- Actin, alpha 1
-
Actin, alpha skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTA1 gene.[1][2]
Actin alpha 1 which is expressed in skeletal muscle is one of six different actin isoforms which have been identified. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha actins are a major constituent of the contractile apparatus.[3]
Contents
Skeletal actin gene expression
Skeletal alpha actin expression is induced by stimuli and conditions known to cause muscle formation.[4] Such conditions result in fusion of committed cells (satellite cells) into myotubes, to form muscle fibers. Skeletal actin itself, when expressed, causes expression of several other "myogenic genes", which are essential to muscle formation.[5] One key transcription factor that activates skeletal actin gene expression is Serum Response Factor ("SRF"), a protein that binds to specific sites on the promoter DNA of the actin gene.[6] SRF may bring a number of other proteins to the promoter of skeletal actin, such as andogen receptor, and thereby contribute to induction of skeletal actin gene expression by androgenic (often termed "anabolic") steroids.[7]
Interactions
Actin, alpha 1 has been shown to interact with TMSB4X,[8][9] MIB2[10] and PRKCE.[11]
See also
- Actin
- ACTB
References
- ^ Mogensen J, Kruse TA, Borglum AD (Mar 1999). "Assignment of the human skeletal muscle [FC12]a-actin gene (ACTA1) to chromosome 1q42.13-->q42.2 by radiation hybrid mapping". Cytogenet Cell Genet 83 (3-4): 224–5. doi:10.1159/000015184. PMID 10072583.
- ^ Gunning P, Ponte P, Okayama H, Engel J, Blau H, Kedes L (Aug 1983). "Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed". Mol Cell Biol 3 (5): 787–95. PMC 368601. PMID 6865942. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=368601.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ACTA1 actin, alpha 1, skeletal muscle". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=58.
- ^ Bandman, E (1992). "Contractile protein isoforms in muscle development.". Developmental biology 154 (2): 273–83. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(92)90067-Q. PMID 1358730.
- ^ Gunning, PW; Ferguson, V; Brennan, KJ; Hardeman, EC (2001). "Alpha-skeletal actin induces a subset of muscle genes independently of muscle differentiation and withdrawal from the cell cycle.". Journal of cell science 114 (Pt 3): 513–24. PMID 11171321.
- ^ Belaguli, NS; Zhou, W; Trinh, TH; Majesky, MW; Schwartz, RJ (1999). "Dominant negative murine serum response factor: alternative splicing within the activation domain inhibits transactivation of serum response factor binding targets.". Molecular and cellular biology 19 (7): 4582–91. PMC 84256. PMID 10373507. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=84256.
- ^ Vlahopoulos, S; Zimmer, WE; Jenster, G; Belaguli, NS; Balk, SP; Brinkmann, AO; Lanz, RB; Zoumpourlis, VC et al. (2005). "Recruitment of the androgen receptor via serum response factor facilitates expression of a myogenic gene.". The Journal of biological chemistry 280 (9): 7786–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413992200. PMID 15623502.
- ^ Ballweber, Edda; Hannappel Ewald, Huff Thomas, Stephan Harald, Haener Markus, Taschner Nicole, Stoffler Daniel, Aebi Ueli, Mannherz Hans Georg (Jan. 2002). "Polymerisation of chemically cross-linked actin:thymosin beta(4) complex to filamentous actin: alteration in helical parameters and visualisation of thymosin beta(4) binding on F-actin". J. Mol. Biol. (England) 315 (4): 613–25. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5281. ISSN 0022-2836. PMID 11812134.
- ^ Safer, D; Sosnick T R, Elzinga M (May. 1997). "Thymosin beta 4 binds actin in an extended conformation and contacts both the barbed and pointed ends". Biochemistry (UNITED STATES) 36 (19): 5806–16. doi:10.1021/bi970185v. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 9153421.
- ^ Takeuchi, Tamotsu; Heng Henry H Q, Ye Christine J, Liang Sheng-Ben, Iwata Jun, Sonobe Hiroshi, Ohtsuki Yuji (Oct. 2003). "Down-regulation of a novel actin-binding molecule, skeletrophin, in malignant melanoma". Am. J. Pathol. (United States) 163 (4): 1395–404. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63497-9. ISSN 0002-9440. PMC 1868282. PMID 14507647. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1868282.
- ^ England, Karen; Ashford David, Kidd Daniel, Rumsby Martin (Jun. 2002). "PKC epsilon is associated with myosin IIA and actin in fibroblasts". Cell. Signal. (England) 14 (6): 529–36. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00277-7. ISSN 0898-6568. PMID 11897493.
External links
Further reading
- Snásel J, Pichová I (1997). "The cleavage of host cell proteins by HIV-1 protease.". Folia Biol. (Praha) 42 (5): 227–30. doi:10.1007/BF02818986. PMID 8997639.
- Di Fiore PP, Scita G (2002). "Eps8 in the midst of GTPases.". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34 (10): 1178–83. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(02)00064-X. PMID 12127568.
- Ogawa H, Shiraki H, Matsuda Y, Nakagawa H (1978). "Interaction of adenylosuccinate synthetase with F-actin.". Eur. J. Biochem. 85 (2): 331–7. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12243.x. PMID 648524.
- den Hartigh JC, van Bergen en Henegouwen PM, Verkleij AJ, Boonstra J (1992). "The EGF receptor is an actin-binding protein.". J. Cell Biol. 119 (2): 349–55. doi:10.1083/jcb.119.2.349. PMC 2289650. PMID 1383230. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2289650.
- Adams LD, Tomasselli AG, Robbins P, et al. (1992). "HIV-1 protease cleaves actin during acute infection of human T-lymphocytes.". AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 8 (2): 291–5. doi:10.1089/aid.1992.8.291. PMID 1540415.
- Levine BA, Moir AJ, Patchell VB, Perry SV (1992). "Binding sites involved in the interaction of actin with the N-terminal region of dystrophin.". FEBS Lett. 298 (1): 44–8. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80019-D. PMID 1544421.
- Rijken PJ, Hage WJ, van Bergen en Henegouwen PM, et al. (1992). "Epidermal growth factor induces rapid reorganization of the actin microfilament system in human A431 cells.". J. Cell. Sci. 100 ( Pt 3): 491–9. PMID 1808202.
- Tomasselli AG, Hui JO, Adams L, et al. (1991). "Actin, troponin C, Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein and pro-interleukin 1 beta as substrates of the protease from human immunodeficiency virus.". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (22): 14548–53. PMID 1907279.
- Shoeman RL, Kesselmier C, Mothes E, et al. (1991). "Non-viral cellular substrates for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease.". FEBS Lett. 278 (2): 199–203. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(91)80116-K. PMID 1991513.
- Winder SJ, Walsh MP (1990). "Smooth muscle calponin. Inhibition of actomyosin MgATPase and regulation by phosphorylation.". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (17): 10148–55. PMID 2161834.
- Kabsch W, Mannherz HG, Suck D, et al. (1990). "Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex.". Nature 347 (6288): 37–44. doi:10.1038/347037a0. PMID 2395459.
- Takahashi K, Hiwada K, Kokubu T (1988). "Vascular smooth muscle calponin. A novel troponin T-like protein.". Hypertension 11 (6 Pt 2): 620–6. PMID 2455687.
- Taylor A, Erba HP, Muscat GE, Kedes L (1989). "Nucleotide sequence and expression of the human skeletal alpha-actin gene: evolution of functional regulatory domains.". Genomics 3 (4): 323–36. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(88)90123-1. PMID 2907503.
- Shen BW, Josephs R, Steck TL (1986). "Ultrastructure of the intact skeleton of the human erythrocyte membrane.". J. Cell Biol. 102 (3): 997–1006. doi:10.1083/jcb.102.3.997. PMC 2114132. PMID 2936753. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2114132.
- Burgess DR, Broschat KO, Hayden JM (1987). "Tropomyosin distinguishes between the two actin-binding sites of villin and affects actin-binding properties of other brush border proteins.". J. Cell Biol. 104 (1): 29–40. doi:10.1083/jcb.104.1.29. PMC 2117036. PMID 3793760. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2117036.
- Kedes L, Ng SY, Lin CS, et al. (1986). "The human beta-actin multigene family.". Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 98: 42–6. PMID 3842206.
- Hanauer A, Levin M, Heilig R, et al. (1983). "Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human skeletal muscle alpha actin.". Nucleic Acids Res. 11 (11): 3503–16. doi:10.1093/nar/11.11.3503. PMC 325982. PMID 6190133. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=325982.
- Bretscher A, Weber K (1980). "Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner.". Cell 20 (3): 839–47. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-X. PMID 6893424.
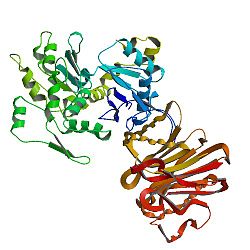
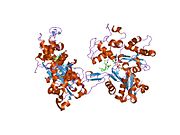
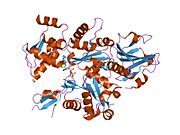
PDB gallery 1atn: Atomic structure of the actin:DNASE I complex1c0g: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF 1:1 COMPLEX BETWEEN GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1 AND A DICTYOSTELIUM/TETRAHYMENA CHIMERA ACTIN (MUTANT 228: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/E360H)1d4x: Crystal Structure of Caenorhabditis Elegans Mg-ATP Actin Complexed with Human Gelsolin Segment 1 at 1.75 A resolution.1eqy: COMPLEX BETWEEN RABBIT MUSCLE ALPHA-ACTIN: HUMAN GELSOLIN DOMAIN 11esv: COMPLEX BETWEEN LATRUNCULIN A:RABBIT MUSCLE ALPHA ACTIN:HUMAN GELSOLIN DOMAIN 11h1v: GELSOLIN G4-G6/ACTIN COMPLEX1hlu: STRUCTURE OF BOVINE BETA-ACTIN-PROFILIN COMPLEX WITH ACTIN BOUND ATP PHOSPHATES SOLVENT ACCESSIBLE1ijj: THE X-RAY CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX BETWEEN RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE ACTIN AND LATRUNCULIN A AT 2.85 A RESOLUTION1j6z: UNCOMPLEXED ACTIN1kxp: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN VITAMIN D-BINDING PROTEIN IN COMPLEX WITH SKELETAL ACTIN1lcu: Polylysine Induces an Antiparallel Actin Dimer that Nucleates Filament Assembly: Crystal Structure at 3.5 A Resolution1lot: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE COMPLEX OF ACTIN WITH VITAMIN D-BINDING PROTEIN1m8q: Molecular Models of Averaged Rigor Crossbridges from Tomograms of Insect Flight Muscle1ma9: Crystal structure of the complex of human vitamin D binding protein and rabbit muscle actin1mdu: Crystal structure of the chicken actin trimer complexed with human gelsolin segment 1 (GS-1)1mvw: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1nlv: Crystal Structure Of Dictyostelium Discoideum Actin Complexed With Ca ATP And Human Gelsolin Segment 11nm1: Crystal Structure of D. Dicsoideum Actin Complexed With Gelsolin Segment 1 and Mg ATP at 1.8 A Resolution1nmd: Crystal Structure of D. Discoideum Actin-Gelsolin Segment 1 Complex Crystallized In Presence Of Lithium ATP1nwk: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MONOMERIC ACTIN IN THE ATP STATE1o18: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o19: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1a: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1b: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1c: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1d: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1e: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1f: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1o1g: MOLECULAR MODELS OF AVERAGED RIGOR CROSSBRIDGES FROM TOMOGRAMS OF INSECT FLIGHT MUSCLE1p8z: Complex Between Rabbit Muscle alpha-Actin: Human Gelsolin Residues Val26-Glu1561qz5: Structure of rabbit actin in complex with kabiramide C1qz6: Structure of rabbit actin in complex with jaspisamide A1rdw: Actin Crystal Dynamics: Structural Implications for F-actin Nucleation, Polymerization and Branching Mediated by the Anti-parallel Dimer1rfq: Actin Crystal Dynamics: Structural Implications for F-actin Nucleation, Polymerization and Branching Mediated by the Anti-parallel Dimer1rgi: Crystal structure of gelsolin domains G1-G3 bound to actin1s22: Absolute Stereochemistry of Ulapualide A1sqk: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CIBOULOT IN COMPLEX WITH SKELETAL ACTIN1t44: Structural basis of actin sequestration by thymosin-B4: Implications for arp2/3 activation1wua: The structure of Aplyronine A-actin complex1y64: Bni1p Formin Homology 2 Domain complexed with ATP-actin1yxq: Crystal structure of actin in complex with swinholide A2a3z: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of WASP with Actin-DNAse I2a40: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of WAVE with Actin-DNAse I2a41: Ternary complex of the WH2 Domain of WIP with Actin-DNAse I2a42: Actin-DNAse I Complex2a5x: Crystal Structure of a Cross-linked Actin Dimer2asm: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Reidispongiolide A2aso: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Sphinxolide B2asp: Structure of Rabbit Actin In Complex With Reidispongiolide C2btf: THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE PROFILIN-BETA-ACTIN2d1k: Ternary complex of the WH2 domain of mim with actin-dnase I2ff3: Crystal structure of Gelsolin domain 1:N-wasp V2 motif hybrid in complex with actin2ff6: Crystal structure of Gelsolin domain 1:ciboulot domain 2 hybrid in complex with actin2fxu: X-ray Structure of Bistramide A- Actin Complex at 1.35 A resolution.2gwj: SpvB ADP-ribosylated actin: hexagonal crystal form2gwk: SpvB ADP-ribosylated actin: orthorhombic crystal form2hf3: Crystal structure of monomeric Actin in the ADP bound state2hf4: Crystal structure of Monomeric Actin in its ATP-bound state2hmp: Uncomplexed actin cleaved with protease ECP322oan: Structure of oxidized beta-actin2q1n: Actin Dimer Cross-linked Between Residues 41 and 3742q31: Actin Dimer Cross-linked Between Residues 41 and 374 and proteolytically cleaved by subtilisin between residues 47 and 48.2q36: Actin Dimer Cross-linked between Residues 191 and 374 and complexed with Kabiramide CProteins of the cytoskeleton Human I (MYO1A, MYO1B, MYO1C, MYO1D, MYO1E, MYO1F, MYO1G, MYO1H) · II (MYH1, MYH2, MYH3, MYH4, MYH6, MYH7, MYH7B, MYH8, MYH9, MYH10, MYH11, MYH13, MYH14, MYH15, MYH16) · III (MYO3A, MYO3B) · V (MYO5A, MYO5B, MYO5C) · VI (MYO6) · VII (MYO7A, MYO7B) · IX (MYO9A, MYO9B) · X (MYO10) · XV (MYO15A) · XVIII (MYO18A, MYO18B) · LC (MYL1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL4, MYL5, MYL6, MYL6B, MYL7, MYL9, MYLIP, MYLK, MYLK2, MYLL1)OtherOtherEpithelial keratins
(soft alpha-keratins)Ungrouped alphaNot alphaType 3Type 4Type 5OtherOtherNonhuman Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 1 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.