- Martinique
-
Martinique — Overseas region of France — 
Flag
LogoCountry  France
FrancePrefecture Fort-de-France Departments 1 Government - President Josette Manin Area - Total 1,128 km2 (435.5 sq mi) Population (2007-01-01)[1] - Total 397,730 - Density 352.6/km2 (913.2/sq mi) Time zone ECT (UTC-04) GDP/ Nominal € 7.9 billion (2008)[2] GDP per capita € 19,607 (2008)[1] NUTS Region FR9 Website Prefecture, Region, Department Martinique (French pronunciation: [maʁtinik]) is an island in the eastern Caribbean Sea, with a land area of 1,128 km2 (436 sq mi). Like Guadeloupe, it is an overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. To the northwest lies Dominica, to the south St Lucia, and to the southeast Barbados. As with the other overseas departments, Martinique is one of the twenty-seven regions of France (being an overseas region) and an integral part of the Republic. The first European to encounter the island was Christopher Columbus in 1502.
As part of France, Martinique is part of the European Union, and its currency is the Euro. Its official language is French, although many of its inhabitants also speak Antillean Creole (Créole Martiniquais).
Contents
History
Main article: History of MartiniqueThe island was occupied first by Arawaks, then by Caribs. It was charted by Columbus in 1493, but Spain had little interest in the territory. It was claimed by France in 1635 and, despite several interludes of British occupation, once during the Seven Years' War and twice during the Napoleonic Wars, has remained a French possession. In 1946, the French National Assembly voted unanimously to transform the colony into an overseas department.
Politics
Main article: Politics of MartiniqueThe inhabitants of Martinique are French citizens with full political and legal rights. Martinique sends four deputies to the French National Assembly and two senators to the French Senate.
Subdivisions
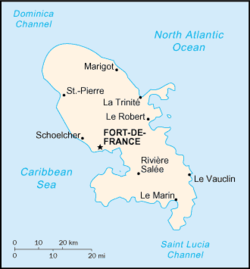
Main article: Arrondissements of the Martinique departmentFurther information: Communes of the Martinique department and Cantons of the Martinique departmentMartinique is divided into four arrondissements, 34 communes, and 45 cantons.
Geography
Main article: Geography of MartiniqueLocation: Caribbean, island in the Caribbean Sea, north of St. Lucia and south of Dominica
Geographic coordinates: 14°40′N 61°00′W / 14.667°N 61°W
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area:
total: 1,100 square kilometres (420 sq mi)
land: 1,060 square kilometres (410 sq mi)
water: 40 square kilometres (15 sq mi)Environment
The north of the island is mountainous and lushly forested. It features four ensembles of pitons (volcanoes) and mornes (mountains): the Piton Conil on the extreme North, which dominates the Dominica Channel; Mount Pelée, an active volcano; the Morne Jacob; and the Pitons du Carbet, an ensemble of five extinct volcanoes covered with rainforest and dominating the Bay of Fort de France at 1,196 metres (3,924 ft).
The highest of the island's many mountains, at 1,397 metres (4,583 ft), is the famous volcano Mount Pelée. Its volcanic ash has created gray and black sand beaches in the north (in particular between Anse Ceron and Anse des Gallets), contrasting markedly from the white sands of Les Salines in the south.
The south is more easily traversed, though it still features some impressive geographic features. Because it is easier to travel and because of the many beaches and food facilities throughout this region, the south receives the bulk of the tourist traffic. The beaches from Pointe de Bout, through Diamant (which features right off the coast of Roche de Diamant), St. Luce, the continent of St. Anne and down to Les Salines are popular.
Economy
Main article: Economy of MartiniqueThe economy of Martinique is based on trade. Agriculture accounts for about 6% of GDP and the small industrial sector for 11%. Sugar production has declined, with most of the sugarcane now used for the production of rum. Banana exports are increasing, going mostly to France. The bulk of meat, vegetable, and grain requirements must be imported, contributing to a chronic trade deficit that requires large annual transfers of aid from France. Tourism has become more important than agricultural exports as a source of foreign exchange. The majority of the work force is employed in the service sector and in administration.
Infrastructure
Main articles: Transportation in Martinique and Communications in MartiniqueMartinique Aimé Césaire International Airport serves the island.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of MartiniqueHistorical population 1700
estimate1738
estimate1848
estimate1869
estimate1873
estimate1878
estimate1883
estimate1888
estimate1893
estimate1900
estimate1954
census1961
census1967
census1974
census1982
census1990
census1999
census2006
census2007
estimate2008
estimate24,000 74,000 120,400 152,925 157,805 162,861 167,119 175,863 189,599 203,781 239,130 292,062 320,030 324,832 328,566 359,572 381,427 397,732 400,000 402,000 Official figures from past censuses and INSEE estimates. Culture
Main article: Culture of MartiniqueSee also: Music of Martinique and Music of Martinique and GuadeloupeAs an overseas département of France, Martinique's culture blends French and Caribbean influences. The city of Saint-Pierre (destroyed by a volcanic eruption of Mount Pelée), was often referred to as the "Paris of the Lesser Antilles". Following traditional French custom, many businesses close at midday to allow a lengthy lunch, then reopen later in the afternoon. The official language is French.
Many Martinicans speak Martiniquan Creole, a subdivision of Antillean Creole that is virtually identical to the varieties spoken in neighboring English-speaking islands of Saint Lucia and Dominica. Martiniquan Creole is based on French, Carib and African languages with elements of English, Spanish, and Portuguese. It continues to be used in oral storytelling traditions and other forms of speech and to a lesser extent in writing. Its use is predominant among friends and close family. Though it is normally not used in professional situations, members of the media and politicians have begun to use it more frequently as a way to redeem national identity and prevent cultural assimilation by mainland France. Indeed, unlike other varieties of French creole such as Mauritian Creole, Martinican Creole is not readily understood by speakers of Standard French due to significant differences in grammar, syntax, vocabulary and pronunciation, though over the years it has progressively adapted features of Standard French
Most of Martinique's population is descended from enslaved Africans brought to work on sugar plantations during the colonial era, generally mixed with some French, Amerindian (Carib people), Indian (Tamil), Lebanese or Chinese ancestry. Between 5 and 10% of the population is of Indian (Tamil) origin. The island also boasts a small Syro-Lebanese community, a small but increasing Chinese community, and the Béké community, descendants of European ethnic groups of the first French and British settlers, who still dominate parts of the agricultural and trade sectors of the economy. Whites represent 5% of the population.[3]
The Béké people (which totals around 5,000 people in the island, most of them of aristocratic origin by birth or after buying the title) generally live in mansions on the Atlantic coast of the island (mostly in the François - Cap Est district). In addition to the island population, the island hosts a metropolitan French community, most of which lives on the island on a temporary basis (generally from 3 to 5 years).
There are an estimated 260,000 people of Martiniquan origin living in mainland France, most of them in the Paris region.
Today, the island enjoys a higher standard of living than most other Caribbean countries. French products are easily available, from Chanel fashions to Limoges porcelain. Studying in the métropole (mainland France, especially Paris) is common for young adults. Martinique has been a vacation hotspot for many years, attracting both upper-class French and more budget-conscious travelers.
Martinique has a hybrid cuisine, mixing elements of African, French, Carib Amerindian and South Asian traditions. One of its most famous dishes is the Colombo (compare Tamil word kuzhambu for gravy or broth), a unique curry of chicken (curry chicken), meat or fish with vegetables, spiced with a distinctive masala of Tamil origins, sparked with tamarind, and often containing wine, coconut milk, cassava and rum. A strong tradition of Martiniquan desserts and cakes incorporate pineapple, rum, and a wide range of local ingredients.
In popular culture
- Martinique is the main setting of the 1944 film To Have and Have Not starring Humphrey Bogart and Lauren Bacall.
- The island is mentioned in the songs "Kokomo" by The Beach Boys, and "Uffington wassail" by Half Man Half Biscuit.
- In the gothic soap opera Dark Shadows, the characters of Angelique Bouchard Collins, Josette du Pres, and Josette's family are from Martinique.
- Martinique was featured in the 1999 remake of The Thomas Crown Affair, and in the movie Sugar Cane Alley.
- Setting of Caridad Bravo Adams' novel Corazón Salvaje.
- Much of the 1979 Italian thriller Concorde Affaire '79 took place on and around the island.
- The Bugs Bunny cartoon "8 Ball Bunny"' saw Bugs and a showbiz penguin called Playboy stranded on Martinique.
- "Martinique Blue" was a popular color used by automotive builder Pontiac, a division of General Motors, on 1978 Firebirds and Trans Ams. Also known as cowl tag color code 24.
- Martinique is one of the hotel areas at Disney's Caribbean Beach Resort a tropical island themed hotel in Walt Disney World.
- In Pirates of the Caribbean: On Stranger Tides, Angelica (Penélope Cruz) while talking to Captain Jack Sparrow (Johnny Depp), mentions that the last time he left her was at "La Martinique"
In literature
- Martinique is the main setting of Patrick Chamoiseau's novel Solibo Magnificent.
- Martinique is referenced frequently in Jean Rhys' novel Wide Sargasso Sea as the previous home of the protagonist's mother and caretaker.
- Aimé Césaire's seminal poem, "Notebook on Return to My Native Land," envisions the poet's imagined journey back to his homeland Martinique to find it in a state of colossal poverty and psychological inferiority due to the French colonial presence.
Miscellaneous topics
- Antillean Creole
- Créolité
- Aimé Césaire
- Patrick Chamoiseau
- Guy Deslaurier
- Frantz Fanon
- Édouard Glissant
- Holidays in Martinique
- Jimmy Philémond-Montout
- Négritude
- Ronny Turiaf
- Scouts et Guides de Martinique
See also
- Bibliography of Martinique
- Index of Martinique-related articles
- 2009 French Caribbean general strikes
- Caribbean Sea
- Colonial and Departmental Heads of Martinique
- Lesser Antilles
- List of Martinique-related topics
- Overseas departments and territories of France
References
- ^ a b (French) INSEE. "INSEE Martinique". http://www.insee.fr/fr/ppp/bases-de-donnees/recensement/populations-legales/departement.asp?dep=972&annee=2007.
- ^ (French) IEDOM. "L’Institut d’Émission des Départements d’Outre-mer, rapport 2009 Martinique". http://www.iedom.fr/IMG/pdf/ra2009_martinique.pdf.
- ^ Martinique: People: Ethnic Groups. World Factbook of CIA
External links
- Government
- Prefecture Région Martinique - Official site
- Regional Council of Martinique Official site
- General information
- Travel
- Martinique Tourism Authority - Official site
- Martinique travel guide from Wikitravel
- A glance at Martinique - Documentary by Ali Sattarpour
Martinique Politics History Battles and Invasions of Martinique Invasion of Martinique (1759) · Invasion of Martinique (1762) · Battle of Martinique (1779) · Battle of Martinique (1780) · Battle of Martinique (1794) · Invasion of Martinique (1809)Geography Economy Culture Index  Overseas departments and territories of France
Overseas departments and territories of FranceInhabited areas  Special status
Special statusUninhabited areas Pacific Ocean French Southern and
Antarctic LandsBanc du Geyser4 · Bassas da India4 · Europa Island4 · Glorioso Islands3, 4, 5 · Juan de Nova Island4 · Tromelin Island4, 51 Also known as overseas regions. 2 Claimed by Comoros. 3 Claimed by Madagascar. 4 Claimed by Seychelles. 5 Claimed by Mauritius. Outermost regions of European Union states Portugal 
Spain France French Guiana • Guadeloupe • Martinique • Réunion • Saint Barthélemy • Saint-Martin
Countries and territories of the Caribbean Sovereign states Other republicsDependencies and other areas by parent state United KingdomNetherlandsAruba · Bonaire · Curaçao · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint MaartenFranceGuadeloupe · Martinique · St. Barthélemy · St. MartinUnited StatesCountries and dependencies of North America Sovereign states - Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Canada
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- France
- (Guadeloupe
- Martinique)
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Netherlands
- (Bonaire
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius)
- Panama
- St. Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
Dependencies DenmarkFranceNetherlandsUnited KingdomUnited States Regions of France - Alsace
- Aquitaine
- Auvergne
- Burgundy
- Brittany
- Centre
- Champagne-Ardenne
- Corsica
- Franche-Comté
- Île-de-France
- Languedoc-Roussillon
- Limousin
- Lorraine
- Midi-Pyrénées
- Nord-Pas-de-Calais
- Lower Normandy
- Upper Normandy
- Pays de la Loire
- Picardy
- Poitou-Charentes
- Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
- Rhône-Alpes
- Overseas regions:
- French Guiana
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Mayotte
- Réunion
Departments of France 01 Ain · 02 Aisne · 03 Allier · 04 Alpes-de-Haute-Provence · 05 Hautes-Alpes · 06 Alpes-Maritimes · 07 Ardèche · 08 Ardennes · 09 Ariège · 10 Aube · 11 Aude · 12 Aveyron · 13 Bouches-du-Rhône · 14 Calvados · 15 Cantal · 16 Charente · 17 Charente-Maritime · 18 Cher · 19 Corrèze · 2A Corse-du-Sud · 2B Haute-Corse · 21 Côte-d'Or · 22 Côtes-d'Armor · 23 Creuse · 24 Dordogne · 25 Doubs · 26 Drôme · 27 Eure · 28 Eure-et-Loir · 29 Finistère · 30 Gard · 31 Haute-Garonne · 32 Gers · 33 Gironde · 34 Hérault · 35 Ille-et-Vilaine · 36 Indre · 37 Indre-et-Loire · 38 Isère · 39 Jura · 40 Landes · 41 Loir-et-Cher · 42 Loire · 43 Haute-Loire · 44 Loire-Atlantique · 45 Loiret · 46 Lot · 47 Lot-et-Garonne · 48 Lozère · 49 Maine-et-Loire · 50 Manche · 51 Marne · 52 Haute-Marne · 53 Mayenne · 54 Meurthe-et-Moselle · 55 Meuse · 56 Morbihan · 57 Moselle · 58 Nièvre · 59 Nord · 60 Oise · 61 Orne · 62 Pas-de-Calais · 63 Puy-de-Dôme · 64 Pyrénées-Atlantiques · 65 Hautes-Pyrénées · 66 Pyrénées-Orientales · 67 Bas-Rhin · 68 Haut-Rhin · 69 Rhône · 70 Haute-Saône · 71 Saône-et-Loire · 72 Sarthe · 73 Savoie · 74 Haute-Savoie · 75 Paris · 76 Seine-Maritime · 77 Seine-et-Marne · 78 Yvelines · 79 Deux-Sèvres · 80 Somme · 81 Tarn · 82 Tarn-et-Garonne · 83 Var · 84 Vaucluse · 85 Vendée · 86 Vienne · 87 Haute-Vienne · 88 Vosges · 89 Yonne · 90 Territoire de Belfort · 91 Essonne · 92 Hauts-de-Seine · 93 Seine-Saint-Denis · 94 Val-de-Marne · 95 Val-d'Oise
Overseas departments: 971 Guadeloupe · 972 Martinique · 973 French Guiana · 974 Réunion · 976 MayotteOutlying territories of European countries Territories under European sovereignty but closer to or on continents other than Europe (see inclusion criteria for further information) Denmark France Clipperton Island · French Guiana · French Polynesia · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Mayotte · New Caledonia · Réunion · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Wallis and FutunaItaly Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain United
KingdomAnguilla · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsCoordinates: 14°40′N 61°00′W / 14.667°N 61°W
Leadership & Men 
Expeditionary Raids Battles Action off Galveston Light · Battle of CherbourgList of ships of the Confederate States Navy Categories:- Departments of France
- Martinique
- Caribbean countries
- Lesser Antilles
- Outermost regions of the European Union
- Overseas departments of France
- Regions of France
- French-speaking countries
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.