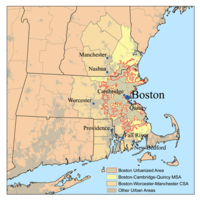
- Greater Boston
-
Boston–Cambridge–Quincy
Common name: Greater BostonLargest city Boston Other cities Cambridge
QuincyPopulation Ranked 10th in the U.S. - Total 4,522,858 (2008 est.)[1] - Density 947 /sq. mi.
366 /km²Area 4,674 sq. mi.
12,105 km²State(s) Massachusetts
New HampshireElevation - Highest point 635 feet (194 m) - Lowest point 0 feet (0 m) Greater Boston is the area of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts surrounding the city of Boston. Due to ambiguity in usage, the size of the area referred to can be anywhere between that of the metropolitan statistical area (MSA) of Boston and that of the city's combined statistical area (CSA) which includes the metro areas of Providence, Rhode Island and Worcester, Massachusetts.
By contrast, Metro Boston is usually reserved to signify the "inner core" surrounding the City of Boston,[citation needed] while "Greater Boston" usually at least overlaps the North and South Shores, as well as MetroWest and the Merrimack Valley.
Greater Boston is tenth in population among U.S. metropolitan statistical areas in the United States, home to over 4.6 million people as of the 2010 U.S. Census and is ranked fifth among CSA's, having over 7.6 million people.[2]
Greater Boston has many sites and people significant to American history and culture, particularly the American Revolution, civil rights, literature, and politics, and is one of the nation's centers of education, finance, industry, and tourism, with the sixth-largest Gross metropolitan product in the country and 12th-largest in the world.
Contents
Definitions
Light Blue represents the area in Massachusetts known as Greater Boston, while Dark Blue represents the Metro-Boston area[specify][citation needed] and Red represents Boston proper, the City of Boston.
Metropolitan Area Planning Council
The most restrictive definition of the Greater Boston area is the region administered by the Metropolitan Area Planning Council (MAPC).[3] The MAPC is a regional planning organization created by the Massachusetts legislature to oversee transportation infrastructure and economic development concerns in the Boston area. The MAPC includes 101 cities and towns that are grouped into eight subregions. These include most of the area within the region's outer circumferential highway, I-495. The population of the MAPC district is 3,066,394 (as of 2000), in an area of 1,422 square miles (3,680 km2),[3] of which 39% is forested and an additional 11% is water, wetland, or other open space.[4]
The eight subregions and their principal towns are: Inner Core (Boston), Minuteman (Route 2 corridor), MetroWest (Framingham), North Shore (Peabody), North Suburban (Woburn), South Shore (Route 3 corridor), SouthWest (Franklin), and Three Rivers (Norwood).
Notably excluded from the MAPC and its partner planning body, the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization, are the Merrimack Valley cities of Lowell, Lawrence, and Haverhill, much of Plymouth County, and all of Bristol County; these areas have their own regional planning bodies.
New England City and Town Area
The urbanized area surrounding Boston serves as the core of a definition used by the U.S. Census Bureau known as the New England city and town area. The set of towns containing the core urbanized area plus surrounding towns with strong social and economic ties to the core area is defined as the Boston-Cambridge-Quincy, MA-NH Metropolitan NECTA.[5] The Boston NECTA is further subdivided into several NECTA divisions, which are listed below. The Boston, Framingham, and Peabody NECTA divisions together correspond roughly to the MAPC area. The total population of the Boston NECTA was 4,540,941 (as of 2000).
- Boston-Cambridge-Quincy, MA NECTA Division (97 towns)
- Framingham, MA NECTA Division (13 towns)
- Peabody, MA NECTA Division (7 towns)
- Brockton-Bridgewater-Easton, MA NECTA Division (Old Colony region) (12 towns)
- Haverhill-North Andover-Amesbury, MA-NH NECTA Division (Merrimack Valley region) (25 towns)
- Lawrence-Methuen-Salem, MA-NH NECTA Division (part of Merrimack Valley region) (3 towns)
- Lowell-Billerica-Chelmsford, MA-NH NECTA Division (Northern Middlesex region) (9 towns)
- Nashua, NH-MA NECTA Division (21 towns)
- Taunton-Norton-Raynham, MA NECTA Division (part of Southeastern region) (6 towns)
Metropolitan statistical area
An alternative definition used by the U.S. Census Bureau, using counties as building blocks instead of towns, is the Boston-Cambridge-Quincy, MA-NH Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is further subdivided into four metropolitan divisions. The metropolitan statistical area has a total population of approximately 4.4 million and is the tenth-largest in the United States. The components of the metropolitan area with their estimated 2005 populations are listed below.
- Boston-Cambridge-Quincy, MA-NH Metropolitan Statistical Area (4,411,835)
- Boston-Quincy, MA Metropolitan Division (1,800,432)
- Norfolk County, Massachusetts
- Plymouth County, Massachusetts
- Suffolk County, Massachusetts
- Cambridge-Newton-Framingham, MA Metropolitan Division (1,459,011)
- Middlesex County, Massachusetts
- Essex County, MA Metropolitan Division (738,301)
- Essex County, Massachusetts
- Rockingham County-Strafford County, NH Metropolitan Division (414,091)
- Rockingham County, New Hampshire
- Strafford County, New Hampshire
- Boston-Quincy, MA Metropolitan Division (1,800,432)
Combined statistical area
A wider functional metropolitan area based on commuting patterns is also defined by the Census Bureau as the Boston-Worcester-Manchester, MA-RI-NH Combined Statistical Area. This area consists of the metropolitan areas of Manchester, Worcester, and Providence, in addition to Greater Boston. The total population (as of 2005) for the extended region is 7,427,336. The following areas, along with the above MSA, are included in the Combined Statistical Area:
- Worcester, MA Metropolitan Statistical Area (783,262)
- Worcester County, Massachusetts
- Providence-New Bedford-Fall River, RI-MA Metropolitan Statistical Area (1,622,520)
- Bristol County, Massachusetts
- Bristol County, Rhode Island
- Kent County, Rhode Island
- Newport County, Rhode Island
- Providence County, Rhode Island
- Washington County, Rhode Island
- Concord, NH Micropolitan Statistical Area (146,681)
- Merrimack County, New Hampshire
- Laconia, NH Micropolitan Statistical Area (61,547)
- Belknap County, New Hampshire
- Manchester-Nashua, NH Metropolitan Statistical Area (401,291)
- Hillsborough County, New Hampshire
Principal cities and towns
Boston metropolitan area
The Census Bureau defines the following as principal cities in the Boston NECTA[5] using criteria developed for what the Office of Management and Budget calls a Core Based Statistical Area:[6]
These, in decreasing order of population, are the ten largest cities in the Boston NECTA (2008):
City 2008
population[7][8]Boston 620,535 Cambridge 105,596 Lowell 103,615 Brockton 93,007 Quincy 92,339 Lynn 86,957 Newton 82,139 Somerville 75,662 Lawrence 70,014 Satellite areas
These larger cities fall within the CSA definition of Greater Boston only
- Fall River
- Fitchburg
- Leominster
- New Bedford
- Taunton
- Brockton
- Manchester
- Providence
- Warwick
- Worcester
Major companies
- Companies along, inside or outside I-495:
- Abbott Laboratories, in Worcester (Pharmaceutical laboratory)
- Advanced Cell Technology, in Worcester (Research laboratory)
- AMD, in Marlborough
- Analog Devices, in Norwood
- Avid Technology, Inc, in Tewksbury (Headquarters)
- Bain & Company, in Boston (Headquarters)
- Bain Capital, in Boston (Headquarters)
- BJ's Wholesale Club, Inc., in Natick (Headquarters)
- Bose Corporation, in Framingham (Headquarters)
- Boston Properties, Inc., in Boston (Headquarters)
- Boston Scientific Corporation, in Natick (Headquarters)
- Boston Scientific Corporation, in Marlborough
- David Clark Company, in Worcester (manufacturer of space suits)
- Diebold, in Marlborough (Regional Headquarters)
- EMC Corporation, in Hopkinton (Headquarters)
- Evergreen Solar, in Marlborough (Headquarters)
- Hewlett-Packard Company, in Marlborough (Regional Headquarters)
- Intel Corporation, in Hudson
- Marshalls, Inc, in Framingham (Headquarters)
- The MathWorks, in Natick
- Monster.com, in Maynard (Headquarters)
- Morgan Construction Company, in Worcester, rolling steel mill technology
- Philips Electronics North America, in Andover (Regional Headquarters)
- Philips Healthcare, in Andover (Global Headquarters) and Framingham
- Red Hat, in Westford (Engineering Headquarters)
- Reed & Barton in Taunton (Factory & Headquarters)
- Saint-Gobain, in Worcester
- Sepracor, Inc., in Marlborough (Headquarters)
- Staples, Inc., in Framingham (Headquarters)
- Stop & Shop, in Quincy (Headquarters)
- TJX Corporation, in Framingham (Headquarters)
- TripAdvisor, LLC, in Needham (Headquarters)
- WB Mason, in Brockton (Headquarters)
- Wyman-Gordon, in Grafton, complex metal components and products
- Companies along or inside I-95 (Route 128), not including Boston:
- Akamai Technologies, in Cambridge
- BBN Technologies, in Cambridge (Headquarters)
- Biocell Center, in Medford (North American Headquarters)
- Biogen Idec, in Cambridge
- Carl Zeiss SMT, in Peabody (North American Headquarters)
- Dunkin' Donuts, in Canton (Headquarters)
- Genzyme Corporation, in Cambridge (Headquarters)
- Genzyme Corporation, in Waltham (R&D)
- General Electric Aviation, in Lynn
- Greater Boston Tickets,[where?]
- Haemonetics, in Braintree
- IBM, in Waltham, Cambridge and Littleton
- ITA Software, in Cambridge (Headquarters)
- InterSystems Corporation, in Cambridge (Headquarters)
- iRobot Corporation, in Burlington (Headquarters)
- LogMeIn, in Woburn (Headquarters)
- Meditech, in Westwood (Headquarters)
- Millennium Pharmaceuticals, in Cambridge
- National Amusements (Parent company of CBS and Viacom), in Dedham (Headquarters)
- National Grid, in Waltham (US Headquarters)
- Novartis AG, Inc, in Cambridge (Research Headquarters)
- Novell, Inc., in Waltham
- Oracle Corporation in Burlington
- Osram Sylvania in Danvers (Headquarters)
- Parametric Technology Corporation in Needham (Headquarters)
- Philips Lighting in Burlington
- Progress Software in Bedford (Headquarters)
- Raytheon, in Waltham (Headquarters)
- Reebok, in Canton (U.S. Headquarters)
- Sun Microsystems, in Burlington
- Teradyne, in North Reading (Headquarters)
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, in Waltham (Headquarters)
- Major companies inside Boston proper:
- American Tower (headquarters)
- Au Bon Pain (headquarters)
- Bain & Company (headquarters)
- Bentley Motors (U.S. headquarters)
- Boston Consulting Group (headquarters)
- Fidelity Investments (headquarters)
- The Gillette Company, now owned by Procter & Gamble (headquarters)
- Houghton Mifflin Harcourt (headquarters)
- John Hancock Financial Services, Inc, now the United States division of Canada's Manulife Financial
- Liberty Mutual (headquarters)
- New Balance Athletic Shoe, Inc. (headquarters)
- Putnam Investments (headquarters)
- Sonesta International Hotels Corp. (headquarters)
- State Street Corporation (headquarters)
- Wayfair (headquarters)
- Zipcar (headquarters)
Demographics
Greater Boston has a sizable Jewish community, estimated at between 210,000 people,[11][12] and 261,000[13] or 5–6% of the Greater Boston metro population, compared with about 2% for the nation as a whole. Contrary to national trends, the number of Jews in Greater Boston has been growing, fueled by the fact that 60% of children in Jewish mixed-faith families are raised Jewish, compared with roughly one in three nationally.[11]
The City of Boston also has one of the largest LGBT populations per capita. It ranks 5th of all major cities in the country (behind San Francisco, and slightly behind Seattle, Atlanta, and Minneapolis respectively), with 12.3% of the city recognizing themselves as gay, lesbian, or bisexual.[14]
Sports
Club Sport League Stadium Established League Titles Boston Bruins Ice hockey National Hockey League TD Garden (Boston) 1924 6 Stanley Cups
7 Eastern Conference TitlesBoston Cannons Lacrosse Major League Lacrosse Harvard Stadium (Boston) 2001 None Boston Celtics Basketball National Basketball Association TD Garden (Boston) 1946 17 NBA Championships
21 Eastern Conference TitlesBoston Red Sox Baseball Major League Baseball (AL) Fenway Park (Boston) 1901 7-time MLB World Series Champions
12 American League PennantsNew England Patriots Football National Football League (American Football Conference) Gillette Stadium (Foxboro) 1960
(as Boston Patriots)3-time Super Bowl Champions
6-time AFC ChampionsNew England Revolution Soccer Major League Soccer Gillette Stadium (Foxboro) 1995 1 US Open Cup
1 SuperLigaAnnual sporting events include:
- The Boston Marathon, which follows a course from Hopkinton to Boston
- The Head of the Charles Regatta
Higher education
A long time center of higher education, the area includes many community colleges, two-year schools, and internationally prominent undergraduate and graduate institutions. The graduate schools include highly regarded schools of law, medicine, business, technology, international relations, public health, education, and religion.
See also: Boston, Massachusetts#Education , List of colleges and universities in metropolitan Boston, and List of colleges and universities in MassachusettsTransportation
Highways
- Central Artery/Tunnel Project (Interstate 93 within Boston)
- Interstate 95: North to New Hampshire and Maine; south to Providence, Rhode Island and beyond. Largely concurrent with MA-128
- U.S. 1
- Interstate 93: North to New Hampshire; south to Canton
- U.S. Route 3
- Massachusetts Route 2: Northwest and west
- The Massachusetts Turnpike (Interstate 90): West to Framingham, Massachusetts and beyond
- Massachusetts Route 9: Western suburbs, to Framingham and Pittsfield
- Massachusetts Route 24: South toward Newport, Rhode Island
- Massachusetts Route 3: Southeast through South Shore to Cape Cod
- Massachusetts Route 128 (I-95/I-93): Circumferential Highway (close to Boston)
- Interstate 495: Circumferential (farther from Boston)
- Route 128 is sometimes regarded as the unofficial boundary of the Greater Boston region, especially to the north and south. When the name Greater Boston is used in a more inclusive sense, I-495 is sometimes regarded as the boundary.
Bridges and tunnels
- Callahan Tunnel, carrying Route 1A Northbound
- Sumner Tunnel, carrying Route 1A Southbound
- Ted Williams Tunnel, carrying I-90
- Thomas P. O'Neill Jr. Tunnel, carrying I-93 and Routes 1 and 3 concurrently.
- Tobin Bridge, carrying Route 1
- Zakim Bunker Hill Bridge, carrying Interstate 93, Route 1 and Route 3 concurrently.
Airports
- Logan International Airport in Boston, 3 mi (5 km) northeast of downtown Boston, New England's largest transportation center.
- Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester, New Hampshire
- T. F. Green Airport in Providence, Rhode Island
- Hanscom Field in Bedford
- Norwood Memorial Airport
- Worcester Regional Airport
- Beverly Airport
Rail and bus
- Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA, generally known as the "T".)
- Red Line: Cambridge–Braintree and Boston (Mattapan)
- Orange Line: Boston (Jamaica Plain)–Malden
- Green Line: Cambridge–Brookline and Newton
- Blue Line: Boston–Revere
- Silver Line South Station–Logan Airport and Downtown–Dudley Square
- MBTA Commuter Rail
- Old Colony Lines serving Plymouth County
- Providence/Stoughton Line serving northern Bristol County, connecting to Providence, Rhode Island
- Fairmount Line shuttle service from South Station
- Franklin Line serving western Norfolk County
- Greenbush Line serving Boston's South Shore
- Needham Line serving Boston suburbs and Needham
- Framingham/Worcester Line serving southwestern Middlesex County, connecting to Worcester
- Fitchburg Line serving northwestern Middlesex County, connecting to Fitchburg
- Lowell Line serving northern Middlesex County
- Haverhill/Reading Line and Newburyport/Rockport Line serving Essex County & Boston's North Shore
- Amtrak service to New York City and Washington, D.C.
- Amtrak Downeaster service to Maine from North Station
The first railway line in the United States was in Quincy. See Neponset River.
The following Regional Transit Authorities have bus service that connects with MBTA commuter rail stations:
- Brockton Area Transit Authority
- Cape Ann Transportation Authority
- Greater Attleboro Taunton Regional Transit Authority
- Lowell Regional Transit Authority
- Merrimack Valley Regional Transit Authority
- MetroWest Regional Transit Authority
- Montachusett Regional Transit Authority
- Worcester Regional Transit Authority
Ocean transportation
- Port of Boston (Massport)
- Cape Cod Canal
Geography
- Rivers
- Hills
Major Cities Cities and towns
100k-250kCities and towns
25k-99kAttleboro • Braintree • Brockton • Central Falls • Chelsea • Concord • Coventry • Cranston • Cumberland • Dover • East Providence • Everett • Fall River • Fitchburg • Framingham • Franklin • Gloucester • Haverhill • Johnston • Lawrence • Leominster • Lynn • Malden • Marlborough • Medford • Melrose • Methuen • Nashua • New Bedford • Newport • Newton • North Kingstown • North Providence • Pawtucket • Plymouth • Quincy • Revere • Rochester • Salem • Somerville • South Kingstown • Taunton • Wakefield • Waltham • Warwick • Watertown • West Warwick • Westerly • Weymouth • Woburn • WoonsocketCities and towns
10k-25kAmesbury • Barrington • Beverly • Bristol • Burrillville • East Greenwich • Gardner • Laconia • Lincoln • Middletown • Narragansett, Rhode Island • Newburyport • North Smithfiel • Peabody • Portsmouth (Rhode Island) • Portsmouth (New Hampshire) • Scituate • Smithfield • Somersworth • Southbridge • Tiverton • Warren • WinthropSub-regions  Commonwealth of Massachusetts
Commonwealth of MassachusettsBoston (capital) Topics Index · Administrative divisions · Congressional districts · Culture · Demographics · Economy · Education · Elections · Geography · Geology · Government · History · Images · Music · People · Politics · Sports · State symbols · Transportation · Villages · Visitor Attractions · Windmills
Regions The Berkshires · Blackstone Valley · Cape Ann · Cape Cod · Central Massachusetts · Greater Boston · The Islands · Merrimack Valley · MetroWest · Montachusett-North County · North Shore · Pioneer Valley · Quabbin Valley · Southeastern Massachusetts · South Coast · South County · South Shore · Western Massachusetts
Counties Cities
(see all
municipalities)Agawam · Amesbury · Attleboro · Barnstable · Beverly · Boston · Braintree · Bridgewater · Brockton · Cambridge · Chelsea · Chicopee · Easthampton · Everett · Fall River · Fitchburg · Franklin · Gardner · Gloucester · Greenfield · Haverhill · Holyoke · Lawrence · Leominster · Lowell · Lynn · Malden · Marlborough · Medford · Melrose · Methuen · New Bedford · Newburyport · Newton · North Adams · Northampton · Palmer · Peabody · Pittsfield · Quincy · Randolph · Revere · Salem · Somerville · Southbridge · Springfield · Taunton · Waltham · Watertown · Westfield · West Springfield · Weymouth · Winthrop · Woburn · Worcester
Note: Municipalities not listed above have a town meeting form of government. Municipalities listed above in italics have a city form of government, but have retained the name prefix "Town of " as part of their official names. State of New Hampshire
State of New HampshireConcord (capital) Topics History | Geography | People | Government | Delegations | Constitution | General Court | Executive Council | Governor | Supreme Court | Elections | Visitor attractions
Regions Counties Belknap | Carroll | Cheshire | Coös | Grafton | Hillsborough | Merrimack | Rockingham | Strafford | Sullivan
Cities Berlin | Claremont | Concord | Dover | Franklin | Keene | Laconia | Lebanon | Manchester | Nashua | Portsmouth | Rochester | Somersworth
Towns Acworth | Albany | Alexandria | Allenstown | Alstead | Alton | Amherst | Andover | Antrim | Ashland | Atkinson | Auburn | Barnstead | Barrington | Bartlett | Bath | Bedford | Belmont | Bennington | Benton | Bethlehem | Boscawen | Bow | Bradford | Brentwood | Bridgewater | Bristol | Brookfield | Brookline | Campton | Canaan | Candia | Canterbury | Carroll | Center Harbor | Charlestown | Chatham | Chester | Chesterfield | Chichester | Clarksville | Colebrook | Columbia | Conway | Cornish | Croydon | Dalton | Danbury | Danville | Deerfield | Deering | Derry | Dorchester | Dublin | Dummer | Dunbarton | Durham | East Kingston | Easton | Eaton | Effingham | Ellsworth | Enfield | Epping | Epsom | Errol | Exeter | Farmington | Fitzwilliam | Francestown | Franconia | Freedom | Fremont | Gilford | Gilmanton | Gilsum | Goffstown | Gorham | Goshen | Grafton | Grantham | Greenfield | Greenland | Greenville | Groton | Hampstead | Hampton | Hampton Falls | Hancock | Hanover | Harrisville | Hart's Location | Haverhill | Hebron | Henniker | Hill | Hillsborough | Hinsdale | Holderness | Hollis | Hooksett | Hopkinton | Hudson | Jackson | Jaffrey | Jefferson | Kensington | Kingston | Lancaster | Landaff | Langdon | Lee | Lempster | Lincoln | Lisbon | Litchfield | Littleton | Londonderry | Loudon | Lyman | Lyme | Lyndeborough | Madbury | Madison | Marlborough | Marlow | Mason | Meredith | Merrimack | Middleton | Milan | Milford | Milton | Monroe | Mont Vernon | Moultonborough | Nelson | New Boston | Newbury | New Castle | New Durham | Newfields | New Hampton | Newington | New Ipswich | New London | Newmarket | Newport | Newton | Northfield | North Hampton | Northumberland | Northwood | Nottingham | Orange | Orford | Ossipee | Pelham | Pembroke | Peterborough | Piermont | Pittsburg | Pittsfield | Plainfield | Plaistow | Plymouth | Randolph | Raymond | Richmond | Rindge | Rollinsford | Roxbury | Rumney | Rye | Salem | Salisbury | Sanbornton | Sandown | Sandwich | Seabrook | Sharon | Shelburne | South Hampton | Springfield | Stark | Stewartstown | Stoddard | Strafford | Stratford | Stratham | Sugar Hill | Sullivan | Sunapee | Surry | Sutton | Swanzey | Tamworth | Temple | Thornton | Tilton | Troy | Tuftonboro | Unity | Wakefield | Walpole | Warner | Warren | Washington | Waterville Valley | Weare | Webster | Wentworth | Westmoreland | Whitefield | Wilmot | Wilton | Winchester | Windham | Windsor | Wolfeboro | Woodstock
Townships Atkinson and Gilmanton Academy Grant | Bean's Grant | Bean's Purchase | Cambridge | Chandler's Purchase | Crawford's Purchase | Cutt's Grant | Dix's Grant | Dixville | Erving's Location | Green's Grant | Hadley's Purchase | Hale's Location | Kilkenny | Livermore | Low and Burbank's Grant | Martin's Location | Millsfield | Odell | Pinkham's Grant | Sargent's Purchase | Second College Grant | Success | Thompson and Meserve's Purchase | Wentworth's Location
 State of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations
State of Rhode Island and Providence PlantationsProvidence (capital) Topics Culture | Delegations | Geography | Government | History | Thirteen Colonies | Colonial Colleges | Images | Narragansett Indian Tribe | People | Visitor attractions | State symbols
Regions Counties: Bristol | Kent | Newport | Providence | Washington | Geographic: Blackstone Valley | Block Island
Cities Central Falls | Cranston | East Providence | Newport | Pawtucket | Providence | Warwick | Woonsocket
Towns Barrington | Bristol | Burrillville | Charlestown | Coventry | Cumberland | East Greenwich | Exeter | Foster | Glocester | Hopkinton | Jamestown | Johnston | Lincoln | Little Compton | Middletown | Narragansett | New Shoreham (Block Island) | North Kingstown | North Providence | North Smithfield | Portsmouth | Richmond | Scituate | Smithfield | South Kingstown | Tiverton | Warren | Westerly | West Greenwich | West Warwick
References
- ^ Census.gov, Retrieved November 30, 2009
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Population of Combined Statistical Areas: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2009" (CSV). 2007 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. 2008-03-27. http://www.census.gov/population/estimates/metro_general/2007/CSA-EST2007-alldata.csv. Retrieved 2008-04-02.
- ^ a b "About MAPC". Metropolitan Area Planning Council. Archived from the original on 2007-02-21. http://web.archive.org/web/20070221050155/http://www.mapc.org/about_mapc.html. Retrieved 2007-05-14.
- ^ "Transportation Plan – Overview". Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization. 2009. http://www.ctps.org/bostonmpo/3_programs/1_transportation_plan/plan.html. Retrieved 2009-09-27.
- ^ a b "New England City and Town Areas and Principal Cities". U.S. Census Bureau. November 2008. http://www.census.gov/population/www/metroareas/lists/2008/List8.txt. Retrieved September 14, 2009.
- ^ "Standards for Defining Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas". Office of Management and Budget. December 27, 2000. http://www.census.gov/population/www/metroareas/files/00-32997.pdf. Retrieved September 14, 2009.
- ^ "Table 5: Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Minor Civil Divisions in Massachusetts, Listed Alphabetically Within County: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008" (Microsoft XLS). U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/tables/SUB-EST2008-05-25.xls. Retrieved 2009-07-16.
- ^ "Table 5: Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Minor Civil Divisions in New Hampshire, Listed Alphabetically Within County: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008" (Microsoft XLS). U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/tables/SUB-EST2008-05-33.xls. Retrieved September 14, 2009.
- ^ "2009 Globe 100 – Top Massachusetts-based employers – The Boston Globe". The Boston Globe. 2010-01-19. http://www.boston.com/business/globe/globe100/globe_100_2009/mass_based_employers/.
- ^ UCSO.indiana.edu
- ^ a b Michael Paulson (2006-11-10). "Jewish population in region rises". Boston Globe. http://www.boston.com/news/local/articles/2006/11/10/jewish_population_in_region_rises/. Retrieved 2009-11-29.
- ^ "Cities with the Largest Jewish Population in the Diaspora". adherents.com. http://www.adherents.com/largecom/com_judaism.html#cities. Retrieved 2009-11-29.
- ^ "Metro Area Membership Report". The Association of Religion Data Archives. http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/metro/1123_2000.asp. Retrieved 2009-11-29.
- ^ "12.9% in Seattle are gay or bisexual, second only to S.F., study says". The Seattle Times (The Seattle Times Company). 2006. http://seattletimes.nwsource.com/ABPub/zoom/html/2003432941.html. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
Further reading
- Wilson, Susan (2005). The Literary Trail of Greater Boston: A Tour of Sites in Boston, Cambridge, and Concord, Revised Edition. Commonwealth Editions. ISBN 1889833673. An informative guidebook, with facts and data about literary figures, publishers, bookstores, libraries, and other historic sites on the newly designated Literary Trail of Greater Boston.
- Warner, Sam, Jr. (2001). Greater Boston: Adapting Regional Traditions to the Present. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 0812217691.
50 largest metropolitan statistical areas in the United States by population - New York
- Los Angeles
- Chicago
- Dallas–Fort Worth
- Philadelphia
- Houston
- Washington
- Miami
- Atlanta
- Boston
- Memphis
- Louisville
- Richmond
- Oklahoma City
- Hartford
- New Orleans
- Buffalo
- Raleigh
- Birmingham
- Salt Lake City
Categories:- Geography of Boston, Massachusetts
- Metropolitan areas of Massachusetts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.