- Follicular thyroid cancer
-
Follicular thyroid cancer Classification and external resources 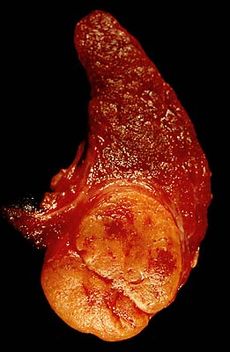
Gross pathological section of a follicular thyroid adenoma (tumor at the bottom).ICD-10 C73 ICD-9 193 OMIM 188470 eMedicine med/804 MeSH D013964 Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for 15% of thyroid cancer which occurs more commonly in women of over 50 years old. Thyroglobulin (Tg) can be used as a tumor marker for well-differentiated follicular thyroid cancer.
Contents
Classification
It is impossible to distinguish between follicular adenoma and carcinoma on cytological grounds. If fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) suggests follicular neoplasm, thyroid lobectomy should be performed to establish the histopathological diagnosis. Features sine qua non for the diagnosis of follicular carcinoma are capsular invasion and vascular invasion by tumor cells.
- Follicular carcinoma tends to metastasize to lung and bone via the bloodstream.
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma commonly metastasizes to cervical lymph nodes.
HMGA2 has been proposed as a marker to identify malignant tumors.[1]
Treatment
Treatment is usually surgical, followed by radioiodine.
Initial treatment
- If follicular cells are found on cytological testing, it is common to carry out hemithyroidectomy to distinguish between follicular adenoma and follicular carcinoma on histopathological examination, proceeding to completion thyroidectomy and postoperative radioiodine ablation where carcinoma is confirmed. This way total thyroidectomy is not carried out unnecessarily.
- Thyroidectomy is invariably followed by radioiodine treatment at levels from 50 to 200 millicuries following two weeks of a low iodine diet (LID). Occasionally treatment must be repeated if annual scans indicate remaining cancerous tissue. Some physicians favor administering the maximum safe dose (calculated based on a number of factors), while others favor administering smaller doses, which may still be effective in ablating all thyroid tissue. I-131 is used for ablation of the thyroid tissue.
Minimally invasive thyroidectomy has been used in recent years in cases where the nodules are small.[2]
Finding disease recurrence
Some studies have shown that thyroglobulin (Tg) testing combined with neck ultrasound is more productive in finding disease recurrence than full- or whole-body scans (WBS) using radioactive iodine. However, current protocol (in the USA) suggests a small number of clean annual WBS are required before relying on Tg testing plus neck ultrasound. When needed, whole body scans consist of withdrawal from thyroxine medication and/or injection of recombinant human Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). In both cases, a low iodine diet regimen must also be followed to optimize the takeup of the radioactive iodine dose. Low dose radioiodine of a few millicuries is administered. Full body nuclear medicine scan follows using a gamma camera. Scan doses of radioactive iodine may be I131 or I123.
Recombinant human TSH, commercial name Thyrogen, is produced in cell culture from genetically engineered hamster cells.
Hurthle cell variant
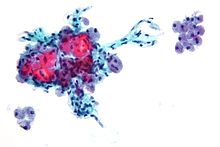 Micrograph of a Hurthle cell neoplasm.
Micrograph of a Hurthle cell neoplasm.
Hurthle cell thyroid cancer is often considered a variant of follicular cell carcinoma.[3][4] Hurthle cell forms are more likely than follicular carcinomas to be bilateral and multifocal and to metastasize to lymph nodes. Like follicular carcinoma, unilateral hemithyroidectomy is performed for non-invasive disease, and total thyroidectomy for invasive disease
Prognosis
The overall 5-year survival rate for follicular thyroid cancer is 91%, and the 10-year survival rate is 85%.[5]
By overall cancer staging into stages I to IV, follicular thyroid cancer has a 5-year survival rate of 100% for stages I and II, 71% for stage III, and 50% for stage IV.[6]
Associated mutations
Approximately one-half of follicular thyroid carcinomas have mutations in the Ras subfamily of oncogenes, most notably HRAS, NRAS, and KRAS.[7] Also, a chromosomal translocation specific for follicular thyroid carcinomas is one between paired box gene 8 (PAX-8), a gene important in thyroid development, and the gene encoding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ 1 (PPARγ1), a nuclear hormone receptor contributing to terminal differentiation of cells. The PAX8-PPARγ1 fusion is present in approximately one-third of follicular thyroid carcinomas, specifically those cancers with a t(2;3)(q13;p25) translocation, permitting juxtaposition of portions of both genes.[7] Tumors tend carry either a RAS mutation or a PAX8-PPARγ1 fusion, and only rarely are both genetic abnormalities present in the same case.[7] Thus, follicular thyroid carcinomas seem to arise by two distinct and virtually nonoverlapping molecular pathways.[7]
References
- ^ Belge G, Meyer A, Klemke M et al. (2008). "Upregulation of HMGA2 in thyroid carcinomas: A novel molecular marker to distinguish between benign and malignant follicular neoplasias". Genes Chromosomes Cancer 47 (1): 56–63. doi:10.1002/gcc.20505. PMID 17943974.
- ^ Hegazy MA, Khater AA, Setit AE et al. (2007). "Minimally invasive video-assisted thyroidectomy for small follicular thyroid nodules". World J Surg 31 (9): 1743–50. doi:10.1007/s00268-007-9147-7. PMID 17653588.
- ^ Kushchayeva Y, Duh QY, Kebebew E, D'Avanzo A, Clark OH (2007). "Comparison of clinical characteristics at diagnosis and during follow-up in 118 patients with Hurthle cell or follicular thyroid cancer". Am J Surg 195 (4): 457–62. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.06.001. PMID 18070728.
- ^ Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP. "Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers" in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (Eds) Cancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 11 ed. 2008.
- ^ Numbers from National Cancer Database in the US, from Page 10 in: F. Grünwald; Biersack, H. J.; Grںunwald, F. (2005). Thyroid cancer. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-540-22309-6. (Note:Book also states that the 14% 10-year survival for anaplastic thyroid cancer was overestimated
- ^ cancer.org > Thyroid Cancer By the American Cancer Society. In turn citing: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual (7th ed).
- ^ a b c d Chapter 20 in: Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson. Robbins Basic Pathology. Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 1-4160-2973-7. 8th edition.
Tumors: endocrine gland neoplasia (C73–C75/D34–D35, 193–194/226–227) Pancreas/
islets of LangerhansHypothalamic/
pituitary axes
+parathyroidPituitaryThyroidThyroid cancer (malignant): epithelial cell /carcinoma (Papillary, Follicular/Hurthle cell) · parafollicular cell (Medullary) · AnaplasticBenign: Thyroid adenoma · Struma ovariiParathyroidGonadssee genital neoplasiaPinealoma Pinealoblastoma · PineocytomaMEN Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
