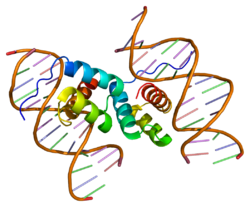
- PDX1
-
Pdx1 (Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1), also known as insulin promoter factor 1, is a transcription factor necessary for pancreatic development and β-cell maturation. Pdx1 (in rodents), otherwise known as Ipf1 (in humans), is the gene encoding it.[1]
Contents
Function
Pancreatic development
In embryonic development, Pdx1 is expressed by a population of cells in the posterior foregut region of the definitive endoderm, and Pdx1+ epithelial cells give rise to the developing pancreatic buds, and eventually, the whole of the pancreas—its exocrine, endocrine, and ductal cell populations.[2] Pancreatic Pdx1+ cells first arise at mouse embryonic day 8.5-9.0 (E8.5-9.0), and Pdx1 expression continues until E12.0-E12.5,[3] after which Pdx1 expression decreases and the pancreas is formed—other transcription factors are expressed, controlling the fates of the cells of the newly formed pancreas.[4] Homozygous Pdx1 knockout mice form pancreatic buds but fail to develop a pancreas,[4] and transgenic mice in which tetracycline application results in death of Pdx1+ cells are almost completely apancreatic if doxycycline (tetracycline derivative) is administered throughout the pregnancy of these transgenic mice, illustrating the necessity of Pdx1+ cells in pancreatic development.[3]
β-cell Maturation
Pdx1 is also necessary for β-cell maturation: developing β-cells co-express Pdx1, Nkx6-1, and insulin, a process that results in the silencing of MafB and the expression of MafA, a necessary switch in maturation of β-cells.[2] Pdx1 appears to also play a role in the fating of endocrine cells, encoding for insulin and somatostatin, two pancreatic endocrine products, while repressing glucagon. Thus, Pdx1 expression apparently favors the production of insulin+ β-cells and somatostatin+Δ-cells rather than glucagon+ α-cells.
Transcriptional Network
Pdx1+ pancreatic progenitor cells also co-express Hlxb9, Hnf6, Ptf1a and Nkx6-1, and these progenitor cells form the initial pancreatic buds, which further proliferate and branch in response to FGF-10 signaling. Afterwards, fating of the pancreatic cells begins; a population of cells has Notch signaling inhibited, and subsequently, expresses Ngn3. This Ngn3+ population is a transient population of pancreatic endocrine progenitors that gives rise to the α, β, Δ, PP, and ε cells of the Islets of Langerhans.[3] Other cells will give rise to the exocrine and ductal pancreatic cell populations.
Pathology
Mutations in the Pdx1 gene may be involved in several pancreatic pathologies, possibly diabetes mellitus.[5]
Interactions
Pdx1 has been shown to interact with MAFA.[6]
References
- ^ Stoffel M, Stein R, Wright CV, Espinosa R, Le Beau MM, Bell GI (July 1995). "Localization of human homeodomain transcription factor insulin promoter factor 1 (IPF1) to chromosome band 13q12.1". Genomics 28 (1): 125–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1120. PMID 7590740.
- ^ a b D'Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, Kelly OG, Agulnick AD, Smart NG, Moorman MA, Kroon E, Carpenter MK, Baetge EE (November 2006). "Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (11): 1392–401. doi:10.1038/nbt1259. PMID 17053790.
- ^ a b c Stanger BZ, Tanaka AJ, Melton DA (February 2007). "Organ size is limited by the number of embryonic progenitor cells in the pancreas but not the liver". Nature 445 (7130): 886–91. doi:10.1038/nature05537. PMID 17259975.
- ^ a b Liew CG, Shah NN, Briston SJ, Shepherd RM, Khoo CP, Dunne MJ, Moore HD, Cosgrove KE, Andrews PW (2008). "PAX4 enhances beta-cell differentiation of human embryonic stem cells". PLoS ONE 3 (3): e1783. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001783. PMC 2262135. PMID 18335054. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2262135.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PDX1 pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3651.
- ^ Zhao, Li; Guo Min, Matsuoka Taka-Aki, Hagman Derek K, Parazzoli Susan D, Poitout Vincent, Stein Roland (Mar. 2005). "The islet beta cell-enriched MafA activator is a key regulator of insulin gene transcription". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 280 (12): 11887–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409475200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15665000.
Further reading
- Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J, & Douglas A. Melton DA (2008). "In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to β-cells". Nature 454 (7209): 627–32. doi:10.1038/nature07314. PMID 18754011.
- Hui H, Perfetti R (2002). "Pancreas duodenum homeobox-1 regulates pancreas development during embryogenesis and islet cell function in adulthood.". Eur. J. Endocrinol. 146 (2): 129–41. doi:10.1530/eje.0.1460129. PMID 11834421.
- Leonard J, Peers B, Johnson T, et al. (1994). "Characterization of somatostatin transactivating factor-1, a novel homeobox factor that stimulates somatostatin expression in pancreatic islet cells.". Mol. Endocrinol. 7 (10): 1275–83. doi:10.1210/me.7.10.1275. PMID 7505393.
- Stoffel M, Stein R, Wright CV, et al. (1995). "Localization of human homeodomain transcription factor insulin promoter factor 1 (IPF1) to chromosome band 13q12.1.". Genomics 28 (1): 125–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1120. PMID 7590740.
- Inoue H, Riggs AC, Tanizawa Y, et al. (1996). "Isolation, characterization, and chromosomal mapping of the human insulin promoter factor 1 (IPF-1) gene.". Diabetes 45 (6): 789–94. doi:10.2337/diabetes.45.6.789. PMID 8635654.
- Waeber G, Thompson N, Nicod P, Bonny C (1997). "Transcriptional activation of the GLUT2 gene by the IPF-1/STF-1/IDX-1 homeobox factor.". Mol. Endocrinol. 10 (11): 1327–34. doi:10.1210/me.10.11.1327. PMID 8923459.
- Watada H, Kajimoto Y, Kaneto H, et al. (1997). "Involvement of the homeodomain-containing transcription factor PDX-1 in islet amyloid polypeptide gene transcription.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 229 (3): 746–51. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.1875. PMID 8954967.
- Marshak S, Totary H, Cerasi E, Melloul D (1997). "Purification of the beta-cell glucose-sensitive factor that transactivates the insulin gene differentially in normal and transformed islet cells.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (26): 15057–62. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.26.15057. PMC 26355. PMID 8986763. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=26355.
- Stoffers DA, Zinkin NT, Stanojevic V, et al. (1997). "Pancreatic agenesis attributable to a single nucleotide deletion in the human IPF1 gene coding sequence.". Nat. Genet. 15 (1): 106–10. doi:10.1038/ng0197-106. PMID 8988180.
- Sharma S, Jhala US, Johnson T, et al. (1997). "Hormonal regulation of an islet-specific enhancer in the pancreatic homeobox gene STF-1.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (5): 2598–604. PMC 232109. PMID 9111329. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=232109.
- Carty MD, Lillquist JS, Peshavaria M, et al. (1997). "Identification of cis- and trans-active factors regulating human islet amyloid polypeptide gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (18): 11986–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.18.11986. PMID 9115263.
- Macfarlane WM, Smith SB, James RF, et al. (1997). "The p38/reactivating kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade mediates the activation of the transcription factor insulin upstream factor 1 and insulin gene transcription by high glucose in pancreatic beta-cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (33): 20936–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.33.20936. PMID 9252422.
- Macfarlane WM, Frayling TM, Ellard S, et al. (1999). "Missense mutations in the insulin promoter factor-1 gene predispose to type 2 diabetes.". J. Clin. Invest. 104 (9): R33–9. doi:10.1172/JCI7449. PMC 481047. PMID 10545530. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=481047.
- Hani EH, Stoffers DA, Chèvre JC, et al. (1999). "Defective mutations in the insulin promoter factor-1 (IPF-1) gene in late-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus.". J. Clin. Invest. 104 (9): R41–8. doi:10.1172/JCI7469. PMC 409821. PMID 10545531. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=409821.
- Glick E, Leshkowitz D, Walker MD (2000). "Transcription factor BETA2 acts cooperatively with E2A and PDX1 to activate the insulin gene promoter.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (3): 2199–204. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.3.2199. PMID 10636926.
- Schwartz PT, Perez-Villamil B, Rivera A, et al. (2000). "Pancreatic homeodomain transcription factor IDX1/IPF1 expressed in developing brain regulates somatostatin gene transcription in embryonic neural cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (25): 19106–14. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000655200. PMID 10751390.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination.". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=310948.
- Liu Y, MacDonald RJ, Swift GH (2001). "DNA binding and transcriptional activation by a PDX1.PBX1b.MEIS2b trimer and cooperation with a pancreas-specific basic helix-loop-helix complex.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (21): 17985–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100678200. PMID 11279116.
- Samaras SE, Cissell MA, Gerrish K, et al. (2002). "Conserved sequences in a tissue-specific regulatory region of the pdx-1 gene mediate transcription in Pancreatic beta cells: role for hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 beta and Pax6.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (13): 4702–13. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.13.4702-4713.2002. PMC 133887. PMID 12052878. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=133887.
- Zhou J, Pineyro MA, Wang X, et al. (2002). "Exendin-4 differentiation of a human pancreatic duct cell line into endocrine cells: involvement of PDX-1 and HNF3beta transcription factors.". J. Cell. Physiol. 192 (3): 304–14. doi:10.1002/jcp.10143. PMID 12124776.
PDB gallery External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription factors and intracellular receptors (1) Basic domains (1.1) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP)Activating transcription factor (AATF, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) · AP-1 (c-Fos, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JDP2, c-Jun, JUNB, JUND) · BACH (1, 2) · BATF · BLZF1 · C/EBP (α, β, γ, δ, ε, ζ) · CREB (1, 3, L1) · CREM · DBP · DDIT3 · GABPA · HLF · MAF (B, F, G, K) · NFE (2, L1, L2, L3) · NFIL3 · NRL · NRF (1, 2, 3) · XBP1(1.2) Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)ATOH1 · AhR · AHRR · ARNT · ASCL1 · BHLHB2 · BMAL (ARNTL, ARNTL2) · CLOCK · EPAS1 · FIGLA · HAND (1, 2) · HES (5, 6) · HEY (1, 2, L) · HES1 · HIF (1A, 3A) · ID (1, 2, 3, 4) · LYL1 · MESP2 · MXD4 · MYCL1 · MYCN · Myogenic regulatory factors (MyoD, Myogenin, MYF5, MYF6) · Neurogenins (1, 2, 3) · NeuroD (1, 2) · NPAS (1, 2, 3) · OLIG (1, 2) · Pho4 · Scleraxis · SIM (1, 2) · TAL (1, 2) · Twist · USF1(1.3) bHLH-ZIP(1.4) NF-1(1.5) RF-X(1.6) Basic helix-span-helix (bHSH)(2) Zinc finger DNA-binding domains (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4)subfamily 1 (Thyroid hormone (α, β), CAR, FXR, LXR (α, β), PPAR (α, β/δ, γ), PXR, RAR (α, β, γ), ROR (α, β, γ), Rev-ErbA (α, β), VDR)
subfamily 2 (COUP-TF (I, II), Ear-2, HNF4 (α, γ), PNR, RXR (α, β, γ), Testicular receptor (2, 4), TLX)
subfamily 3 (Steroid hormone (Androgen, Estrogen (α, β), Glucocorticoid, Mineralocorticoid, Progesterone), Estrogen related (α, β, γ))
subfamily 4 NUR (NGFIB, NOR1, NURR1) · subfamily 5 (LRH-1, SF1) · subfamily 6 (GCNF) · subfamily 0 (DAX1, SHP)(2.2) Other Cys4(2.3) Cys2His2General transcription factors (TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE (1, 2), TFIIF (1, 2), TFIIH (1, 2, 4, 2I, 3A, 3C1, 3C2))
ATBF1 · BCL (6, 11A, 11B) · CTCF · E4F1 · EGR (1, 2, 3, 4) · ERV3 · GFI1 · GLI-Krüppel family (1, 2, 3, REST, S2, YY1) · HIC (1, 2) · HIVEP (1, 2, 3) · IKZF (1, 2, 3) · ILF (2, 3) · KLF (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17) · MTF1 · MYT1 · OSR1 · PRDM9 · SALL (1, 2, 3, 4) · SP (1, 2, 4, 7, 8) · TSHZ3 · WT1 · Zbtb7 (7A, 7B) · ZBTB (16, 17, 20, 32, 33, 40) · zinc finger (3, 7, 9, 10, 19, 22, 24, 33B, 34, 35, 41, 43, 44, 51, 74, 143, 146, 148, 165, 202, 217, 219, 238, 239, 259, 267, 268, 281, 295, 300, 318, 330, 346, 350, 365, 366, 384, 423, 451, 452, 471, 593, 638, 644, 649, 655)(2.4) Cys6(2.5) Alternating composition(3) Helix-turn-helix domains (3.1) HomeodomainARX · CDX (1, 2) · CRX · CUTL1 · DBX (1, 2) · DLX (3, 4, 5) · EMX2 · EN (1, 2) · FHL (1, 2, 3) · HESX1 · HHEX · HLX · Homeobox (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B13, C4, C5, C6, C8, C9, C10, C11, C12, C13, D1, D3, D4, D8, D9, D10, D11, D12, D13) · HOPX · IRX (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MKX) · LMX (1A, 1B) · MEIS (1, 2) · MEOX2 · MNX1 · MSX (1, 2) · NANOG · NKX (2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-5, 3-1, 3-2, 6-1, 6-2) · NOBOX · PBX (1, 2, 3) · PHF (1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 16, 17, 20, 21A) · PHOX (2A, 2B) · PITX (1, 2, 3) · POU domain (PIT-1, BRN-3: A, B, C, Octamer transcription factor: 1, 2, 3/4, 6, 7, 11) · OTX (1, 2) · PDX1 · SATB2 · SHOX2 · VAX1 · ZEB (1, 2)(3.2) Paired box(3.3) Fork head / winged helix(3.4) Heat Shock Factors(3.5) Tryptophan clusters(3.6) TEA domain(4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts (4.1) Rel homology region(4.2) STAT(4.3) p53(4.4) MADS box(4.6) TATA binding proteins(4.7) High-mobility group(4.10) Cold-shock domainCSDA, YBX1(4.11) Runt(0) Other transcription factors (0.2) HMGI(Y)(0.3) Pocket domain(0.6) Miscellaneoussee also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Transcription factors
- Chromosome 13 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.