- Naxos syndrome
-
Naxos syndrome Classification and external resources 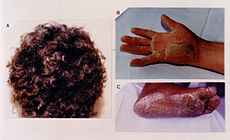
Cutaneous phenotype of Naxos disease: woolly hair (A), palmar (B) and plantar (C) keratoses.OMIM 601214 Naxos syndrome (also known as "Diffuse non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and cardiomyopathy,"[1] "Diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma with woolly hair and arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy firstly described in Naxos island by Dr Nikos Protonotarios,"[1] and "Naxos disease"[1]) is a cutaneous condition characterized by a palmoplantar keratoderma.[1] The prevalence of the syndrome is about 1 person in 1000 in the Hellenic islands.
It has been associated with mutations in the genes encoding desmoplakin and plakoglobin.[2]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ McKoy G, Protonotarios N, Crosby A, et al. (June 2000). "Identification of a deletion in plakoglobin in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy with palmoplantar keratoderma and woolly hair (Naxos disease)". Lancet 355 (9221): 2119–24. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02379-5. PMID 10902626. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(00)02379-5.
Categories:- Dermatology stubs
- Genodermatoses
- Palmoplantar keratodermas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
