daily living and can lead to lifestyle becoming severely limited, it may also result in psychological distress.
See also
- Congenital lymphedema
- Lymphotherapy
References
- ^ Photos courtesy of Amy's Lymphedema Story
- ^ a b Jarvis, C. (2004). Physical Examination and Health Assessment (fifth ed.). St. Louis, Missouri: Saunders Elsevier. pp. 530–553. ISBN 1416051880.
- ^ Brunner, L.; Suddarth, D. (1988). Textbook of Medical Surgical Nursing (sixth ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: JB Lippincott Company. p. 659. ISBN 0781799899.
- ^ Jarvis, C. (2004). Physical Examination and Health Assessment (fifth ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Saunders Elsevier. pp. 530–553. ISBN 1416051880.
- ^ Ward, Leigh C (2006). "Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Proven Utility in Lymphedema Risk Assessment and Therapeutic Monitoring". Lymphatic Research and Biology 4 (1): 51–6. doi:10.1089/lrb.2006.4.51. PMID 16569209.
- ^ "Lymphatic filariasis: The disease and its control. Fifth report of the WHO Expert Committee on Filariasis". World Health Organization technical report series 821: 1–71. 1992. PMID 1441569.
- ^ http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2001/WHO_CDS_CPE_CEE_2001.26a.pdf
- ^ Benoit Blondeau; Lawrence L Tretbar; Morgan, Cheryl E.; Simon J. Simonian (2007). Lymphedema: Diagnosis and Treatment. Springer. ISBN 1-84628-548-8.[page needed]
- ^ Szuba, Andrzej; Achalu, Radha; Rockson, Stanley G. (2002). "Decongestive lymphatic therapy for patients with breast carcinoma-associated lymphedema". Cancer 95 (11): 2260–7. doi:10.1002/cncr.10976. PMID 12436430.
- ^ a b http://www.lymphnet.org/pdfDocs/nlntreatment.pdf
- ^ dotmed.com December 27, 2006 Low Level Laser FDA Cleared for the Treatment of Lymphedema. (accessed 9 November 09)
- ^ National Cancer Institute: Low-level laser therapy accessed 9 November 09
- ^ Carati, Colin J.; Anderson, Sandy N.; Gannon, Bren J.; Piller, Neil B. (2003). "Treatment of postmastectomy lymphedema with low-level laser therapy". Cancer 98 (6): 1114–22. doi:10.1002/cncr.11641. PMID 12973834.
- ^ Martin, MB; Kon, ND; Kawamoto, EH; Myers, RT; Sterchi, JM (1984). "Postmastectomy angiosarcoma". The American surgeon 50 (10): 541–5. PMID 6541442.
- ^ Chopra, S; Ors, F; Bergin, D (2007). "MRI of angiosarcoma associated with chronic lymphoedema: Stewart Treves syndrome". British Journal of Radiology 80 (960): e310–3. doi:10.1259/bjr/19441948. PMID 18065640.
- ^ Requena, Luis; Sangueza, Omar P. (1998). "Cutaneous vascular proliferations. Part III. Malignant neoplasms, other cutaneous neoplasms with significant vascular component, and disorders erroneously considered as vascular neoplasms". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 38 (2): 143–75; quiz 176–8. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70237-3. PMID 9486670.
External links
- Lymphedema at the Open Directory Project
Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARUngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixEB
and relatedJEB (JEB-H, Mitis, Generalized atrophic, JEB-PA)related: Costello syndrome · Kindler syndrome · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome · Skin fragility syndrome ·Naegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromeHyperkeratosis/
keratinopathydiffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkPathology: lymphatic disease: Lymphatic vessel disease (I88–I89, 457) Lymph vessels Lymphedema: Primary lymphedema (Congenital lymphedema, Lymphedema praecox, Lymphedema tarda, Lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome, Milroy's disease) · Secondary lymphedema (Bullous lymphedema, Factitial lymphedema, Postinflammatory lymphedema, Postmastectomy lymphangiosarcoma)
Waldmann diseasePathology: hemodynamics Decreases general: Anemic infarct · Hemorrhagic infarct
regional: Myocardial infarction · Cerebral infarction · Splenic infarction · Limb infarctionIncreases general Bruise/Hematoma: Petechia · Purpura · Ecchymosis
regional: head (Epistaxis, Hemoptysis, Intracranial hemorrhage, Hyphema, Subconjunctival hemorrhage) · torso (Hemothorax, Hemopericardium, Pulmonary hematoma) · abdomen (Gastrointestinal bleeding, Haemobilia, Hemoperitoneum, Hematocele, Hematosalpinx ) · joint (Hemarthrosis)general: Anasarca · Angioedema/Lymphedema · Exudate/Transudate
regional: Cerebral edema · Pulmonary edema · Hydrothorax · Ascites/hydroperitoneum · HydrosalpinxOtherCategories:- Lymphatic system
- Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
- Disability
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.