- Mastocytosis
-
Mastocytosis Classification and external resources 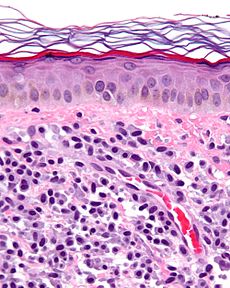
Micrograph of mastocytosis. Skin biopsy. H&E stain.ICD-10 Q82.2, C96.2 ICD-9 757.33, 202.6 ICD-O: 9741/3 OMIM 154800 DiseasesDB 7864 eMedicine derm/258 med/1401 MeSH D008415 Mastocytosis is a group of rare disorders of both children and adults caused by the presence of too many mast cells (mastocytes) and CD34+ mast cell precursors in a person's body.[1]
Contents
Classification
Mastocytosis can occur in a variety of forms:
- Most cases are cutaneous (confined to the skin only), and there are several forms. The most common cutaneous mastocytosis is urticaria pigmentosa (UP), more common in children. Telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans (TMEP) is a much rarer form of cutaneous mastocytosis that affects adults.[2]
- Systemic mastocytosis involves the internal organs, usually in addition to involving the skin. Mast cells collect in various tissues and can affect organs such as the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.
- Other types of mast cell disease include:
Signs and symptoms
When too many mast cells exist in a person's body and undergo degranulation, the additional chemicals can cause a number of symptoms which can vary over time and can range in intensity from mild to severe. Because mast cells play a role in allergic reactions, the symptoms of mastocytosis often are similar to the symptoms of an allergic reaction. They may include, but are not limited to:[3]
- Fatigue
- Skin lesions (urticaria pigmentosa) and itching
- Abdominal discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Food and drug intolerance
- Olfactive intolerance
- Infections (bronchitis, rhinitis, and conjunctivitis)
- Ear/nose/throat inflammation
- Anaphylaxis (shock from allergic or immune causes)
- Episodes of very low blood pressure (including shock) and faintness
- Bone or muscle pain
- Decreased bone density
- Headache
- Ocular discomfort
- Malabsorption
Pathophysiology
Mast cells are located in connective tissue, including the skin, the linings of the stomach and intestine, and other sites. They play an important role in helping defend these tissues from disease. By releasing chemical "alarms" such as histamine, mast cells attract other key players of the immune defense system to areas of the body where they are needed.
Mast cells seem to have other roles as well. Because they gather together around wounds, mast cells may play a part in wound healing. For example, the typical itching felt around a healing scab may be caused by histamine released by mast cells. Researchers also think mast cells may have a role in the growth of blood vessels (angiogenesis). No one with too few or no mast cells has been found, which indicates to some scientists we may not be able to survive with too few mast cells.
Mast cells express a cell surface receptor, c-kit[4] (CD117), which is the receptor for stem cell factor (scf). In laboratory studies, scf appears to be important for the proliferation of mast cells. Mutations of the c-kit receptor, leading to uncontrolled stimulation of the receptor, is a cause for the disease. Inhibiting the tyrosine kinase receptor with imatinib (see below) may reduce the symptoms of mastocytosis.
Diagnosis
Doctors can diagnose urticaria pigmentosa (cutaneous mastocytosis, see above) by seeing the characteristic lesions that are dark-brown and fixed. A small skin sample (biopsy) may help confirm the diagnosis.
By taking a biopsy from a different organ, such as the bone marrow, the doctor can diagnose systemic mastocytosis. Using special techniques on a bone marrow sample, the doctor looks for an increase in mast cells. Another sign of this disorder is high levels of certain mast-cell chemicals and proteins in a person's blood and sometimes in the urine.
Epidemiology
No one is sure how many people have either type of mastocytosis, but mastocytosis generally has been considered to be an "orphan disease" (orphan diseases affect 200,000 or fewer people in the United States). Mastocytosis, however, often may be misdiagnosed, especially because it typically occurs secondary to another condition, and thus may occur more frequently than assumed.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for mastocytosis, but there are a number of medicines to help treat the symptoms:
- Antihistamines block receptors targeted by histamine released from mast cells. Both H1 and H2 blockers may be helpful.
- Leukotriene antagonists block receptors targeted by leukotrienes released from mast cells.
- Mast cell stabilizers help prevent mast cells from releasing their chemical contents. Cromolyn sodium oral solution (Gastrocrom / Cromoglicate) is the only medicine specifically approved by the U.S. FDA for the treatment of mastocytosis. Ketotifen is available in Canada and Europe, but is only available in the U.S. as eye drops (Zaditor).
- Proton pump inhibitors help reduce production of gastric acid, which is often increased in patients with mastocytosis. Excess gastric acid can harm the stomach, esophagus and small intestine.
- Epinephrine constricts blood vessels and opens airways to maintain adequate circulation and ventilation when excessive mast cell degranulation has caused anaphylaxis.
- Salbutamol and other beta-2 agonists open airways that can constrict in the presence of histamine.
- Corticosteroids can be used topically, inhaled, or systemically to reduce inflammation associated with mastocytosis.
- Antidepressants are an important and often overlooked tool in the treatment of mastocytosis. The stress and physical discomfort of any chronic disease may increase the likelihood of a patient developing depression. Depression and other neurological symptoms have been noted in mastocytosis.[5] Some antidepressants, such as doxepin, are themselves potent antihistamines and can help relieve physical as well as cognitive symptoms.
- Dihydropyridines, calcium channel blockers, are sometimes used to treat high blood pressure. At least one clinical study suggested nifedipine, one of the dihydropyridines, may reduce mast cell degranulation in patients who exhibit urticaria pigmentosa. A 1984 study by Fairly et al. included a patient with symptomatic urticaria pigmentosa who responded to nifedipine at dose of 10 mg po tid.[6] However, nifedipine has not been approved by the FDA for treatment of mastocytosis.
In rare cases in which mastocytosis is cancerous or associated with a blood disorder, the patient may have to use steroids and/or chemotherapy. The novel agent imatinib (Glivec or Gleevec) has been found to be effective in certain types of mastocytosis.[7]
There are clinical trials currently underway testing stem cell transplants as a form of treatment.
There are support groups for persons suffering from mastocytosis. Involvement can be emotionally therapeutic for some patients.
Research
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases scientists have been studying and treating patients with mastocytosis for several years at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Clinical Center.
Some of the most important research advances for this rare disorder include improved diagnosis of mast cell disease and identification of growth factors and genetic mechanisms responsible for increased mast cell production. Researchers are currently evaluating approaches to improve ways to treat mastocytosis.
Scientists also are focusing on identifying disease-associated mutations (changes in genes). NIH scientists have identified some mutations, which may help researchers understand the causes of mastocytosis, improve diagnosis, and develop better treatments.
History
Scientists first described urticaria pigmentosa in 1869.[8] Systemic mastocytosis was first reported by French scientists in 1936.[9]
See also
- Mast cell tumors are found in many species of animals.
References
- ^ Horny HP, Sotlar K, Valent P (2007). "Mastocytosis: state of the art". Pathobiology 74 (2): 121–32. doi:10.1159/000101711. PMID 17587883.
- ^ Ellis DL (1996). "Treatment of telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans with the 585-nm flashlamp-pumped dye laser". Dermatol Surg 22 (1): 33–7. doi:10.1016/1076-0512(95)00388-6. PMID 8556255.
- ^ Hermine O, Lortholary O, Leventhal PS, et al. (2008). Soyer, H. Peter. ed. "Case-Control Cohort Study of Patients' Perceptions of Disability in Mastocytosis". PLoS ONE 3 (5): e2266. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002266. PMC 2386235. PMID 18509466. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2386235.
- ^ Orfao A, Garcia-Montero AC, Sanchez L, Escribano L (2007). "Recent advances in the understanding of mastocytosis: the role of KIT mutations". Br. J. Haematol. 138 (1): 12–30. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06619.x. PMID 17555444.
- ^ Rogers MP, Bloomingdale K, Murawski BJ, Soter NA, Reich P, Austen KF (1986). "Mixed organic brain syndrome as a manifestation of systemic mastocytosis". Psychosom Med 48 (6): 437–47. PMID 3749421. http://www.psychosomaticmedicine.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=3749421.
- ^ Fairley JA, Pentland AP, Voorhees JJ (1984). "Urticaria pigmentosa responsive to nifedipine". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 11 (4 Pt 2): 740–3. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(84)70233-7. PMID 6491000.
- ^ Droogendijk HJ, Kluin-Nelemans HJ, van Doormaal JJ, Oranje AP, van de Loosdrecht AA, van Daele PL (2006). "Imatinib mesylate in the treatment of systemic mastocytosis: a phase II trial". Cancer 107 (2): 345–51. doi:10.1002/cncr.21996. PMID 16779792.
- ^ Nettleship E, Tay W (1869). "Reports of Medical and Surgical Practice in the Hospitals of Great Britain". Br Med J 2 (2): 323–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.455.323. PMC 2260962. PMID 20745623. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2260962.
- ^ Sézary A, Levy-Coblentz G, Chauvillon P (1936). "Dermographisme et mastocytose". Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphilol 43: 359–61.
- Based on an informative page by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
External links
Myeloid hematological malignancy/leukemia histology (ICD-O 9590–9989, C81–C96, 200–208) CFU-GM/
and other granulocytesCFU-GMOtherCFU-BasoCFU-EosMEP CFU-MegCFU-EMD (Refractory anemia, Refractory anemia with excess of blasts, Chromosome 5q deletion syndrome, Sideroblastic anemia, Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia)CFU-Mast Mastocytosis: Diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis · Erythrodermic mastocytosis · Generalized eruption of cutaneous mastocytosis (adult type) · Generalized eruption of cutaneous mastocytosis (childhood type) · Mast cell sarcoma · Solitary mastocytoma · Systemic mastocytosis · Xanthelasmoidal mastocytosisMultiple/unknown Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARUngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixrelated: Costello syndrome · Kindler syndrome · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome · Skin fragility syndrome ·Naegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromediffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkCategories:- Dermal and subcutaneous growths
- Immune system disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
