- Saint Helena
-
For other uses, see Saint Helena (disambiguation).
Saint Helena 

Flag Coat of arms Motto: "Loyal and Unshakeable" Anthem: "God Save the Queen"
"My Saint Helena Island" (unofficial)
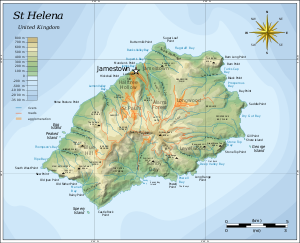
Capital Jamestown
15°56′S 5°43′W / 15.933°S 5.717°WOfficial language(s) English Demonym Saint Helenian† Government British overseas territory - Monarch Elizabeth II - Governor Mark Andrew Capes Part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha - Charter granted 1657 - Colonised
(East India Company)1659 - Crown colony
(Company rule ends)22 April 1834[1] - Current constitution 1 September 2009 Area - Total 122 km2
47 sq miPopulation - February 2008 census 4,255[2] - Density 35/km2
90.6/sq miCurrency Saint Helena pound ( SHP)Time zone GMT (UTC+0) Drives on the left ISO 3166 code SH Internet TLD .sh Calling code +290 † or simply Helenian; informally the islanders are referred to as "Saints" Saint Helena (
 /ˌseɪnt həˈliːnə/ saynt-hə-lee-nə), named after St Helena of Constantinople, is an island of volcanic origin in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the British overseas territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha[3] which also includes Ascension Island and the islands of Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about 16 by 8 kilometres (10 by 5 mi) and has a population of 4,255 (2008 census).[2]
/ˌseɪnt həˈliːnə/ saynt-hə-lee-nə), named after St Helena of Constantinople, is an island of volcanic origin in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the British overseas territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha[3] which also includes Ascension Island and the islands of Tristan da Cunha. Saint Helena measures about 16 by 8 kilometres (10 by 5 mi) and has a population of 4,255 (2008 census).[2]The island was uninhabited when discovered by the Portuguese in 1502. It is one of the most isolated islands in the world. For centuries, it was an important stopover for ships sailing to Europe from Asia and South Africa. The British also used the island as a place of exile, most notably for Napoleon I, Dinuzulu kaCetshwayo and more than 5,000 Boer prisoners. Saint Helena is now Britain's second oldest remaining colony (now termed overseas territory), after Bermuda.
Contents
History
Main article: History of Saint HelenaEarly history, 1502–1658
Most historical accounts state that the island was discovered on 21 May 1502 by the Galician navigator João da Nova sailing at the service of the Portuguese Crown, and that he named it "Santa Helena" after Helena of Constantinople. Another theory holds that the island found by De Nova was actually Tristan da Cunha 2,430 kilometres (1,510 mi) to its south,[4] and that Saint Helena was discovered by some of the ships attached to the squadron of Estêvão da Gama expedition on 30 July 1503 (as reported in the account of clerk Thomé Lopes).[5][6][7]
The Portuguese found the island uninhabited, with an abundance of trees and fresh water. They imported livestock, fruit trees and vegetables, and built a chapel and one or two houses. Though they formed no permanent settlement, the island was an important rendezvous point and source of food for ships travelling from Asia to Europe.
Englishman Sir Francis Drake probably located the island on the final lap of his circumnavigation of the world (1577–1580).[8] Further visits by other English explorers followed, and, once St Helena’s location was more widely known, English ships of war began to lie in wait in the area to attack Portuguese India carracks on their way home. In developing their Far East trade, the Dutch also began to frequent the island. The Portuguese and Spanish soon gave up regularly calling at the island, partly because they used ports along the West African coast, but also because of attacks on their shipping, the desecration of their chapel and religious icons, destruction of their livestock and destruction of plantations by Dutch and English sailors.
The Dutch Republic formally made claim to St Helena in 1633, although there is no evidence that they ever occupied, colonised or fortified it. By 1651, the Dutch had mainly abandoned the island in favour of their colony at the Cape of Good Hope.
East India Company, 1658–1815
In 1657, Oliver Cromwell[9] granted the English East India Company a charter to govern St Helena and the following year the Company decided to fortify the island and colonise it with planters. The first governor, Captain John Dutton, arrived in 1659, and from that date St Helena was Britain’s second oldest colony (after Bermuda). A fort and houses were built. After the Restoration of the English monarchy in 1660, the East India Company received a Royal Charter giving it the sole right to fortify and colonise the island. The fort was renamed James Fort and the town Jamestown, in honour of the Duke of York, later James II of England.
Between January and May 1673 the Dutch East India Company forcibly took the island, before English reinforcements restored English East India Company control. The Company experienced difficulty attracting new immigrants, and unrest and rebellion fomented among the inhabitants. Ecological problems, including deforestation, soil erosion, vermin and drought, led Governor Isaac Pyke to suggest in 1715 that the population be moved to Mauritius, but this was not acted upon and the Company continued to subsidise the community because of the island's strategic location. A census in 1723 recorded 1,110 people, including 610 slaves.
Eighteenth-century governors tried to tackle the island's problems by extending tree plantations, improving fortifications, eliminating corruption, building a hospital, tackling the neglect of crops and livestock, controlling the consumption of alcohol and introducing legal reforms. From about 1770, the island enjoyed a lengthy period of prosperity. Captain James Cook visited the island in 1775 on the final leg of his second circumnavigation of the world. St James' Church was erected in Jamestown in 1774 and in 1791-2 Plantation House was built, and has since been the official residence of the Governor.
On leaving the University of Oxford, in 1676, Edmond Halley visited Saint Helena and set up an observatory with a 24-foot-long (7.3 m) aerial telescope with the intention of studying stars from the Southern Hemisphere.[10] The site of this telescope is near St Mathew's Church in Hutt's Gate, in the Longwood district. The 680m high hill there is named for him and is called Halley's Mount.
The importation of slaves was made illegal in 1792. Governor Robert Patton (1802–1807) recommended that the Company import Chinese labour to supplement the rural workforce. The labourers arrived in 1810, and their numbers reached 600 by 1818. Many were allowed to stay, and their descendents became integrated into the population. An 1814 census recorded 3,507 people on the island.
British rule 1815–1821, and Napoleon's exile
In 1815 the British government selected Saint Helena as the place of detention of Napoleon Bonaparte. He was brought to the island in October 1815 and lodged at Longwood, where he died on 5 May 1821. During this period, St Helena remained in the East India Company’s possession, but the British government met additional costs arising from guarding Napoleon. The island was strongly garrisoned with British troops, and naval ships circled the island.
The 1817 census recorded 821 white inhabitants, a garrison of 820 men, 618 Chinese indentured labourers, 500 free blacks and 1,540 slaves. In 1818, Governor Hudson Lowe initiated the emancipation of the slaves.
British East India Company, 1821–1834
After Napoleon's death the thousands of temporary visitors were soon withdrawn and the East India Company resumed full control of Saint Helena. Owing to Napoleon's praise of St Helena’s coffee during his exile on the island, the product enjoyed a brief popularity in Paris in the years after his death. The importation of slaves was banned in 1792, but the phased emancipation of over 800 resident slaves did not take place until 1827, some six years before legislation to ban slavery in the colonies was passed by the British Parliament.[11]
British rule, a Crown colony, 1834–1981
Under the provisions of the 1833 India Act, control of St Helena was passed from the East India Company to the British Crown, becoming a crown colony.[1] Subsequent administrative cost-cutting triggered the start of a long-term population decline whereby those who could afford to do so tended to leave the island for better opportunities elsewhere. The latter half of the 19th century saw the advent of steam ships not reliant on trade winds, as well as the diversion of Far East trade away from the traditional South Atlantic shipping lanes to a route via the Red Sea (which, prior to the building of the Suez Canal involved a short overland section). These factors contributed to a decline in the number of ships calling at the island from 1,100 in 1855 to only 288 in 1889.
In 1840, a British naval station established to suppress the African slave trade was based on the island, and between 1840 and 1849 over 15,000 freed slaves, known as "Liberated Africans" were landed there. In 1900 and 1901, over 6,000 Boer prisoners were held on the island, and the population reached its all-time high of 9,850 in 1901.
In 1858, the French emperor Napoleon III successfully gained the possession, in the name of the French government, of Longwood House and the lands around it, last residence of Napoleon I (who died there in 1821). It is still French property, administered by a French representative and under the authority of the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
A local industry manufacturing fibre from New Zealand flax was successfully reestablished in 1907 and generated considerable income during the First World War. Ascension Island was made a dependency of St Helena in 1922, and Tristan da Cunha followed in 1938. During World War II, the United States built Wideawake airport on Ascension in 1942, but no military use was made of St Helena.
During this period, the island enjoyed increased revenues through the sale of flax, with prices peaking in 1951. However, the industry declined because of transportation costs and competition from synthetic fibres. The decision by the British Post Office to use synthetic fibres for their mailbags was a further blow, contributing to the closure of the island's flax mills in 1965.
From 1958, the Union Castle shipping line gradually reduced its service calls to the island. Curnow Shipping, based in Avonmouth, replaced the Union-Castle Line mailship service in 1977, using the RMS (Royal Mail Ship) St Helena.
1981 to present
The British Nationality Act 1981 reclassified St Helena and the other Crown colonies as British Dependent Territories. The islanders lost their status as "Citizens of the United Kingdom and Colonies" and thus lost the right of abode in Britain. For the next 20 years, many could find only low-paid work with the island government, and the only available overseas employment was on the Falkland Islands and Ascension Island. The Development and Economic Planning Department, which still operates, was formed in 1988 to contribute to raising the living standards of the people of St Helena.
In 1989, Prince Andrew launched the replacement RMS St Helena to serve the island; the vessel was specially built for the Cardiff–Cape Town route and features a mixed cargo/passenger layout.
The St Helena Constitution took effect in 1989 and provided that the island would be governed by a Governor and Commander-in-Chief, and an elected Executive and Legislative Council. In 2002, the British Overseas Territories Act restored full passports to the islanders, and renamed the Dependent Territories (including St Helena) the British Overseas Territories. In 2009, St Helena and its two territories received equal status under a new constitution, and the British Overseas Territory was renamed Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha.
In 2011, the UK government announced it would invest in a £200m airport on the Island, which would benefit them in the long term, as £26m a year in aid would no longer be required. It is expected the airport will be up at running by 2015. The aims of the airport are to reduce prices of transportation of goods, increase tourism by more than 50 fold and to create new job opportunities. Flying to the Island will only be available from South Africa, according to the 2011 plans.
Geography, flora and fauna
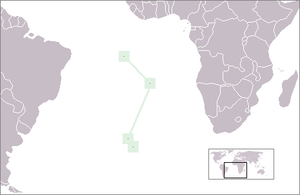
Main articles: Geography of Saint Helena, Wildlife of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, and Flora of Saint HelenaPositions of (from north to south) Ascension Island, Saint Helena and Tristan da Cunha in the South Atlantic Ocean
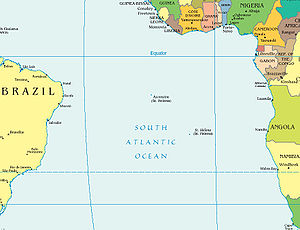
Saint Helena is one of the most isolated places in the world, located in the South Atlantic Ocean more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) from the nearest major landmass. The island is associated with two other isolated islands in southern Atlantic, also British territories — Ascension Island about 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) to the due northwest in more equatorial waters and Tristan da Cunha, which is well outside the tropics 2,430 kilometres (1,510 mi) to the south.[12] The island is situated in the Western Hemisphere and has the same longitude as Cornwall in the United Kingdom.
The island of Saint Helena has a total area of 122 km2 (47 sq mi), and is composed largely of rugged terrain of volcanic origin (the last volcanic eruptions occurred roughly 7 million years ago).[13] The centre is covered by forest, of which some has been planted, including the Millennium Forest project. The highland areas contain most of the island's endemic flora, fauna, insects and birds. The coastal areas are barren, covered in volcanic rock and are warmer and drier than the centre of the island. There are no native land mammals on St Helena, but rabbits, rats and mice have been introduced, as well as feral cats and dogs.
The highest point of the island is Diana's Peak at 818 m (2,684 ft). In 1996 it became the island's first national park. In 2000 a project began to replant part of the lost Great Wood, called the Millennium Forest, and is now managed by the Saint Helena National Trust, established in 2002.
When the island was discovered, it was covered with unique indigenous vegetation, including a remarkable cabbage tree species. The flora of Saint Helena contains a high proportion of endemic species. The island's hinterland must have been a dense tropical forest but the coastal areas were probably quite green as well. The modern landscape is very different, with widespread bare rock in the lower areas, although inland it is green, mainly due to introduced vegetation. The dramatic change in landscape must be attributed to the introduction of goats and the introduction of new vegetation. As a result, the string tree (Acalypha rubrinervis) and the St Helena olive (Nesiota elliptica) are now extinct, and many of the other endemic plants are threatened with extinction.
There are several rocks and islets off the coast, including: Castle Rock, Speery Island, The Needle, Lower Black Rock, Upper Black Rock (South), Bird Island (Southwest), Black Rock, Thompson's Valley Island, Peaked Island, Egg Island, Lady's Chair, Lighter Rock (West), Long Ledge (Northwest), Shore Island, George Island, Rough Rock Island, Flat Rock (East), The Buoys, Sandy Bay Island, The Chimney, White Bird Island and Frightus Rock (Southeast), all of which are within one kilometre of the shore.
The national bird of St Helena is the Saint Helena Plover, known locally as the Wirebird. It appears on the coat of arms of Saint Helena and on the flag.[14]
Climate
See also: Jamestown, Saint_Helena#ClimateThe climate of Saint Helena is tropical, marine and mild, tempered by the Benguela Current and trade winds which blow almost continuously.[15][16] The climate varies noticeably across the island. Temperatures in Jamestown, on the north leeward shore, range between 21–28 °C (70–82 °F) in the summer (January to April) and 17–24 °C (63–75 °F) during the remainder of the year. The temperatures in the central areas are, on average, 5-6 °C (9-11 °F) lower.[16] Jamestown also has a very low annual rainfall, while 750–1,000 mm (30–39 in) falls per year on the higher ground and the south coast, where it is also noticeably cloudier.[17] There are weather recording stations in the Longwood and Blue Hill districts.
Administrative divisions
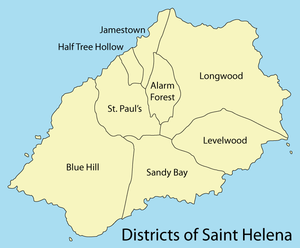
See also: Category:Parishes of Saint HelenaSaint Helena is divided into eight districts,[18] each with a community centre. The districts also serve as statistical subdivisions and electoral areas. The four most populated districts send two representatives each to the Legislative Council, and the remaining districts send one representative each.
District
balance
[clarification needed]Area[19]
km2Area
sq miPop.
1998Pop.
2008[2]Pop./km²
2008Alarm Forest 5.9 2.3 289 276 46.8 Blue Hill 36.5 14.1 177 153 4.2 Half Tree Hollow 1.6 0.6 1,140 901 563.1 Jamestown 3.6 1.4 884 714 198.3 Levelwood 14.0 5.4 376 316 22.6 Longwood 33.4 12.9 960 715 21.4 Sandy Bay 15.3 5.9 254 205 13.4 Saint Paul's 11.4 4.4 908 795 69.7 Royal Mail Ship
St. Helena[clarification needed]– – 149 171 – Jamestown
Harbour– – 20 9 – Total 121.7 47.0 5,157 4,255 35.0 Politics
Main article: Politics of Saint HelenaExecutive authority in Saint Helena is invested in Queen Elizabeth II and is exercised on her behalf by the Governor of Saint Helena. The Governor is appointed by the Queen on the advice of the British government. Defence and Foreign Affairs remain the responsibility of the United Kingdom.
There are fifteen seats in the Legislative Council of Saint Helena, a unicameral legislature. Twelve of the fifteen members are elected in elections held every four years. The other three members are the Governor and two ex officio officers. The Executive Council consists of the Governor, two ex officio officers, and six elected members of the Legislative Council appointed by the Governor. There is no elected Chief Minister, and the Governor acts as the head of government.
Both Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha have an Administrator appointed to represent the Governor of Saint Helena.
One commentator has observed that, notwithstanding the high unemployment resulting from the loss of full passports during 1981–2002, the level of loyalty to the British monarchy by the St Helena population is probably not exceeded in any other part of the world.[20] King George VI is the only reigning monarch to have visited the island. This was in 1947 when the King, accompanied by Queen Elizabeth (later the Queen Mother), Princess Elizabeth (later Queen Elizabeth II) and Princess Margaret were travelling to South Africa. Prince Philip arrived at St Helena in 1957 and then his son Prince Andrew visited as a member of the armed forces in 1984 and his sister the Princess Royal arrived in 2002.
Demographics
 Jamestown, from above
Jamestown, from above Main article: Demographics of Saint Helena
Main article: Demographics of Saint HelenaSaint Helena was first settled by the English in 1659, and the island presently has a population of about 4,250 inhabitants, mainly descended from people from Britain – settlers ("planters") and soldiers – and slaves who were brought there from the beginning of settlement – initially from Africa (the Cape Verde Islands, Gold Coast and west coast of Africa are mentioned in early records), then India and Madagascar. Eventually the planters felt there were too many slaves and no more were imported after 1792.
In 1840, St Helena became a provisioning station for the British West Africa Squadron,[15] preventing slavery to Brazil (mainly), and many thousands of slaves were freed on the island. These were all African, and about 500 stayed while the rest were sent on to the West Indies and Cape Town, and eventually to Sierra Leone.
Imported Chinese labourers arrived in 1810, reaching a peak of 618 in 1818, after which numbers were reduced. Only a few older men remained after the British Crown took over the government of the island from the East India Company in 1834. The majority were sent back to China, although records in the Cape suggest that they never got any further than Cape Town. There were also a very few Indian lascars who worked under the harbour master.
 Jamestown, the capital of Saint Helena
Jamestown, the capital of Saint Helena
The citizens of Saint Helena hold British Overseas Territories citizenship. On 21 May 2002, full British citizenship was restored by the British Overseas Territories Act 2002.[21] See also British nationality law.
During periods of unemployment, there has been a long pattern of emigration from the island since the post-Napoleonic period. The majority of "Saints" emigrated to the UK, South Africa, and in the early years, Australia. The population has steadily declined since the late 1980s and has dropped from 5,157 at the 1998 census to 4,255 in 2008. In the past emigration was characterised by young unaccompanied persons leaving to work on long-term contracts on Ascension and the Falkland Islands, but since "Saints" were re-awarded UK citizenship in 2002, emigration to the UK by a wider range of wage-earners has accelerated due to the prospect of higher wages and better progression prospects.
Saint Helena is one of the few territories in the world which has never had a recorded HIV / AIDS case.[22]
Religion
See also: Category:Religion in Saint HelenaThe majority of people belong to the Anglican Communion, being members of the Diocese of St Helena, which includes Ascension Island, and which has its own Bishop residing on St Helena. The 150th Anniversary of the Diocese was celebrated in June 2009. Other Christian denominations on the island include: Roman Catholic (since 1852), Salvation Army (since 1884), Baptist (since 1845), and, in more recent times, Seventh-day Adventist (since 1949), New Apostolic, and Jehovah's Witness (one out of every 35 residents is a Jehovah's Witness, the highest ratio in the world).[23] The Baha'i Faith has also been represented on the island since 1954.
Tristan da Cunha and Ascension
Tristan da Cunha, settled since 1815, has a population of fewer than three hundred inhabitants of mainly British, Irish, Italian and St Helenian descent. Christianity is the main religion, mainly Anglican and some Roman Catholic.
Ascension Island has no native inhabitants. It is a working island with a transient population of approximately 1,000, made up mainly of members of the American and British militaries, supporting civilian contractors who serve on the joint Anglo-American airbase, and members of their families (a few of whom were born on the island). There are also some Cable & Wireless and local government employees.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Saint Helena- Some of the data in this section has been sourced from the Government of St Helena Sustainable Development Plan.[24]
The island had a monocrop economy until 1966, based on the cultivation and processing of New Zealand flax for rope and string. St Helena's economy is now very weak, and the island is almost entirely sustained by aid from the British government. The public sector dominates the economy, accounting for about half of gross domestic product (GDP). Inflation was running at 3.6% in 2005. There have been recent increases in the cost of fuel, power and all imported goods.
The Saint Helena tourist industry is heavily based on the promotion of Napoleon's imprisonment. A golf course also exists and the possibility for sportfishing tourism is great. Three hotels operate on the island but since the arrival of tourists is directly linked to the arrival and departure schedule of the RMS (Royal Mail Ship), occupancy levels are very low at about 10%. Some 1,180 short- and long-term visitors arrived on the island in 2005.
Saint Helena produces what is said to be the most expensive coffee in the world. It also produces and exports Tungi Spirit, made from the fruit of the prickly or cactus pears, Opuntia ficus-indica ("Tungi" is the local St Helenian name for the plant). Ascension Island, Tristan da Cunha and Saint Helena all issue their own postage stamps which provide a significant income.
Economic statistics
Quoted at constant 2002 prices, GDP fell from £12.4 million in 1999/2000 to £11.2 million in 2005/6. Imports are mainly from the UK and South Africa and amounted to £6.4 million in 2004/5 (quoted on an FOB basis). Exports are much smaller, amounting to £0.24 million in 2004/5. Exports mainly comprise fish and coffee. Philatelic sales were £0.06 million that year. The limited number of visiting tourists spent about £0.43 million in 2004/05, representing a contribution to GDP of 3.1%.
Public expenditure rose from £10.2 million in 2001/02 to £12.3 million in 2005/06. The contribution of UK budgetary aid to total SHG government expenditure rose from £4.6 million in to £6.4 million over the same period. Wages and salaries represent about 38% of recurrent expenditure.
Unemployment levels are low (50 in 2004 compared with 342 in 1998). The economy is dominated by the public sector, the number of government positions only falling slightly from 1,163 in 2002 to 1,142 in 2006. Public sector employment is characterised by high turnover rates, mainly due to emigration. St Helena’s private sector employs approximately 45 per cent of the employed labour force and is largely dominated by small and micro businesses with 218 private businesses employing 886 in 2004.
Household survey results suggest that the percentage of households who spend less than £20 per week on a per capita basis fell from 27% to 8% between 2000 and 2004, implying a decline in income poverty. Nevertheless, 22% of the population claimed social security benefit in 2006/7, although most of these are aged over 60 – this sector represents 20% of the population.
Banking and currency
In 1821, Saul Solomon issued a token copper currency of 70,560 halfpennies Payable at St Helena by Solomon, Dickson and Taylor — presumably London partners — which circulated alongside the East India Company's local coinage until the Crown took over the Island in 1836. The coin remains readily available to collectors.
Today Saint Helena has its own currency, the Saint Helena pound which is at parity with the pound sterling. The government of Saint Helena produces its own coinage and banknotes. The Bank of Saint Helena was established on Saint Helena and Ascension Island in the year 2004. It has branches in Jamestown on Saint Helena, and Georgetown, Ascension Island and it took over the business of the St. Helena government savings bank and the Ascension Island Savings Bank.[25]
For more information on currency in the wider region, see the Sterling Currency in the South Atlantic and the Antarctic.
Transport
Main article: Transport on Saint Helena RMS St Helena in James Bay
RMS St Helena in James Bay
Saint Helena is one of the most remote islands in the world, has no commercial airports, and travel to the island is by ship only. A large military airfield is located on Ascension Island, with two Friday flights to RAF Brize Norton, England (as from September 2010). These RAF flights offer a limited number of seats to civilians. The ship RMS Saint Helena runs between St Helena and Cape Town, also visiting Ascension Island and Walvis Bay, and occasionally voyaging north to Tenerife and Portland, UK. It berths in James Bay, St Helena approximately thirty times per year.[26] The RMS Saint Helena was due for decommissioning in 2010. However, its service life has been extended indefinitely until the airstrip is completed.[citation needed]
After a long period of rumour and consultation, the British government announced plans to construct an airport in Saint Helena in March 2005 and the airport was originally expected to be completed by 2010. However constant delays by the British government[citation needed] meant an approved bidder, the Italian firm Impregilo, was not chosen until 2008, and then the project was put on hold in November 2008, allegedly due to new financial pressures brought on by the credit-crunch. By January 2009, construction had not commenced and no final contracts had been signed, and Governor Andrew Gurr departed for London in an attempt to try and speed up the process and solve the problems. On 22 July 2010, the British government agreed to help pay for the new airstrip using taxpayer money.[27] In November 2011 a new deal between the British government and South African company Basil Read was signed and now means the airport is proposed to open in 2015, with flights to and from South Africa.[28]
A minibus offers a basic service to carry people around Saint Helena, with most services designed to take people into Jamestown for a few hours on weekdays to conduct their business.
Media and communications
See also: Communications in Saint HelenaRadio
Radio St Helena,[29] which started operations on Christmas Day 1967, provides a local radio service that has a range of about 100 km from the island, and also broadcasts internationally on Shortwave Radio (11092.5 kHz) on one day a year.[30] The station presents news, features and music in collaboration with its sister newspaper, the St Helena Herald.
Saint FM[31] provides a local radio service for the island which is also available on internet radio[32] and relayed in Ascension Island. The station is not government funded. It was launched in January 2005. It broadcasts news, features and music in collaboration with its sister newspaper, the St Helena Independent.
Television
St Helena Broadcasting Service will broadcast television in 2014 on channel 1.[clarification needed] Cable & Wireless offers television for the island via three DStv (digital satellite TV) channels.
Telecommunications
Cable and Wireless provide the telecommunications service in the territory. Saint Helena has the international calling code +290 which, since 2006, Tristan da Cunha shares. Telephone numbers are 4 digits long. Numbers start with 1-9, with 8xxx being reserved for Tristan da Cunha numbers and 2xxx for Jamestown.[33]
Internet
Saint Helena has a 10/3.6 Mbit/s[citation needed] internet link via Cable & Wireless International UK.
This is offered on 4 contract levels from lite £20 per month to gold at £120 per month. Both Internet and phone service are subject to sun outages.
Local newspapers
The island has two local newspapers, both of which are available on the internet. The St Helena Herald[34] has been published by the partially publicly funded St Helena News Media Services (SHNMS) since 2000. The St Helena Independent[35] has been published since November 2005.
Funding
In October 2008, the St Helena government announced that the island’s media must choose whether they obtained revenue from government subsidies or from advertising. They could not do both. On this basis, the partly publicly subsidised Media Services, which publishes the St Helena Herald and broadcasts on Radio St Helena, would no longer be allowed to run advertisements.[36] Simultaneously, the St Helena Independent and Saint FM announced that they would need to increase advertising rates, which barely covered the cost of producing adverts.
Culture and society
See also: Public holidays in Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da CunhaEducation
Education is free and compulsory between the ages of 5 and 16.[37] There are three first schools, three middle schools, and one secondary school for 11-18 year olds. The British examination system is followed. There is no tertiary education institution in Saint Helena.
Sport
Sports played on the island include association football, cricket, volleyball, tennis, golf, shooting sports and yachting. Saint Helena has sent teams to a number of Commonwealth Games. Saint Helena is a member of the International Island Games Association.[38] The Saint Helena cricket team is due to make its debut in international cricket in Division Three of the African region of the World Cricket League in 2011.
The Governor's Cup is a yacht race (and the first prize) between Cape Town and Saint Helena island, held every two years in December/January; the most recent event was in December 2010. In Jamestown a timed run takes place up Jacob's Ladder every year, with people coming from all over the world to take part.
Scouting
Main article: Scouting and Guiding on Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da CunhaThere are scouting and guiding groups on Saint Helena and Ascension Island. Scouting was established on Saint Helena island in 1912.[39] Lord and Lady Baden-Powell visited the Scouts on Saint Helena on the return from their 1937 tour of Africa. The visit is described in Lord Baden-Powell's book entitled African Adventures.[40]
See also
- Outline of Saint Helena
- Saint Helena National Trust
- Saint Helena Police Service
References
- ^ a b The St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009 "...the transfer of rule of the island to His Majesty’s Government on 22 April 1834 under the Government of India Act 1833, now called the Saint Helena Act 1833" (Schedule Preamble)
- ^ a b c [1]
- ^ The St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Constitution Order 2009, see "Explanatory note"
- ^ article: Tristan da Cunha (distance)
- ^ A.H. Schulenburg, 'The discovery of St Helena: the search continues'. Wirebird: The Journal of the Friends of St Helena, Issue 24 (Spring 2002), pp. 13–19.
- ^ Duarte Leite, História dos Descobrimentos, Vol. II (Lisbon: Edições Cosmos, 1960), 206.
- ^ de Montalbodo, Paesi Nuovamente Retovati & Nuovo Mondo da Alberico Vesputio Fiorentino Intitulato (Venice: 1507)
- ^ Drake and St Helena, privately published by Robin Castell in 2005
- ^ History: St. Helena homepage
- ^ Gazetteer - p. 7. MONUMENTS IN FRANCE - page 338
- ^ New research published on http://www.fosh.org.uk; shortened extract published in the St Helena Independent on the 3rd June 2011.
- ^ article: Tristan da Cunha
- ^ Natural History of Saint Helena
- ^ "Bird Watching". St Helena Tourism. http://www.sthelenatourism.com/pages/bird_watching.html. Retrieved 17 January 2011.
- ^ a b CIA World Factbook
- ^ a b About St Helena, St Helena News Media Services
- ^ BBC Weather Centre
- ^ St Helena Independent, 3 October 2008 page 2
- ^ GeoHive St Helena
- ^ Smallman, David L., Quincentenary, a Story of St Helena, 1502–2002; Jackson, E. L. St Helena: The Historic Island, Ward, Lock & Co, London, 1903
- ^ St Helena celebrates the restoration of full citizenship, Telegraph, 22 May 2002
- ^ Blair, David (25 May 2006). "St Helena 'risks importing Aids'". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/africaandindianocean/sainthelena/1519390/St-Helena-risks-importing-Aids.html. Retrieved 23 May 2010.
- ^ Watchtower.org
- ^ News.co.sh[dead link]
- ^ The Bank of Saint Helena
- ^ RMS St Helena Voyage Schedules
- ^ Saint Helena to get airstrip
- ^ BBC News Remote UK island colony of St Helena to get airport (3 November 2011)
- ^ News.co.sh
- ^ Dexter, G. (2009, October). A goal for the DX season: target ten for '10. Popular Communications, 28(2), 11-14.
- ^ Saint.fm
- ^ Saint.fm
- ^ World Telephone Numbering Guide Saint Helena and Tristan da Cunha
- ^ News.co.sh
- ^ Saint.fm
- ^ Governor Broadcast & St Helena Independent, both on 31 October 2008
- ^ "Territories and Non-Independent Countries". 2001 Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor. Bureau of International Labor Affairs, U.S. Department of Labor (2002). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Island Games St Helena profile
- ^ ScoutBaseUK A Scouting Timeline
- ^ "A Baden-Powell Bibliography". July 2007. http://www.scouting.milestones.btinternet.co.uk/bpbooks.htm. Retrieved 2009-07-07.
Further reading
- Gosse, Philip Saint Helena, 1502–1938 ISBN 0-904614-39-5
- Smallman, David L., Quincentenary, a Story of St Helena, 1502–2002 ISBN 1-87229-47-6
- Jackson, E. L. St Helena: The Historic Island, Ward, Lock & Co, London, 1903
- Cannan, Edward Churches of the South Atlantic Islands 1502–1991 ISBN 0-904614-48-4
- George, Barbara B. St Helena — the Chinese Connection (2002) ISBN 1-899489-22
- Cross, Tony St Helena including Ascension Island and Tristan Da Cunha ISBN 0-7153-8075-3
- Brooke, T. H., A History of the Island of St Helena from its Discovery by the Portuguese to the Year 1806”, Printed for Black, Parry and Kingsbury, London, 1808
- Hakluyt, The Principal Navigations Voyages Traffiques & Discoveries of the English Nation, from the Prosperous Voyage of M. Thomas Candish esquire into the South Sea, and so around about the circumference of the whole earth, begun in the yere 1586, and finished 1588, 1598–1600, Volume XI.
- Darwin, Charles, Geological Observations on the Volcanic Islands, Chapter 4, Smith, Elder & Co., London, 1844.
- Duncan, Francis, A Description of the Island Of St Helena Containing Observations on its Singular Structure and Formation and an Account of its Climate, Natural History, and Inhabitants, London, Printed For R Phillips, 6 Bridge Street, Blackfriars, 1805
- Janisch, Hudson Ralph, Extracts from the St Helena Records, Printed and Published at the “Guardian” Office by Benjamin Grant, St Helena, 1885
- Van Linschoten, Iohn Huighen, His Discours of Voyages into ye Easte & West Indies, Wolfe, London, 1598
- Melliss, John C. M., St Helena: A Physical, Historical and Topographical Description of the Island Including Geology, Fauna, Flora and Meteorology, L. Reeve & Co, London, 1875
- Schulenburg, A. H., St Helena Historiography, Philately, and the "Castella" Controversy”, South Atlantic Chronicle: The Journal of the St Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Philatelic Society, Vol.XXIII, No.3, pp. 3–6, 1999
- Bruce, I. T., Thomas Buce: St Helena Postmaster and Stamp Designer, Thirty years of St Helena, Ascension and Tristan Philately, pp 7–10, 2006, ISBN 1-890454-37-0
- Crallan, Hugh, Island of St Helena, Listing and Preservation of Buildings of Architectural and Historic Interest, 1974
- Kitching, G. C., A Handbook of St Helena Including a short History of the island Under the Crown
- Eriksen, Ronnie, St Helena Lifeline, Mallet & Bell Publications, Norfolk, 1994, ISBN 0-620-15055-6
- Denholm, Ken, South Atlantic Haven, a Maritime History for the Island of St Helena, published and printed by the Education Department of the Government of St Helena
- Evans, Dorothy, Schooling in the South Atlantic Islands 1661–1992, Anthony Nelson, 1994, ISBN 0-904614-51-4
- Hibbert, Edward, St Helena Postal History and Stamps”, Robson Lowe Limited, London, 1979
- Weider, Ben & Hapgood, David The Murder of Napoleon (1999) ISBN 1-58348-150-8
- Chaplin, Arnold, A St Helena's Who's Who or a Directory of the Island During the Captivity of Napoleon, published by the author in 1914. This has recently been republished under the title Napoleon’s Captivity on St Helena 1815–1821, Savannah Paperback Classics, 2002, ISBN 1-902366-12-3
- Holmes, Rachel: Scanty Particulars: The Scandalous Life and Astonishing Secret of James Barry, Queen Victoria's Most Eminent Military Doctor, Viking Press, 2002, ISBN 0-375-5055-6
- Shine, Ian, Serendipity in St Helena, a Genetical and medical Study of an isolated Community, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1970 ISBN 0-0801-2794-0
- Dampier, William, Piracy, Turtles & Flying Foxes, 2007, Penguin Books, 2007, pp 99–104, ISBN 0-1410-2541-4
- Clements, B.; "St Helena:South Atlantic Fortress"; Fort, (Fortress Study Group), 2007 (35), pp75–90
External links
- The Official Government Website of Saint Helena
- Friends of St Helena – supporting St Helena and providing information about the island since since 1988
- The Saint Helena Virtual Library and Archive
- Saint Helena Island Information website
- Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha entry at The World Factbook
- Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Helena
- Saint Helena travel guide from Wikitravel
- Saint Helena Travel Guide from Travellerspoint
- The Official Website for St Helena Tourism
- Saint Helena Herald
- Webcam showing Jamestown
- The first website on St Helena — since 1995
- The St Helena Institute – Dedicated to St Helena and Dependencies research since 1997
- BBC News: Life on one of the world's most remote islands
- St Helena Association (UK)
- Saint Helena at the Open Directory Project
- Main sites and dwellings of the island during Napoleon's captivity
 Saint Helena
Saint HelenaAscension Island  Tristan da Cunha
Tristan da CunhaJamestown (capital)
Half Tree Hollow
Saint Paul's
LongwoodGeorgetown (chief settlement)
Two Boats Village
RAF Ascension IslandArticles Related to Saint Helena British Overseas Territories and Crown dependencies Overseas territories Anguilla · Bermuda · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Gibraltar · Montserrat · Pitcairn Islands · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha1 · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands · Turks and Caicos Islands
Crown dependencies Sovereign base areas Outlying territories of European countries Territories under European sovereignty but closer to or on continents other than Europe (see inclusion criteria for further information)Denmark France Italy Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain United
KingdomAnguilla · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsBritish Empire and Commonwealth of Nations Legend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of NationsEurope18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1763–1782 Minorca
1798–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands20th century
1921-1937 Irish Free StateNorth America17th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
1607–1776 Virginia
since 1619 Bermuda
1620–1691 Plymouth Colony
1629–1691 Massachusetts Bay Colony
1632–1776 Maryland
1636–1776 Connecticut
1636–1776 Rhode Island
1637–1662 New Haven Colony
1663–1712 Carolina
1664–1776 New York
1665–1674 and 1702-1776 New Jersey
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
1674–1702 East Jersey
1674–1702 West Jersey
1680–1776 New Hampshire
1681–1776 Pennsylvania
1686–1689 Dominion of New England
1691–1776 Massachusetts18th century
1701–1776 Delaware
1712–1776 North Carolina
1712–1776 South Carolina
1713–1867 Nova Scotia
1733–1776 Georgia
1763–1873 Prince Edward Island
1763–1791 Quebec
1763–1783 East Florida
1763–1783 West Florida
1784–1867 New Brunswick
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
1818–1846 Columbia District / Oregon Country1
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1853–1863 Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands
1858–1866 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
1866–1871 Vancouver Island and British Columbia
1867–1931 *Dominion of Canada2
20th century
1907–1949 Dominion of Newfoundland31Occupied jointly with the United States
2In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. see Canada's name.
3Gave up self-rule in 1934, but remained a de jure Dominion until it joined Canada in 1949.Latin America and the Caribbean17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *Saint Kitts.2C 1623 to 1700|St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago
20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation4Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
Africa18th century
1792–1961 Sierra Leone
1795–1803 Cape Colony19th century
1806–1910 Cape Colony
1810–1968 Mauritius
1816–1965 Gambia
1856–1910 Natal
1868–1966 Basutoland (Lesotho)
1874–1957 Gold Coast (Ghana)
1882–1922 Egypt
1884–1966 Bechuanaland (Botswana)
1884–1960 British Somaliland
1887–1897 Zululand
1888–1894 Matabeleland
1890–1965 Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe) 5
1890–1962 Uganda
1890–1963 Zanzibar (Tanzania)
1891–1964 Nyasaland (Malawi)
1891–1907 British Central Africa Protectorate
1893–1968 Swaziland
1895–1920 East Africa Protectorate
1899–1956 Anglo-Egyptian Sudan20th century
1900–1914 Northern Nigeria
1900–1914 Southern Nigeria
1900–1910 Orange River Colony
1900–1910 Transvaal Colony
1906–1954 Nigeria Colony
1910–1931 South Africa
1911–1964 Northern Rhodesia (Zambia)
1914–1954 Nigeria Colony and Protectorate
1915–1931 South West Africa (Namibia)
1919–1960 Cameroons (Cameroon) 6
1920–1963 Kenya
1922–1961 Tanganyika (Tanzania) 6
1954–1960 Nigeria
1979–1980 Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe) 55Southern Rhodesia issued a Unilateral Declaration of Independence in 1965 (as Rhodesia) and returned to British control in 1979.
6League of Nations mandateAsia18th century
1702–1705 Côn Đảo
1757–1947 Bengal (West Bengal (India) and Bangladesh)
1762–1764 Manila
1795–1948 Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1796–1965 Maldives19th century
1812-1824 Banka (Sumatra)
1812-1824 Billiton (Sumatra)
1819–1826 British Malaya (Peninsular Malaysia and Singapore)
1826–1946 Straits Settlements
1839–1967 Colony of Aden
1839–1842 Afghanistan
1841–1997 Hong Kong
1841–1941 Kingdom of Sarawak (Malaysia)
1858–1947 British India (India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, Burma)
1879–1919 Afghanistan
1882–1963 British North Borneo (Malaysia)
1885–1946 Unfederated Malay States
1888–1984 Sultanate of Brunei
1888–1946 Sultanate of Sulu
1891–1971 Muscat and Oman protectorate
1892–1971 Trucial States protectorate
1895–1946 Federated Malay States
1898–1930 Weihai Garrison
1878–1960 Cyprus20th century
1918–1961 Kuwait protectorate
1920–1932 Iraq6
1921–1946 Transjordan6
1923–1948 Palestine6
1945–1946 South Vietnam
1946–1963 Sarawak (Malaysia)
1946–1963 Singapore
1946–1948 Malayan Union
1948–1957 Federation of Malaya (Malaysia)
since 1960 Akrotiri and Dhekelia (before as part of Cyprus)
since 1965 British Indian Ocean Territory (before as part of Mauritius and the Seychelles)Oceania18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land/Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands7
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony/Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1841–1907 Colony of New Zealand
1851–1901 Victoria
1874–1970 Fiji8
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands7
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)7
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands9
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands1020th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue7
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1942 Nauru
1945–1968 Nauru
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea117Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
8Suspended member
9Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
10Now the *Solomon Islands
11Now *Papua New GuineaAntarctica and South Atlantic17th century
since 1659 St. Helena1219th century
since 1815 Ascension Island12
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha12
since 1833 Falkland Islands1320th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory14
since 1908 South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands13, 1412Since 2009 part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Ascension Island (1922—) and Tristan da Cunha (1938—) were previously dependencies of St Helena
13Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982
14Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands)Portuguese Empire North Africa15th century
1415–1640 Ceuta
1458–1550 Alcácer Ceguer (El Qsar es Seghir)
1471–1550 Arzila (Asilah)
1471–1662 Tangier
1485–1550 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1487– middle 16th century Ouadane
1488–1541 Safim (Safi)
1489 Graciosa16th century
1505–1769 Santa Cruz do Cabo
de Gué (Agadir)
1506–1525 Mogador (Essaouira)
1506–1525 Aguz (Souira Guedima)
1506–1769 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1513–1541 Azamor (Azemmour)
1515 São João da Mamora (Mehdya)
1577–1589 Arzila (Asilah)Sub-Saharan Africa15th century
1455–1633 Arguin
1470–1975 Portuguese São Tomé1
1474–1778 Annobón
1478–1778 Fernando Poo (Bioko)
1482–1637 Elmina (São Jorge
da Mina)
1482–1642 Portuguese Gold Coast
1496–1550 Madagascar (part)
1498–1540 Mascarene Islands16th century
1500–1630 Malindi
1500–1975 Portuguese Príncipe1
1501–1975 Portuguese E. Africa
(Mozambique)
1502–1659 St. Helena
1503–1698 Zanzibar
1505–1512 Quíloa (Kilwa)
1506–1511 Socotra
1557–1578 Portuguese Accra
1575–1975 Portuguese W. Africa
(Angola)
1588–1974 Cacheu2
1593–1698 Mombassa (Mombasa)17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Cape Verde
1645–1888 Ziguinchor
1680–1961 São João Baptista de Ajudá
1687–1974 Portuguese Bissau2
18th century
1728–1729 Mombassa (Mombasa)
1753–1975 Portuguese São Tomé and Príncipe
19th century
1879–1974 Portuguese Guinea
1885–1975 Portuguese Congo1 Part of São Tomé and Príncipe from 1753. 2 Part of Portuguese Guinea from 1879. Southwest Asia16th century
1506–1615 Gamru (Bandar-Abbas)
1507–1643 Sohar
1515–1622 Hormuz (Ormus)
1515–1648 Quriyat
1515–? Qalhat
1515–1650 Muscat
1515?–? Barka
1515–1633? Julfar (Ras al-Khaimah)
1521–1602 Bahrain (Muharraq and Manama)
1521–1529? Qatif
1521?–1551? Tarut Island
1550–1551 Qatif
1588–1648 Matrah17th century
1620–? Khor Fakkan
1621?–? As Sib
1621–1622 Qeshm
1623–? Khasab
1623–? Libedia
1624–? Kalba
1624–? Madha
1624–1648 Dibba Al-Hisn
1624?–? Bandar-e KongIndian subcontinent15th century
1498–1545 Laccadive Islands
(Lakshadweep)16th century
Portuguese India
· 1500–1663 Cochim (Kochi)
· 1502–1661 Quilon (Coulão/Kollam)
· 1502–1663 Cannanore (Kannur)
· 1507–1657 Negapatam (Nagapatnam)
· 1510–1962 Goa
· 1512–1525 Calicut (Kozhikode)
· 1518–1619 Chaul
· 1523–1662 Mylapore
· 1528–1666 Chittagong
· 1531–1571 Chalium
· 1534–1601 Salsette Island
· 1534–1661 Bombay (Mumbai)
· 1535–1739 Baçaím (Vasai-Virar)
· 1536–1662 Cranganore (Kodungallur)
· 1540–1612 Surat
· 1548–1658 Tuticorin (Thoothukudi)16th century (continued)
Portuguese India (continued)
· 1559–1962 Daman and Diu
· 1568–1659 Mangalore
· 1579–1632 Hugli
· 1598–1610 Masulipatnam (Machilipatnam)
1518–1521 Maldives
1518–1658 Portuguese Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1558–1573 Maldives
17th century
Portuguese India
· 1687–1749 Mylapore
18th century
Portuguese India
· 1779–1954 Dadra and Nagar HaveliEast Asia and Oceania16th century
1511–1641 Portuguese Malacca
1512–1621 Ternate
· 1576–1605 Ambon
· 1578–1650 Tidore
1512–1665 Makassar
1553–1999 Portuguese Macau
1571–1639 Decima (Dejima, Nagasaki)17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Timor (East Timor)1
19th century
Portuguese Macau
· 1864–1999 Coloane
· 1849–1999 Portas do Cerco
· 1851–1999 Taipa
· 1890–1999 Ilha Verde
20th century
Portuguese Macau
· 1938–1941 Lapa and Montanha (Hengqin)1 1975 is the year of East Timor's Declaration of Independence and subsequent invasion by Indonesia. In 2002, East Timor's independence was recognized by Portugal & the world.
North America and the North Atlantic Ocean16th century
1500–1579? Terra Nova (Newfoundland)
1500–1579? Labrador
1516–1579? Nova ScotiaCentral and South America16th century
1500–1822 Brazil
1536–1620 Portuguese Barbados17th century
1680–1777 Nova Colônia do Sacramento
19th century
1808–1822 Cisplatina (Uruguay)English-speaking world Countries and territories where English is the national language or the native language of the majority.
Africa Saint HelenaAmericas Anguilla · Antigua and Barbuda · The Bahamas · Barbados · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Canada · Cayman Islands · Dominica · Falkland Islands · Grenada · Guyana · Jamaica · Montserrat · Saba · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands · Trinidad and Tobago · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States · United States Virgin IslandsEurope Oceania Countries and territories where English is an official language, but not the majority language.
Africa Americas Asia Europe Oceania American Samoa · Christmas Island · Cocos (Keeling) Islands · Cook Islands · Fiji · Guam · Kiribati · Marshall Islands · Micronesia · Nauru · Niue · Northern Mariana Islands · Palau · Papua New Guinea · Pitcairn Islands · Samoa · Solomon Islands · Tokelau · Tuvalu · VanuatuCategories:- Saint Helena
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Volcanoes of Saint Helena
- States and territories established in 1659
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.