- Kindler syndrome
-
Kindler syndrome Classification and external resources OMIM 173650 DiseasesDB 32778 eMedicine derm/943 Kindler syndrome (also known as "Bullous acrokeratotic poikiloderma of Kindler and Weary,"[1], "Congenital poikiloderma with blisters and keratoses,"[1] "Congenital poikiloderma with bullae and progressive cutaneous atrophy,"[1] "Hereditary acrokeratotic poikiloderma,"[1] "Hyperkeratosis–hyperpigmentation syndrome,"[2]:511 "Acrokeratotic poikiloderma," and "Weary–Kindler syndrome"[3]:558) is a rare congenital disease of the skin caused by a mutation in the KIND1 gene.
Contents
Diagnosis
Infants and young children with Kindler syndrome have a tendency to blister with minor trauma and are prone to sunburns. As individuals with Kindler syndrome age, they tend to have fewer problems with blistering and photosensitivity. However, pigment changes and thinning of the skin become more prominent.[citation needed]
Genetics
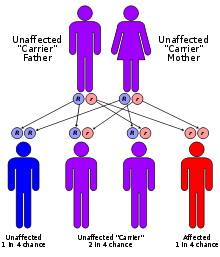
Kindler syndrome is an autosomal recessive genodermatosis. The KIND1 gene mutated in Kindler syndrome codes for the protein kindlin-1, which is thought to be active in the interactions between actin and the extracellular matrix.[4] Kindler syndrome was first described in 1954 by Theresa Kindler.[5]
See also
- Rothmund–Thomson syndrome
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- ^ a b c d Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071380760.
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0721629210.
- ^ Siegel, Dh; Ashton, Gh; Penagos, Hg; Lee, Jv; Feiler, Hs; Wilhelmsen, Kc; South, Ap; Smith, Fj; Prescott, Ar; Wessagowit, V; Oyama, N; Akiyama, M; Al, Aboud, D; Al, Aboud, K; Al, Githami, A; Al, Hawsawi, K; Al, Ismaily, A; Al-Suwaid, R; Atherton, Dj; Caputo, R; Fine, Jd; Frieden, Ij; Fuchs, E; Haber, Rm; Harada, T; Kitajima, Y; Mallory, Sb; Ogawa, H; Sahin, S; Shimizu, H; Suga, Y; Tadini, G; Tsuchiya, K; Wiebe, Cb; Wojnarowska, F; Zaghloul, Ab; Hamada, T; Mallipeddi, R; Eady, Ra; Mclean, Wh; Mcgrath, Ja; Epstein, Eh (July 2003). "Loss of Kindlin-1, a Human Homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans Actin–Extracellular-Matrix Linker Protein UNC-112, Causes Kindler Syndrome". American journal of human genetics 73 (1): 174–87. doi:10.1086/376609. ISSN 0002-9297. PMC 1180579. PMID 12789646. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1180579.
- ^ Kindler T (1954). "Congenital poikiloderma with traumatic bulla formation and progressive cutaneous atrophy". Br. J. Dermatol. 66 (3): 104–11. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1954.tb12598.x. PMID 13149722.
External links
Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARUngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixEB
and relatedNaegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromeHyperkeratosis/
keratinopathydiffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkArrestin Myelin Pulmonary surfactant Cell adhesion molecule IgSF CAM: OFC7
Cadherin: DSG1 (Striate palmoplantar keratoderma 1) · DSG2 (Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia 10) · DSG4 (LAH1) · DSC2 (Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia 11)
Integrin: see cell surface receptor deficienciesTetraspanin TSPAN7 (X-Linked mental retardation 58) · TSPAN12 (Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy 5)Other KIND1 (Kindler syndrome) · HFE (HFE hereditary hemochromatosis) · DYSF (Distal muscular dystrophy, Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2B)Categories:- Genodermatoses
- Rare diseases
- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Papulosquamous hyperkeratotic cutaneous conditions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.