- Cockayne syndrome
-
Cockayne syndrome Classification and external resources ICD-10 Q87.1 (ILDS Q87.110) ICD-9 759.8 OMIM 216400 133540 216411 DiseasesDB 2907 eMedicine ped/424 MeSH D003057 Cockayne syndrome (also called Weber-Cockayne syndrome, or Neill-Dingwall syndrome) is a rare autosomal recessive,[1] congenital disorder characterized by growth failure, impaired development of the nervous system, abnormal sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity), and premature aging.[2] Hearing loss and eye abnormalities (pigmentary retinopathy) are other common features, but problems with any or all of the internal organs are possible. It is associated with a group of disorders called leukodystrophies. The underlying disorder is a defect in a DNA repair mechanism.[3]
It is named after English physician Edward Alfred Cockayne (1880–1956). Neill-Dingwall syndrome was named after Mary M. Dingwall and Catherine A. Neill.[4]
Contents
Forms of Cockayne syndrome (CS)
- CS Type I, the classic form, is characterized by normal fetal growth with the onset of abnormalities in the first two years of life. Impairment of vision, hearing, and the central and peripheral nervous systems progressively degenerate until death in the first or second decade of life.
- CS Type II, otherwise known as connatal CS, involves very little neurological development after birth. Death usually occurs by age seven. This specific type has also been designated as cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal (COFS) syndrome.[5][6] COFS syndrome can be further subdivided into several conditions (COFS types 1, 2, 3 (associated with xeroderma pigmentosum) and 4).[7]
- CS Type III, characterized by late onset, is rare and milder than Types I and II.
- Xeroderma pigmentosum-Cockayne syndrome (XP-CS) occurs when an individual also suffers from xeroderma pigmentosum, another DNA repair disease. Some symptoms of each disease are expressed.
Genetics
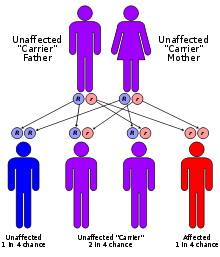 Cockayne syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Cockayne syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Cockayne syndrome is classified genetically as follows:
Type OMIM Gene A 216400 ERCC8 B 133540 ERCC6 C 216411 none known Mutations in the ERCC6 and ERCC8 genes are the cause of Cockayne syndrome. The proteins made by these genes are involved in repairing damaged DNA via the transcription-coupled repair mechanism, particularly the DNA in active genes. If either the ERCC6 or the ERCC8 gene is altered, DNA damage is not repaired. As this damage accumulates, it can lead to malfunctioning cells or cell death.
Mutations in the ERCC6 gene mutation makes up ~70% of cases.
Physical appearance
Persons with this syndrome have smaller than normal head sizes, are of short stature, their eyes appear sunken, and they have an "aged" look.
See also
- Accelerated aging disease
- Biogerontology
- Degenerative disease
- Genetic disorder
- CAMFAK syndrome — thought to be a form (or subset) of Cockayne syndrome[8]
External links
- Share and Care Cockayne Syndrome Network
- cockayne at NIH/UW GeneTests
- This article incorporates some public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
- 'Amy and Friends' — a friendly charity based in the UK supporting children with Cockayne Syndome
References
- ^ Bertola, Dr; Cao, H; Albano, Lm; Oliveira, Dp; Kok, F; Marques-Dias, Mj; Kim, Ca; Hegele, Ra (2006). "Cockayne syndrome type A: novel mutations in eight typical patients". Journal of human genetics 51 (8): 701–5. doi:10.1007/s10038-006-0011-7. PMID 16865293.
- ^ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (10th ed.). Saunders. p. 575. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Hoeijmakers JH (October 2009). "DNA damage, aging, and cancer". N. Engl. J. Med. 361 (15): 1475–85. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804615. PMID 19812404. http://www.nejm.org/doi/abs/10.1056/NEJMra0804615?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3dpubmed.
- ^ Cockayne's syndrome at Who Named It?
- ^ http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/Disease_Search.php?lng=EN&data_id=1649&Disease_Disease_Search_diseaseGroup=Cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal-syndrome&Disease_Disease_Search_diseaseType=Pat&Disease(s) concerned=COFS-syndrome--Cerebrooculofacioskeletal-syndrome-&title=COFS-syndrome--Cerebrooculofacioskeletal-syndrome-&search=Disease_Search_Simple
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) Cerebrooculofacioskeletal Syndrome 1; COFS1 -214150
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) Cerebrooculofacioskeletal Syndrome 2; COFS2 -610756
Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) Xeroderma Pigmentosum, Complementation Group G; XPG -278780
Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) Cerebrooculofacioskeletal Syndrome 4; COFS4 -610758 - ^ http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=GB&Expert=1317
Congenital abnormality · multiple abnormalities (Q87, 759.7) Craniofacial Short stature 1q21.1 deletion syndrome · Aarskog–Scott syndrome · Cockayne syndrome · Cornelia de Lange Syndrome · Dubowitz syndrome · Noonan syndrome · Robinow syndrome · Silver–Russell syndrome · Seckel syndrome · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome-Turner syndromeLimbs Overgrowth Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl Bardet–Biedl syndrome · Laurence-Moon syndromeCombined/other,
known locus3 (Zimmerman-Laband syndrome) · 4/13 (Fraser syndrome) · 8 (Branchio-oto-renal syndrome) · 12 (Keutel syndrome, Timothy syndrome) · 15 (Marfan syndrome) · 19 (Donohue syndrome)Metabolic disease: DNA replication and DNA repair-deficiency disorder DNA replication Separation/initiation: RNASEH2A (Aicardi–Goutières syndrome 4)
Termination/telomerase: DKC1 (Dyskeratosis congenita)DNA repair Cockayne syndrome/DeSanctis–Cacchione syndrome · Thymine dimer (Xeroderma pigmentosum) · IBIDS syndromeOtherRecQ helicase (Bloom syndrome, Werner syndrome, Rothmund–Thomson syndrome/Rapadilino syndrome) · Fanconi anemia · Li-Fraumeni syndrome · Severe combined immunodeficiencysee also DNA replication, DNA repair
B structural (perx, skel, cili, mito, nucl, sclr) · DNA/RNA/protein synthesis (drep, trfc, tscr, tltn) · membrane (icha, slcr, atpa, abct, othr) · transduction (iter, csrc, itra), trfkCategories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Rare diseases
- Neurological disorders
- Syndromes
- Genodermatoses
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
