- List of sovereign states
-
"List of nations" and "List of countries" redirect here. For other country lists, see Lists of countries and territories. For other national lists, see Lists of nations. For non-sovereign dependencies, see Dependent territory.
This is a list of sovereign states giving an overview of states around the world with information on the status and recognition of their sovereignty.
The list contains 204 entries. The states are divided using two distinct methods:
- The membership within the United Nations system column divides the states into two categories: 194 states that are either member states or observer states in the United Nations,[1] and 10 other states.
- The sovereignty disputes column divides the states into two categories: 13 states whose sovereignty is disputed and 191 other states.
Compiling a list such as this can be a difficult and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerning the criteria for statehood. For more information on the criteria used to determine the contents of this list, please see the criteria for inclusion section below.
Contents
List of states
Name in English, and the official, national, and other important languages of the state [Note 1] Membership within the UN System [Note 2] Sovereignty dispute [Note 3] Further information on status and recognition of sovereignty [Note 5] UN member states or observer states Abkhazia → Abkhazia  Afghanistan – Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
Afghanistan – Islamic Republic of Afghanistan
UN member state None  Albania – Republic of Albania
Albania – Republic of Albania
- Albanian: Shqipëria – Republika e Shqipërisë
UN member state None  Algeria – People's Democratic Republic of Algeria
Algeria – People's Democratic Republic of Algeria
- Arabic: الجزائر – الجمهورية الجزائرية الديمقراطية الشعبية → Al Jazā'ir – Al Jumhūrīyah al Jazā'irīyah ad Dīmuqrāţīyah ash Sha‘bīyah
UN member state None  Andorra – Principality of Andorra
Andorra – Principality of Andorra
- Catalan: Andorra – Principat d’Andorra
UN member state None Andorra is a co-principality in which the office of head of state is jointly held ex officio by the French president and the bishop of the Roman Catholic diocese of Urgell,[3] who himself is appointed by the Holy See.  Angola – Republic of Angola
Angola – Republic of Angola
- Portuguese: Angola – República de Angola
UN member state None  Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda
- English: Antigua and Barbuda
UN member state None Antigua and Barbuda is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] with 1 autonomous region, Barbuda.[Note 7][4]  Argentina – Argentine Republic [Note 8]
Argentina – Argentine Republic [Note 8]
- Spanish: Argentina – República Argentina
UN member state None Argentina is a federation of 23 provinces and 1 autonomous city. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, which are administered by the United Kingdom.[5] Argentina claims Argentine Antarctica as part of its national territory, officially a department of the province of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica, and South Atlantic Islands, which overlaps with the claims of the UK and Chile.[Note 9][6]  Armenia – Republic of Armenia
Armenia – Republic of Armenia
- Armenian: Հայաստան – Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն → Hayastan – Hayastani Hanrapetut’yun
UN member state None Armenia is not recognised by one UN member: Pakistan.[7][8]  Australia – Commonwealth of Australia
Australia – Commonwealth of Australia
- English: Australia – Commonwealth of Australia
UN member state None Australia is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] and a federation of 6 states and 10 territories. The external territories of Australia are:  Austria – Republic of Austria
Austria – Republic of Austria
- German: Österreich – Republik Österreich
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Austria is a federation of 9 states (Bundesländer).  Azerbaijan – Republic of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan – Republic of Azerbaijan
- Azerbaijani: Azərbaycan – Azərbaycan Respublikası
UN member state None Azerbaijan contains 2 autonomous regions, Nakhchivan and Nagorno-Karabakh (Dağlıq Qarabağ).[Note 7] In Nagorno-Karabakh, a de facto state has been established.  Bahamas – Commonwealth of The Bahamas
Bahamas – Commonwealth of The Bahamas
- English: The Bahamas – Commonwealth of The Bahamas
UN member state None The Bahamas is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Bahrain – Kingdom of Bahrain
Bahrain – Kingdom of Bahrain
- Arabic: البحرين – مملكة البحرين → Al Baḩrayn – Mamlakat al Baḩrayn
UN member state None  Bangladesh – People's Republic of Bangladesh
Bangladesh – People's Republic of Bangladesh
- Bengali: বাংলাদেশ – গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ → Bāṁlādesh – Gaṇaprajātantrī Bāṁlādesh
UN member state None  Barbados
Barbados
- English: Barbados
UN member state None Barbados is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Belarus – Republic of Belarus
Belarus – Republic of Belarus
- Belarusian: Беларусь – Рэспубліка Беларусь → Bielarus' – Respublika Bielarus'
- Russian: Беларусь – Республика Беларусь → Belarus' – Respublika Belarus'
UN member state None  Belgium – Kingdom of Belgium
Belgium – Kingdom of Belgium
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Belgium is a federation divided into linguistic communities and regions.  Belize
Belize
- English: Belize
UN member state None Belize is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Benin – Republic of Benin [Note 10]
Benin – Republic of Benin [Note 10]
- French: Bénin – République du Bénin
UN member state None  Bhutan – Kingdom of Bhutan
Bhutan – Kingdom of Bhutan
- Dzongkha: འབྲུག་ཡུལ་ – འབྲུག་རྒྱལ་ཁབ་ → Druk Yul – Druk Gyalkhap
UN member state None  Bolivia – Plurinational State of Bolivia
Bolivia – Plurinational State of Bolivia
UN member state None  Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina
UN member state None Bosnia and Herzegovina is a federation of 2 constituent units: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Republika Srpska.[Note 11]  Botswana – Republic of Botswana
Botswana – Republic of Botswana
UN member state None  Brazil – Federative Republic of Brazil
Brazil – Federative Republic of Brazil
- Portuguese: Brasil – República Federativa do Brasil
UN member state None Brazil is a federation of 26 states and 1 federal district.  Brunei – State of Brunei, Abode of Peace
Brunei – State of Brunei, Abode of Peace
UN member state None Brunei claims sovereignty over part of the Spratly Islands.[Note 12]  Bulgaria – Republic of Bulgaria
Bulgaria – Republic of Bulgaria
- Bulgarian: България – Република България → Bǎlgarija – Republika Bǎlgarija
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Burkina Faso [Note 13]
Burkina Faso [Note 13]
- French: Burkina Faso
UN member state None  Burma – Republic of the Union of Myanmar [Note 14][11]
Burma – Republic of the Union of Myanmar [Note 14][11]
- Burmese: မြန်မာပြည် – ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော် → Myanma – Pyidaungzu Myanma Naingngandaw
UN member state None  Burundi – Republic of Burundi
Burundi – Republic of Burundi
UN member state None  Cambodia – Kingdom of Cambodia
Cambodia – Kingdom of Cambodia
- Khmer: កម្ពុជា – ព្រះរាជាណាចក្រ កម្ពុជា → Kâmpŭchéa – Preăhréachéanachâkr Kâmpŭchéa
UN member state None  Cameroon – Republic of Cameroon
Cameroon – Republic of Cameroon
UN member state None  Canada [Note 15]
Canada [Note 15]
UN member state None Canada is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] and a federation of 10 provinces and 3 territories.  Cape Verde – Republic of Cape Verde
Cape Verde – Republic of Cape Verde
- Portuguese: Cabo Verde – República de Cabo Verde
UN member state None  Central African Republic
Central African Republic
UN member state None  Chad – Republic of Chad
Chad – Republic of Chad
UN member state None  Chile – Republic of Chile
Chile – Republic of Chile
- Spanish: Chile – República de Chile
UN member state None Easter Island and the Juan Fernández Islands are "special territories" of Chile in the Valparaíso Region. Chile claims part of Antarctica as a commune in its Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region. Its claim overlaps with those of the UK and Argentina.[Note 9]  China – People's Republic of China[Note 16]
China – People's Republic of China[Note 16]
- Chinese: 中国 – 中华人民共和国 → Zhōnggúo – Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó
- Mongolian:
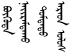 [Note 17] → Bügüde Nayiramdaqu Dumdadu Arad Ulus
[Note 17] → Bügüde Nayiramdaqu Dumdadu Arad Ulus - Tibetan: རྒྱ་ནག – ཀྲུང་ ཧྭ་ མི་ དམངས་ སྤྱི་ མཐུན་ རྒྱལ་ ཁབ། → Zhunghua Mimang Jitun Gyalkab
- Kazakh: جۇڭگو – جۇڭحۋا حالىق رەسپۋبليكاسى → Juñgo – Juñxwa Xalıq Respwblïkası
- Korean: 중국 – 중화인민공화국 → Jungguk – Junghwa Inmin Gonghwaguk
- Uyghur: جۇڭگو – جۇڭخۇا خەلق جۇمھۇرىيىت → Junggo – Jungxua Xelq Jumhuriyiti
- Zhuang: Cunghgoz – Cunghvaz Yinzminz Gunghozgoz[12][13]
UN member state Claimed by the Republic of China The People's Republic of China (PRC) contains five autonomous regions, Guangxi, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia, Xinjiang and Tibet.[Note 7] Additionally, it has sovereignty over the Special Administrative Regions of: It also claims:
- Taiwan and associated islands, Kinmen, Matsu, the Pratas and Itu Aba, which are governed by the Republic of China (which claims sovereignty over the whole of China);[Note 18]
- The Paracel Islands (disputed);[Note 19]
- The Spratly Islands (disputed);[Note 12]
- South Tibet (governed by India as part of Arunachal Pradesh).
Aksai Chin, controlled by the PRC, is claimed by India as a part of Jammu and Kashmir.[Note 20] The PRC is not recognised by 22 UN member states and the Holy See, which instead recognise the ROC.[Note 21]
China, Republic of (Taiwan) → Taiwan  Colombia – Republic of Colombia
Colombia – Republic of Colombia
- Spanish: Colombia – República de Colombia
UN member state None  Comoros – Union of the Comoros
Comoros – Union of the Comoros
UN member state None Comoros is a federation of 3 islands, and claims Mayotte, currently part of France, as a fourth.[Note 22][14] Comoros also disputes French sovereignty over Banc du Geyser.[5]  Congo, Democratic Republic of the (Congo-Kinshasa) [Note 23]
Congo, Democratic Republic of the (Congo-Kinshasa) [Note 23]
- French: République démocratique du Congo
UN member state None  Congo, Republic of the (Congo-Brazzaville)
Congo, Republic of the (Congo-Brazzaville)
- French: République du Congo
UN member state None  Costa Rica – Republic of Costa Rica
Costa Rica – Republic of Costa Rica
- Spanish: Costa Rica – República de Costa Rica
UN member state None  Côte d'Ivoire – Republic of Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
Côte d'Ivoire – Republic of Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- French: Côte d'Ivoire – République de Côte d'Ivoire
UN member state None  Croatia – Republic of Croatia
Croatia – Republic of Croatia
- Croatian: Hrvatska – Republika Hrvatska
UN member state None  Cuba – Republic of Cuba
Cuba – Republic of Cuba
- Spanish: Cuba – República de Cuba
UN member state None  Cyprus – Republic of Cyprus
Cyprus – Republic of Cyprus
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] The northeastern part of the island is the de facto state of Northern Cyprus. Cyprus is not recognised by one UN member: Turkey.[Note 24]  Czech Republic [Note 25]
Czech Republic [Note 25]
- Czech: Česko – Česká republika
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Denmark – Kingdom of Denmark
Denmark – Kingdom of Denmark
- Danish: Danmark – Kongeriget Danmark
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] The Kingdom of Denmark also includes two self-governing countries.[Note 26]
 Faroe Islands (Føroyar/Færøerne)
Faroe Islands (Føroyar/Færøerne) Greenland (Kalaallit Nunaat/Grønland)
Greenland (Kalaallit Nunaat/Grønland)
 Djibouti – Republic of Djibouti
Djibouti – Republic of Djibouti
UN member state None  Dominica – Commonwealth of Dominica
Dominica – Commonwealth of Dominica
- English: Dominica – Commonwealth of Dominica
UN member state None  Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
UN member state None  East Timor – Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste [Note 27]
East Timor – Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste [Note 27]
- Portuguese: Timor-Leste – República Democrática de Timor-Leste
- Tetum: Timor Lorosa'e – Repúblika Demokrátika Timor Lorosa'e
UN member state None  Ecuador – Republic of Ecuador
Ecuador – Republic of Ecuador
- Spanish: Ecuador – República del Ecuador
UN member state None  Egypt – Arab Republic of Egypt
Egypt – Arab Republic of Egypt
- Arabic: مصر –جمهوريّة مصرالعربيّة → Mişr – Jumhūrīyat Mişr al ‘Arabīyah
UN member state None  El Salvador – Republic of El Salvador
El Salvador – Republic of El Salvador
- Spanish: El Salvador – República de El Salvador
UN member state None  Equatorial Guinea – Republic of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea – Republic of Equatorial Guinea
- Spanish: Guinea Ecuatorial – República de Guinea Ecuatorial
- French: Guinée Équatoriale – République de Guinée équatoriale
- Portuguese: Guiné Equatorial – República da Guiné Equatorial
UN member state None  Eritrea – State of Eritrea
Eritrea – State of Eritrea
UN member state None  Estonia – Republic of Estonia
Estonia – Republic of Estonia
- Estonian: Eesti – Eesti Vabariik
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Ethiopia – Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
Ethiopia – Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
- Amharic: ኢትዮጵያ – የኢትዮጵያ ፈደራላዊ ዲሞክራሲያዊ ሪፐብሊክ → Ityop'iya – Ityop'iya Fe̱de̱ralawi Dimokrasiyawi Ripe̱blik
UN member state None Ethiopia is a federation of 9 regions and 2 chartered cities.  Fiji – Republic of Fiji
Fiji – Republic of Fiji
- Fijian: Viti – Matanitu ko Viti
- English: Fiji – Republic of Fiji
- Hindustani: फ़िजी / فیجی – फ़िजी गणराज्य / فیجی رپبلک → Fijī – Fijī dvip samooh ganarajya [15]
UN member state None Fiji contains 1 autonomous region, Rotuma.[Note 7][16][17]  Finland – Republic of Finland
Finland – Republic of Finland
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  France – French Republic
France – French Republic
- French: France – République française
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] French overseas regions/departments (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte and Réunion) are full, integral parts of France. The French Republic also includes the overseas territories of:
- Clipperton Island
 French Polynesia
French Polynesia New Caledonia
New Caledonia- Saint-Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Wallis and Futuna
- French Southern and Antarctic Lands (includes the Antarctic claim of Adélie Land).[Note 9]
Clipperton Island is a possession of the government. French sovereignty over Banc du Geyser, Bassas da India, Europa Island, Glorioso Islands, Juan de Nova Island, Mayotte, and Tromelin Island is disputed in part by Madagascar, Mauritius, Seychelles and the Comoros.[5]
 Gabon – Gabonese Republic
Gabon – Gabonese Republic
- French: Gabon – République gabonaise
UN member state None  The Gambia – Republic of The Gambia
The Gambia – Republic of The Gambia
- English: The Gambia – Republic of The Gambia
UN member state None  Georgia
Georgia
- Georgian: საქართველო → Sak’art’velo
UN member state None Georgia contains 2 autonomous regions, Adjara and Abkhazia.[Note 7] In Abkhazia and South Ossetia, de facto states have been formed.  Germany – Federal Republic of Germany
Germany – Federal Republic of Germany
- German: Deutschland – Bundesrepublik Deutschland
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Germany is a federation of 16 federated states (Länder).  Ghana – Republic of Ghana
Ghana – Republic of Ghana
- English: Ghana – Republic of Ghana
UN member state None  Greece – Hellenic Republic
Greece – Hellenic Republic
- Demotic Greek: Ελλάδα – Ελληνική Δημοκρατία → Elláda – Ellinikí Dimokratía
- Katharevousa Greek: Ελλάς – Ελληνική Δημοκρατία → Ellás – Ellinikí Dimokratía
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Mount Athos is an autonomous part of Greece that is jointly governed by the multinational "Holy Community" on the mountain and a civil governor appointed by the Greek government.[18]  Grenada
Grenada
- English: Grenada
UN member state None Grenada is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Guatemala – Republic of Guatemala
Guatemala – Republic of Guatemala
- Spanish: Guatemala – República de Guatemala
UN member state None  Guinea – Republic of Guinea
Guinea – Republic of Guinea
- French: Guinée – République de Guinée
UN member state None  Guinea-Bissau – Republic of Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau – Republic of Guinea-Bissau
- Portuguese: Guiné-Bissau – República da Guiné-Bissau
UN member state None  Guyana – Co-operative Republic of Guyana
Guyana – Co-operative Republic of Guyana
- English: Guyana – Co-operative Republic of Guyana
UN member state None All land west of the Essequibo River is claimed by Venezuela.[5]  Haiti – Republic of Haiti
Haiti – Republic of Haiti
- French: Haïti – République d’Haïti
- Haitian Creole: Ayiti – Repiblik d’Ayiti
UN member state None Holy See → Vatican City None  Honduras – Republic of Honduras
Honduras – Republic of Honduras
- Spanish: Honduras – República de Honduras
UN member state None  Hungary – Republic of Hungary
Hungary – Republic of Hungary
- Hungarian: Magyarország – Magyar Köztársaság
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Iceland – Republic of Iceland
Iceland – Republic of Iceland
- Icelandic: Ísland – Lýðveldið Ísland
UN member state None  India – Republic of India
India – Republic of India
- Hindi: भारत – भारत गणराज्य → Bhārat – Bhāratīya Gaṇarājya
- English: India – Republic of India
- Assamese: ভাৰত – ভাৰত গণৰাজ্য → Bhārôt – Bhārôt Gôṇrājẏô
- Bengali: ভারত – ভারতীয় প্রজাতন্ত্র → Bhārôt – Bhārôtīyô Prôjātôntrô
- Bhojpuri: भारत – भारत गणराज्य → Bhārat – Bhārat Gaṇrādzya
- Gujarati: ભારત – ભારત ગણરાજ્ય → Bhārat – Bhārat Gaṇrājya
- Kannada: ಭಾರತ – ಭಾರತ ಗಣರಾಜ್ಯ → Bhārata – Bhārata Gaṇarājya
- Kashmiri: ہِندوستان → Hindustān
- Konkani: भारत – भारोत गोणराज → Bhārot – Bhārot Goṇrāj
- Maithili: भारत – भारत गणराज्य → Bhārat – Bhārat Ganarājya
- Malayalam: ഭാരതം – ഭാരത ഗണരാജ്യം → Bhārataṃ – Bhārata Gaṇarājyaṃ
- Marathi: भारत – भारतीय प्रजासत्ताक → Bhārat – Bhāratīy Pradzāsattāk
- Meitei: ভারত – ভারত গণরাজ্য → Bhārata – Bhārata Gaṇarājya
- Nepali: भारत – भारत गणराज्य → Bhārat – Bhārat Gaṇrādzya
- Oriya: ଭାରତ – ଭାରତ ଗଣରାଜ୍ଯ → Bhārôt – Bhārôt Gôṇrājẏô
- Punjabi: ਭਾਰਤ – ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਤੰਤਰ → Bhārat – Bhārat Gaṇtãtar
- Sanskrit: भारतम् – भारत गणराज्यम् → Bhārat – Bhāratam Gaṇarājyam
- Sindhi: भारत गणराज्य, هندستانڀارت – भारत, ڀارت → Bhāratu – Bhārat Ganarājya
- Tamil: இந்தியா – இந்தியக் குடியரசு → Intiyā – Intiyak Kuṭiyaracu
- Telugu: భారత్ – భారత గణతంత్ర రాజ్యము → Bhārata – Bhārata Gaṇataṃtra Rājyamu
- Urdu: جمہوریہ بھارت – جمہوریہ بھارت → Bhārat – Jumhūrīyâ-e Bhārat [19]
UN member state None India is a federation of 28 states and 7 union territories. Indian sovereignty over Arunachal Pradesh is disputed by the People's Republic of China.[5] India claims sovereignty over the whole of Kashmir, but administers only part of it as the federated state of Jammu and Kashmir.[Note 20]  Indonesia – Republic of Indonesia
Indonesia – Republic of Indonesia
- Indonesian: Indonesia – Republik Indonesia
UN member state None Indonesia has 3 provinces with official special autonomy status: Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam, Papua, and West Papua.[Note 7]  Iran – Islamic Republic of Iran
Iran – Islamic Republic of Iran
- Persian: ایران – جمهوری اسلامی ایران → Īrān – Jomhūrī-ye Eslāmī-ye Īrān
UN member state None  Iraq – Republic of Iraq
Iraq – Republic of Iraq
UN member state None Iraq is a federation[Note 22][21] of 18 governorates, 3 of which make up the autonomous Iraqi Kurdistan.[Note 7]  Ireland [Note 29]
Ireland [Note 29]
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] The Constitution of Ireland asserts the aspiration towards creating a United Ireland by peaceful means.[22]
 Israel – State of Israel
Israel – State of Israel
UN member state None Israel annexed East Jerusalem, and occupies the Golan Heights[23] and parts of the West Bank. These areas are not internationally-recognised as being part of Israel.[5] Israel no longer has a permanent military presence in the Gaza Strip, following its unilateral disengagement, but is still considered the occupying power under international law.[24][25][26][27][28] Israel is not recognised as a state by 33 members of the UN.  Italy – Italian Republic
Italy – Italian Republic
- Italian: Italia – Repubblica Italiana
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Italy has 5 autonomous regions, Aosta Valley, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Sardinia, Sicily and Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol.[Note 7] Ivory Coast → Côte d'Ivoire  Jamaica
Jamaica
- English: Jamaica
UN member state None Jamaica is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Japan
Japan
UN member state None Japan disputes Russian administration of the South Kuril Islands.  Jordan – Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
Jordan – Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
- Arabic: الأردن – المملكة الأردنّيّة الهاشميّة → Al Urdun – Al Mamlakah al Urdunīyah al Hāshimīyah
UN member state None  Kazakhstan – Republic of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan – Republic of Kazakhstan
UN member state None  Kenya – Republic of Kenya
Kenya – Republic of Kenya
UN member state None  Kiribati – Republic of Kiribati
Kiribati – Republic of Kiribati
- Gilbertese: Kiribati – Ribaberiki Kiribati
- English: Kiribati – Republic of Kiribati
UN member state None  Korea, North – Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Korea, North – Democratic People's Republic of Korea
- Korean: 조선 – 조선민주주의인민공화국 → Chosŏn – Chosŏn-minjujuŭi-inmin-konghwaguk
UN member state Claimed by South Korea North Korea is not recognised by two UN members: Japan and South Korea.[Note 31][29]  Korea, South – Republic of Korea
Korea, South – Republic of Korea
- Korean: 한국 – 대한민국 → Han’guk – Taehan Min’guk
UN member state Claimed by North Korea South Korea contains 1 autonomous region, Jeju-do.[Note 7][30] South Korea is not recognised by one UN member: North Korea.[Note 31] Kosovo → Kosovo  Kuwait – State of Kuwait
Kuwait – State of Kuwait
- Arabic: الكويت – دولة الكويت → Al Kuwayt – Dawlat al Kuwayt
UN member state None  Kyrgyzstan – Kyrgyz Republic
Kyrgyzstan – Kyrgyz Republic
UN member state None  Laos – Lao People's Democratic Republic
Laos – Lao People's Democratic Republic
- Lao: ລາວ – ສາທາລະນະລັດປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ → Lao – Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxôn Lao
UN member state None  Latvia – Republic of Latvia
Latvia – Republic of Latvia
- Latvian: Latvija – Latvijas Republika
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Lebanon – Lebanese Republic
Lebanon – Lebanese Republic
UN member state None  Lesotho – Kingdom of Lesotho
Lesotho – Kingdom of Lesotho
UN member state None  Liberia – Republic of Liberia
Liberia – Republic of Liberia
- English: Liberia – Republic of Liberia
UN member state None  Libya
Libya
- Arabic: ليبيا → Lībyā
UN member state None The former government of Muammar Gaddafi, which claims to be the sole legitimate representative of the Libyan people, still has some international recognition (see Foreign relations of the National Transitional Council and Foreign relations of Libya under Gaddafi).  Liechtenstein – Principality of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein – Principality of Liechtenstein
- German: Liechtenstein – Fürstentum Liechtenstein
UN member state None  Lithuania – Republic of Lithuania
Lithuania – Republic of Lithuania
- Lithuanian: Lietuva – Lietuvos Respublika
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Luxembourg – Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
Luxembourg – Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg – Groussherzogdem Lëtzebuerg
- French: Luxembourg – Grand-Duché du Luxembourg
- German: Luxemburg – Großherzogtum Luxemburg
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Macedonia – Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia – Republic of Macedonia
- Macedonian: Македонија – Република Македонија → Makedonija – Republika Makedonija
- Albanian: Maqedonia - Republika e Maqedonisë
UN member state None Because of the Macedonia naming dispute, the country is referred to by the UN and a number of states and international organizations as "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia".  Madagascar – Republic of Madagascar
Madagascar – Republic of Madagascar
UN member state None Madagascar claims the French territories of Banc du Geyser, Juan de Nova Island, and the Glorioso Islands.[5]  Malawi – Republic of Malawi
Malawi – Republic of Malawi
UN member state None  Malaysia
Malaysia
UN member state None Malaysia is a federation of 13 states and 3 federal territories. Malaysia claims part of the Spratly Islands.[Note 12]  Maldives – Republic of Maldives
Maldives – Republic of Maldives
- Dhivehi: ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ – ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ → Dhivehi Raajje – Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa
UN member state None  Mali – Republic of Mali
Mali – Republic of Mali
- French: Mali – République du Mali
UN member state None  Malta – Republic of Malta
Malta – Republic of Malta
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Marshall Islands – Republic of the Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands – Republic of the Marshall Islands
- Marshallese: Aelōn̄ in M̧ajeļ – Aolepān Aorōkin M̧ajeļ[32]
- English: Marshall Islands – Republic of the Marshall Islands
UN member state None Under Compact of Free Association with the United States.  Mauritania – Islamic Republic of Mauritania
Mauritania – Islamic Republic of Mauritania
UN member state None  Mauritius – Republic of Mauritius
Mauritius – Republic of Mauritius
- English: Mauritius – Republic of Mauritius
- French: Île Maurice – République de Maurice
- Mauritian Creole: Moris – Repiblik Moris
UN member state None Mauritius has an autonomous island, Rodrigues.[Note 7] Mauritius claims the British Indian Ocean Territory and the French island of Tromelin.[5]  Mexico – United Mexican States
Mexico – United Mexican States
- Spanish: México – Estados Unidos Mexicanos
UN member state None Mexico is a federation of 31 states and 1 federal district.  Micronesia, Federated States of
Micronesia, Federated States of
- English: Federated States of Micronesia
UN member state None Under Compact of Free Association with the United States. The Federated States of Micronesia is a federation of 4 states.  Moldova – Republic of Moldova
Moldova – Republic of Moldova
UN member state None Moldova has the autonomous regions of Gagauzia and Transnistria, the latter of which has established a de facto state.  Monaco – Principality of Monaco
Monaco – Principality of Monaco
- French: Monaco – Principauté de Monaco
- Monegasque: Múnegu – Principatu de Múnegu
- Italian: Monaco – Principato di Monaco
UN member state None  Mongolia
Mongolia
- Mongolian: Монгол улс → Mongol uls
UN member state None  Montenegro
Montenegro
- Montenegrin: Црна Гора → Crna Gora
UN member state None  Morocco – Kingdom of Morocco
Morocco – Kingdom of Morocco
UN member state None Morocco claims sovereignty over Western Sahara and controls most of it, which is disputed by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. Morocco disputes Spanish sovereignty over Ceuta, Melilla and the "Plazas de soberanía".[5]  Mozambique – Republic of Mozambique
Mozambique – Republic of Mozambique
- Portuguese: Moçambique – República de Moçambique
UN member state None Myanmar → Burma Nagorno-Karabakh → Nagorno-Karabakh  Namibia – Republic of Namibia
Namibia – Republic of Namibia
- English: Namibia – Republic of Namibia
UN member state None  Nauru – Republic of Nauru
Nauru – Republic of Nauru
UN member state None  Nepal – Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal
Nepal – Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal
- Nepali: नेपाल – संघिय लोकतन्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल → Nepāl – Saṁghīya Loktāntrik Gaṇatantra Nepāl
UN member state None Nepal is a federation composed of 14 zones.  Netherlands – Kingdom of the Netherlands
Netherlands – Kingdom of the Netherlands
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] The Kingdom of the Netherlands consists of four constituent countries: The monarch and her ministers form the government of the kingdom as well as the government of the country the Netherlands. Following the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles in 2010, Curaçao and Sint Maarten have become constituent countries, which, alongside Aruba, enjoy considerable autonomy. The other three islands (Bonaire, Saba, Sint Eustatius) became special municipalities of the Netherlands.
The designation "Netherlands" can refer to either one of the Kingdom's constituent countries or to the short name for the Kingdom (e.g., in international organizations). The Kingdom of the Netherlands as a whole is a member of the EU, but EU law applies only to parts within Europe.
 New Zealand
New Zealand
UN member state None New Zealand is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] and has responsibilities for (but has no sovereignty over) two freely associated states: Cook Islands and Niue are recognized by a number of states. They established diplomatic relatations with 31 and 6 UN members respectively.[34][35][36]
Cook Islands and Niue are sovereign subjects of international law. UN recognized the full treaty-making capacity of the Cook Islands in 1992 and that of Niue in 1994.[37]
Cook Islands and Niue are members of UN specialized agencies without any specifications or limitations. Cook Islands is member of FAO, ICAO, IFAD, IMO, UNESCO, WHO, WMO and Niue is member of FAO, IFAD, UNESCO, WHO, WMO.
New Zealand also has the dependent territories of:
The Tokelauan government claims sovereignty over Swains Island, part of American Samoa, a territory of the United States.[38] New Zealand does not recognize the Tokelauan claim.[39]
 Nicaragua – Republic of Nicaragua
Nicaragua – Republic of Nicaragua
- Spanish: Nicaragua – República de Nicaragua
UN member state None Nicaragua contains 2 autonomous regions, Atlántico Sur and Atlántico Norte.[Note 7]  Niger – Republic of Niger
Niger – Republic of Niger
UN member state None  Nigeria – Federal Republic of Nigeria
Nigeria – Federal Republic of Nigeria
UN member state None Nigeria is a federation of 36 states and 1 federal territory. Northern Cyprus → Northern Cyprus North Korea → Korea, Democratic People's Republic of  Norway – Kingdom of Norway
Norway – Kingdom of Norway
- Bokmål: Norge – Kongeriket Norge
- Nynorsk: Noreg – Kongeriket Noreg
UN member state None Svalbard is an integral part of Norway, but has a special status due to the Spitsbergen Treaty. Bouvet Island is a dependent territory of Norway. Norway also claims Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land as dependent territories of Norway, as part of the Norwegian Antarctic Territory.[Note 9]
 Oman – Sultanate of Oman
Oman – Sultanate of Oman
- Arabic: عُمان – سلطنة عُمان → ʿUmān – Salţanat ʿUmān
UN member state None  Pakistan – Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Pakistan – Islamic Republic of Pakistan
UN member state None Pakistan is a federation of 4 provinces, 1 capital territory, and tribal regions. Pakistan disputes Indian sovereignty over Kashmir. It exercises control over some areas, but does not explicitly claim any part of it,[40][41] instead regarding it as a disputed territory.[42][43] The portions that it controls are divided into two polities, administered separately from Pakistan proper:[Note 20]  Palau – Republic of Palau
Palau – Republic of Palau
UN member state None Under Compact of Free Association with the United States. Palestine → Palestine  Panama – Republic of Panama
Panama – Republic of Panama
- Spanish: Panamá – República de Panamá
UN member state None  Papua New Guinea – Independent State of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea – Independent State of Papua New Guinea
UN member state None Papua New Guinea is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] with 1 autonomous region, Bougainville.[Note 7]  Paraguay – Republic of Paraguay
Paraguay – Republic of Paraguay
UN member state None  Peru – Republic of Peru
Peru – Republic of Peru
UN member state None  Philippines – Republic of the Philippines
Philippines – Republic of the Philippines
UN member state None The Philippines contains two autonomous regions, the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao[Note 7] and the Cordillera Administrative Region.[45] The Philippines administers Scarborough Shoal and some of the Spratly Islands,[Note 12] and claims sovereignty over the Macclesfield Bank and Sabah, which is part of Malaysia.[5]  Poland – Republic of Poland
Poland – Republic of Poland
- Polish: Polska – Rzeczpospolita Polska
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Portugal – Portuguese Republic
Portugal – Portuguese Republic
- Portuguese: Portugal – República Portuguesa
- Mirandese: Pertual – República Pertuesa
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Portugal contains 2 autonomous regions, Azores and Madeira.[Note 7] Portugal does not recognize Spanish sovereignty over Olivenza and Táliga.[5] Pridnestrovie → Transnistria  Qatar – State of Qatar
Qatar – State of Qatar
- Arabic: قطر – دولة قطر → Qaţar – Dawlat Qaţar
UN member state None  Romania
Romania
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Russia – Russian Federation
Russia – Russian Federation
- Russian: Россия – Российская Федерация → Rossiya – Rossiyskaya Federatsiya
UN member state None Russia is officially a federation of 83 federal subjects (republics, oblasts, krais, autonomous okrugs, federal cities, and an autonomous oblast). Several of the federal subjects are ethnic republics.[Note 7] Sovereignty over the South Kuril Islands is disputed by Japan.  Rwanda – Republic of Rwanda
Rwanda – Republic of Rwanda
- Kinyarwanda: Rwanda – Republika y'u Rwanda
- French: Rwanda – République du Rwanda
- English: Rwanda – Republic of Rwanda
UN member state None Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic → Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic  Saint Kitts and Nevis – Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis – Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis
- English: Saint Kitts and Nevis – Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis
UN member state None Saint Kitts and Nevis is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] and is a federation [Note 22] of 14 parishes.  Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia
- English: Saint Lucia
UN member state None Saint Lucia is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- English: Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
UN member state None Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Samoa – Independent State of Samoa
Samoa – Independent State of Samoa
UN member state None  San Marino – Republic of San Marino
San Marino – Republic of San Marino
- Italian: San Marino – Repubblica di San Marino
UN member state None  São Tomé and Príncipe – Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe – Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe
- Portuguese: São Tomé e Príncipe – República Democrática de São Tomé e Príncipe
UN member state None São Tomé and Príncipe contains 1 autonomous province, Príncipe.[Note 7]  Saudi Arabia – Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia – Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Arabic: السعودية – المملكة العربيّة السّعوديّة → As Su‘ūdīyah – Al Mamlakah al ‘Arabīyah as Su‘ūdīyah
UN member state None  Senegal – Republic of Senegal
Senegal – Republic of Senegal
- French: Sénégal – République du Sénégal
UN member state None  Serbia – Republic of Serbia
Serbia – Republic of Serbia
- Serbian: Србија – Република Србија → Srbija – Republika Srbija
UN member state None Serbia contains 2 autonomous regions, Vojvodina and Kosovo and Metohija.[Note 7] Most of the latter is under the de facto control of the Republic of Kosovo.  Seychelles – Republic of Seychelles
Seychelles – Republic of Seychelles
UN member state None Seychelles claims the British Indian Ocean Territory.[5]  Sierra Leone – Republic of Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone – Republic of Sierra Leone
- English: Sierra Leone – Republic of Sierra Leone
UN member state None  Singapore – Republic of Singapore
Singapore – Republic of Singapore
UN member state None  Slovakia – Slovak Republic
Slovakia – Slovak Republic
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Slovenia – Republic of Slovenia
Slovenia – Republic of Slovenia
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
- English: Solomon Islands
UN member state None The Solomon Islands is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Somalia – Somali Republic
Somalia – Somali Republic
UN member state None Somalia is presently divided with its official government (TFG) controlling only part of the country. Puntland and Galmudug have declared themselves as autonomous regions of Somalia (a claim that the TFG does not recognise),[47][Need quotation to verify] while Somaliland has formed an unrecognised de facto state. Somaliland → Somaliland  South Africa – Republic of South Africa
South Africa – Republic of South Africa
- Afrikaans: Suid-Afrika – Republiek van Suid-Afrika
- English: South Africa – Republic of South Africa
- Northern Sotho: Afrika-Borwa – Rephaboliki ya Afrika-Borwa
- Sotho: Afrika Borwa – Rephaboliki ya Afrika Borwa
- Southern Ndebele: Sewula Afrika – iRiphabliki yeSewula Afrika
- Swazi: Ningizimu Afrika – iRiphabhulikhi yeNingizimu Afrika
- Tsonga: Afrika Dzonga – Riphabliki ra Afrika Dzonga
- Tswana: Aforika Borwa – Rephaboliki ya Aforika Borwa
- Venda: Afurika Tshipembe – Riphabuḽiki ya Afurika Tshipembe
- Xhosa: uMzantsi Afrika – iRiphabliki yaseMzantsi Afrika
- Zulu: Ningizimu Afrika – iRiphabliki yaseNingizimu Afrika
UN member state None South Korea → Korea, Republic of South Ossetia → South Ossetia  South Sudan – Republic of South Sudan
South Sudan – Republic of South Sudan
- English: South Sudan – Republic of South Sudan
UN member state None Disputes Abyei with the Republic of the Sudan.[5]  Spain – Kingdom of Spain
Spain – Kingdom of Spain
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] Spain is divided into autonomous communities and cities.[Note 7] Sovereignty over Ceuta, Isla de Alborán, Isla Perejil, Islas Chafarinas, Melilla and Peñón de Alhucemas is disputed by Morocco. Sovereignty over Olivenza and Táliga is disputed by Portugal. Spain calls for sovereignty over Gibraltar.[5]  Sri Lanka – Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka – Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
- Sinhala: ශ්රී ලංකා – ශ්රී ලංකා ප්රජාතාන්ත්රික සමාජවාදී ජනරජය → Shrī Laṁkā – Shrī Laṁkā Prajātāntrika Samājavādī Janarajaya
- Tamil: இலங்கை – இலங்கை சனநாயக சோசலிசக் குடியரசு → Ilaṅkai – Ilaṅkai Jaṉanāyaka Choṣhalichak Kuṭiyarachu
UN member state None Formerly known as Ceylon.  Sudan – Republic of the Sudan
Sudan – Republic of the Sudan
UN member state None Sudan is a federation of 15 states. Disputes Abyei with South Sudan. Sudan, South → South Sudan  Suriname – Republic of Suriname
Suriname – Republic of Suriname
- Dutch: Suriname – Republiek Suriname
UN member state None  Swaziland – Kingdom of Swaziland
Swaziland – Kingdom of Swaziland
- English: Swaziland – Kingdom of Swaziland
- Swazi: eSwatini – Umbuso weSwatini
UN member state None  Sweden – Kingdom of Sweden
Sweden – Kingdom of Sweden
- Swedish: Sverige – Konungariket Sverige
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4]  Switzerland – Swiss Confederation
Switzerland – Swiss Confederation
UN member state None Switzerland is a federation of 26 cantons.  Syria – Syrian Arab Republic
Syria – Syrian Arab Republic
- Arabic: سورية – الجمهوريّة العربيّة السّوريّة → Sūrīyah – Al Jumhūrīyah al ‘Arabīyah as Sūrīyah
UN member state None Israel occupies the Golan Heights.[23] Taiwan (Republic of China) → Taiwan  Tajikistan – Republic of Tajikistan
Tajikistan – Republic of Tajikistan
- Tajik: Тоҷикистон – Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон → Tojikiston – Jumhurii Tojikiston
UN member state None Tajikistan contains 1 autonomous region, Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Province.[Note 7]  Tanzania – United Republic of Tanzania
Tanzania – United Republic of Tanzania
UN member state None Tanzania contains 1 autonomous region, Zanzibar.[Note 7]  Thailand – Kingdom of Thailand
Thailand – Kingdom of Thailand
- Thai: ประเทศไทย – ราชอาณาจักรไทย → Prathet Thai – Ratcha Anachak Thai
UN member state None Timor-Leste → East Timor  Togo – Togolese Republic
Togo – Togolese Republic
- French: Togo – République togolaise
UN member state None  Tonga – Kingdom of Tonga
Tonga – Kingdom of Tonga
UN member state None Transnistria → Transnistria  Trinidad and Tobago – Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago – Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
- English: Trinidad and Tobago – Republic of Trinidad and Tobago
UN member state None Trinidad and Tobago contains 1 autonomous region, Tobago.[Note 7]  Tunisia – Republic of Tunisia
Tunisia – Republic of Tunisia
UN member state None  Turkey – Republic of Turkey
Turkey – Republic of Turkey
- Turkish: Türkiye – Türkiye Cumhuriyeti
UN member state None  Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
- Turkmenian: Türkmenistan
UN member state None  Tuvalu
Tuvalu
UN member state None Tuvalu is a Commonwealth realm.[Note 6]  Uganda – Republic of Uganda
Uganda – Republic of Uganda
UN member state None  Ukraine
Ukraine
UN member state None Ukraine contains 1 autonomous region, Crimea.[Note 7]  United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
- Arabic: اَلإمَارَات – اَلإمَارَات اَلْعَرَبِيَّة اَلْمُتَّحِدَة → Al Imārāt – Al Imārāt al ‘Arabīyah al Muttaḩidah
UN member state None The United Arab Emirates is a federation of 7 emirates.  United Kingdom – United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
United Kingdom – United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- English: United Kingdom – United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- Scots: Unitit Kinrick o Great Breetain an Northren Ireland
- Scottish Gaelic: Rìoghachd Aonaichte na Breatainn Mòire agus Èireann a Tuath
- Welsh: Teyrnas Unedig Prydain Fawr a Gogledd Iwerddon[49]
UN member state None Member of the EU.[Note 4] The United Kingdom is a Commonwealth realm[Note 6] consisting of four countries: England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. The United Kingdom has the following overseas territories: - Akrotiri and Dhekelia
 Anguilla
Anguilla Bermuda
Bermuda British Indian Ocean Territory (disputed by Mauritius and Seychelles)[5]
British Indian Ocean Territory (disputed by Mauritius and Seychelles)[5] British Virgin Islands
British Virgin Islands Cayman Islands
Cayman Islands Falkland Islands (disputed by Argentina)[5]
Falkland Islands (disputed by Argentina)[5] Gibraltar (status disputed by Spain)
Gibraltar (status disputed by Spain) Montserrat
Montserrat Pitcairn Islands
Pitcairn Islands Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands British Antarctic Territory [Note 9] (disputed by Argentina and Chile)
British Antarctic Territory [Note 9] (disputed by Argentina and Chile)
The British monarch has direct sovereignty over three self-governing Crown dependencies:
 United States – United States of America
United States – United States of America
UN member state None The United States is a federation of 50 states, 1 federal district, and the incorporated territory of Palmyra Atoll. The United States has sovereignty over the following inhabited possessions and commonwealths:  American Samoa (including Swains Island, disputed by Tokelau)
American Samoa (including Swains Island, disputed by Tokelau) Guam
Guam Northern Mariana Islands
Northern Mariana Islands Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico U.S. Virgin Islands
U.S. Virgin Islands
In addition, there are uninhabited possessions of the United States in the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea: Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Navassa Island, and Wake Island. The United States also asserts claims to Bajo Nuevo Bank and Serranilla Bank.[5]
 Uruguay – Eastern Republic of Uruguay
Uruguay – Eastern Republic of Uruguay
- Spanish: Uruguay – República Oriental del Uruguay
UN member state None  Uzbekistan – Republic of Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan – Republic of Uzbekistan
UN member state None Uzbekistan contains 1 autonomous region, Karakalpakstan.[Note 7]  Vanuatu – Republic of Vanuatu
Vanuatu – Republic of Vanuatu
UN member state None  Vatican City – State of the Vatican City
Vatican City – State of the Vatican City
UN observer state None Administered by the Holy See, a sovereign entity with diplomatic ties to 178 states. The Holy See is a permanent observer of the UN in the category of "Non-member State"[52] and a member of the IAEA, ITU, UPU, and WIPO. The Vatican City is governed by officials appointed by the Pope, who is the Bishop of the Archdiocese of Rome and ex officio sovereign of Vatican City. The Holy See also administers a number of extraterritorial properties in Italy).  Venezuela – Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
Venezuela – Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
- Spanish: Venezuela – República Bolivariana de Venezuela
UN member state None Venezuela is a federation of 23 states, 1 capital district, and federal dependencies.  Vietnam – Socialist Republic of Vietnam
Vietnam – Socialist Republic of Vietnam
- Vietnamese: Việt Nam – Cộng Hòa Xã Hội Chủ Nghĩa Việt Nam
UN member state None Vietnam claims sovereignty over the Paracel[Note 19] and Spratly Islands.[Note 12][5]  Yemen – Republic of Yemen
Yemen – Republic of Yemen
- Arabic: اليمن – الجمهوريّة اليمنية → Al Yaman – Al Jumhūrīyah al Yamanīyah
UN member state None  Zambia – Republic of Zambia
Zambia – Republic of Zambia
UN member state None  Zimbabwe – Republic of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe – Republic of Zimbabwe
UN member state None ↑ UN member states and observer states ↑ ↓ States with no membership to the UN ↓  Abkhazia – Republic of Abkhazia
Abkhazia – Republic of Abkhazia
No membership Claimed by Georgia Recognised by Russia, Nauru, Nicaragua, Tuvalu[53], Vanuatu, Venezuela,[54] South Ossetia and Transnistria.[55] Claimed in whole by Georgia as the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia.  Kosovo – Republic of Kosovo
Kosovo – Republic of Kosovo
Not a UN member state, but member of one or more related agencies Claimed by Serbia Kosovo unilaterally declared independence in 2008 and it has received diplomatic recognition from 85 UN member states and the Republic of China. Pursuant to United Nations Security Council Resolution 1244, Kosovo is formally under the administration of the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo. Serbia continues to maintain its sovereignty claim over Kosovo. Other UN member states and non UN member states continue to recognise Serbian sovereignty or have taken no position on the question. Kosovo is a member of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group. The Republic of Kosovo has de facto control over most of the territory, with limited control in North Kosovo.  Nagorno-Karabakh – Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
Nagorno-Karabakh – Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
- Armenian: Լեռնային Ղարաբաղ – Լեռնային Ղարաբաղի Հանրապետություն → Leṙnalin Ġarabaġ – Leṙnayin Ġarabaġi Hanrapetut‘yun
No membership Claimed by Azerbaijan A de facto independent state,[56][57] recognised only by Abkhazia,[58] South Ossetia[58] and Transnistria.[58][59]. Claimed in whole by Azerbaijan.[60]  Northern Cyprus – Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus – Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
- Turkish: Kuzey Kıbrıs – Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti
No membership Claimed by the Republic of Cyprus Recognised only by Turkey. It has participated as an observer state of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation under the name "Turkish Cypriot State" since 1979. In addition, the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic regards TRNC as sovereign but Azerbaijan has not followed suit.[citation needed] Northern Cyprus is claimed in whole by the Republic of Cyprus.[61]  Palestine – State of Palestine
Palestine – State of Palestine
- Arabic: فلسطين – دولة فلسطين → Dawlat Filasṭin
Not a UN member state, but member of one or more related agencies[62] Disputed The declared State of Palestine has received diplomatic recognition from 127 states.[63] The proclaimed state has no agreed territorial borders, or effective control on the territory that it proclaimed.[64] The Palestinian National Authority is an interim administrative body formed as a result of the Oslo Accords that exercises limited autonomous jurisdiction within the Palestinian territories. In foreign relations, the State of Palestine is represented by the Palestine Liberation Organization, which has permanent observer status at the United Nations General Assembly as a non-member entity.[52]  Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
No membership Claimed by Morocco Recognised by 84 other states. It is a founding member of the African Union and the Asian-African Strategic Partnership formed at the 2005 Asian-African Conference. The territories under its control, the so-called Free Zone, are claimed in whole by Morocco as part of its Southern Provinces. In turn, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic claims the part of Western Sahara to the west of the Moroccan Wall controlled by Morocco. Its government resides in exile in Tindouf, Algeria.  Somaliland – Republic of Somaliland
Somaliland – Republic of Somaliland
No membership Claimed by Somalia A de facto independent state,[65][66][67] not diplomatically recognised by any other state, claimed in whole by the Somali Republic.[68]  South Ossetia – Republic of South Ossetia
South Ossetia – Republic of South Ossetia
No membership Claimed by Georgia A de facto independent state,[69] recognised by Russia, Nicaragua, Nauru, Venezuela,[54] Abkhazia and Transnistria.[55] Claimed in whole by Georgia as the Provisional Administrative Entity of South Ossetia.[70]  Taiwan – Republic of China[Note 16]
Taiwan – Republic of China[Note 16]
Former UN Member (1945–1971); Member or participant in some UN-related organizations as "Chinese Taipei" (see right)
Claimed by the People's Republic of China A state competing for recognition with the People's Republic of China as the government of China since 1949. The Republic of China controls the island of Taiwan and associated islands, Quemoy, Matsu, the Pratas and parts of the Spratly Islands,[Note 12] and has not renounced claims over its annexed territories on the mainland.[71] The Republic of China is recognised by 23 states as of 2011, including the Holy See. The territory of the Republic of China is claimed in whole by the People's Republic of China.[Note 18] The Republic of China participates in the World Health Organization and a number of non-UN international organizations such as the World Trade Organization, International Olympic Committee and others under a variety of pseudonyms, most commonly "Chinese Taipei".  Transnistria – Transnistrian Moldovan Republic (Pridnestrovie, Trans-Dniester)
Transnistria – Transnistrian Moldovan Republic (Pridnestrovie, Trans-Dniester)
- Russian: Приднестровье – Приднестровская Молдавская Республика → Pridnestrovye – Pridnestrovskaya Moldavskaya Respublika
- Ukrainian: Придністров'я – Придністровська Молдавська Республіка → Pridnistrov'ya – Pridnistrovs'ka Moldavs'ka Respublika
- Romanian: Транснистрия – Република Молдовеняскэ Нистрянэ → Transnistria – Republica Moldovenească Nistreană
No membership Claimed by Moldova A de facto independent state, recognised only by Abkhazia and South Ossetia.[55] Claimed in whole by Moldova as the Territorial Unit of Transnistria.[72] ↑ States with no membership to the UN ↑ Criteria for inclusion
The dominant customary international law standard of statehood is the declarative theory of statehood that defines the state as a person of international law if it "possess[es] the following qualifications: (a) a permanent population; (b) a defined territory; (c) government; and (d) capacity to enter into relations with the other states." Debate exists on the degree to which recognition should be included as a criterion of statehood. The declarative theory of statehood, an example of which can be found in the Montevideo Convention, argues that statehood is purely objective and recognition of a state by other states is irrelevant. On the other end of the spectrum, the constitutive theory of statehood defines a state as a person under international law only if it is recognized as sovereign by other states. For the purposes of this list, included are all states that either:
- (a) have declared independence and are often regarded as having control over a permanently populated territory
or
- (b) are recognized as a sovereign state by at least one other sovereign state
Note that in some cases there is a divergence of opinion over the interpretation of the first point, and whether an entity satisfies it is disputed.
On the basis of the above criteria, this list includes the following 204 entities:[73][Note 34]
- 201 States recognized by at least one UN member state
- Two states that control a permanently populated territory and are recognized only by non-UN member states: Nagorno-Karabakh Republic, Transnistria
- One state that controls a permanently populated territory and is not recognized by any other state: Somaliland
See also
- Sovereign state
- List of international rankings
- List of sovereign states by formation date
- Lists of sovereign states by year
- List of country-name etymologies
- List of territorial disputes
- Table of administrative divisions by country
- List of micronations
- Terra nullius
- Template:Clickable world map
Notes
- ^ The names of the items in the list are given in English, as well as in the official, national, major minority, and historically important languages of the state. Where applicable, names in other languages are included in their original script, along with a transliteration in Roman characters. Except where mentioned, the source for the names in their official languages is the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names (UNGEGN, retrieved 24 February 2011), which uses romanisation systems approved by the United Nations. The sources for flags are the main articles on these states. When other sources are used, these sources are mentioned. For a gallery of flags, see Gallery of sovereign-state flags.
- ^ This column indicates whether or not a state is a member of the United Nations.[2] It also indicates which non-member states participate in the United Nations System through membership in the International Atomic Energy Agency or one of the specialized agencies of the United Nations. All United Nations members belong to at least one specialized agency and are parties to the statute of the International Court of Justice.
- ^ This column indicates whether or not a state is the subject of a major sovereignty dispute. Only states that are claimed in whole by another sovereign state are mentioned. Minor territorial disputes are detailed in the Further information.. column.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab The member states of the European Union have transferred part of their sovereignty in the form of legislative, executive, and judicial powers to the institutions of the EU, which is an example of supranationalism. The EU has 27 member states.[9]
- ^ Information is included on:
- the extent to which a state's sovereignty is recognised internationally. More information can be found at List of states with limited recognition,
- membership in the European Union,[Note 4] where applicable,
- any overseas dependencies, if applicable, which are generally not part of the territory of the sovereign state,
- federal structure of the state, where applicable. More information can be found at Federated state,
- any autonomous areas inside the territory of the sovereign state,
- any situations where one person is the Head of State of more than one state,
- any major territorial disputes,
- any governments in exile recognised by at least one state.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Commonwealth realms are members of the Commonwealth of Nations in which the head of state is Queen Elizabeth II. The realms are sovereign states; see Relationship of the realms.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x For more information on divisions with a high degree of autonomy, see the List of autonomous areas by country.
- ^ The Argentine Constitution (Art. 35) recognises the following denominations for Argentina: "United Provinces of the Río de la Plata", "Argentine Republic" and "Argentine Confederation"; furthermore, it establishes the usage of "Argentine Nation" for purposes of legislation.
- ^ a b c d e f g The continent of Antarctica, including its outlying islands south of 60°S, are held in abeyance under the terms of the Antarctic Treaty System. Under this treaty, territorial claims in this region are neither recognised nor disputed. Claimant countries are Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom, with all those save Argentina and Chile mutually recognising each others claims.
- ^ Formerly referred to as Dahomey, its official name until 1975.
- ^ For more information about the division of Bosnia and Herzegovina, see Dayton Agreement and the text of The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina (14 December 1995). Office of the High Representative. Retrieved 28 February 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f The sovereignty over the Spratly Islands is disputed by People's Republic of China, the Republic of China, Vietnam, and in part by Brunei, Malaysia, and the Philippines. Except for Brunei, each of these countries occupies part of the islands (see List of territorial disputes).
- ^ Also known as Burkina; formerly referred to as Upper Volta, its official name until 1984.
- ^ Burma's official short form name as used by the United Nations is "Myanmar". The government changed the state's official name in English from "Union of Myanmar" to "Republic of the Union of Myanmar" in October 2010.
- ^ The legal name for Canada is the sole word; an officially sanctioned, though disused, name is Dominion of Canada (which includes its legal title); see: Name of Canada, Dominion.
- ^ a b The People's Republic of China (PRC) is commonly referred to as "China", while the Republic of China (ROC) is commonly referred to as "Taiwan". The ROC is also occasionally known diplomatically as Chinese Taipei, along with other names.
- ^ Rendered in unicode as ᠪᠦᠭᠦᠳᠡ ᠨᠠᠶᠢᠷᠠᠮᠳᠠᠬᠤ ᠳᠤᠮᠳᠠᠳᠤ ᠠᠷᠠᠳ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ
- ^ a b In 1949, the Republic of China government led by the Kuomintang (KMT) lost the Chinese Civil War to the Communist Party of China (CPC) and set up a provisional capital in Taipei. The CPC established the PRC. As such, the political status of the ROC and the legal status of Taiwan (alongside the territories currently under ROC jurisdiction) are in dispute. In 1971, the United Nations gave the China seat to the PRC and the ROC withdrew from the UN. Most states recognise the PRC to be the sole legitimate representative of all China, and the UN classifies Taiwan as "Taiwan, Province of China". The ROC has de facto relations with most sovereign states. A significant political movement within Taiwan advocates Taiwan independence.
- ^ a b The Chinese sovereignty over the Paracel Islands is disputed by Vietnam and the Republic of China (see List of territorial disputes);
- ^ a b c Sovereignty over Kashmir is disputed between India and Pakistan; smaller parts are disputed by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China. Kashmir is divided between India, Pakistan and the PRC. See the List of territorial disputes.
- ^ See also Dates of establishment of diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China and Foreign relations of the People's Republic of China.
- ^ a b c More information on more or less federal structures can be found at a List of federations.
- ^ Abbreviated as DRC, and also known as Congo-Kinshasa. Formerly referred to as Zaire, its official name from 1971 to 1997.
- ^ See Foreign relations of Cyprus and Cyprus dispute.
- ^ A simpler official short-form name has been encouraged by the Czech government: the English variant Czechia remains uncommon, but variants in Czech (Česko) and some other languages are more popular. See Name of the Czech Republic
- ^ For more information, see Rigsfællesskabet.
- ^ The government of East Timor uses "Timor-Leste" as the English translation.
- ^ Åland was demilitarised by the Treaty of Paris in 1856, which was later affirmed by the League of Nations in 1921, and in a somewhat different context reaffirmed in the treaty on Finland's admission to the European Union in 1995.
- ^ The Irish state is often referred to as the Republic of Ireland (its official description but not its name). Sometimes this is done to distinguish the state from the island of Ireland as a whole. However, sometimes it is done for political reasons and is contentious.
- ^ See Names of Japan for more detail.
- ^ a b Both North Korea and South Korea claim to be the sole legitimate government of Korea. See also Foreign relations of North Korea and Foreign relations of South Korea.
- ^ Moldovan is often considered to be the same language as Romanian, see Moldovan language.
- ^ Romanization in Pinyin.
- ^ The non-state sovereign entity Order of Malta is not included. It claims neither statehood nor any territory. Entities considered to be micronations are not included. It is often up to debate whether a micronation truly controls its claimed territory. Also omitted from this list are all uncontacted peoples, either who live in societies that cannot be defined as states or whose statuses as such are not definitively known.
References
- ^ "United Nations Member States". United Nations. 3 July 2006. http://www.un.org/en/members/index.shtml. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ Press Release ORG/1469 (3 July 2006), retrieved 28 February 2011)
- ^ "Andorra country profile". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/country_profiles/992562.stm#leaders. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ Government of Antigua and Barbuda. "Chapter 44: The Barbuda Local Government Act". Laws of Antigua and Barbuda. http://www.laws.gov.ag/acts/chapters/cap-44.pdf. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "Disputes - International". CIA World Factbook. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2070.html. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ Government of the United States, Congress, Office of Technology Assessment (1989). Polar prospects: a minerals treaty for Antarctica. United States Government Printing Office. p. 43. ISBN 9781428922327. "Mutual recognition of claims has been limited to Australia, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom ... Chile and Argentina do not recognize each other's claims ..."
- ^ Pakistan Worldview - Report 21 - Visit to Azerbaijan Senate of Pakistan — Senate foreign relations committee, 2008
- ^ Nilufer Bakhtiyar: "For Azerbaijan Pakistan does not recognise Armenia as a country" 13 September 2006 [14:03] - Today.Az
- ^ Europa, retrieved 28 February 2011
- ^ There are 33 other official languages in Bolivia. Source for the Aymara, Guaraní, and Quechua is the Consulate General of Brazil in Santa Cruz de la Sierra. "Datos de Bolivia". Government of Brazil. http://www.consbras.org.bo/bolivia/bolivia.html. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ^ "Myanmar gets new flag, official name, anthem". Reuters. 21 October 2010. http://ca.reuters.com/article/topNews/idCATRE69K2HM20101021. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ a b c d Source for names in regional and minority languages is the Federal Foreign Office of Germany (see Bibliography)
- ^ Names in additional regional and minority languages are taken from Geonames. "China". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/coucn.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Constitution of Comoros, Art. 1.
- ^ Source for the Hindustani, which uses both the Hindi and Urdu script, is Geonames. "Fiji". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/coufj.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ "Rotuma Act". Laws of Fiji (1978 ed.). Suva, Fiji: Government of Fiji. 1927. http://www.itc.gov.fj/lawnet/fiji_act/cap122.html. Retrieved 2010-07-10.[dead link]
- ^ Government of Fiji, Office of the Prime Minister (1978). "Chapter 122: Rotuma Act". Laws of Fiji. University of the South Pacific. http://www.paclii.org/fj/legis/consol_act/ra103/. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ^ Constitution of Greece, Art. 105.
- ^ Source for the names in recognised regional and national languages is Geonames. "India". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/couin.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Source for the official name in Kurdish is the Kurdistan Regional Government. "Official website". http://www.krg.org/. Retrieved 2010-07-15.
- ^ Source: Iraqi constitution
- ^ "Constitution of Ireland – Burnreacht na hÉireann". Government of Ireland. http://www.constitution.ie/reports/ConstitutionofIreland.pdf. Retrieved 8 November 2011. "Article 3: It is the firm will of the Irish Nation...to unite all the people who share the territory of the island of Ireland...recognising that a united Ireland shall be brought about only by peaceful means"
- ^ a b Occupied territory:
- "Israeli-occupied Golan Heights" (Central Intelligence Agency. CIA World Factbook 2010, Skyhorse Publishing Inc., 2009. pg. 339. ISBN 1602397279.)
- "...the United States considers the Golan Heights to be occupied territory subject to negotiation and Israeli withdrawal..." ("title=CRS Issue Brief for Congress: Israeli-United States Relations", Congressional Research Service, April 5, 2002. pg. 5. Retrieved August 1, 2010.) * "Occupied Golan Heights" (Travel advice: Israel and the Occupied Palestinian Territories, UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved August 1, 2010.) * "In the ICRC's view, the Golan is an occupied territory." (ICRC activities in the occupied Golan during 2007, International Committee of the Red Cross, April 24, 2008.) * "...occupied Syrian Golan Heights..." (The Arab Peace Initiative, 2002, www.al-bab.com. Retrieved August 1, 2010.) * In 2008, a plenary session of the United Nations General Assembly voted by 161–1 in favour of a motion on the "occupied Syrian Golan" that reaffirmed support for UN Resolution 497. (General Assembly adopts broad range of texts, 26 in all, on recommendation of its fourth Committee, including on decolonization, information, Palestine refugees, United Nations, December 5, 2008.)
- ^ Gold, Dore; Institute for Contemporary Affairs (26 August 2005). "Legal Acrobatics: The Palestinian Claim that Gaza is Still "Occupied" Even After Israel Withdraws". Jerusalem Issue Brief, Vol. 5, No. 3. Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. http://www.jcpa.org/brief/brief005-3.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ Bell, Abraham (28 January 2008). "International Law and Gaza: The Assault on Israel's Right to Self-Defense". Jerusalem Issue Brief, Vol. 7, No. 29. Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. http://www.jcpa.org/brief/brief005-3.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ "Address by Foreign Minister Livni to the 8th Herzliya Conference" (Press release). Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Israel. 22 January 2008. http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/Government/Speeches+by+Israeli+leaders/2008/Address+by+FM+Livni+to+the+8th+Herzliya+Conference+22-Jan-2008.htm?DisplayMode=print. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ Salih, Zak M. (17 November 2005). "Panelists Disagree Over Gaza’s Occupation Status". University of Virginia School of Law. http://www.law.virginia.edu/html/news/2005_fall/gaza.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ "Israel: 'Disengagement' Will Not End Gaza Occupation". Human Rights Watch. 29 October 2004. http://www.hrw.org/english/docs/2004/10/29/isrlpa9577.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ "Treaty on Basic Relations between Japan and the Republic of Korea". http://www.ioc.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~worldjpn/documents/texts/docs/19650622.T1E.html. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ^ Keun Min. "Greetings". Jeju Special Self-Governing Province. http://english.jeju.go.kr/contents/index.php?mid=02. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ^ Source for the Jawi script and Tamil and Chinese romanisations is Geonames. "Malaysia". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/coumy.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Source for the formal native version is Geonames. "Marshall Islands". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/coumh.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Source for the Berber is the "Royal institute of the Amazigh culture" (in Berber). Government of Morocco. http://www.ircam.ma/amz/index.php. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
- ^ Federal Foreign Office of Germany (November 2009). "Beziehungen zu Deutschland". Government of Germany. http://www.auswaertiges-amt.de/diplo/de/Laenderinformationen/Cookinseln/Bilateral.html. Retrieved 2010-07-16. For more information, see Foreign relations of the Cook Islands.
- ^ China Internet Information Centre (13 December 2007). "Full text of joint communique on the establishment of diplomatic relations between China and Niue". Xinhua News Agency. http://www.china.org.cn/english/international/235447.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ Republic of Nauru Permanent Mission to the United Nations. "Foreign Affairs". United Nations. http://www.un.int/nauru/foreignaffairs.html. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ http://untreaty.un.org/cod/repertory/art102/english/rep_supp8_vol6-art102_e_advance.pdf
- ^ Radio New Zealand International (26 March 2007). "American Samoa governor ready to resist Tokelau’s claim to Swains Island". Radio New Zealand Ltd. http://www.rnzi.com/pages/news.php?op=read&id=31024. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ Government of New Zealand; Government of Tokelau (8 October 2007). "Draft Constitution of Tokelau – English". New Zealand Ministry of Foreign Affairs & Trade. http://www.mfat.govt.nz/Foreign-Relations/Pacific/Tokelau/Tokelau-Constitution-(English).php. Retrieved 2010-07-16.
- ^ Constitution of Pakistan, Art. 1.
- ^ Aslam, Tasnim (11 December 2006). "'Pakistan Does Not Claim Kashmir As An Integral Part...'". Outlook India (The Outlook Group). http://www.outlookindia.com/article.aspx?233374.
- ^ Williams, Kristen P. (2001). Despite nationalist conflicts: theory and practice of maintaining world peace. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 154–155. ISBN 9780275969349. http://books.google.com/?id=OYmurpH3ahsC.
- ^ Pruthi, R.K. (2001). An Encyclopaedic Survey Of Global Terrorism In 21St Century. Anmol Publications Pvt. Ltd.. pp. 120–121. ISBN 9788126110919. http://books.google.com/?id=C3yDkKDbZ3YC.
- ^ Source for the Ayamara and Quechua is Geonames. "Peru". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/coupe.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ "EXECUTIVE ORDER NO. 220 July 15, 1987". http://www.lawphil.net/executive/execord/eo1987/eo_220_1987.html. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Hungarian foreign ministry information sheet
- ^ Weller, Marc; Nobbs, Katherine (2010). Asymmetric Autonomy and the Settlement of Ethnic Conflicts. Philadelphia, United States: University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 9780812242300. http://books.google.com/?id=ru-DIWuuObEC.
- ^ Names in additional regional and minority languages are taken from Geonames. "Spain". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/coues.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Source for the Irish, Scottish, and Welsh is Geonames. "United Kingdom". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/cougb.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Source for the Hawaiian is Geonames. "United States". Fröhlich, Werner. http://www.geonames.de/couus.html. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- ^ Source for the Cyrillic is the Federal Foreign Office of Germany (see Bibliography)
- ^ a b "Non-member States and Entities". United Nations. 29 February 2008. http://www.un.org/en/members/nonmembers.shtml. Retrieved 30 August 2010.
- ^ http://www.mfaabkhazia.net/en/node/1082
- ^ a b "Chavez Backs Abkhazia, South Ossetia". St. Petersburg Times (The Associated Press). 27 July 2010. http://www.times.spb.ru/index.php?action_id=2&story_id=32067. Retrieved 5 June 2011.
- ^ a b c "Абхазия, Южная Осетия и Приднестровье признали независимость друг друга и призвали всех к этому же" (in Russian). newsru.com. 2006-11-17. http://www.newsru.com/russia/17nov2006/aup.html. Retrieved 2011-06-05.
- ^ Krüger, Heiko (2010). The Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict: A Legal Analysis. Springer. p. 55. ISBN 9783642117879. http://books.google.com/books?id=7JDCQu-Us8sC&lpg=PP1&pg=PA55#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- ^ Nikoghosyan, Hovhannes (August 2010). "Kosovo ruling implications for Armenia and Azerbaijan". HULIQ.com (Hareyan Publishing, LLC). http://www.huliq.com/1/803-kosovo-ruling-implications-armenia-and-azerbaijan. Retrieved 2011-04-17.
- ^ a b c Вице-спикер парламента Абхазии: Выборы в НКР соответствуют всем международным стандартам: "Абхазия, Южная Осетия, НКР и Приднестровье уже давно признали независимость друг друга и очень тесно сотрудничают между собой", - сказал вице-спикер парламента Абхазии. ... "...Абхазия признала независимость Нагорно-Карабахской Республики..." - сказал он."
- ^ "In detail: The foreign policy of Pridnestrovie". Pridnestrovie. 2010-05-26. http://pridnestrovie.net/foreignpolicy_full.html. Retrieved 2010-06-29.
- ^ See Regions and territories: Nagorno-Karabakh (17 January 2006). BBC News. Retrieved January 17, 2006.
- ^ See The World Factbook|Cyprus (10 January 2006). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved January 17, 2006.
- ^ "General Conference admits Palestine as UNESCO Member State". UNESCO. 31 October 2011. http://www.unesco.org/new/en/media-services/single-view/news/general_conference_admits_palestine_as_unesco_member_state/. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Palestine Liberation Organization. "Road For Palestinian Statehood: Recognition and Admission". Negotiations Affairs Department. http://www.nad-plo.org/etemplate.php?id=5. Retrieved 2011-07-28.
- ^ See the following on statehood criteria:
- Mendes, Errol (30 March 2010), Statehood and Palestine for the purposes of Article 12 (3) of the ICC Statute, 30 March 2010, pp. 28, 33, http://uclalawforum.com/media/background/gaza/2010-03-30_Mendes-Memo.pdf, retrieved 2011-04-17: "...the Palestinian State also meets the traditional criteria under the Montevideo Convention..."; "...the fact that a majority of states have recognized Palestine as a State should easily fulfill the requisite state practice".
- McKinney, Kathryn M. (1994), "The Legal Effects of the Israeli-PLO Declaration ofPrinciples: Steps Toward Statehood for Palestine", Seattle University Law Review (Seattle University) 18 (93): 97, http://lawpublications.seattleu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1438&context=sulr&sei-redir=1#search=%22palestine+%22constitutive+theory%22+statehood%22, retrieved 2011-04-17: "It is possible, however, to argue for Palestinian statehood based on the constitutive theory".
- McDonald, Avril (Spring 2009), "Operation Cast Lead: Drawing the Battle Lines of the Legal Dispute", Human Rights Brief (Washington College of Law, Center for Human Rights and Humanitarian Law) 25, https://litigation-essentials.lexisnexis.com/webcd/app?action=DocumentDisplay&crawlid=1&doctype=cite&docid=16+Hum.+Rts.+Br.+25&srctype=smi&srcid=3B15&key=74ccae52ba220673512e7784449388f0, retrieved 2011-04-17: "Whether one applies the criteria of statehood set out in the Montevideo Convention or the more widely accepted constitutive theory of statehood, Palestine might be considered a state."
- ^ International Crisis Group (23 May 2006), "Somaliland: Time for African Union leadership", Africa Report (110): 10–13, http://www.operationspaix.net/IMG/pdf/ICG_Somaliland_AU_Leadership_2006-05-23_.pdf, retrieved 2011-04-19
- ^ Mesfin, Berouk (September 2009), "The political development of Somaliland and its conflict with Puntland", ISS Paper (Institute for Security Studies) (200): 8, http://www.somalilandtimes.net/sl/2009/403/P200.pdf, retrieved 2011-04-19
- ^ Arieff, Alexis, "De Facto Statehood? The Strange Case of Somaliland", Yale Journal of International Affairs (Spring/Summer 2008), http://yalejournal.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/083206arieff.pdf, retrieved 2011-04-17
- ^ See Regions and territories: Somaliland (30 December 2005). BBC News. Retrieved January 17, 2006.
- ^ Jansen, Dinah (2009), "The Conflict between Self-Determination and Territorial Integrity: the South Ossetian Paradigm", Geopolitics vs. Global Governance: Reinterpreting International Security (Centre for Foreign Policy Studies, University of Dalhousie): 222–242, ISBN 9781896440613, http://centreforforeignpolicystudies.dal.ca/pdf/gradsymp09/Jansen.pdf
- ^ "Russia condemned for recognizing rebel regions". CNN.com (Cable News Network). 2008-08-26. http://www.cnn.com/2008/WORLD/europe/08/26/russia.vote.georgia/index.html. Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ^ "Ma refers to China as ROC territory in magazine interview". Taipei Times. 2008-10-08. http://www.taipeitimes.com/News/taiwan/archives/2008/10/08/2003425320.
- ^ 'See Regions and territories: Trans-Dniester (13 December 2005). BBC News. Retrieved January 17, 2006.
- ^ The following bullets are grouped according to the availability of sources for the two criteria ((a) and/or (b)). This arrangement is not intended to reflect the relative importance of the two theories. Additional details are discussed in the state's individual entries.
Bibliography
- Federal Foreign Office of Germany (22 April 2009). "Amtliche Bezeichnungen ausländischer Staaten in den Landessprachen" (PDF). Government of Germany. http://www.auswaertiges-amt.de/cae/servlet/contentblob/373536/publicationFile/3858/StaatennamenLandessprache.pdf. Retrieved 2010-07-14.
- Bissio, Roberto Remo, ed (1995). The World: A Third World Guide: 1995/96. Montevideo: Instituto del Tercer Mundo. ISBN 9780855982911. OCLC 476299738.
- "Countries or areas, codes and abbreviations". Statistics Division, United Nations. 1 April 2010. http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49alpha.htm.
- Davis, Tim (19 February 2009). "World Countries and States List". Timdavis.com.au. http://www.timdavis.com.au/data/.
- "Geographic Names". Department of Public Information, Cartographic Section, United Nations. 7 September 2000. http://www.un.org/Depts/Cartographic/english/geoinfo/geoname.pdf.
- "ISO 3166-1 Country names and code elements". International Organization for Standardization. 2010. http://www.iso.org/iso/country_codes/iso_3166_code_lists/country_names_and_code_elements.htm.
- "List of countries, territories and currencies". Publications Office of the European Union. 4 May 2010. http://publications.europa.eu/code/en/en-5000500.htm.
- Madore, David (3 August 2003). "How many countries are there in the world?". Madore.org. http://www.madore.org/~david/misc/countries.html.
- "The World Factbook". United States: Central Intelligence Agency. 2010. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html.
- World of Information (Firm), and International Chamber of Commerce (2003). Middle East Review 2003/04: The Economic and Business Report (27th ed.). London: Kogan Page. p. 161. ISBN 9780749440664. OCLC 51992589. http://books.google.com/?id=NYszJtC66FAC&pg=PA161&dq=%22official+name%22+palestine&q=%22official%20name%22%20palestine.
Lists of sovereign states and dependent territories by continent Continents Supercontinents - Americas
- Eurasia
Lists of sovereign states by year AD (CE) Current
2010s · 2000s · 1990s · 1980s · 1970s · 1960s · 1950s ·
1949 · 1948 · 1947 · 1946 · 1945 · 1944 · 1943 · 1942 · 1941 · 1940 · 1939 · 1938 · 1937 · 1936 · 1935 · 1934 · 1933 · 1932 · 1931 · 1930 · 1929 · 1928 · 1927 · 1926 · 1925 · 1924 · 1923 · 1922 · 1921 · 1920 · 1919 · 1918 · 1917 · 1916 · 1915 · 1914 · 1913 · 1912 · 1911 · 1910 · 1909 · 1908 · 1907 · 1906 · 1905 · 1904 · 1903 · 1902 · 1901 · 1900 · 1899 · 1898 · 1897 · 1896 · 1895 · 1894 · 1893 · 1892 · 1891 · 1890 · 1889 · 1888 · 1887 · 1886 · 1885 · 1884 · 1883 · 1882 · 1881 · 1880 · 1879 · 1878 · 1877 · 1876 · 1875 · 1874 · 1873 · 1872 · 1871 · 1870 · 1869 · 1868 · 1867 · 1866 · 1865 · 1864 · 1863 · 1862 · 1861 · 1860 · 1859 · 1858 · 1857 · 1856 · 1855 · 1854 · 1853 · 1852 · 1851 · 1850 · 1849 · 1848 · 1847 · 1846 · 1845 · 1844 · 1843 · 1842 · 1841 · 1840 · 1839 · 1838 · 1837 · 1836 · 1835 · 1834 · 1833 · 1832 · 1831 · 1830 · 1829 · 1828 · 1827 · 1826 · 1825 · 1824 · 1823 · 1822 · 1821 · 1820 · 1819 · 1818 · 1817 · 1816 · 1815 · 1814 · 1813 · 1812 · 1811 · 1810 · 1809 · 1808 · 1807 · 1806 · 1805 · 1804 · 1803 · 1802 · 1801 · 1800
1776 · 1769 · 1768 · 1661 · 1660 · 1648 · 1528 · 1496 · 1494 · 1400 · 1143 · 1000 · 820 · 661 · 632 · 1BC (BCE) 100 BC
Centuries: 1st BC · 2nd BC · 3rd BC · 4th BC · 5th BC · 6th BC · 7th BC · 8th BC · 9th BC · 10th BC · 11th BC · Before 11th BCCategories:- Lists of sovereign states by year
- Lists of countries
- Indexes of articles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
