- Melilla
-
Melilla — Autonomous City — Autonomous City of Melilla
Ciudad Autónoma de Melilla (Spanish)Port of Melilla 
Flag
Coat of armsLocation of Melilla within Spain Coordinates: 35°18′N 2°57′W / 35.3°N 2.95°WCoordinates: 35°18′N 2°57′W / 35.3°N 2.95°W Country Spain Capital Melilla Government - Mayor-President Juan José Imbroda Ortíz (PP) Area(0.00244% of Spain) - Total 12.3 km2 (4.7 sq mi) Area rank 19th Population (2009) - Total 73,460 - Rank 19th - Density 5,972.4/km2 (15,468.3/sq mi) - Percent 0.16% of Spain Demonym melillan ISO 3166-2 ES-ML Official languages Spanish Statute of Autonomy March 14, 1995 Parliament Cortes Generales Congress 1 deputy (of 350) Senate 2 senators (of 264) Website www.melilla.es Melilla (Spanish pronunciation: [meˈliʎa]) is a 12.3 square kilometres (4.7 sq mi) autonomous city of Spain and an exclave on the north coast of Morocco. Melilla, along with the Spanish exclave Ceuta, is one of the two Spanish territories located in mainland Africa. It was regarded as a part of Málaga province prior to 14 March 1995, when the city's Statute of Autonomy was passed.
Melilla (like Ceuta) was a free port before Spain joined the European Union. As of 2008 it has a population of 73,460. Its population consists of Christians, Muslims (chiefly Riffians), and small minorities of Jews. Both Spanish and Tarifit are widely spoken. Spanish is the only official language, while there have been calls to recognise Tamazight, a standarized version of all Berber languages official in Morocco, as well.[1]
Morocco had previously called for negotiations on the future of Melilla, Ceuta and a number of Mediterranean islands which border it. The majority of the city's population are ethnic Spanish who are opposed to the idea of being ruled by Morocco.[2] A poll conducted by Instituto Opina found that 87.9% of people from mainland Spain consider the two cities to be Spanish.[3]
Contents
History
Melilla was a Phoenician and later Punic establishment under the name of Rusadir. Later it became a part of the Roman province of Mauretania Tingitana. As centuries passed, it went through Vandal, Byzantine and Hispano-Visigothic hands. The political history is similar to that of towns in the region of the Moroccan Rif and southern Spain. Local rule passed through Amazigh, Phoenician, Punic, Roman, Ummayyad, Idrisid, Almoravid, Almohad, Marinid, and then Wattasid rulers. Melilla was part of the Kingdom of Fez when the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon requested Juan Alonso Pérez de Guzmán, 3rd Duke of Medina Sidonia, to take the city.
In the Conquest of Melilla, the duke sent Pedro Estopiñán conquered the city virtually without a fight in 1497,[4] a few years after (1492) Castile had taken control of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada, the last remnant of Al-Andalus. Melilla was immediately threatened with reconquest and was besieged 1694–1696 and 1774–1775. One Spanish officer reflected, "an hour in Melilla, from the point of view of merit, was worth more than thirty years of service to Spain."[5] The Spaniards also experienced much trouble with the neighbouring Rif tribes under Abdelkrim al-Khattabi in the early 1920s.
The current limits of the Spanish territory around the fortress were fixed by treaties with Morocco in 1859, 1860, 1861, and 1894. In the late 19th century, as Spanish influence expanded, Melilla became the only authorised centre of trade on the Rif coast between Tetuan and the Algerian frontier. The value of trade increased, goat skins, eggs and beeswax being the principal exports, and cotton goods, tea, sugar, and candles being the chief imports.
In 1893, the Rif Berbers besieged Melilla, and 25,000 men had to be dispatched against them.
In 1908 two companies, under the protection of El Roghi, a chieftain then ruling the Rif region, started mining lead and iron some 20 kilometres from Melilla. A railway to the mines was begun. In October of that year the Roghi's vassals revolted against him and raided the mines, which remained closed until June 1909. By July the workmen were again attacked and several of them killed. Severe fighting between the Spaniards and the tribesmen followed.
In 1910, the Rif having submitted, the Spaniards restarted the mines and undertook harbour works at Mar Chica, but hostilities broke out again in 1911. In 1921 the Berbers under the leadership of Abd el Krim inflicted a grave defeat on the Spanish (see Battle of Annual), and were not pacified until 1926, when the Spanish Protectorate finally managed to control the area again.
General Francisco Franco used the city as one of his staging grounds for his rebellion in 1936, and a statue of him - the last statue of Franco in Spain - is still prominently featured.
On 6 November 2007, King Juan Carlos I and Queen Sofia visited the city, which caused a massive demonstration of support. The visit also sparked protests from the Moroccan government.[6] It was the first time a Spanish monarch had visited Melilla in 80 years.
Melilla (and Ceuta) have declared the Muslim holiday of Eid al-Adha or Feast of the Sacrifice, as an official public holiday from 2010 onwards. It is the first time a non-Christian religious festival is officially celebrated in Spain since the Reconquista.[7][8]
Geography
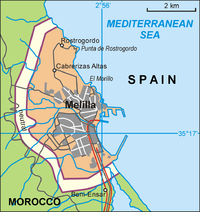
It is located in the northwest of African continent, next to Alboran Sea and off the coast of Granada and Almería. The city layout is arranged in a wide semicircle around the beach and the Port of Melilla, on the eastern side of the peninsula of Cape Tres Forcas, at the foot of Mount Gurugú and the mouth of the Río de Oro, 1 metre above sea level. The urban nucleus was originally a fortress built on a peninsular mound about 30 m in height.
Political status
Melilla and Ceuta are the only two European-Union territories located in mainland Africa.
The government of Morocco has repeatedly requested from Spain the sovereignty of Ceuta and Melilla, of Perejil Island, and of some other small areas lacking permanent population. The Spanish position is that both Ceuta and Melilla are integral parts of the Spanish state, and have been since the 15th century, centuries before Morocco's independence from France in 1956. Morocco denies these claims and maintains that the Spanish presence on or near its coast is a remnant of the colonial past which should be ended. The United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories does not include these Spanish territories.
Subdivisions
Melilla is subdivided into eight neighbourhoods (barrios):[9]
- Barrio de Medina Sidonia
- Barrio del Real
- Barrio de la Victoria
- Barrio de los Héroes de España
- Barrio del General Gómez Jordana
- Barrio del Príncipe de Asturias
- Barrio del Carmen
- Barrio de La Paz
Climate
Climate data for Melilla Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 16
(61)16
(61)17
(63)20
(68)25
(77)27
(81)29
(84)29
(84)25
(77)23
(73)20
(68)17
(63)23 Daily mean °C (°F) 13
(55)13
(55)15
(59)16
(61)18
(64)22
(72)24
(75)25
(77)23
(73)20
(68)17
(63)15
(59)18 Average low °C (°F) 10
(50)11
(52)12
(54)13
(55)15
(59)18
(64)21
(70)22
(72)21
(70)17
(63)13
(55)11
(52)15 Avg. precipitation days 8 9 9 7 6 3 1 2 3 7 7 8 70 Source: Weatherbase[10] Economy
The principal industry is fishing. Cross-border commerce (legal or smuggled) and Spanish and European grants and wages are the other income sources.
Melilla is regularly connected to the Peninsula by air - and sea traffic and also economically connected to Morocco: most of its fruits and vegetables are imported across the border. Also, Moroccans in the city's influence area are attracted to it: 36,000 Moroccans cross the border daily to work, shop, or trade goods.[citation needed]
City culture and society
Melilla's Capilla de Santiago or James's Chapel, by the city walls, is the only genuine Gothic architecture in Africa.
In the first quarter of the 20th century, Melilla became a thriving port benefitting from the recently established Protectorate of Spanish Morocco in the contiguous Rif. The new architectural style of Modernisme was expressed by a new bourgeois class. This style, frequently referred to as the Catalan version of Art Nouveau, was extremely popular in the early part of the 20th century in Spain.
The workshops inspired by the Catalan architect, Enrique Nieto, continued in the modernist style, even after Modernisme went out of fashion elsewhere. Accordingly, Melilla has the second most important concentration of Modernist works in Spain after Barcelona.
Melilla has been praised as an example of multiculturalism, being a small city in which one can find up to three major religions represented. However, the Christian majority of the past, constituting around 65% of the population at one point, has been shrinking, while the number of Muslims has steadily increased to its present 45% of the population due to immigration from Muslim countries.[citation needed]
Jews, who had lived in Melilla for centuries, have been leaving the Spanish North African city in more recent years (from 20% of the population before World War II to less than 5% today). Most of the Jewish population has left to Israel and Venezuela. There is a small, autonomous, and commercially important Hindu community present in Melilla, as well. The culture in this little city is thus virtually divided into two halves;[citation needed] one being European and the other Amazigh. While the first is represented all over the rest of the country, the second, being represented only in this little part of Spain, is considered by some, especially in the mainland, to be foreign.
The amateur radio call sign used for both cities is EA9.[11]
Immigration
There is considerable pressure by African refugees to enter Melilla, a part of the European Union. The border is secured by the Melilla border fence, a six-metre-tall double fence with watch towers, yet refugees frequently manage to cross it illegally, avoiding the attempts by Spanish police to take them back to their home countries. Detection wires, tear gas dispensers, radar, and day/night vision cameras are planned to increase security and prevent illegal immigration. In October 2005, over 700 sub-Saharan migrants tried to enter Spanish territory from the Moroccan border.[citation needed]
Transportation
Melilla is connected to the Spanish cities of Málaga, Madrid, Granada and Almería by air as well as to Málaga and Almería by ferry. Air Nostrum flies from Melilla Airport to Almeria, Granada, Valencia and Madrid. Ándalus Líneas Aéreas will fly from Melilla to Palma de Mallorca, Barcelona, Málaga and Girona. It is possible to travel from Melilla to Morocco on foot, however an ONCF train from nearby Beni Ansar is probably the most convenient method of travel.
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Melilla is twinned with:
See also
- Plazas de soberanía - Spanish exclaves on the Moroccan coast
- List of Mayor-Presidents of Melilla
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Málaga
- Melilla (Spanish Congress Electoral District)
- Ceuta
- UD Melilla
- List of Spanish Colonial Wars in Morocco
- Spanish Morocco
References
- ^ http://www.lukor.com/not-esp/locales/0412/03150841.htm
- ^ http://www.economist.com/node/999729
- ^ http://www.angus-reid.com/polls/29196/spaniards_review_ceuta_and_melilla_situation/
- ^ http://www.ayuntamiento.es/comunidades_melilla.php
- ^ Rezette, p. 41
- ^ Mohamed VI "condena" y "denuncia" la visita "lamentable" de los Reyes de España a Ceuta y Melilla · ELPAÍS.com
- ^ Muslim Holiday in Ceuta and Melilla
- ^ Public Holidays and Bank Holidays for Spain
- ^ http://www.melilla.es/mandar.php/15108/4268_383.pdf
- ^ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Melilla". http://www.weatherbase.com/weather/weatherall.php3?s=83306&refer=&units=metric.
- ^ http://www.ac6v.com/prefixes.htm#E
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.External links
- (Spanish) Official pages
- Official Tourism
- (Spanish) Melilla en Internet Journal
- (Spanish) Monuments of Melilla Official
- Spain's North African enclaves
- A Childhood Lost in the Cracks of Europe's Border
- Melilla in Google Maps
- Map of Melilla
- Melilla photo gallery
- (Spanish) Easter of Melilla
Phoenician cities and colonies Algeria: Hippo Regius · Ikosium · Guelma · Iol · Rus Icada · Rus Azuz · Iom · Honaine · Pomoria · Cirta · Rus Ucurru · Rus Aghoun · Rus Ipir · Qart Ina · Siga · Timgad · Lambese · Djémila · Uzinaza · Cuicul · Altava · Igligili · Imonium · Sitifis · Auzia · Rapidum · Portus Magnus · Tipaza · Cyprus: Kition · Italy: Karalis · Lilybaeum · Motya · Nora · Olbia · Panormus · Solki · Soluntum · Tharros · Lebanon: Amia · Ampi · Arqa · Baalbek · Berut · Botrys · Gebal · Sarepta · Sur · Sydon · Tripolis · Libya: Leptis Magna · Oea · Sabratha · Malta: Gozo · Mauritania: Cerne · Morocco: Arambys · Caricus Murus · Lixus · Tingis · Portugal: Olissipona · Ossonoba · Spain: Abdera · Abyla · Akra Leuke · Gadir · Herna · Ibossim · Mahón · Malaca · Onoba · Qart Hadašt · Rusadir · Sexi · Syria: Amrit · Arwad · Safita · Ugarit · Tunisia: Carthage · Hadrumetum · Hippo Diarrhytos · Kerkouane · Leptis Parva · Thanae · Thapsus · Utica · Turkey: Myriandrus · Phoenicus · Gibraltar
Autonomies of Spain Autonomous communities 
Autonomous cities - Ceuta
- Melilla
Plazas de soberanía Seville (Andalusia) · Zaragoza (Aragon) · Oviedo (Principality of Asturias) · Palma (Balearic Islands) · Vitoria-Gasteiz (Basque Country) · Santa Cruz de Tenerife & Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (Canary Islands) ·
Santander (Cantabria) · No capital (Castile and León) · Toledo (Castile-La Mancha) · Barcelona (Catalonia) · Mérida (Extremadura) · Santiago de Compostela (Galicia) · Logroño (La Rioja) · Madrid (Community of Madrid) ·
Murcia (Region of Murcia) · Pamplona (Navarre) · Valencia (Valencian Community) · Ceuta1 · Melilla11 Autonomous cities.Outlying territories of European countries Territories under European sovereignty but closer to or on continents other than Europe (see inclusion criteria for further information)Denmark France Italy Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain Canary Islands · Ceuta · Melilla · Plazas de soberanía (Islas Chafarinas • Peñón de Alhucemas • Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera)United
KingdomAnguilla · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsCategories:- Melilla
- Autonomous cities of Spain
- Exclaves
- Port cities in Africa
- Mediterranean port cities and towns in Spain
- NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
- Special territories of the European Union
- Morocco–Spain border crossings
- Territorial disputes of Spain
- States and territories established in 1995
- Territorial disputes of Morocco
- Nador
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.