- Gibraltar
-
This article is about the British overseas territory. For other uses, see Gibraltar (disambiguation).Gibraltar


Flag Coat of arms Motto: Nulli Expugnabilis Hosti (Latin)
"Conquerable by no enemy."1Anthem: God Save the Queen (official), Gibraltar Anthem (national song)[1] Location of Gibraltar (dark green)– in Europe (green & dark gray)
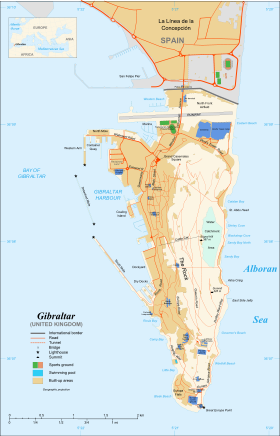
– in the European Union (green) — [Legend]Map of GibraltarCapital Gibraltar
36°8′N 5°21′W / 36.133°N 5.35°WLargest Most populated district
WestsideOfficial language(s) English Unofficial languages
VernacularSpanish
LlanitoEthnic groups Gibraltarian (of mixed Genoese, Maltese, Portuguese and Andalusian descent), other British, Moroccan and Indian Demonym Gibraltarian Government British Overseas Territory - Head of state HM Queen Elizabeth II - Governor Sir Adrian Johns - Chief Minister Peter Caruana Event Date - Captured 4 August 1704[2] - Ceded 11 April 1713[3] (Treaty of Utrecht) - National Day 10 September - Constitution Day 29 January Area - Total 6.8 km2 (229th)
2.6 sq mi- Water (%) 0% Population - 2009 estimate 29,431 (211th) - Density 4,328/km2 (3rd)
11,320/sq miGDP (PPP) 2011 estimate - Total £1 Billion - Per capita £27,468 (n/a) HDI (n/a) n/a (n/a) (n/a) Currency Pound Sterling £3 ( GBP)Time zone CET (UTC+1) - Summer (DST) CEST (UTC+2) Date formats dd/mm/yyyy Drives on the right4 ISO 3166 code GI Internet TLD .gi5 Calling code 3506 Patron saint Bernard of Clairvaux & Our Lady of Europe 1 Gibraltar.gov.gi 2 As a Special Member State territory of the United Kingdom. 3 Coins and sterling notes are issued by the Government of Gibraltar. 4 Unlike all other UK dependencies but the BIOT. 5 The .eu domain is also used, as it is shared with other European Union members. 6 Before 10 February 2007, 9567 from Spain. Gibraltar (
 /dʒɨˈbrɔːltər/) is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of 6.843 square kilometres (2.642 sq mi), it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region. At its foot is the densely populated city area, home to almost 30,000 Gibraltarians and other nationalities.[4]
/dʒɨˈbrɔːltər/) is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of 6.843 square kilometres (2.642 sq mi), it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region. At its foot is the densely populated city area, home to almost 30,000 Gibraltarians and other nationalities.[4]An Anglo-Dutch force captured Gibraltar from Spain in 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The territory was subsequently ceded to Britain "in perpetuity" under the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713. It was an important base for the British Royal Navy; today its economy is based largely on tourism, financial services, and shipping.[5][6]
The sovereignty of Gibraltar is a major point of contention in Anglo-Spanish relations as Spain asserts a claim to the territory.[6] Gibraltarians resoundingly rejected proposals for Spanish sovereignty in a 1967 referendum and again in 2002. Under Gibraltar constitution of 2006, Gibraltar governs its own affairs, though some powers, such as defence and foreign relations, remain the responsibility of the UK Government.
Contents
Etymology
The name Gibraltar is the Spanish derivation of the Arabic name Jabal Tāriq (جبل طارق), meaning "mountain of Tariq".[7] It refers to the geological formation, the Rock of Gibraltar, which in turn was named after the Berber Umayyad general Tariq ibn-Ziyad who led the initial incursion into Iberia in advance of the main Moorish force in 711 under the command of Umayyad Caliph Al-Walid I. Earlier, it was known as Mons Calpe, one of the Pillars of Hercules. Today, Gibraltar is colloquially referred to as Gib or the Rock.
History
Main article: History of Gibraltar View of the northern face of the Moorish Castle's Tower of Homage, Gibraltar's first permanent settlement, built around 711.
View of the northern face of the Moorish Castle's Tower of Homage, Gibraltar's first permanent settlement, built around 711.
Evidence of Neanderthal habitation in Gibraltar between 128,000 and 24,000 BC has been discovered at Gorham's Cave, making Gibraltar the last known holdout of the Neanderthals.[8] Within recorded history, the first inhabitants were the Phoenicians, around 950 BC. Subsequently, Gibraltar became known as one of the Pillars of Hercules, after the Greek legend of the creation of the Strait of Gibraltar by Heracles. The Carthaginians and Romans also established semi-permanent settlements. After the collapse of the Roman Empire, Gibraltar came briefly under the control of the Vandals. The area later formed part of the Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania until the Islamic conquest of Iberia in 711 AD. Seven centuries of Moorish control ended when Gibraltar was recaptured by the Duke of Medina Sidonia in 1462 as part of the Spanish Reconquista.
After the conquest, King Henry IV assumed the title of King of Gibraltar, establishing it as part of the municipal area of the Campo Llano de Gibraltar.[9] Six years later Gibraltar was restored to the Duke of Medina Sidonia who sold it in 1474 to a group of Jewish conversos from Córdoba and Seville in exchange for maintaining the garrison of the town for two years, after which time the 4,350 Jews were expelled by the Duke as part of the Inquisition.[10] In 1501 Gibraltar passed back to the hands of the Spanish Crown and Isabella I of Castile issued a Royal Warrant granting Gibraltar the coat of arms that it still uses today.
In 1704, during the War of the Spanish Succession, a combined Anglo-Dutch force captured the town of Gibraltar, leading to a permanent exodus of the existing population to the surrounding areas of the Campo de Gibraltar. Under the terms of the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht Gibraltar was ceded to Britain in perpetuity. Spain unsuccessfully attempted to regain control during the Great Siege of Gibraltar which lasted from 1779 to 1783.
Gibraltar became a key base for the British Royal Navy and played an important role prior to the Battle of Trafalgar and during the Crimean War of 1854–56, due to its strategic location. Its strategic value increased with the opening of the Suez Canal as it lay on the sea route between the UK and the British Empire east of Suez. In the later 19th century there were major investments in improving the fortifications and the port.[11]
During World War II, Gibraltar's civilian population was evacuated (mainly to London, England, but also to parts of Morocco, Madeira and Jamaica) and the Rock was strengthened as a fortress. Spanish dictator Francisco Franco's reluctance to allow the German Army onto Spanish soil frustrated a German plan to capture the Rock, codenamed Operation Felix. In the 1950s, Franco renewed Spain's claim to sovereignty over Gibraltar and restricted movement between Gibraltar and Spain. Gibraltarians voted overwhelmingly to remain under British sovereignty in a 1967 referendum which led to the passing of the Gibraltar Constitution Order in 1969. In response, Spain completely closed the border with Gibraltar and severed all communication links.[12] The border with Spain was partially reopened in 1982, and fully reopened in 1985 prior to Spain's accession to the European Community.
In a referendum held in 2002, Gibraltarians rejected by an overwhelming majority (99%) a proposal of shared sovereignty on which Spain and Britain were said to have reached "broad agreement".[13][14] The British government has committed itself to respecting the Gibraltarians' wishes.[15] A new Constitution Order was approved in referendum in 2006. A process of tripartite negotiations started in 2006 between Spain, Gibraltar and the UK, ending some restrictions and dealing with disputes in some specific areas such as air movements, customs procedures, telecommunications, pensions and cultural exchange.[16]
Government and politics
 Western, John Mackintosh Square entrance to the Gibraltar Parliament.
Western, John Mackintosh Square entrance to the Gibraltar Parliament. Main articles: Politics of Gibraltar, Disputed status of Gibraltar, and Foreign relations of Spain#Disputes - international
Main articles: Politics of Gibraltar, Disputed status of Gibraltar, and Foreign relations of Spain#Disputes - internationalGibraltar is a British overseas territory. The British Nationality Act 1981 granted Gibraltarians full British citizenship.
Under its current Constitution, Gibraltar has almost complete internal democratic self-government through an elected parliament,[17][18][19][20] elected for a term of up to four years. The unicameral Parliament presently consists of seventeen elected members, and the Speaker who is not elected, but appointed by a resolution of the Parliament.[21] The Government consists of ten elected members. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who is represented by the Governor of Gibraltar. Defence, foreign policy and internal security are formally the responsibility of the Governor; judicial and other appointments are also made on behalf of the Queen in consultation with the head of the elected government.[22][23][24][25][26][26][27]
The 2007 election was contested by the Gibraltar Social Democrats (GSD), Gibraltar Socialist Labour Party (GSLP)-Gibraltar Liberal Party (GLP) Alliance, the Progressive Democratic Party (PDP) and two independents. Two parties which fielded candidates in the 2003 election did not present candidates in the 2007 election; the Reform Party was wound up and Gibraltar Labour Party absorbed into the GSD in a merger in 2005. A new party, the PDP, was formed in 2006 and fielded candidates in the 2007 election, but none were elected. Three political parties are currently represented in the Parliament: the governing GSD, and two opposition parties – the GSLP and the GLP which are in an electoral alliance and form a single parliamentary grouping. The head of Government is the Chief Minister (as of June 2010, Peter Caruana QC[28]). All local political parties oppose any transfer of sovereignty to Spain, instead supporting self-determination. The main UK opposition parties also support this policy and it is UK Government policy not to engage in talks about the sovereignty of Gibraltar without the consent of the people of Gibraltar.[29]
Gibraltar is part of the European Union, having joined via the Single European Act 1972 and British Treaty of Accession in 1973, with exemption from some areas such as the Customs union and Common Agricultural Policy. The Treaties relating to coal and steel, agriculture and fisheries do not apply simply because Gibraltar does not produce any of those resources. After a ten-year campaign for the right to vote in European Elections, from 2004, the people of Gibraltar participated in elections for the European Parliament as part of the South West England constituency.[30]
Geography
 View of the Rock of Gibraltar from Algeciras Bay depicting Westside and the town area, 2006.
View of the Rock of Gibraltar from Algeciras Bay depicting Westside and the town area, 2006.
The territory covers 6.843 square kilometres (2.642 sq mi) and shares a 1.2-kilometre (0.75 mi) land border with Spain. On the Spanish side lies the town of La Línea de la Concepción, a municipality of the province of Cádiz. The Spanish hinterland forms the comarca of Campo de Gibraltar (literally Gibraltar Countryside). The shoreline measures 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) in length. There are two coasts (sides) of Gibraltar – the East Side, which contains the settlements of Sandy Bay and Catalan Bay, and the Westside, where the vast majority of the population lives. Gibraltar has no administrative divisions but is divided into seven Major Residential Areas.
Having negligible natural resources and few natural freshwater resources, limited to natural wells in the north, until recently Gibraltar used large concrete and/or natural rock water catchments to collect rainwater. Fresh water from the boreholes is supplemented by two desalination plants: a reverse osmosis plant, constructed in a tunnel within the rock, and a multi-stage flash distillation plant at North Mole.[31]
Gibraltar's terrain consists of the 426-metre (1,398 ft) high Rock of Gibraltar made of Jurassic limestone, and the narrow coastal lowland surrounding it.[32] It contains many tunnelled roads, most of which are still operated by the military and closed to the general public.
Climate
Main article: Climate of GibraltarGibraltar has a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification Csa),[33][34] with mild winters and warm summers. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry. Its average annual temperature is 18 °C (64 °F): about 21 °C (70 °F) during the day and 15 °C (59 °F) at night. In the coldest month, January, the temperature ranges from 11–18 °C (52–64 °F) during the day and 9–14 °C (48–57 °F) at night, the average sea temperature is 15–16 °C (59–61 °F). In the warmest month, August, the typically temperature ranges from 25–31 °C (77–88 °F) during the day, above 20 °C (68 °F) at night, the average sea temperature is 22 °C (72 °F).[35]
Climate data for Gibraltar Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 16
(61)17
(63)18
(64)20
(68)23
(73)25
(77)28
(82)29
(84)26
(79)23
(73)19
(66)17
(63)21.8
(71.2)Daily mean °C (°F) 13
(55)14
(57)15
(59)17
(63)19
(66)22
(72)24
(75)25
(77)23
(73)20
(68)17
(63)14
(57)18.6
(65.4)Average low °C (°F) 10
(50)11
(52)12
(54)13
(55)15
(59)18
(64)20
(68)21
(70)19
(66)17
(63)14
(57)11
(52)15
(59.1)Precipitation mm (inches) 152
(5.98)98
(3.86)106
(4.17)59
(2.32)25
(0.98)4
(0.16)1
(0.04)3
(0.12)23
(0.91)55
(2.17)114
(4.49)127
(5)767
(30.2)Avg. rainy days 10 7 10 6 4 1 0 1 2 5 7 10 63 Sunshine hours 186.0 196.0 217.0 240.0 310.0 330.0 341.0 341.0 270.0 217.0 180.0 186.0 3,014 Source: BBC Weather [36] Flora and fauna
Gibraltar candytuft growing at the Gibraltar Botanic Gardens. See also: List of mammals of Gibraltar, List of birds of Gibraltar, and List of reptiles and amphibians of Gibraltar
See also: List of mammals of Gibraltar, List of birds of Gibraltar, and List of reptiles and amphibians of GibraltarOver 500 different species of flowering plants grow on the Rock. One of them, the Gibraltar candytuft (Iberis gibraltarica), is endemic to Gibraltar, being the only place in Europe where it is found growing in the wild. It is the symbol of the Upper Rock nature reserve. Among the wild trees that grow all around the Rock, olive and pine trees are some of the most common.
Most of the Rock's upper area is covered by a nature reserve, which is home to around 230 Barbary Macaques (commonly confused with apes), the only wild monkeys found in Europe.[37] The Macaca sylvanus species, is listed as endangered by the IUCN Red List and is declining. In the Middle Atlas mountains, are the three quarters of world population. Recent genetic studies and historical documents point to their presence on the Rock before its capture by the British. A superstition analogous to that of the ravens at the Tower of London states that if the monkeys ever leave, so will the British. In 1944 British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, was so concerned about the dwindling monkey population that he sent a message to the Colonial Secretary requesting that something be done about the situation.[38] Other mammals found in Gibraltar include rabbits, foxes and bats. Dolphins and whales are frequently seen in the Bay of Gibraltar. Migrating birds are very common and Gibraltar is home to the only Barbary Partridges found on the European continent.
In 1991 Graham Watson, MEP for Gibraltar, highlighted conservationists' fears that urban development, tourism and invasive plant species were threatening Gibraltar's own plants as well as birds and bat species.[39]
Economy
Main article: Economy of GibraltarThe British military traditionally dominated Gibraltar's economy, with the naval dockyard providing the bulk of economic activity. This however, has diminished over the last twenty years, and is estimated to account for only 7% of the local economy, compared to over 60% in 1984. Today, Gibraltar's economy is dominated by four main sectors – financial services, internet gaming, shipping and tourism (including retail for visitors).[40]
In the early 2000s, many bookmakers and online gaming operators relocated to Gibraltar to benefit from operating in a regulated jurisdiction with a favourable corporate tax regime. However, this corporate tax regime for non-resident controlled companies was phased out by January 2011 and replaced by an across the board Corporate Tax rate of 10%.[41]
Tourism is also a significant industry. Gibraltar is a popular port for cruise ships and attracts day visitors from resorts in Spain. The Rock is a popular tourist attraction, particularly among British tourists and residents in the southern coast of Spain. It is also a popular shopping destination, and all goods and services are VAT free. Many of the large British high street chains have branches or franchises in Gibraltar including Marks & Spencer and Mothercare. Branches and franchises of international retailers such as Tommy Hilfiger and Sunglass Hut are also present in Gibraltar, as is the Spanish clothing company Mango.
A number of British and international banks have operations based in Gibraltar. Jyske Bank claims to be the oldest bank in the country, based on Jyske's acquisition in 1987 of Banco Galliano, which began operations in Gibraltar in 1855. An ancestor of Barclays, the Anglo-Egyptian Bank, entered in 1888, and Credit Foncier (now Crédit Agricole) entered in 1920.
In 1967, Gibraltar enacted the Companies (Taxation and Concessions) Ordinance (now an Act), which provided for special tax treatment for international business.[42] This was one of the factors leading to the growth of professional services such as private banking and captive insurance management. Gibraltar has several positive attributes as a financial centre, including a common law legal system and access to the EU single market in financial services. The Financial Services Commission (FSC),[43] which was established by an ordinance in 1989 (now an Act) that took effect in 1991, regulates the finance sector.[44] In 1997, the Department of Trade and Industry established its Gibraltar Finance Centre (GFC) Division to facilitate the development the financial sector development.
The currency of Gibraltar is the Gibraltar Pound, issued by the Government of Gibraltar under the terms of the 1934 Currency Notes Act. These banknotes are legal tender in Gibraltar alongside Bank of England banknotes.[45][46] In a currency board arrangement, these notes are issued against reserves of sterling.[46][47][48] Clearing and settlement of funds is conducted in sterling.[49] Coins in circulation follow British denominations but have separate designs. Most retail outlets in Gibraltar unofficially accept the euro, though some payphones and the Royal Gibraltar Post Office do not.[50]
Demography

 The Anglican Cathedral of the Holy Trinity is the larger of the two cathedrals in Gibraltar.
The Anglican Cathedral of the Holy Trinity is the larger of the two cathedrals in Gibraltar. Main article: Demographics of Gibraltar
Main article: Demographics of GibraltarGibraltar is one of the most densely populated territories in the world, with a population estimated in 2008 of 29,286,[51] equivalent to approximately 4,290 inhabitants per square kilometre (11,100 /sq mi). The growing demand for space is being increasingly met by land reclamation; reclaimed land currently comprises approximately one tenth of the territory's total area.
Ethnic groups
See also: Gibraltarian peopleOne of the main features of Gibraltar’s population is the diversity of their ethnic origins. The demographics of Gibraltar reflects Gibraltarians' racial and cultural fusion of the many European and other economic migrants who came to the Rock over three hundred years, after almost all of the Spanish population left in 1704.
The main ethnic groups, according to the origin of names in the electoral roll, are Britons (27%), Spanish (26%, mostly Andalusians but also some 2% of Minorcans), Genoese and other Italians (19%), Portuguese (11%), Maltese (8%), and Jews (3%). There is a large diversity of other groups such as Moroccans, Indians, French, Austrians, Chinese, Japanese, Polish and Danish.[52]
The Gibraltar Census 2001[53] recorded the breakdown of nationalities in Gibraltar as being 83.22% Gibraltarian, 9.56% "Other British", 3.50% Moroccan, 1.19% Spanish and 1.00% "Other EU".
Language
Main article: Languages of GibraltarThe official language of Gibraltar is English, and is used by the Government and in schools. Most locals are bilingual, also speaking Spanish, due to Gibraltar's proximity to Spain. However, because of the varied mix of ethnic groups which reside there, other languages are also spoken on the Rock. Berber and Arabic are spoken by the Moroccan community, as are Hindi and Sindhi by the Indian community of Gibraltar. Hebrew is also spoken by the Jewish community and the Maltese language is still spoken by some families of Maltese descent.
Gibraltarians often converse in Llanito (pronounced: [ʎaˈnito]).[54] It is an Andalusian Spanish based vernacular and unique to Gibraltar. It consists of an eclectic mix of Andalusian Spanish and British English as well as languages such as Maltese, Portuguese, Italian of the Genoese variety and Haketia (Ladino). Andalusian Spanish is the main constituent of Llanito, but is also heavily influenced by British English. However, it borrows words and expressions of many other languages, with over 500 words of Genoese and Hebrew origin.[55] It also often involves code-switching to English.
Gibraltarians often also call themselves Llanitos.
Religion
Gibraltar's main religion is Christianity. The great majority (78%) of Gibraltarians belong to the Roman Catholic Church. The sixteenth century Saint Mary the Crowned is the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Gibraltar, and also the oldest Catholic church in the territory.
Due largely to the British presence, other Christian denominations are also present. They include the Church of England (7%), whose Cathedral of the Holy Trinity is the cathedral of the Anglican Bishop of Gibraltar in Europe; the Gibraltar Methodist Church,[56] Church of Scotland, various Pentecostal and independent churches mostly influenced by the House Church and Charismatic movements, as well as two Plymouth Brethren congregations. There is also a ward of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, and Jehovah's Witnesses.
The second religion in size is Islam (4% of the population[57]). There is also a large established Hindu population, members of the Bahá'í Faith[58] and a long-established Jewish community.[59][60]
Education
Main article: Education in Gibraltar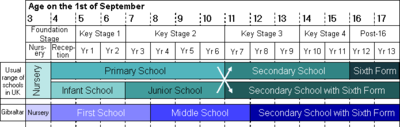 Comparison of school structures in Gibraltar and England.
Comparison of school structures in Gibraltar and England.
Education in Gibraltar generally follows the English system operating within a three tier system. Schools in Gibraltar follow the Key Stage system which teaches the National Curriculum. Gibraltar has fifteen state schools, a MOD school, a private school and a College of Further Education. As there are no facilities in Gibraltar for full-time higher education, all Gibraltarian students must study elsewhere at degree level or equivalent and certain non-degree courses,[61] many in the UK.[citation needed] The Government of Gibraltar operates a scholarship/grant system to provide funding for students studying in the United Kingdom. All Gibraltarian students follow the student loans procedure of the UK, where they apply for a loan from the Student Loans Company which is then reimbursed in full by the Government of Gibraltar. The overwhelming majority of Gibraltarians continue their studies at University.
Health care
All Gibraltarians are entitled to free health care in public wards and clinics at the hospital and primary health care centre. All other British citizens are also entitled to free of charge treatment on the Rock on presentation of a valid British passport during stays of up to 30 days. Other EU nationals are equally entitled to treatment on presentation of a valid European Health Insurance Card. Dental treatment and prescribed medicines are free of charge for Gibraltarian students and pensioners.[62] First-line medical and nursing services are provided at the Primary Care Centre, with more specialised services available at St Bernard's Hospital. Psychiatric care is provided by King George V Hospital.[63] Patients requiring medical treatment not available on the Rock receive it as private patients paid for by the Government of Gibraltar either in the United Kingdom, or more recently in Spain.[citation needed]
Culture
Main article: Culture of GibraltarThe culture of Gibraltar reflects Gibraltarians' diverse origins. While there are Spanish (mostly from nearby Andalusia) and British influences, the ethnic origins of most Gibraltarians are not confined to these ethnicities. Other ethnicities include Genoese, Maltese, Portuguese, and German. A few other Gibraltar residents are Jewish of Sephardic origin, Moroccan, or Indians. British influence remains strong, with English being the language of government, commerce, education, and the media.
Gibraltar's first sovereignty referendum is celebrated annually on Gibraltar National Day (10 September). It is a public holiday, during which most Gibraltarians dress in their national colours of red and white and 30,000 similarly coloured balloons are released, to represent the people of Gibraltar. The 300th anniversary of Gibraltar's capture was celebrated in 2004 on Tercentenary Day (4 August), when in recognition of and with thanks for its long association with Gibraltar, the Royal Navy was given the Freedom of the City of Gibraltar and a human chain of Gibraltarians dressed in red, white and blue, linked hands to encircle the Rock.
The Gibraltar Broadcasting Corporation operates a television and radio station on UHF, VHF and medium-wave. The radio service is also Internet-streamed. Special events and the daily news bulletin are streamed in video. The other local radio service is operated by the British Forces Broadcasting Service which also provides a limited cable television network to HM Forces. The largest and most frequently published newspaper is the Gibraltar Chronicle, Gibraltar’s oldest established daily newspaper and the world’s second oldest English language newspaper to have been in print continuously[64] with daily editions six days a week. Panorama is published on weekdays, and 7 Days, The New People, and Gibsport are weekly.
There exists a small amount of literary writings by native Gibraltarians. The first work of fiction was probably Héctor Licudi's 1929 novel Barbarita, written in Spanish.[65] It is a largely autobiographical account of the adventures of a young Gibraltarian man. Throughout the 1940s and 1950s, several anthologies of poetry were published by Leopoldo Sanguinetti, Albert Joseph Patron, and Alberto Pizzarello. The 1960s were largely dominated by the theatrical works of Elio Cruz and his two highly acclaimed Spanish language plays La Lola se va pá Londre and Connie con cama camera en el comedor.[citation needed] In the 1990s, the Gibraltarian man-of-letters Mario Arroyo published Profiles (1994), a series of bilingual meditations on love, loneliness and death. Of late there have been works by the essayist Mary Chiappe such as her volume of essays Cabbages and Kings (2006) and by academic M. G. Sanchez, author of the novel Rock Black 0–10: A Gibraltar fiction (2006).
A number of local bands play original material and covers. Local venues have begun accepting Gibraltarian bands and those from nearby Spain, resulting in a varied mix of live performances every weekend as well as some weekday nights. Musicians from Gibraltar include Charles Ramirez, the first guitarist invited to play with the Royal College of Music Orchestra,[66] successful rock bands like Breed 77, Melon Diesel and Taxi. Albert Hammond,[67] had top 10 hits in the UK and US, and has written many songs for international artists such as Whitney Houston, Tina Turner and Julio Iglesias among many others.
The cuisine of Gibraltar is the result of the rich diversity of civilizations who held the Rock during its history; from the Berbers of North Africa to the Andalusians and British. The culinary influences include those from Malta, Genoa, Portugal and Andalusia. This marriage of tastes has given Gibraltar an eclectic mix of Arabic, Mediterranean and British cuisines. Calentita, a baked bread-like dish made with chickpea flour, water, olive oil, salt and pepper, is considered Gibraltar's national dish.
Sport
Main article: Sport in GibraltarIn 2007 there were eighteen Gibraltar Sports Associations with official recognition from their respective international governing bodies. Others have submitted applications for recognition which are being considered. The Government supports the many sporting associations financially. Gibraltar also competes in the bi-annual Island Games, which it hosted in 1995. Football is the most popular sport in Gibraltar. The Gibraltar Football Association applied for full membership of UEFA, but their bid was turned down in 2007 in a contentious decision.[68] Cricket enjoys massive popularity in Gibraltar. The Gibraltar national cricket team recently won the European Cricket Championship. Rugby union is fairly popular, and Barbarians and Dragons Gibraltar Selections now play in the Andalusian first division and junior categories respectively. The Gibraltar Rugby Football Union is now applying for membership of Europe's governing body for rugby and await a decision at the end of 2011. A complaint has been received from the Spanish Federation. The Gibraltar Rifle Association (GRA) were the most successful team for Gibraltar at the 2009 Island Games earning four gold medals. The first was won by Heloise Manasco and Stephanie Piri in the ISSF 10m Air Rifle Team event. Heloise later went on to win a second gold in the individual competition. Wayne Piri and Adrian Lugnani took the gold medal in the ISSF 50m Small Bore Team event with Wayne winning the fourth gold for Gibraltar in the individual competition of the same event.
Communications
Main article: Communications in GibraltarGibraltar has a digital telephone exchange supported by a fibre optic and copper infrastructure; the telephone operator Gibtelecom also operates a GSM network. Internet connectivity is available across the fixed network. Local operator CTS is rolling out WiMAX.
International Direct Dialling (IDD) is provided, and Gibraltar was allocated the access code +350 by the International Telecommunication Union. This has been universally valid since 10 February 2007, when the telecom dispute was resolved.
Transport
Main article: Transport in GibraltarWithin Gibraltar, the main form of transport is the car. Motorbikes are also very popular and there is a good modern bus service. Unlike in other British territories, traffic drives on the right, as the territory shares a land border with Spain.
There is a cable car which runs from ground level to the top of the Rock, with an intermediate station at Apes’ Den.
Restrictions on transport introduced by Spanish dictator Francisco Franco closed the land frontier in 1969 and also prohibited any air or ferry connections. In 1982, the land border was reopened. As the result of an agreement signed in Córdoba on 18 September 2006 between Gibraltar, the United Kingdom and Spain,[69] the Spanish government agreed to relax border controls at the frontier that have plagued locals for decades; in return, Britain paid increased pensions to Spanish workers who lost their jobs when Franco closed the border.[70] Telecommunication restrictions were lifted in February 2007 and air links with Spain were restored in December 2006.[71][72]
Gibraltar maintains regular flight connections to London and Manchester. Scheduled flights to Morocco and Madrid proved unsustainable due to insufficient demand.
GB Airways operated a service between Gibraltar and London and other cities for many years. The airline initially flew under the name "Gibraltar Airways". In 1989, and in anticipation of service to cities outside the UK, Gibraltar Airways changed its name to GB Airways with the belief that a new name would incur fewer political problems. As a franchise, the airline operated flights in full British Airways livery. In 2007 GB Airways was purchased by EasyJet[73] who began operating flights under their name in April 2008 when British Airways re-introduced flights to Gibraltar under their name. Monarch Airlines operate a daily scheduled service between Gibraltar and Luton and Manchester. The Spanish national airline, Iberia, operated a daily service to Madrid which ceased due to lack of demand. In May 2009 Ándalus Líneas Aéreas opened a Spanish service[74] which also ceased operations in March 2010.[75] An annual return charter flight to Malta is operated by Maltese national airline, Air Malta.
Gibraltar Airport is unusual not only due to its proximity to the city centre resulting in the airport terminal being within walking distance of much of Gibraltar but also because the runway intersects Winston Churchill Avenue, the main north-south street, requiring movable barricades to close when aircraft land or depart. New roads and a tunnel, which will end the need to stop road traffic when aircraft use the runway, are planned to coincide with the building of a new airport terminal building with an originally estimated completion date of 2009,[76][77] although due to delays this is now more likely to be 2011.
Motorists, and on occasion pedestrians, crossing the border with Spain have been subjected to long delays and searches by the Spanish authorities.[78] Spain has closed the border during disputes or incidents involving the Gibraltar authorities, such as the Aurora cruise ship incident[79] and when fishermen from the Spanish fishing vessel Piraña were arrested for illegal fishing in Gibraltar waters.[80]
The most popular alternative airport for Gibraltar is Málaga Airport in Spain, some 120 kilometres (75 mi) to the east, which offers a wide range of destinations, second to Jerez Airport which is closer to Gibraltar.
Gibraltar receives a large number of visits from cruise ships, and the Strait of Gibraltar is one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world.
Passenger and cargo ships anchor in the Port of Gibraltar. Also, a daily ferry links Gibraltar with Tangier in Morocco. The ferry between Gibraltar and Algeciras, which had been halted in 1969 when Franco severed communications with Gibraltar, was finally reopened on 16 December 2009, served by the Spanish company Transcoma.[81]
The closest train station is San Roque station.
Police
Main article: Royal Gibraltar PoliceSee also: Gibraltar Defence PoliceThe Royal Gibraltar Police (RGP) is, along with the Gibraltar Customs, the principal civilian law enforcement agency in Gibraltar. It is the oldest police force in the Commonwealth of Nations outside the United Kingdom, having being formed when Gibraltar was declared a crown colony on 25 June 1830, shortly after the creation of London's Metropolitan Police in 1829.
In general the Gibraltar force follows British police models in its dress and notably male constables and sergeants on foot patrol wear the traditional headgear of the British "bobby on the beat", correctly known as the custodian helmet. The helmet is traditionally made of cork covered outside by felt or serge like material that matches the tunic.
The force, whose name received the prefix "Royal" in 1992, currently numbers over 220 officers, who are divided into a number of units. These include CID, Drug Squad, Special Branch, Firearms Unit, Scene of Crime Examiners, Traffic Department, Marine Section, and Operations Division.
The current headquarters is at New Mole House Police Station, Rosia Road.
Military
Gibraltar's defence is the responsibility of the tri-service British Forces Gibraltar. In January 2007, the Ministry of Defence announced that the private company – SERCO – would provide services to the base. The announcement resulted in the affected trade unions striking.
- The Royal Gibraltar Regiment provides the army garrison, based at Devils Tower Camp.[82] The regiment was originally a part-time reserve force but the British Army placed it on the permanent establishment in 1990. The regiment includes full-time and part-time soldiers recruited from Gibraltar, as well as British Army regulars posted from other regiments.
- The Royal Navy maintains a squadron at the Rock. The squadron is responsible for the security and integrity of British Gibraltar Territorial Waters (BGTW). The shore establishment at Gibraltar is called HMS Rooke after Sir George Rooke who captured the Rock for Archduke Charles (pretender to the Spanish throne) in 1704. The naval air base was named HMS Cormorant. Gibraltar's strategic position provides an important facility for the Royal Navy and Britain's allies. British and U.S. nuclear submarines frequently visit the Z berths at Gibraltar.[83] A Z berth provides the facility for nuclear submarines to visit for operational or recreational purposes, and for non-nuclear repairs. During the Falklands War, an Argentine plan to attack British shipping in the harbour using frogmen (Operation Algeciras) was foiled.[84] The naval base also played a part in supporting the task force sent by Britain to recover the Falklands.
- The Royal Air Force station at Gibraltar forms part of Headquarters British Forces Gibraltar. Although aircraft are no longer permanently stationed at RAF Gibraltar, a variety of RAF aircraft make regular visits to the Rock and the airfield also houses a section from the Met Office.
The Rock is believed to be a SIGINT listening post.[85] Its strategic position provides a key GCHQ and National Security Agency location for Mediterranean and North African coverage.[86]
Town twinnings
- Current
Gibraltar is currently twinned with the following European towns:
 Funchal, Madeira, Portugal (2009)[87][88][89]
Funchal, Madeira, Portugal (2009)[87][88][89] Ballymena, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom (2006)[90]
Ballymena, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom (2006)[90]
- Past
Gibraltar was once twinned with the following British town:
See also
- Outline of Gibraltar
- British Overseas Territories
- Gibraltar in popular culture
- Gibraltarian people
- List of Gibraltarians
References
- ^ "Gibraltar: National anthem". CIA World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/gi.html. Retrieved 25 September 2011. "National anthem: name: "Gibraltar Anthem" . . . note:adopted 1994; serves as a local anthem; as a territory of the United Kingdom, "God Save the Queen" remains official (see United Kingdom)"
- ^ Gibraltar was captured on 24 July 1704, Old Style, and 4 August 1704, New Style
- ^ The treaty was signed on 31 March 1713, Old Style, and 11 April 1713, New Style – Peace and Friendship Treaty of Utrecht between France and Great Britain
- ^ "Abstract of Statistics 2009, Statistics Office of the Government of Gibraltar". p. 2. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/images/stories/PDF/statistics/2009/Abstract%20of%20Statistics%20Report%202009%20Website.pdf. The civilian population includes Gibraltarian residents, other British residents (including the wives and families of UK-based servicemen, but not the servicemen themselves) and non-British residents. Visitors and transients are not included. In 2009, this broke down into 23,907 native born, 3,129 UK British, 2,395 Other for a total population of 29,431. On census night there were 31,623 people present in Gibraltar.
- ^ Country Profiles: Gibraltar, Foreign and Commonwealth Office, 6 May 2010; retrieved 15 May 2010
- ^ a b Informe sobre la cuestión de Gibraltar, Spanish Foreign Ministry (Spanish)
- ^ "History of Gibraltar". Government of Gibraltar. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/gov_depts/port/port_index.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ Choi, Charles (2006). "Gibraltar". MSNBC. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/14817677/. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ^ Maurice Harvey (1996). Gibraltar. A History. Spellmount Limited. pp. 50–51. ISBN 1-86227-103-8.
- ^ Maurice Harvey (1996). Gibraltar. A History. Spellmount Limited. pp. 51–52. ISBN 1-86227-103-8.
- ^ William Godfrey Fothergill Jackson (1990). The Rock of the Gibraltarians: A History of Gibraltar. Gibraltar Books. p. 257. ISBN 9780948466144. http://books.google.com/books?id=zmKTPwAACAAJ. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
- ^ Cahoon, Ben (2000). "Gibraltar". WorldStatesmen. http://www.worldstatesmen.org/Gibraltar.html. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Regions and territories: Gibraltar". British Broadcasting Corporation. 18 July 2007. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/country_profiles/3851047.stm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Mark Oliver; Sally Bolton, Jon Dennis, Matthew Tempest (4 August 2004). "Gibraltar". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/gibraltar/story/0,,634007,00.html. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Corrected transcript of evidence taken before the Foreign Affairs Select Committee; 28 March 2008; Answer to Question 257 by Jim Murphy: [T]he UK Government will never – "never" is a seldom-used word in politics – enter into an agreement on sovereignty without the agreement of the Government of Gibraltar and their people. In fact, we will never even enter into a process without that agreement.
- ^ "World Factbook". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/gi.html. Retrieved 15 June 2010.
- ^ Parliament.uk, UK House of Commons Foreign Affairs Committee 2007–2008 Report, pg 16
- ^ Telegraph.co.uk, David Blair, Gibraltar makes plans for self-government, Daily Telegraph, 28 February 2002 "GIBRALTAR'S parliament approved an ambitious package of constitutional reform yesterday designed to give the colony almost complete self-government."
- ^ "Gibraltar". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/233245/Gibraltar. Retrieved 18 August 2009. "Gibraltar is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom and is self-governing in all matters but defence."
- ^ "Laws of Gibraltar – On-line Service". Gibraltarlaws.gov.gi. http://www.gibraltarlaws.gov.gi/constitution.php. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "The Gibraltar Parliament". Gibraltar.gov.gi. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/the-gibraltar-parliament. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ TheCommonwealth.org, The Secretariat of the Commonwealth: "The governor represents the British monarch who is head of state and retains direct responsibility for all matters not specifically allocated to local ministers: principally external affairs, defence and internal security"
- ^ PriceWaterhouseCoopers, "About Gibraltar"
- ^ GPA.gi, Gibraltar Police Authority, About the Gibraltar Police Authority – Other Duties and Responsibilities – Accountability: "1. to be accountable to the Governor on policing aspects of national security including internal security (section 12); 2. to be accountable to the Government for those parts of the Annual Policing Plan which do not relate to national security (section 15)."
- ^ Gibraltar.gov.gi, Gibraltar Chief Minister’s address at the United Nations Committee of 24 on 5 June 2007: The new Constitution "maximises self Government in all areas of Governance except defence, external affairs and internal security which, under our own Constitution vest in the Governor as a matter of distribution of powers."
- ^ a b BBC News website, Regions and territories: Gibraltar "Gibraltar is self-governing in all areas except defence and foreign policy."
- ^ Legco.gov.hk, Page 6, "Lords of Appeal in Ordinary in the House of Lords are appointed by the Queen on the recommendation of the Prime Minister, but the Lord Chancellor's opinion is generally sought. This method of appointment is a matter of practice and convention, not of written law."
- ^ "Gibraltar Chronicle". http://www.chronicle.gi/. Retrieved 16 March 2010.
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons. "Statement by the Minister for Europe". Publications.parliament.uk. http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm200708/cmselect/cmfaff/147/8032602.htm. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "Gibraltar should join South West for elections to European Parliament". Electoral Commission. 28 August 2003. Archived from the original on 5 December 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071205011910/http://www.electoralcommission.org.uk/media-centre/newsreleasereviews.cfm/news/226. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Gibraltar Water Supply". AquaGib. http://www.aquagib.gi/gibraltar_water_supply.html. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Gibraltar.gov.uk[dead link]
- ^ CIA Factbook – Geographic location
- ^ The Maltese Islands, Department of Information – Malta.
- ^ "Gibraltar Climate Guide". http://www.weather2travel.com/climate-guides/gibraltar/gibraltar.php. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
- ^ "BBC Weather | Gibraltar". BBC News. 2010-01-29. http://news.bbc.co.uk/weather/forecast/46. Retrieved 2011-11-06.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan (2008) Barbary Macaque: Macaca sylvanus, Globaltwitcher.com, ed. Nicklas Stromberg
- ^ Casciani, Dominic (22 July 2004). "Churchill sends telegram to protect apes". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/3917987.stm. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ Bruno Waterfield Whitehall gaffe 'gives Gibraltar's shores to Spain. The Daily Telegraph, 7 Nov 2009
- ^ Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Europe. Gibraltar (British Overseas Territory) Last reviewed: 6 May 2010. http://www.fco.gov.uk/en/travel-and-living-abroad/travel-advice-by-country/country-profile/europe/gibraltar/?profile=economy
- ^ "Tax Information". Government of Gibraltar. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/e-business/taxation. Retrieved 9 May 2011.
- ^ "Microsoft Word - 1983-13o.doc" (PDF). http://www.gibraltarlaws.gov.gi/articles/1983-13o.pdf. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "Financial Services Commission". Fsc.gi. http://www.fsc.gi/fsc/home.htm. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "Microsoft Word - 2007-03o.doc" (PDF). http://www.gibraltarlaws.gov.gi/articles/2007-03o.pdf. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ European Central Bank Monthly Bulletin, April 2006, page 96
- ^ a b "Currency Notes Act, Section 6". Government of Gibraltar. 11 May 1934. http://www.gibraltarlaws.gov.gi/articles/1934-06o.pdf. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Managing a Global Enterprise, William R. Feist, James A. Heely, Min H. Lu, page 40
- ^ Currency Board Arrangements, Tomás J. T. Baliño, Charles Enoch, International Monetary Fund, page 1
- ^ Madge, A; A. Simons (June 2000). "Gibraltar". Guardian International Currency Corp. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071011135336/http://guardianfx.com/information/europe/gibraltar.html. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Noble, John; Forsyth, Susan; Hardy, Paula; Hannigan, Des (2005). Andalucía. Lonely Planet. p. 221. ISBN 978-1740596763.
- ^ Statistics Office, Government of Gibraltar: Abstract of Statistics 2008[dead link]
- ^ Archer, Edward G.: Gibraltar, identity and empire. Routledge Advances in European Politics
- ^ Census of Gibraltar 2001.[dead link]
- ^ "Culture of Gibraltar". Everyculture. http://www.everyculture.com/Ge-It/Gibraltar.html#orientation. Retrieved 5 October 2007.
- ^ "Gibraltar Ethnologue profile". Ethnologue. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=eng#Gibraltar. Retrieved 21 September 2007.
- ^ "Gibraltar Methodist Church". The Methodist Church. http://www.methodist.org.gi/. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Abstract of Statistics 2008, Office of Statistics, Government of Gibraltar[dead link]
- ^ "''Official Gilbraltarian Baha'i Website''". Gibnet.com. http://www.gibnet.com/bahai/. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "People". Official Government of Gibraltar London website. 2005. Archived from the original on 13 October 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071013194341/http://gibraltar.gov.uk/hol/people.asp. Retrieved 6 November 2007.
- ^ Jacobs, Joseph. "Gibraltar". JewishEncyclopedia.com. http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/view.jsp?artid=220&letter=G. Retrieved 6 November 2007.
- ^ "Education & Training". Government of Gibraltar. 7 April 2003. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/gov_depts/education/education_index.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.[dead link]
- ^ "Gibraltar Health". TravelPuppy. http://travelpuppy.com/gibraltar/health.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Gibraltar Health Authority". Gha.gi. http://www.gha.gi/httpdocs/index.htm. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "Gibraltar: Fact File". Birmingham UK International Directory – Gibraltar. http://www.birminghamuk.com/cities/gibinfo.htm. Retrieved 31 August 2007.
- ^ Yborra Aznar, José Juan (2004). "La ciudad perdida: Gibraltar en la obra de Héctor Licudi" (in Spanish). Eúphoros (7): 317–326. ISSN 1575-0205. http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/oaiart?codigo=1973665.
- ^ Mascarenhas, Alice. "Always a Pleasure to Perform in Gibraltar". The Gibraltar Chronicle. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070928050953/http://www.chronicle.gi/Features/Charles+Ramirez/charles+ramirez.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Newsletter No". Friends of Gibraltar Heritage Society. 70 November 2004. Archived from the original on 1 December 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071201121115/http://www.foghs.org.uk/nl/70.pdf. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Munro, Jim (26 January 2007). "UEFA snub the Rock". London: The Sun. http://www.thesun.co.uk/sol/homepage/sport/football/article29250.ece.
- ^ "Communiqué of the ministerial meeting of the forum of dialogue on Gibraltar". Government of Gibraltar. 18 September 2006. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/pensions/Ministerial_Statement.pdf. Retrieved 17 October 2008.[dead link]
- ^ Government of Gibraltar (18 September 2006). "Trilateral Forum. Ministerial Statement on Pensions". http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/latest_news/press_releases/2006/Ministerial_Statement_On_Pensions.pdf. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ "Press Release. Airport Agreement". Government of Gibraltar. 18 September 2006. http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/latest_news/press_releases/2006/271-2006.pdf. Retrieved 17 October 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Spain restores Gibraltar air link". British Broadcasting Corporation. 16 December 2006. http://news.bbc.co.uk/go/rss/-/2/hi/europe/6198314.stm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Government of Gibraltar. "Press Release: Government of Gibraltar Reaction to GB Sale". http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/latest_news/press_releases/2007/239-2007.pdf. Retrieved 16 October 2008.
- ^ "Regional Andalusia airline begins Gibraltar-Madrid airbridge". MercoPress. http://en.mercopress.com/2009/04/30/regional-andalusia-airline-begins-gibraltar-madrid-airbridge. Retrieved 9 March 2010.
- ^ "Andalus drops Gibraltar". Panorama.gi. http://www.panorama.gi/localnews/headlines.php?action=view_article&article=5758&offset=0. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ Government of Gibraltar. "Press Release: New Air Terminal, tunnel under the runway and new road leading to all parts of Gibraltar north of the runway". http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/latest_news/press_releases/2007/111-2007.pdf. Retrieved 17 October 2008. and images of the proposals: "Press Release: New Terminal Building". http://www.gibraltar.gov.gi/latest_news/press_releases/2007/111-2007-images.pdf. Retrieved 17 October 2008.
- ^ "The Chief Minister presented the plans for an ambitious new terminal building for Gibraltar Airport". 7 Days Gibraltar. http://www.7daysgibraltar.com/article.php?id=655. Retrieved 21 December 2007.
- ^ The Committee Office, House of Commons. "Frontier restrictions". Publications.parliament.uk. http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm199899/cmselect/cmfaff/366/36605.htm. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ Scotsman.com News: Spanish seal border as virus ship docks, retrieved 16 October 2007
- ^ "Fishermen block frontier". Panorama.gi. http://www.panorama.gi/localnews/headlines.php?action=view_article&article=1615. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ New ferry 'repairs 40 year gap' says Spanish Diplomat, Gibraltar Chronicle, 17 December 2009
- ^ "HIVE Location overview – Gibraltar". Ministry of Defence. December 2007. http://www.mod.uk/NR/rdonlyres/1B9B3D6A-1D09-49B1-9209-3AE16C1614F8/0/20080201_gibraltar_lo.pdf. Retrieved January 2010.
- ^ "House of Commons Hansard Written Answers". Parliament of the United Kingdom. 9 November 1999. http://www.parliament.the-stationery-office.co.uk/pa/cm199798/cmhansrd/vo981109/text/81109w21.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Giles Tremlett in Madrid. "Guardian.co.uk". The Guardian. UK. http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2004/jul/24/gibraltar.falklands. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ Vest, Jason; Wayne Madsen (1 March 1999). "Foreign-operated accommodation site that provides occasional SIGINT product to the USSS". http://jya.com/nsa-scs.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Early 20th century communications interception in Spain: a historical perspective". Statewatch. http://www.statewatch.org/news/2004/aug/10spain-gib-comint.htm. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ Searle, Dominique (12 May 2009). "Gibraltar-Madeira Twinning". Gibraltar Chronicle. http://www.chronicle.gi/headlines_details.php?id=16040. Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ^ "Gibraltar Twinned". madeira4u. 15 May 2009. http://www.madeira4u.com/blog.html/4163. Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ^ Searle, Dominique (27 May 2009). "Twinned". Gibraltar Chronicle. http://www.chronicle.gi/headlines_details.php?id=16201. Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ^ "Mayor set for Gibraltar – Ballymena twinning". Gibraltar News Online. 25 April 2006. http://www.gibraltarnewsonline.com/2006/04/25/mayor-set-for-gibraltar-ballymena-twinning/. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Newsletter No 24". Friends of Gibraltar Heritage Society. October 2005. Archived from the original on 1 December 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071201121105/http://www.foghs.org.uk/nl/74.pdf. Retrieved 20 December 2007.
Bibliography
- Abulafia, David (2011). The Great Sea: A Human History of the Mediterranean. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-713-99934-1. http://books.google.com/books?id=dKcQPBV0UdQC.
- Bond, Peter (2003). "Gibraltar's Finest Hour The Great Siege 1779–1783". 300 Years of British Gibraltar 1704–2004 (1st ed.). Gibraltar: Peter-Tan Publishing Co.. pp. 28–29.
- Chartrand, René (July 2006). Gibraltar 1779–1783: The Great Siege. Patrice Courcelle (1st ed.). Gibraltar: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 9781841769776. http://www.ospreypublishing.com/title_detail.php/title=S9770.
- Drinkwater, John: A history of the siege of Gibraltar, 1779–1783: With a description and account of that garrison from the earliest periods London, 1862.
- Falkner, James: FIRE OVER THE ROCK: The Great Siege of Gibraltar 1779–1783, Pen and Sword, 2009
- Harvey, Robert: A Few Bloody Noses: The American War of Independence, London, 2001
- Rodger, N. A. M.: The Command of the Ocean: A Naval History of Britain, 1649–1815, London, 2006
- Norwich, John Julius: The Middle Sea: a history of the Mediterranean, Random House, 2006
- Sugden, John: Nelson: A Dream of Glory, London, 2004
- Syrett, David: Admiral Lord Howe: A Biography, London, 2006.
- Maria Monti, Ángel: Historia de Gibraltar: dedicada a SS. AA. RR., los serenisimos señores Infantes Duques de Montpensier, Imp. Juan Moyano, 1852
- Maria Montero, Francisco: Historia de Gibraltar y de su campo, Imprenta de la Revista Médica, 1860
- Uxó Palasí, José: Referencias en torno al bloqueo naval durante los asedios, Almoraima. n.º 34, 2007
External links
- Interactive Map of Gibraltar
- Gibraltar.com – Complete information portal for Gibraltar
- Government of Gibraltar
- TheGibraltarian.com – Startpage of Gibraltar: TV, Radio, News, Chatroulette, Forum, Map, Links
Capitals of European states and territories Capitals of non-sovereign territories or constituent nations shown in SmallCaps Western Northern Central Southern Eastern Amsterdam, 6 Netherlands
Andorra la Vella, Andorra
Belfast, Northern Ireland
Brussels, 5 Belgium
Douglas, Isle of Man 4
Cardiff, Wales
Dublin, Ireland
Edinburgh, Scotland
Lisbon, Portugal
London, United Kingdom, England
Luxembourg, Luxembourg
Madrid, Spain
Monaco, Monaco
Paris, France
Saint Helier, Jersey 4
Saint Peter Port, Guernsey 4Ankara, Turkey 1
Athens, Greece
Gibraltar, Gibraltar 4
Nicosia, Cyprus 2
North Nicosia, Northern Cyprus 2, 3
Podgorica, Montenegro
Pristina, Kosovo 3
Rome, Italy
San Marino, San Marino
Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Skopje, Republic of Macedonia
Sofia, Bulgaria
Tirana, Albania
Valletta, Malta
Vatican City, Vatican CityAstana, Kazakhstan 1
Baku, Azerbaijan 1
Bucharest, Romania
Chişinău, Moldova
Kiev, Ukraine
Minsk, Belarus
Moscow, Russia 1
Stepanakert, Nagorno-Karabakh 2, 3
Sukhumi, Abkhazia 2, 3
Tbilisi, Georgia 1
Tiraspol, Transnistria 3
Tskhinvali, South Ossetia 2, 3
Yerevan, Armenia 11 Transcontinental country. 2 Entirely in Southwest Asia but having socio-political connections with Europe. 3 Partially recognised country. 4 Crown Dependency or Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom. 5 Also the seat of the European Union, see Location of European Union institutions and Brussels and the European Union. 6 Also the capital of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. 7 Also the capital of the Kingdom of Denmark. British Overseas Territories Crown Dependencies Constituent countries The Valley, Anguilla
Hamilton, Bermuda
Rothera, British Antarctic Territory
Diego Garcia, British Indian Ocean Territory
Road Town, British Virgin Islands
George Town, Cayman Islands
Stanley, Falkland Islands
Gibraltar, Gibraltar
Plymouth (de jure), Brades (de facto), Montserrat
Adamstown, Pitcairn Islands
Jamestown, Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Grytviken (de jure), King Edward Point (de facto), Sth Georgia & Sth Sandwich Islands
Episkopi Cantonment, Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Cockburn Town, Turks and Caicos IslandsSaint Helier, Jersey
Saint Peter Port, Guernsey
Douglas, Isle of ManLondon, England and the United Kingdom
Edinburgh, Scotland
Cardiff, Wales
Belfast, Northern IrelandGeographic locale Countries and territories of the Mediterranean Sea Gibraltar and the United Kingdom British Overseas Territories and Crown dependencies Overseas territories Anguilla · Bermuda · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Gibraltar · Montserrat · Pitcairn Islands · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha1 · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands · Turks and Caicos Islands
Crown dependencies Sovereign base areas 1 includes Saint Helena · Ascension Island · Tristan da Cunha
² includes Alderney · SarkBritish Empire and Commonwealth of Nations Legend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of NationsEurope18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1763–1782 Minorca
1798–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands20th century
1921-1937 Irish Free StateNorth America17th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
1607–1776 Virginia
since 1619 Bermuda
1620–1691 Plymouth Colony
1629–1691 Massachusetts Bay Colony
1632–1776 Maryland
1636–1776 Connecticut
1636–1776 Rhode Island
1637–1662 New Haven Colony
1663–1712 Carolina
1664–1776 New York
1665–1674 and 1702-1776 New Jersey
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
1674–1702 East Jersey
1674–1702 West Jersey
1680–1776 New Hampshire
1681–1776 Pennsylvania
1686–1689 Dominion of New England
1691–1776 Massachusetts18th century
1701–1776 Delaware
1712–1776 North Carolina
1712–1776 South Carolina
1713–1867 Nova Scotia
1733–1776 Georgia
1763–1873 Prince Edward Island
1763–1791 Quebec
1763–1783 East Florida
1763–1783 West Florida
1784–1867 New Brunswick
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
1818–1846 Columbia District / Oregon Country1
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1853–1863 Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands
1858–1866 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
1866–1871 Vancouver Island and British Columbia
1867–1931 *Dominion of Canada2
20th century
1907–1949 Dominion of Newfoundland31Occupied jointly with the United States
2In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. see Canada's name.
3Gave up self-rule in 1934, but remained a de jure Dominion until it joined Canada in 1949.Latin America and the Caribbean17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *Saint Kitts.2C 1623 to 1700|St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago
20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation4Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
Africa18th century
1792–1961 Sierra Leone
1795–1803 Cape Colony19th century
1806–1910 Cape Colony
1810–1968 Mauritius
1816–1965 Gambia
1856–1910 Natal
1868–1966 Basutoland (Lesotho)
1874–1957 Gold Coast (Ghana)
1882–1922 Egypt
1884–1966 Bechuanaland (Botswana)
1884–1960 British Somaliland
1887–1897 Zululand
1888–1894 Matabeleland
1890–1965 Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe) 5
1890–1962 Uganda
1890–1963 Zanzibar (Tanzania)
1891–1964 Nyasaland (Malawi)
1891–1907 British Central Africa Protectorate
1893–1968 Swaziland
1895–1920 East Africa Protectorate
1899–1956 Anglo-Egyptian Sudan20th century
1900–1914 Northern Nigeria
1900–1914 Southern Nigeria
1900–1910 Orange River Colony
1900–1910 Transvaal Colony
1906–1954 Nigeria Colony
1910–1931 South Africa
1911–1964 Northern Rhodesia (Zambia)
1914–1954 Nigeria Colony and Protectorate
1915–1931 South West Africa (Namibia)
1919–1960 Cameroons (Cameroon) 6
1920–1963 Kenya
1922–1961 Tanganyika (Tanzania) 6
1954–1960 Nigeria
1979–1980 Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe) 55Southern Rhodesia issued a Unilateral Declaration of Independence in 1965 (as Rhodesia) and returned to British control in 1979.
6League of Nations mandateAsia18th century
1702–1705 Côn Đảo
1757–1947 Bengal (West Bengal (India) and Bangladesh)
1762–1764 Manila
1795–1948 Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1796–1965 Maldives19th century
1812-1824 Banka (Sumatra)
1812-1824 Billiton (Sumatra)
1819–1826 British Malaya (Peninsular Malaysia and Singapore)
1826–1946 Straits Settlements
1839–1967 Colony of Aden
1839–1842 Afghanistan
1841–1997 Hong Kong
1841–1941 Kingdom of Sarawak (Malaysia)
1858–1947 British India (India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, Burma)
1879–1919 Afghanistan
1882–1963 British North Borneo (Malaysia)
1885–1946 Unfederated Malay States
1888–1984 Sultanate of Brunei
1888–1946 Sultanate of Sulu
1891–1971 Muscat and Oman protectorate
1892–1971 Trucial States protectorate
1895–1946 Federated Malay States
1898–1930 Weihai Garrison
1878–1960 Cyprus20th century
1918–1961 Kuwait protectorate
1920–1932 Iraq6
1921–1946 Transjordan6
1923–1948 Palestine6
1945–1946 South Vietnam
1946–1963 Sarawak (Malaysia)
1946–1963 Singapore
1946–1948 Malayan Union
1948–1957 Federation of Malaya (Malaysia)
since 1960 Akrotiri and Dhekelia (before as part of Cyprus)
since 1965 British Indian Ocean Territory (before as part of Mauritius and the Seychelles)Oceania18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land/Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands7
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony/Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1841–1907 Colony of New Zealand
1851–1901 Victoria
1874–1970 Fiji8
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands7
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)7
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands9
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands1020th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue7
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1942 Nauru
1945–1968 Nauru
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea117Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
8Suspended member
9Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
10Now the *Solomon Islands
11Now *Papua New GuineaAntarctica and South Atlantic17th century
since 1659 St. Helena1219th century
since 1815 Ascension Island12
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha12
since 1833 Falkland Islands1320th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory14
since 1908 South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands13, 1412Since 2009 part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Ascension Island (1922—) and Tristan da Cunha (1938—) were previously dependencies of St Helena
13Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982
14Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands)Geography of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognitionDependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Climate of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territoriesOther entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Phoenician cities and colonies Algeria: Hippo Regius · Ikosium · Guelma · Iol · Rus Icada · Rus Azuz · Iom · Honaine · Pomoria · Cirta · Rus Ucurru · Rus Aghoun · Rus Ipir · Qart Ina · Siga · Timgad · Lambese · Djémila · Uzinaza · Cuicul · Altava · Igligili · Imonium · Sitifis · Auzia · Rapidum · Portus Magnus · Tipaza · Cyprus: Kition · Italy: Karalis · Lilybaeum · Motya · Nora · Olbia · Panormus · Solki · Soluntum · Tharros · Lebanon: Amia · Ampi · Arqa · Baalbek · Berut · Botrys · Gebal · Sarepta · Sur · Sydon · Tripolis · Libya: Leptis Magna · Oea · Sabratha · Malta: Gozo · Mauritania: Cerne · Morocco: Arambys · Caricus Murus · Lixus · Tingis · Portugal: Olissipona · Ossonoba · Spain: Abdera · Abyla · Akra Leuke · Gadir · Herna · Ibossim · Mahón · Malaca · Onoba · Qart Hadašt · Rusadir · Sexi · Syria: Amrit · Arwad · Safita · Ugarit · Tunisia: Carthage · Hadrumetum · Hippo Diarrhytos · Kerkouane · Leptis Parva · Thanae · Thapsus · Utica · Turkey: Myriandrus · Phoenicus · Gibraltar
Categories:- Gibraltar
- Arabic words and phrases
- Capitals in Europe
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Headlands of Europe
- Jewish Spanish history
- Peninsulas of Europe
- Umayyad Caliphate
- Western Europe
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

![Location of Gibraltar (dark green)– in Europe (green & dark gray)– in the European Union (green) — [Legend]](/pictures/enwiki/50/250px-Location_Gibraltar_EU.png)