- Lamellar ichthyosis
-
Ichthyosis lamellaris Classification and external resources ICD-10 Q80.2 OMIM 242300 DiseasesDB 30052 eMedicine derm/190 MeSH D017490 Lamellar ichthyosis, also known as ichthyosis lammellaris and nonbullous congenital ichthyosis, is a rare inherited skin disorder, affecting around 1 in 600,000 people.
Contents
Presentation
Affected babies are born in a collodion membrane, a shiny waxy outer layer to the skin. This is shed 10–14 days after birth, revealing the main symptom of the disease, extensive scaling of the skin caused by hyperkeratosis. With increasing age, the scaling tends to be concentrated around joints in areas such as the groin, the armpits, the inside of the elbow and the neck. The scales often tile the skin and may resemble fish scales.
Collodion baby
In medicine, the term collodion baby applies to newborns who appear to have an extra layer of skin (known as a collodion membrane) that has a collodion-like quality. It is a descriptive term, not a specific diagnosis or disorder (as such, it is a syndrome).[1]
Appearance and treatment at birth
The appearance is often described as a shiny film looking like a layer of vaseline. The eyelids and mouth may have the appearance of being forced open due to the tightness of the skin. There can be associated eversion of the eyelids (ectropion).
Collodion baby can have severe medical consequences, mainly because the baby can lose heat and fluid through the abnormal skin. This can lead to hypothermia and dehydration.[2] Strategies to prevent these problems are the use of emollients or nursing the baby in a humidified incubator.[3] There is also an increased risk of skin infection and mechanical compression, leading to problems like limb ischemia.[1][2][3] There is also a risk of intoxication by cutaneous absorption of topical products, for example salicylate intoxication (similar to aspirin overdose) due to keratolytics.[4]
The condition is not thought to be painful or in itself distressing to the child. Nursing usually takes place in a neonatal intensive care unit, and good intensive care seems to have improved the prognosis markedly.[1] The collodion membrane should peel off or "shed" 2 to 4 weeks after birth, revealing the underlying skin disorder.
The condition can resemble but is different from harlequin type ichthyosis.
Long term course
The appearance can be caused by several skin diseases, and it is most often not associated with other birth defects.[2] In most cases, the baby develops an ichthyosis or ichthyosis-like condition or other rare skin disorder.
Most cases (approximately 75%) of collodion baby will go on to develop a type of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (either lamellar ichthyosis or congenital ichthyosiform erythrodema).[5]
In around 10% of cases the baby sheds this layer of skin and has normal skin for the rest of its life.[2][5] This is known as self-healing collodion baby.
The remaining 15% of cases are caused by a variety of diseases involving keratinization disorders.[5] Known causes of collodion baby include ichthyosis vulgaris and trichothiodystrophy.[3] Less well documented causes include Sjögren-Larsson syndrome, Netherton syndrome, Gaucher disease type 2, congenital hypothyroidism, Conradi syndrome, Dorfman-Chanarin syndrome, ketoadipiaciduria, koraxitrachitic syndrome, ichthyosis variegata and palmoplantar keratoderma with anogenital leukokeratosis.[3] Since many of these conditions have an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, they are rare and can be associated with consanguinity.[3]
Tests that can be used to find the cause of collodion baby include examination of the hairs, blood tests and a skin biopsy.
Genetics
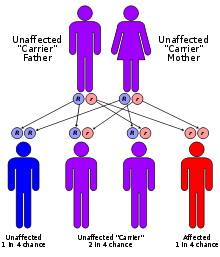
This condition is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder[6]:561, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and both parents must carry one copy of the defective gene in order to have a child born with the disorder. Carriers of a recessive gene usually do not show any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
One form of ichthyosis lamellaris (LI1) is associated with a deficiency of the enzyme keratinocyte transglutaminase.
Genes involved include:
Type OMIM Gene Locus LI1 242300 TGM1 14 LI2 601277 ABCA12 2q34 LI3 604777 CYP4F22 9p13.12 LI5 606545 ? 17p Associated medical problems
Overheating: The scaling of the skin prevents normal sweating so hot weather and/or vigorous exercise can cause problems.
Eye problems: The eyelids can be pulled down by the tightness of the skin and this can make eyelids (but usually just the lower one) very red and they are prone to drying and irritation.
Constriction bands: Very rarely children with this condition can have tight bands of skin around their fingers or toes (usually at the tips) that can prevent proper blood circulation to the area.
Hair loss: Severe scaling of the skin on the scalp can lead to patchy loss of hair, but this is rarely permanent.
Treatments
As with all types of ichthyosis, there is no cure but the symptoms can be relieved.
- Moisturizers
- Prevention of overheating
- Eye drops (to prevent the eyes from becoming dried out)
- Systemic Retinoids (Isotretinoin and acitretin are very effective, but careful monitoring for toxicity is required. Only severe cases may require intermittent therapy.)[7]
Psychological therapy or support may be required as well.
See also
- Ichthyosis
- Congenital ichthyosiform erythrodema
- Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma
References
- ^ a b c Larrègue M, Ottavy N, Bressieux JM, Lorette J (1986). "[Collodion baby: 32 new case reports]" (in French). Ann Dermatol Venereol 113 (9): 773–85. PMID 3548541.
- ^ a b c d Van Gysel D, Lijnen RL, Moekti SS, de Laat PC, Oranje AP (September 2002). "Collodion baby: a follow-up study of 17 cases". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 16 (5): 472–5. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2002.00477.x. PMID 12428840. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0926-9959&date=2002&volume=16&issue=5&spage=472.
- ^ a b c d e Taïeb A, Labrèze C (September 2002). "Collodion baby: what's new". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 16 (5): 436–7. doi:10.1046/j.1468-3083.2002.00478.x. PMID 12428832. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0926-9959&date=2002&volume=16&issue=5&spage=436.
- ^ Yamamura S, Kinoshita Y, Kitamura N, Kawai S, Kobayashi Y (2002). "Neonatal salicylate poisoning during the treatment of a collodion baby". Clin Pediatr (Phila) 41 (6): 451–2. PMID 12166800. http://cpj.sagepub.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12166800.
- ^ a b c Dermatology at the Millennium, By Delwyn Dyall-Smith, Robin Marks, Page 586, Published by Informa Health Care, 1999, ISBN 1-85070-005-2
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Fitzpatrick clinical dermatology
External links
- F.I.R.S.T. - Foundation for Ichthyosis and Related Skin Types at http://www.scalyskin.org/
- British Ichthyosis Support Group (ISG)
Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARCongenital ichthyosiform erythroderma: Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis · Lamellar ichthyosis (Harlequin type ichthyosis)UngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixEB
and relatedJEB (JEB-H, Mitis, Generalized atrophic, JEB-PA)related: Costello syndrome · Kindler syndrome · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome · Skin fragility syndrome ·Naegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromeHyperkeratosis/
keratinopathydiffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkGenetic disorder, membrane: ABC-transporter disorders ABCA ABCA1 (Tangier disease) · ABCA3 (Surfactant metabolism dysfunction 3) · ABCA4 (Stargardt disease 1, Retinitis pigmentosa 19) · ABCA12 (Harlequin-type ichthyosis, Lamellar ichthyosis 2)ABCB ABCC ABCC2 (Dubin–Johnson syndrome) · ABCC6 (Pseudoxanthoma elasticum) · ABCC7 (Cystic fibrosis) · ABCC8 (HHF1, TNDM2) · ABCC9 (Dilated cardiomyopathy 1O)ABCD ABCG see also ABC transporters
B structural (perx, skel, cili, mito, nucl, sclr) · DNA/RNA/protein synthesis (drep, trfc, tscr, tltn) · membrane (icha, slcr, atpa, abct, othr) · transduction (iter, csrc, itra), trfkCategories:- Genodermatoses
- Rare diseases
- Autosomal recessive disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.