- Thoracic duct
-
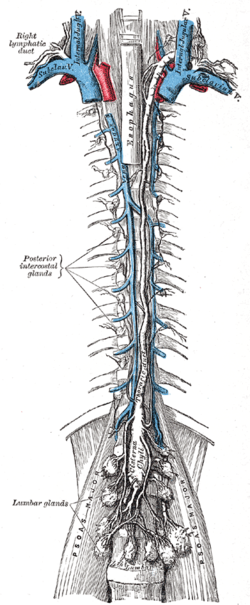
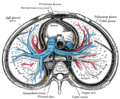
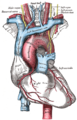
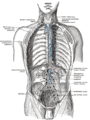
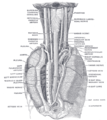
Lymph: Thoracic duct The thoracic and right lymphatic ducts. (Thoracic duct is thin vertical white line at center.) Modes of origin of thoracic duct. a. Thoracic duct. a’. Cisterna chyli. b, c’ Efferent trunks from lateral aortic glands. d. An efferent vessel which pierces the left crus of the diaphragm. e. f. Lateral aortic glands. h. Retroaortic glands. i. Intestinal trunk. j. Descending branch from intercostal lymphatics. Latin ductus thoracicus Gray's subject #176 690 Source cisterna chyli Drains to junction of the left subclavian vein and left internal jugular vein MeSH Thoracic+Duct Dorlands/Elsevier Thoracic duct In human anatomy, the thoracic duct of the lymphatic system is the largest lymphatic vessel in the body. It is also known as the left lymphatic duct, alimentary duct, chyliferous duct, and Van Hoorne's canal.
It collects most of the lymph in the body (except that from the right arm and the right side of the chest, neck and head, and lower left lobe of the lung, which is collected by the right lymphatic duct) and drains into the systemic (blood) circulation at the left brachiocephalic vein between the left subclavian and left internal jugular veins.
Contents
Location
In adults, the thoracic duct is typically 38-45cm in length and an average diameter of about 5mm. It usually starts from the level of the second lumbar vertebra and extends to the root of the neck.
It originates in the abdomen from the confluence of the right and left lumbar trunk and the intestinal trunk, forming a significant pathway upward called the cisterna chyli.
It extends vertically in the chest and curves posteriorly to the left carotid artery and left internal jugular vein at the C7 vertebral level to empty into the junction of the left subclavian vein and left jugular vein, below the clavicle, near the shoulders.
It traverses the diaphragm at the aortic aperture and ascends the posterior mediastinum between the descending thoracic aorta (to its left) and the azygos vein (to its right).
Volume, mechanism, and direction of flow
In adults, the thoracic duct transports up to 4 L of lymph per day.
The lymph transport in the thoracic duct is mainly caused by the action of breathing, aided by the duct's smooth muscle and by internal valves which prevent the lymph from flowing back down again.
There are also two valves at the junction of the duct with the left subclavian vein, to prevent the flow of venous blood into the duct.
Clinical significance
When the thoracic duct is blocked or damaged a large amount of lymph can quickly accumulate in the pleural cavity, this situation is called chylothorax.
The first sign of a malignancy (especially an intraabdominal one) may be an enlarged Virchow's node, a lymph node in the left supraclavicular area, in the vicinity where the thoracic duct empties into the left subclavian vein.
Additional images
See also
References
External links
- Anatomy at MUN thorax/lymph
- SUNY Figs 21:05-02 - "The thoracic duct and azygos venous network."
- SUNY Anatomy Image 8901
- Human anatomy at Dartmouth figures/chapter_24/24-5.HTM
- "thoracic duct" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Diagram at anatomyatlases.org
- Ultrasound Imaging the thoracic duct
- Instruction video for Ultrasound examination of the thoracic duct
Chest parietal: Parasternal · Intercostal · Superior diaphragmatic
visceral: Tracheobronchial (Superior tracheobronchial nodes · Inferior tracheobronchial nodes · Bronchopulmonary nodes · Paratracheal lymph nodes, Intrapulmonary nodes)
Right lymphatic duct · Thoracic duct · Bronchomediastinal lymph trunkM: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc
Lymphatic system - Lymphatic trunks and ducts (TA A12.4.01, GA 8.690) Path details ... Blood → Interstitial fluid → Lymph →
Lymph capillary → Afferent lymph vessel (Lymphatic vessel) → Lymph node → Efferent lymph vessel (Lymphatic vessel) →
Lymph trunk (Subclavian lymph trunk • Jugular lymph trunk • Bronchomediastinal lymph trunk • Intestinal lymph trunk → Cisterna chyli • Lumbar lymph trunk → Cisterna chyli) → Lymph duct {Right lymphatic duct and Thoracic duct (left side)} →
Subclavian vein (right and left) → Blood ...Other concepts M: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc
Categories:- Lymphatics of the torso
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.