- Myotilin
-
Myotilin 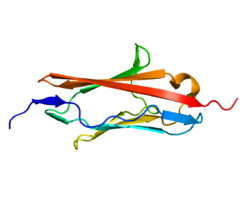
Rendering based on PDB 2KDG.Available structures PDB 2KDG, 2KKQ Identifiers Symbols MYOT; LGMD1; LGMD1A; TTID External IDs OMIM: 604103 MGI: 1889800 HomoloGene: 4942 GeneCards: MYOT Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • actin binding
• protein binding
• structural constituent of muscleCellular component • cytoplasm
• actin cytoskeleton
• sarcomere
• sarcolemmaBiological process • muscle contraction Sources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 9499 58916 Ensembl ENSG00000120729 ENSMUSG00000024471 UniProt Q9UBF9 A0A509 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001135940.1 NM_001033621.3 RefSeq (protein) NP_001129412.1 NP_001028793.1 Location (UCSC) Chr 5:
137.2 – 137.22 MbChr 18:
44.49 – 44.52 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Myotilin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYOT gene.[1][2][3]
Striated muscle sarcomeres are highly organized structures composed of actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments that slide past each other during contraction. The integrity of sarcomeres is controlled by a set of structural proteins, among which are titin (TTN; MIM 188840), a giant molecule that contains several immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains and associates with thin and thick filaments, and alpha-actinin (ACTN1; MIM 102575), an actin cross-linking protein. Mutations in several sarcomeric and sarcolemmal proteins have been shown to result in muscular dystrophy and cardiomyopathy.[supplied by OMIM][3]
Myotilin (myofibrillar titin-like protein) also known as TTID (TiTin Immunoglobulin Domain) is a skeletal muscle protein that is found within the Z-disc of sarcomeres. It is mutated in various forms of muscular dystrophy:- Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy type 1A (LGMD1A)
- Myofibrillar Myopathy (MFM)
- Spheroid Body Myopathy
- Distal MyopathyMyotilin was originally identified as a novel alpha-actinin binding partner with two Ig-like domains, that localised to the Z-disc.[4] The C2-type Ig-like domains reside at the C-terminal half, and are most homologous to Ig domains 2-3 of palladin and Ig domains 4-5 of myopalladin and more distantly related to Z-disc Ig domains 7 and 8 of titin. By contrast, the N-terminal part of myotilin is unique, consisting of a serine-rich region with no homology to known proteins. Several disease-associated mutations involve serine residues within the serine-rich domain. Myotilin expression in human tissues is mainly restricted to striated muscles and nerves. In muscles, myotilin is predominantly found within the Z-discs. Myotilin forms homodimers and binds alpha-actinin, actin[5], Filamin C[6], FATZ-1[7] and ZASP[8]. Myotilin induces the formation of actin bundles in vitro and in non-muscle cells. A ternary complex myotilin/actin/alpha-actinin can be observed in vitro and actin bundles formed in this conditions appear more tightly packed than those induced by alpha-actinin alone. It was demonstrated that myotilin stabilises F-actin by slowing down the disassembly rate. Ectopic overexpression of truncated myotilin causes the disruption of nascent myofibrils and the co-accumulation of myotilin and titin in amorphous cytoplasmic precipitates. In mature sarcomeres, wild-type myotilin co-localises with alpha-actinin and Z-disc titin, showing the striated pattern typical of sarcomeric proteins. Targeted disruption of myotilin gene in mice does not cause significant alteration in muscle function[9]. On the other hand, transgenic mice with mutated myotilin develop muscle dystrophy[10].
References
- ^ Godley LA, Lai F, Liu J, Zhao N, Le Beau MM (Nov 1999). "TTID: A novel gene at 5q31 encoding a protein with titin-like features". Genomics 60 (2): 226–33. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5912. PMID 10486214.
- ^ Salmikangas P, Mykkanen OM, Gronholm M, Heiska L, Kere J, Carpen O (Aug 1999). "Myotilin, a novel sarcomeric protein with two Ig-like domains, is encoded by a candidate gene for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy". Hum Mol Genet 8 (7): 1329–36. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.7.1329. PMID 10369880.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: MYOT myotilin". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=9499.
- ^ Salmikangas, P., et al., Myotilin, a novel sarcomeric protein with two Ig-like domains, is encoded by a candidate gene for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet, 1999. 8(7): p. 1329-36
- ^ Salmikangas, P., et al., Myotilin, the limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1A (LGMD1A) protein, cross-links actin filaments and controls sarcomere assembly. Hum Mol Genet, 2003. 12(2): p. 189-203
- ^ van der Ven, P.F., et al., Indications for a novel muscular dystrophy pathway. gamma-filamin, the muscle-specific filamin isoform, interacts with myotilin. J Cell Biol, 2000. 151(2): p. 235-48
- ^ Gontier, Y., et al., The Z-disc proteins myotilin and FATZ-1 interact with each other and are connected to the sarcolemma via muscle-specific filamins. J Cell Sci, 2005. 118(Pt 16): p. 3739-49.
- ^ von Nandelstadh, P., et al., A class III PDZ binding motif in myotilin and FATZ families binds Enigma family proteins – a common link for Zdisc myopathies. Mol Cell Biol, 2009.
- ^ Moza M, et al. Targeted deletion of the muscular dystrophy gene myotilin does not perturb muscle structure or function in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2007, 27(1):244-252
- ^ Garvey, S.M., et al., Transgenic mice expressing the myotilin T57I mutation unite the pathology associated with LGMD1A and MFM. Hum Mol Genet, 2006. 15(15): p. 2348-62
External links
Further reading
- Speer MC, Yamaoka LH, Gilchrist JH, et al. (1992). "Confirmation of genetic heterogeneity in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy: linkage of an autosomal dominant form to chromosome 5q.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 50 (6): 1211–7. PMC 1682558. PMID 1598902. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1682558.
- Dixon MJ, Read AP, Donnai D, et al. (1991). "The gene for Treacher Collins syndrome maps to the long arm of chromosome 5.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49 (1): 17–22. PMC 1683211. PMID 1676560. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1683211.
- Bartoloni L, Horrigan SK, Viles KD, et al. (1999). "Use of a CEPH meiotic breakpoint panel to refine the locus of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1A (LGMD1A) to a 2-Mb interval on 5q31.". Genomics 54 (2): 250–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5579. PMID 9828127.
- Hauser MA, Horrigan SK, Salmikangas P, et al. (2000). "Myotilin is mutated in limb girdle muscular dystrophy 1A.". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (14): 2141–7. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.14.2141. PMID 10958653.
- van der Ven PF, Wiesner S, Salmikangas P, et al. (2000). "Indications for a novel muscular dystrophy pathway. gamma-filamin, the muscle-specific filamin isoform, interacts with myotilin.". J. Cell Biol. 151 (2): 235–48. doi:10.1083/jcb.151.2.235. PMC 2192634. PMID 11038172. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2192634.
- Hauser MA, Conde CB, Kowaljow V, et al. (2003). "myotilin Mutation found in second pedigree with LGMD1A.". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71 (6): 1428–32. doi:10.1086/344532. PMC 378586. PMID 12428213. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=378586.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Salmikangas P, van der Ven PF, Lalowski M, et al. (2003). "Myotilin, the limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1A (LGMD1A) protein, cross-links actin filaments and controls sarcomere assembly.". Hum. Mol. Genet. 12 (2): 189–203. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg020. PMID 12499399.
- Battle MA, Maher VM, McCormick JJ (2003). "ST7 is a novel low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) with a cytoplasmic tail that interacts with proteins related to signal transduction pathways.". Biochemistry 42 (24): 7270–82. doi:10.1021/bi034081y. PMID 12809483.
- Selcen D, Engel AG (2004). "Mutations in myotilin cause myofibrillar myopathy.". Neurology 62 (8): 1363–71. PMID 15111675.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Witt SH, Granzier H, Witt CC, Labeit S (2005). "MURF-1 and MURF-2 target a specific subset of myofibrillar proteins redundantly: towards understanding MURF-dependent muscle ubiquitination.". J. Mol. Biol. 350 (4): 713–22. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.05.021. PMID 15967462.
- Gontier Y, Taivainen A, Fontao L, et al. (2006). "The Z-disc proteins myotilin and FATZ-1 interact with each other and are connected to the sarcolemma via muscle-specific filamins.". J. Cell. Sci. 118 (Pt 16): 3739–49. doi:10.1242/jcs.02484. PMID 16076904.
- von Nandelstadh P, Grönholm M, Moza M, et al. (2005). "Actin-organising properties of the muscular dystrophy protein myotilin.". Exp. Cell Res. 310 (1): 131–9. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.06.027. PMID 16122733.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network.". Nature 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Foroud T, Pankratz N, Batchman AP, et al. (2006). "A mutation in myotilin causes spheroid body myopathy.". Neurology 65 (12): 1936–40. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000188872.28149.9a. PMID 16380616.
- Garvey SM, Senderek J, Beckmann JS, et al. (2006). "Myotilin is not the causative gene for vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness with distal myopathy (VCPDM).". Ann. Hum. Genet. 70 (Pt 3): 414–6. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00252.x. PMID 16674563.
- Pénisson-Besnier I, Talvinen K, Dumez C, et al. (2006). "Myotilinopathy in a family with late onset myopathy.". Neuromuscul. Disord. 16 (7): 427–31. doi:10.1016/j.nmd.2006.04.009. PMID 16793270.
Histology: muscle tissue (TH H2.00.05, H3.3) Smooth
muscleStriated
muscleMembrane/
extracellularIntracellularDystrophin · Dystrobrevin (A, B) · Syntrophin (A, B1, B2, G1, G2) · Syncoilin · Dysbindin · Synemin/desmuslin
related: NOS1 · Caveolin 3GeneralNeuromuscular junction · Motor unit · Muscle spindle · Excitation-contraction coupling · Sliding filament mechanismBothFiberCellsOtherOther/
ungroupedCategories:- Human proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
