- Tietz syndrome
-
Not to be confused with Tietze syndrome.
Tietz syndrome Classification and external resources ICD-10 E70.3
(ILDS E70.358)OMIM 103500 DiseasesDB 34108 Tietz syndrome, also called Tietz albinism-deafness syndrome or albinism and deafness of Tietz,[1] is an autosomal dominant[2] congenital disorder characterized by deafness and leucism.[3] It is caused by a mutation in the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) gene.[2][4] Tietz syndrome was first described in 1923.[5]
Contents
Cause and Genetics
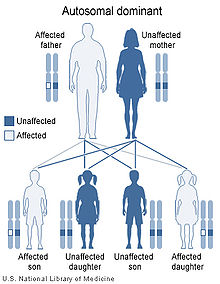
Tietz syndrome is caused by mutations in the MITF gene, located on human chromosome 3p14.1-p12.3.[2][4][6] It is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.[2] This indicates that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 3 is an autosome), and only one copy of the defective gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
See also
References
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 103500
- ^ a b c d Smith SD, Kelley PM, Kenyon JB, Hoover D (Jun 2000). "Tietz syndrome (hypopigmentation/deafness) caused by mutation of MITF" (Free full text). J. Med. Genet. 37 (6): 446–448. doi:10.1136/jmg.37.6.446. PMC 1734605. PMID 10851256. http://jmg.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10851256.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 925. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ a b Amiel J, Watkin PM, Tassabehji M, Read AP, Winter RM (Jan 1998). "Mutation of the MITF gene in albinism-deafness syndrome (Tietz syndrome)". Clin. Dysmorphol. 7 (1): 17–20. doi:10.1097/00019605-199801000-00003. PMID 9546825.
- ^ Tietz W (Sep 1963). "A Syndrome of Deaf-Mutism Associated with Albinism Showing Dominant Autosomal Inheritance" (Free full text). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 15 (3): 259–264. PMC 1932384. PMID 13985019. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1932384.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 156845
External links
- Tietz syndrome; Albinism and complete nerve deafness at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
Pigmentation disorders/Dyschromia (L80–L81, 709.0) Hypo-/
leucismLoss of melanocytesvitiligo: Quadrichrome vitiligo · Vitiligo ponctué · syndromic (Alezzandrini syndrome · Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome)
melanocyte development: Piebaldism · Waardenburg syndrome · Tietz syndromeLoss of melanin/
amelanismalbinism: Oculocutaneous albinism · Ocular albinism
melanosome transfer: Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome · Chédiak–Higashi syndrome · Griscelli syndrome (Elejalde syndrome · Griscelli syndrome type 2 · Griscelli syndrome type 3)
other: Cross syndrome · ABCD syndrome · Albinism–deafness syndrome · Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis · Phylloid hypomelanosis · Progressive macular hypomelanosisLeukoderma w/o
hypomelanosisUngroupedungrouped: Nevus depigmentosus · Postinflammatory hypopigmentation · Pityriasis alba · Vagabond's leukomelanoderma · Yemenite deaf-blind hypopigmentation syndrome · Wende–Bauckus syndromeHyper- ReticulatedDermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis · Pigmentatio reticularis faciei et colli · Reticulate acropigmentation of Kitamura · Reticular pigmented anomaly of the flexures · Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome · Dyskeratosis congenita · X-linked reticulate pigmentary disorder · Galli–Galli disease · Revesz syndromeDiffuse/
circumscribedLentigo/Lentiginosis: Lentigo simplex · Liver spot · Centrofacial lentiginosis · Generalized lentiginosis · Inherited patterned lentiginosis in black persons · Ink spot lentigo · Lentigo maligna · Mucosal lentigines · Partial unilateral lentiginosis · PUVA lentigines
Melasma · Erythema dyschromicum perstans · Lichen planus pigmentosus · Café au lait spot · Poikiloderma (Poikiloderma of Civatte · Poikiloderma vasculare atrophicans) · Riehl melanosisLinearOther/ungroupedAcanthosis nigricans (Acral acanthotic anomaly) · Freckle · Familial progressive hyperpigmentation · Pallister–Killian syndrome · Periorbital hyperpigmentation · Photoleukomelanodermatitis of Kobori · Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation · Transient neonatal pustular melanosisOther
pigmentsiron: Hemochromatosis · Iron metallic discoloration · Pigmented purpuric dermatosis (Schamberg disease, Majocchi's disease, Gougerot–Blum syndrome, Doucas and Kapetanakis pigmented purpura/Eczematid-like purpura of Doucas and Kapetanakis, Lichen aureus, Angioma serpiginosum) · Hemosiderin hyperpigmentationother metals: Argyria · Chrysiasis · Arsenic poisoning · Lead poisoning · Titanium metallic discolorationDyschromatoses Dyschromatosis symmetrica hereditaria · Dyschromatosis universalis hereditariaGenetic disorder, protein biosynthesis: Transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies (1) Basic domains 1.3: Tietz syndrome(2) Zinc finger
DNA-binding domains2.1 (Intracellular receptor): Thyroid hormone resistance · Androgen insensitivity syndrome (PAIS, MAIS, CAIS) · Kennedy's disease · PHA1AD pseudohypoaldosteronism · Estrogen insensitivity syndrome · X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita · MODY 1 · Familial partial lipodystrophy 3 · SF1 XY gonadal dysgenesis
2.2: Barakat syndrome · Tricho–rhino–phalangeal syndrome
2.3: Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome/Pallister-Hall syndrome · Denys–Drash syndrome · Duane-radial ray syndrome · MODY 7 · MRX 89 · Townes–Brocks syndrome · Acrocallosal syndrome · Myotonic dystrophy 2
2.5: Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1(3) Helix-turn-helix domains 3.1: ARX (Ohtahara syndrome, Lissencephaly X2) · HLXB9 (Currarino syndrome) · HOXD13 (SPD1 Synpolydactyly) · IPF1 (MODY 4) · LMX1B (Nail–patella syndrome) · MSX1 (Tooth and nail syndrome, OFC5) · PITX2 (Axenfeld syndrome 1) · POU4F3 (DFNA15) · POU3F4 (DFNX2) · ZEB1 (Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy 3, Fuchs' dystrophy 3) · ZEB2 (Mowat-Wilson syndrome)
3.2: PAX2 (Papillorenal syndrome) · PAX3 (Waardenburg syndrome 1&3) · PAX4 (MODY 9) · PAX6 (Gillespie syndrome, Coloboma of optic nerve) · PAX8 (Congenital hypothyroidism 2) · PAX9 (STHAG3)
3.3: FOXC1 (Axenfeld syndrome 3, Iridogoniodysgenesis, dominant type) · FOXC2 (Lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome) · FOXE1 (Bamforth–Lazarus syndrome) · FOXE3 (Anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis) · FOXF1 (ACD/MPV) · FOXI1 (Enlarged vestibular aqueduct) · FOXL2 (Premature ovarian failure 3) · FOXP3 (IPEX)
3.5: IRF6 (Van der Woude syndrome, Popliteal pterygium syndrome)(4) β-Scaffold factors
with minor groove contacts4.2: Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
4.3: Holt-Oram syndrome · Li-Fraumeni syndrome · Ulnar–mammary syndrome
4.7: Campomelic dysplasia · MODY 3 · MODY 5 · SF1 (SRY XY gonadal dysgenesis, Premature ovarian failure 7) · SOX10 (Waardenburg syndrome 4c, Yemenite deaf-blind hypopigmentation syndrome)
4.11: Cleidocranial dysostosis(0) Other transcription factors 0.6: Kabuki syndromeUngrouped Transcription coregulators Categories:- Autosomal dominant disorders
- Syndromes
- Congenital disorders
- Rare diseases
- Disturbances of human pigmentation
- Transcription factor deficiencies
- Genetic disorder stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.