- Zunich–Kaye syndrome
-
Zunich-Kaye syndrome Classification and external resources ICD-10 GroupMajor.minor ICD-9 xxx OMIM 280000 DiseasesDB 32624 Zunich–Kaye syndrome, also known as Zunich neuroectodermal syndrome, is a rare congenital ichthyosis first described in 1983.[1] It is also referred to as CHIME syndrome, after its main symptoms (colobomas, heart defects, ichthyosiform dermatosis, mental retardation, and either ear defects or epilepsy).[2] It is a congenital[3] syndrome with only a few cases studied and published.[2]
Contents
Symptoms
Associated symptoms range from things such as colobomas of the eyes, heart defects, ichthyosiform dermatosis, mental retardation, and ear abnormalities. Further symptoms that may be suggested include characteristic facies, hearing loss, and cleft palate.
Genetics
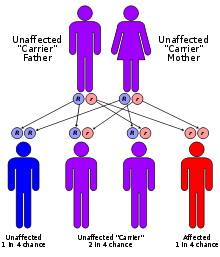
Zunich-Kay syndrome is considered to have an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and two copies of the gene, one from each parent, are required to inherit the disorder. The parents of an individual with autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not have the disorder.
Treatment
Treatment with isotretinoin may induce substantial resolution of skin lesions, but the risk of secondary infection remains.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Zunich J, Kaye CI (1983). "New syndrome of congenital ichthyosis with neurologic abnormalities". Am. J. Med. Genet. 15 (2): 331–3, 335. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320150217. PMID 6192719.
- ^ a b c OrphaNet entry
- ^ Birth Disorder Information Directory - Z
Bibliography
- Schnur RE, Greenbaum BH, Heymann WR, Christensen K, Buck AS, Reid CS (1997). "Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a child with the CHIME neuroectodermal dysplasia syndrome". Am. J. Med. Genet. 72 (1): 24–9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19971003)72:1<24::AID-AJMG5>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID 9295069.
- Shashi V, Zunich J, Kelly TE, Fryburg JS (1995). "Neuroectodermal (CHIME) syndrome: an additional case with long term follow up of all reported cases". J. Med. Genet. 32 (6): 465–9. doi:10.1136/jmg.32.6.465. PMC 1050487. PMID 7666399. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1050487.
- Zunich J, Esterly NB, Holbrook KA, Kaye CI (1985). "Congenital migratory ichthyosiform dermatosis with neurologic and ophthalmologic abnormalities". Arch Dermatol 121 (9): 1149–56. doi:10.1001/archderm.121.9.1149. PMID 4037840.
- Zunich J, Esterly NB, Kaye CI (1988). "Autosomal recessive transmission of neuroectodermal syndrome". Arch Dermatol 124 (8): 1188–9. doi:10.1001/archderm.124.8.1188. PMID 3041916.
- Zunich J, Kaye CI (1984). "Additional case report of new neuroectodermal syndrome". Am. J. Med. Genet. 17 (3): 707–10. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320170324. PMID 6711621.
Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARUngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixEB
and relatedJEB (JEB-H, Mitis, Generalized atrophic, JEB-PA)related: Costello syndrome · Kindler syndrome · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome · Skin fragility syndrome ·Naegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromeHyperkeratosis/
keratinopathydiffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkCategories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Rare diseases
- Syndromes
- Genodermatoses
- Genetic disorders with OMIM but no gene
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.