- Ectodermal dysplasia
-
Ectodermal dysplasia Classification and external resources ICD-10 Q82.4 ICD-9 757.31 DiseasesDB 30597 eMedicine derm/114 MeSH D004476 Ectodermal dysplasia is not a single disorder, but a group of syndromes all deriving from abnormalities of the ectodermal structures.[1]:570 More than 150 different syndromes have been identified.[2] Despite some of the syndromes having different genetic causes the symptoms are sometimes very similar. Diagnosis is usually by clinical observation often with the assistance of family medical histories so that it can be determined whether transmission is autosomal dominant or recessive. Worldwide around 7,000 people have been diagnosed with an ectodermal dysplasia condition. Some ED conditions are only present in single family units and derive from very recent mutations. Ectodermal dysplasias can occur in any race but are much more prevalent in caucasians than any other group and especially in fair Caucasians.
Ectodermal dysplasias are described as "heritable conditions in which there are abnormalities of two or more ectodermal structures such as the hair, teeth, nails, sweat glands, cranial-facial structure, digits and other parts of the body." [1]
Contents
Genetics
ED can be classified by inheritance (autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, and X-linked) or by which structures are involved (hair, teeth, nails, and/or sweat glands).
There are several different types with distinct genetic causes:
- Hay-Wells syndrome, Rapp-Hodgkin syndrome and EEC syndrome are all associated with TP63.[3]
- Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia can be associated with EDA, EDAR, and EDARADD
- Margarita Island ectodermal dysplasia is associated with PVRL1
- Ectodermal dysplasia with skin fragility is associated with PKP1
- Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is associated with GJB6
- Naegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticulariss is associated with KRT14
- Pachyonychia congenita is caused by multiple keratins
- Focal dermal hypoplasia is associated with PORCN
- Ellis–van Creveld syndrome is associated with EVC
- Palmoplantar ectodermal dysplasia refers to several different conditions selectively affecting the hands and feet
Presentation
Hair
Individuals affected by an ED syndrome frequently have abnormalities of the hair follicles. Scalp and body hair may be thin, sparse, and very light in color, even though beard growth in affected males may be normal. The hair may grow very slowly or sporadically and it may be excessively fragile, curly, or even twisted.
Nails
Fingernails and toenails may be thick, abnormally shaped, discolored, ridged, slow-growing, or brittle. The cuticles may be prone to infections.
Skin
The skin may be lightly pigmented. Skin sustaining injury may grow back permanently hypo-pigmented. In some cases, red or brown pigmentation may be present. Skin can be prone to rashes or infections and can be thick over the palms and soles. Care must be taken to prevent cracking, bleeding, and infection.
Sweat glands
Individuals affected by certain ED syndromes cannot perspire. Their sweat glands may function abnormally or may not have developed at all because of inactive proteins in the sweat glands. Without normal sweat production, the body cannot regulate temperature properly. Therefore, overheating is a common problem, especially during hot weather. Access to cool environments is important.
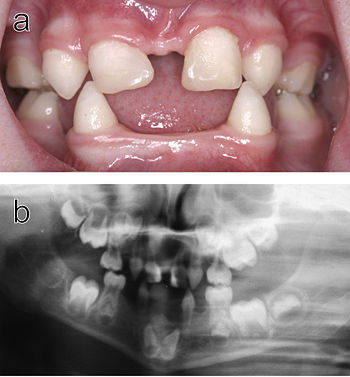 Dental abnormalities in a 5-year-old girl from north Sweden family who suffered from various symptoms of autosomal dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) a) Intraoral view. Note that the upper incisors have been restored with composite material to disguise their original conical shape. b) Orthopantomogram showing absence of ten primary and eleven permanent teeth in the jaws of the same individual.
Dental abnormalities in a 5-year-old girl from north Sweden family who suffered from various symptoms of autosomal dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) a) Intraoral view. Note that the upper incisors have been restored with composite material to disguise their original conical shape. b) Orthopantomogram showing absence of ten primary and eleven permanent teeth in the jaws of the same individual.
Teeth
In the development of tooth buds frequently result in congenitally absent teeth (in many cases a lack of a permanent set) and/or in the growth of teeth that are peg-shaped or pointed. The enamel may also be defective. Cosmetic dental treatment is almost always necessary and children may need dentures as early as two years of age. Multiple denture replacements are often needed as the child grows, and dental implants may be an option in adolescence, once the jaw is fully grown. Nowadays this option of extracting the teeth and substituting them with dental implants is quite common. In other cases, teeth can be crowned. Orthodontic treatment also may be necessary. Because dental treatment is complex, a multi-disciplinary approach is best.
Other features
People with ED often have certain cranial-facial features which can be distinctive, frontal bossing is common, longer or more pronounced chins are frequent, broader noses are also very common. In some types of ED, abnormal development of parts of the eye can result in dryness of the eye, cataracts, and vision defects. Professional eye care can help minimize the effects of ED on vision. Similarly, abnormalities in the development of the ear may cause hearing problems. Respiratory infections can be more common because the normal protective secretions of the mouth and nose are not present. Precautions must be taken to limit infections.[4][5]
Notable cases
One well-known person with ectodermal dysplasia is actor Michael Berryman.
See also
References
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Pinheiro M, Freire-Maia N (November 1994). "Ectodermal dysplasias: a clinical classification and a causal review". Am. J. Med. Genet. 53 (2): 153–62. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320530207. PMID 7856640.
- ^ "Ectodermal Dysplasia: eMedicine Dermatology". http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1110595-overview.
- ^ FAQs / General Description
- ^ Pinheiro M, Freire-Maia N, Gollop TR (January 1985). "Odontoonychodysplasia with alopecia: a new pure ectodermal dysplasia with probable autosomal recessive inheritance". Am. J. Med. Genet. 20 (1): 197–202. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320200123. PMID 2982262.
External links
- Ectodermal Dysplasia Society
- Australian Ectodermal Dysplasia Support Group
- National Foundation for Ectodermal Dysplasias
- Ectodermal Dysplasias patient registry
Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARUngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixrelated: Costello syndrome · Kindler syndrome · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome · Skin fragility syndrome ·Ectodermal dysplasiaNaegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromediffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkCategories:- Genodermatoses
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
