- Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome
-
Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome Classification and external resources OMIM 161000 DiseasesDB 29767 eMedicine derm/736 Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS), also known as chromatophore nevus of Naegeli and Naegeli syndrome,[1][2] is a rare autosomal dominant[3] form of ectodermal dysplasia, characterized by reticular skin pigmentation, diminished function of the sweat glands, the absence of teeth and hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles. One of the most striking features is the absence of fingerprint lines on the fingers.
Naegeli syndrome is similar to Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis,[4] both of which are caused by a specific defect in the keratin 14 protein.
Contents
Cause and Genetics
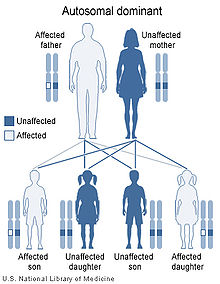
NFJS is caused by mutations in the keratin 14 (KRT14) gene, located on chromosome 17q12-21.[3][5] The disorder is inerited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 17 is an autosome), and only one copy of the defective gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
Eponym
It was named after Oskar Naegeli.[6]
See also
References
- ^ James W, Berger T, Elston D (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. p. 548. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 161000
- ^ a b Lugassy, J; Itin, P; Ishida-Yamamoto, A; Holland, K; Huson, S; Geiger, D; Hennies, Hc; Indelman, M; Bercovich, D; Uitto, J; Bergman, R; Mcgrath, Ja; Richard, G; Sprecher, E (Oct 2006). "Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome and dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis: two allelic ectodermal dysplasias caused by dominant mutations in KRT14". American journal of human genetics 79 (4): 724–30. doi:10.1086/507792. PMC 1592572. PMID 16960809. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1592572.
- ^ Schnur R, Heymann W (1997). "Reticulate hyperpigmentation". Semin Cutan Med Surg. 16 (1): 72–80. doi:10.1016/S1085-5629(97)80038-7. PMID 9125768.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 148066
- ^ synd/1417 at Who Named It?
Congenital malformations and deformations of integument / skin disease (Q80–Q82, 757.0–757.3) Genodermatosis Congenital ichthyosis/
erythrokeratodermiaADARUngroupedIchthyosis bullosa of Siemens · Ichthyosis follicularis · Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome · Ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome · Nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma · Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa · Ichthyosis hystrixrelated: Costello syndrome · Kindler syndrome · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome · Skin fragility syndrome ·Naegeli syndrome/Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Hay–Wells syndrome · Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia · Focal dermal hypoplasia · Ellis–van Creveld syndrome · Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome/Hay–Wells syndromeEhlers–Danlos syndrome · Cutis laxa (Gerodermia osteodysplastica) · Popliteal pterygium syndrome · Pseudoxanthoma elasticum · Van Der Woude syndromediffuse: Diffuse epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma • Palmoplantar keratoderma of Sybert • Mal de Meleda •syndromic (connexin (Bart–Pumphrey syndrome • Clouston's hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia • Vohwinkel syndrome) • Corneodermatoosseous syndrome • plakoglobin (Naxos syndrome) • Scleroatrophic syndrome of Huriez • Olmsted syndrome • Cathepsin C (Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome • Haim–Munk syndrome) • Camisa diseasefocal: Focal palmoplantar keratoderma with oral mucosal hyperkeratosis • Focal palmoplantar and gingival keratosis • Howel–Evans syndrome • Pachyonychia congenita (Pachyonychia congenita type I • Pachyonychia congenita type II) • Striate palmoplantar keratoderma • Tyrosinemia type II)punctate: Acrokeratoelastoidosis of Costa • Focal acral hyperkeratosis • Keratosis punctata palmaris et plantaris • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases • Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome • Porokeratosis plantaris discreta • Spiny keratodermaungrouped: Palmoplantar keratoderma and spastic paraplegia • desmoplakin (Carvajal syndrome) • connexin (Erythrokeratodermia variabilis • HID/KID)OtherMeleda disease · Keratosis pilaris · ATP2A2 (Darier's disease) · Dyskeratosis congenita · Lelis syndromeDyskeratosis congenita · Keratolytic winter erythema · Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans · Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenital and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome · Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei · Keratosis pilarisOthercadherin (EEM syndrome) · immune system (Hereditary lymphedema, Mastocytosis/Urticaria pigmentosa) · Hailey–Hailey
see also Template:Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages, Template:Phakomatoses, Template:Pigmentation disorders, Template:DNA replication and repair-deficiency disorderDevelopmental
anomaliesMidlineOther/ungroupedAplasia cutis congenita · Amniotic band syndrome · Branchial cyst · Cavernous venous malformation
Accessory nail of the fifth toe · Bronchogenic cyst · Congenital cartilaginous rest of the neck · Congenital hypertrophy of the lateral fold of the hallux · Congenital lip pit · Congenital malformations of the dermatoglyphs · Congenital preauricular fistula · Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma · Cystic lymphatic malformation · Median raphe cyst · Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy · Mongolian spot · Nasolacrimal duct cyst · Omphalomesenteric duct cyst · Poland anomaly · Rapidly involuting congenital hemangioma · Rosenthal–Kloepfer syndrome · Skin dimple · Superficial lymphatic malformation · Thyroglossal duct cyst · Verrucous vascular malformation · BirthmarkCategories:- Genetic disorder stubs
- Genodermatoses
- Rare diseases
- Syndromes
- Fingerprints
- Autosomal dominant disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.