- Destrin
-
Destrin (actin binding protein) 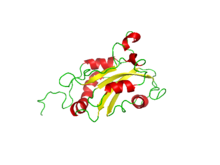
Nuclear magnetic resonance determined configuration of the tertiary structure of Destrin.[1] Identifiers Symbol DSTN Alt. symbols ADF Entrez 11034 HUGO 15750 OMIM 609114 RefSeq NM_006870 UniProt P60981 Other data Locus Chr. 20 p12.1 Destrin or DSTN (also known as actin depolymerizing factor or ADF) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the DSTN gene.[2][3][4] Destrin is a component protein in microfilaments.
The product of this gene belongs to the actin-binding proteins ADF (Actin-Depolymerizing Factor)/cofilin family. This family of proteins is responsible for enhancing the turnover rate of actin in vivo. This gene encodes the actin depolymerizing protein that severs actin filaments (F-actin) and binds to actin monomers (G-actin). Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene.[2]
Contents
Structure
The tertiary structure of destrin was determined by the use of triple-resonance multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR.[1] The secondary and tertiary structures of destrin are similar to the gelsolin family which is another actin-regulating protein family.
There are three ordered layers to destrin which is a globular protein. There is a central β sheet that is composed of one parallel strand and three antiparallel strands. This β sheet is between a long α helix along with a shorter one and two shorter helices on the opposite side. The four helices are parallel to the β strands.[1]
Function
In a variety of eukaryotes, destrin regulates actin in the cytoskeleton. Destrin binds actin and is thought to connect it as gelsolin segment-1 does. Furthermore, the binding of actin by destrin and cofilin is regulated negatively by phosphorylation. Destrin can also sever actin filaments. [1]
References
- ^ a b c d PDB 1AK6; Hatanaka H, Ogura K, Moriyama K, Ichikawa S, Yahara I, Inagaki F (June 1996). "Tertiary structure of destrin and structural similarity between two actin-regulating protein families". Cell 85 (7): 1047–55. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81305-7. PMID 8674111.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: Destrin". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=11034.
- ^ Hawkins M, Pope B, Maciver SK, Weeds AG (September 1993). "Human actin depolymerizing factor mediates a pH-sensitive destruction of actin filaments". Biochemistry 32 (38): 9985–93. doi:10.1021/bi00089a014. PMID 8399167.
- ^ Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2001). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature 414 (6866): 865–71. doi:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
External links
- MeSH Destrin
- Ramachandran Plot for destrin: "MolProbity Ramachandran analysis for 1ak6". www.rcsb.org. http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/images/1AK6_ram_m_500.pdf.
Proteins of the cytoskeleton Human I (MYO1A, MYO1B, MYO1C, MYO1D, MYO1E, MYO1F, MYO1G, MYO1H) · II (MYH1, MYH2, MYH3, MYH4, MYH6, MYH7, MYH7B, MYH8, MYH9, MYH10, MYH11, MYH13, MYH14, MYH15, MYH16) · III (MYO3A, MYO3B) · V (MYO5A, MYO5B, MYO5C) · VI (MYO6) · VII (MYO7A, MYO7B) · IX (MYO9A, MYO9B) · X (MYO10) · XV (MYO15A) · XVIII (MYO18A, MYO18B) · LC (MYL1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL4, MYL5, MYL6, MYL6B, MYL7, MYL9, MYLIP, MYLK, MYLK2, MYLL1)OtherOtherEpithelial keratins
(soft alpha-keratins)Ungrouped alphaNot alphaType 3Type 4Type 5OtherOtherNonhuman see also cytoskeletal defects
B strc: edmb (perx), skel (ctrs), epit, cili, mito, nucl (chro)This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Categories:- Genes on chromosome 20
- Chromosome 20 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
