- Mowat-Wilson syndrome
-
Mowat-Wilson syndrome Classification and external resources
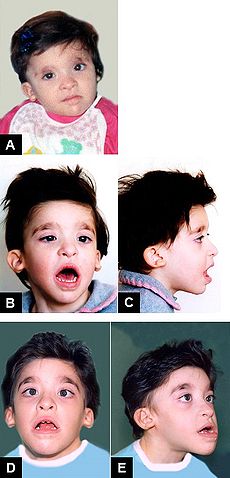
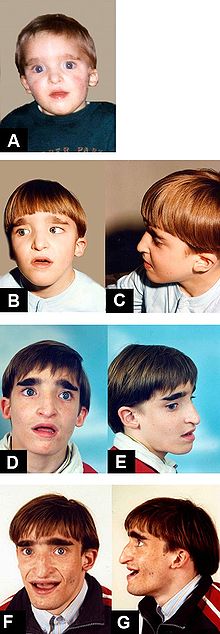
Mowat-Wilson Syndrome, clinical features of Patient 2 at age: (A) 1 year and 6 months; (B-C) 3 years and 5 months; (D-E) 8 years and 1 month.OMIM 235730 DiseasesDB 32975 Mowat Wilson syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that was clinically delineated by Dr. D. R. Mowat and Dr. M. J. Wilson in 1998.[1]
Contents
Presentation
This autosomal dominant disorder is characterized by a number of health defects including Hirschsprung's disease, mental retardation, seizure disorder, delayed growth and motor development, congenital heart disease, genitourinary anomalies and absence of the corpus callosum. However, Hirschsprung's disease is not present in all infants with Mowat-Wilson syndrome and therefore it is not a required diagnostic criterion.[2] Distinctive physical features include microcephaly, narrow chin, cupped ears with uplifted lobes with central depression, deep and widely set eyes, open mouth, wide nasal bridge and a shortened philtrum.
Causes
The disorder is expressed in an autosomal dominant fashion and may result from a de novo (new) mutation or deletions of the ZEB2 (also known as ZFHX1B or SMADIP1) gene on chromosome 2q22. [3]
However, some of those affected by the disease do not have abnormalities of this gene that are currently detectable.[citation needed]
Prognosis
There is no cure for this syndrome. Treatment is supportive and symptomatic. All children with Mowat-Wilson syndrome required early intervention with speech therapy and physical therapy.[2]
References
- ^ "Hirschsprung disease, microcephaly, mental retardation, and characteristic facial features: delineation of a new syndrome and identification of a locus at chromosome 2q22-q23 -- Mowat et al. 35 (8): 617 -- Journal of Medical Genetics". http://jmg.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/abstract/35/8/617. Retrieved 2007-08-23.
- ^ a b Todo A, Harrington JW. New-onset seizures in infant with square facies, hypospadias, and Hirschsprung disease. Consultant for Pediatricians. 2010;9:103-107.
- ^ "ZEB2 - zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2". HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. 11 January 2011. http://www.genenames.org/data/hgnc_data.php?hgnc_id=14881. Retrieved 2 May 2011.
External links
- Centre for Genetics Education in Sydney, Australia (PDF Information Sheet)
- Journal of Medical Genetics Vol 41, e16
- Journal of Medical Genetics Vol 40, 305-10
- Journal of Medical Genetics Vol 35, 617-23
- Documentary about a young man with Mowat-Wilson Syndrome
- extensive links page
- GeneReview of Mowat-Wilson syndrome
Genetic disorder, protein biosynthesis: Transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies (1) Basic domains 1.2: Feingold syndrome · Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
1.3: Tietz syndrome(2) Zinc finger
DNA-binding domains2.1 (Intracellular receptor): Thyroid hormone resistance · Androgen insensitivity syndrome (PAIS, MAIS, CAIS) · Kennedy's disease · PHA1AD pseudohypoaldosteronism · Estrogen insensitivity syndrome · X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita · MODY 1 · Familial partial lipodystrophy 3 · SF1 XY gonadal dysgenesis
2.2: Barakat syndrome · Tricho–rhino–phalangeal syndrome
2.3: Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome/Pallister-Hall syndrome · Denys–Drash syndrome · Duane-radial ray syndrome · MODY 7 · MRX 89 · Townes–Brocks syndrome · Acrocallosal syndrome · Myotonic dystrophy 2
2.5: Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1(3) Helix-turn-helix domains 3.1: ARX (Ohtahara syndrome, Lissencephaly X2) · HLXB9 (Currarino syndrome) · HOXD13 (SPD1 Synpolydactyly) · IPF1 (MODY 4) · LMX1B (Nail–patella syndrome) · MSX1 (Tooth and nail syndrome, OFC5) · PITX2 (Axenfeld syndrome 1) · POU4F3 (DFNA15) · POU3F4 (DFNX2) · ZEB1 (Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy 3, Fuchs' dystrophy 3) · ZEB2 (Mowat-Wilson syndrome)
3.2: PAX2 (Papillorenal syndrome) · PAX3 (Waardenburg syndrome 1&3) · PAX4 (MODY 9) · PAX6 (Gillespie syndrome, Coloboma of optic nerve) · PAX8 (Congenital hypothyroidism 2) · PAX9 (STHAG3)
3.3: FOXC1 (Axenfeld syndrome 3, Iridogoniodysgenesis, dominant type) · FOXC2 (Lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome) · FOXE1 (Bamforth–Lazarus syndrome) · FOXE3 (Anterior segment mesenchymal dysgenesis) · FOXF1 (ACD/MPV) · FOXI1 (Enlarged vestibular aqueduct) · FOXL2 (Premature ovarian failure 3) · FOXP3 (IPEX)
3.5: IRF6 (Van der Woude syndrome, Popliteal pterygium syndrome)(4) β-Scaffold factors
with minor groove contacts4.2: Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
4.3: Holt-Oram syndrome · Li-Fraumeni syndrome · Ulnar–mammary syndrome
4.7: Campomelic dysplasia · MODY 3 · MODY 5 · SF1 (SRY XY gonadal dysgenesis, Premature ovarian failure 7) · SOX10 (Waardenburg syndrome 4c, Yemenite deaf-blind hypopigmentation syndrome)
4.11: Cleidocranial dysostosis(0) Other transcription factors 0.6: Kabuki syndromeUngrouped Transcription coregulators Categories:- Transcription factor deficiencies
- Syndromes
- Rare diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.