- Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
-
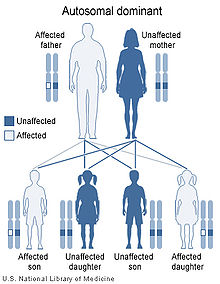
Saethre-Chotzen syndrome Classification and external resources OMIM 101400 DiseasesDB 29331 MeSH D000168 Saethre-Chotzen syndrome (SCS), also known as acrocephalosyndactyly type 3 (ACS III) and Chotzen syndrome,[1] is a very rare autosomal dominant[2] congenital disorder characterized by acrocephalosyndactyly, craniosynostosis (premature closure of one or more of the sutures between the bones of the skull). It is caused by mutations in the TWIST transcription factor (TWIST) gene.[2][3]
Contents
Characteristics
Classic features include:
- synostosis of the coronal sutures of the skull resulting in characteristic faces including ptosis, facial asymmetry and small ears
- syndactyly of the fingers, particularly of the second and third digits
- Intelligence is usually normal. Some affected individuals may have mild to moderate mental retardation.
Cause and genetics
SCS is caused by a mutation in the TWIST gene, located on human chromosome 7p21.[2][3] Autosomal dominant inheritance indicates that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 7 is an autosome), and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
Epidemiology
The incidence of this rare syndrome is estimated at between 1 in 25,000–50,000 live births.
See also
References
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 101400
- ^ a b c Kress, W.; Schropp, C.; Lieb, G.; Petersen, B.; Büsse-Ratzka, M.; Kunz, J.; Reinhart, E.; Schäfer, W. D. et al. (Jan 2006). "Saethre–Chotzen syndrome caused by TWIST 1 gene mutations: functional differentiation from Muenke coronal synostosis syndrome" (Free full text). European Journal of Human Genetics 14 (1): 39–48. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201507. PMID 16251895. http://www.nature.com/ejhg/journal/v14/n1/full/5201507a.html.
- ^ a b Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 601622
External links
Congenital abnormality · multiple abnormalities (Q87, 759.7) Craniofacial Acrocephalosyndactylia (Apert syndrome/Pfeiffer syndrome, Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, Carpenter syndrome, Sakati-Nyhan-Tisdale syndrome)Short stature 1q21.1 deletion syndrome · Aarskog–Scott syndrome · Cockayne syndrome · Cornelia de Lange Syndrome · Dubowitz syndrome · Noonan syndrome · Robinow syndrome · Silver–Russell syndrome · Seckel syndrome · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome-Turner syndromeLimbs Overgrowth Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl Bardet–Biedl syndrome · Laurence-Moon syndromeCombined/other,
known locus3 (Zimmerman-Laband syndrome) · 4/13 (Fraser syndrome) · 8 (Branchio-oto-renal syndrome) · 12 (Keutel syndrome, Timothy syndrome) · 15 (Marfan syndrome) · 19 (Donohue syndrome)Genetic disorder, protein biosynthesis: Transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies (1) Basic domains 1.2: Feingold syndrome · Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
1.3: Tietz syndrome(2) Zinc finger
DNA-binding domains2.1 (Intracellular receptor): Thyroid hormone resistance · Androgen insensitivity syndrome (PAIS, MAIS, CAIS) · Kennedy's disease · PHA1AD pseudohypoaldosteronism · Estrogen insensitivity syndrome · X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita · MODY 1 · Familial partial lipodystrophy 3 · SF1 XY gonadal dysgenesis
2.2: Barakat syndrome · Tricho–rhino–phalangeal syndrome
2.3: Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome/Pallister-Hall syndrome · Denys–Drash syndrome · Duane-radial ray syndrome · MODY 7 · MRX 89 · Townes–Brocks syndrome · Acrocallosal syndrome · Myotonic dystrophy 2
2.5: Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1(3) Helix-turn-helix domains 3.1: ARX (Ohtahara syndrome, Lissencephaly X2) · HLXB9 (Currarino syndrome) · HOXD13 (SPD1 Synpolydactyly) · IPF1 (MODY 4) · LMX1B (Nail–patella syndrome) · MSX1 (Tooth and nail syndrome, OFC5) · PITX2 (Axenfeld syndrome 1) · POU4F3 (DFNA15) · POU3F4 (DFNX2) · ZEB1 (Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy 3, Fuchs' dystrophy 3) · ZEB2 (Mowat-Wilson syndrome)
3.2: PAX2 (Papillorenal syndrome) · PAX3 (Waardenburg syndrome 1&3) · PAX4 (MODY 9) · PAX6 (Gillespie syndrome, Coloboma of optic nerve) · PAX8 (Congenital hypothyroidism 2) · PAX9 (STHAG3)
3.3: FOXC1 (Axenfeld syndrome 3, Iridogoniodysgenesis, dominant type) · FOXC2 (Lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome) · FOXE1 (Bamforth–Lazarus syndrome) · FOXE3 (Anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis) · FOXF1 (ACD/MPV) · FOXI1 (Enlarged vestibular aqueduct) · FOXL2 (Premature ovarian failure 3) · FOXP3 (IPEX)
3.5: IRF6 (Van der Woude syndrome, Popliteal pterygium syndrome)(4) β-Scaffold factors
with minor groove contacts4.2: Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
4.3: Holt-Oram syndrome · Li-Fraumeni syndrome · Ulnar–mammary syndrome
4.7: Campomelic dysplasia · MODY 3 · MODY 5 · SF1 (SRY XY gonadal dysgenesis, Premature ovarian failure 7) · SOX10 (Waardenburg syndrome 4c, Yemenite deaf-blind hypopigmentation syndrome)
4.11: Cleidocranial dysostosis(0) Other transcription factors 0.6: Kabuki syndromeUngrouped Transcription coregulators Categories:- Genetic disorder stubs
- Congenital disorders
- Autosomal dominant disorders
- Rare diseases
- Syndromes
- Transcription factor deficiencies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.