- Pitcairn Islands
-
Pitcairn, Henderson,
Ducie and Oeno IslandsPitkern Ailen

Flag Coat of arms Anthem: "Come ye Blessed"
"God Save the Queen"Capital
(and largest city)Adamstown Official language(s) English (local dialect is Pitkern) Ethnic groups British, Polynesian, or (mixed) Government British Overseas Territory - Sovereign Elizabeth II - Governor/
High CommissionerVictoria Treadell - Mayor Mike Warren Area - Total 47 km2
18.1 sq miPopulation - 2011 estimate 60 (238th (last)) - Density 13/km2 (211th)
34/sq miCurrency New Zealand dollar (alongside the Pitcairn Islands dollar as collectibles) ( NZD)Time zone UTC−08 Internet TLD .pn Calling code none The Pitcairn Islands (
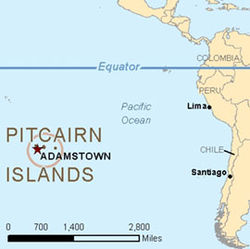
 /ˈpɪtkɛərn/;[1] Pitkern: Pitkern Ailen), officially named the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, form a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean. The islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the Pacific.[2] The four islands – named Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie, and Oeno – are spread over several hundred miles of ocean and have a total land area of about 18 square miles (47 km2). Only Pitcairn, the second largest and measuring about 2 miles (3.2 km) across, is inhabited.
/ˈpɪtkɛərn/;[1] Pitkern: Pitkern Ailen), officially named the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, form a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean. The islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the Pacific.[2] The four islands – named Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie, and Oeno – are spread over several hundred miles of ocean and have a total land area of about 18 square miles (47 km2). Only Pitcairn, the second largest and measuring about 2 miles (3.2 km) across, is inhabited.The islands are best known as home of the descendants of the Bounty mutineers and the Tahitians (or Polynesians) who accompanied them, an event retold in numerous books and films. This history is still apparent in the surnames of many of the islanders. With only about 48 inhabitants[3] (from four families as of 2010: Christian, Warren, Young, and Brown), Pitcairn is the least populous jurisdiction in the world (although it is not a sovereign nation). The United Nations Committee on Decolonisation includes the Pitcairn Islands on the United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories.[4]
Contents
History
The original settlers of the Pitcairn Islands were Polynesians who appear to have lived on Pitcairn and Henderson for several centuries. Although archaeologists believe that Polynesians were living on Pitcairn as late as the 15th century, the islands were uninhabited when they were discovered by Europeans.[5]
Ducie and Henderson Islands were discovered by Portuguese sailor Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, who arrived on 26 January 1606. He named them La Encarnación ("The Incarnation") and San Juan Bautista ("Saint John the Baptist"), respectively. However, some sources express doubt about exactly which of the islands were visited and named by Queirós, suggesting that Queirós’ La Encarnación may actually have been Henderson Island, and San Juan Bautista may have been Pitcairn Island.[6]
Pitcairn Island was sighted on 3 July 1767 by the crew of the British sloop HMS Swallow, commanded by Captain Philip Carteret. It was named after Midshipman Robert Pitcairn, a fifteen-year-old crew member who was the first to sight the island. Robert Pitcairn was the son of British Marine Officer John Pitcairn.
Carteret, who sailed without the newly invented accurate marine chronometer, charted the island at 25° 2’ south and 133° 21’ west of Greenwich, but although the latitude was reasonably accurate the longitude was incorrect by about 3°. This made Pitcairn difficult to find, as highlighted by the failure of Captain James Cook to locate the island in July 1773.[7][8]
Habitation
In 1790, nine of the mutineers from the Bounty and Tahitian companions (six men, 11 women and a baby), some of whom may have been kidnapped from Tahiti, settled on Pitcairn Island and set fire to the Bounty. The wreck is still visible underwater in Bounty Bay. The ship itself was discovered in 1957 by National Geographic explorer Luis Marden. Although the settlers were able to survive by farming and fishing, the initial period of settlement was marked by serious tensions among the settlers. Alcoholism, murder, disease and other ills took the lives of most mutineers and Tahitian men. John Adams and Ned Young turned to the scriptures using the ship's Bible as their guide for a new and peaceful society. Young eventually died of an asthmatic infection. The Pitcairners also converted to Christianity; later they converted from their existing form of Christianity to Seventh-day Adventism after a successful Adventist mission in the 1890s. After the rediscovery of Pitcairn, John Adams was granted amnesty for his mutiny.
The Pitcairn islanders reported that it was not until 27 December 1795 that the first ship since the Bounty was seen from the island, but as it did not approach the land, they could not make out to what nation it belonged. A second appeared some time in 1801, but did not attempt to communicate with them. A third came sufficiently near to see their habitations, but did not venture to send a boat on shore. The American trading ship Topaz under the command of Mayhew Folger was the first to visit the island and communicate with them when they spent 10 hours at Pitcairn in February 1808. A report of Folger's find was forwarded to the Admiralty mentioning the mutineers and a more precise location of the island—25° 2’ S latitude, 130° W longitude[9]—however, this rediscovery was not known to Sir Thomas Staines, who commanded a Royal Navy flotilla of two ships (HMS Briton and HMS Tagus) which found the island at 25° .4’ S (by meridian observation) on 17 September 1814. Staines sent a party ashore and wrote a detailed report for the Admiralty.[10][11][12]
Ducie Island was rediscovered in 1791 by the British Captain Edwards aboard HMS Pandora, while searching for the Bounty mutineers. He named it after Francis Reynolds-Moreton, 3rd Baron Ducie, a captain in the Royal Navy. Henderson Island was rediscovered on 17 January 1819 by a British Captain James Henderson of the British East India Company ship Hercules. On 2 March 1819, Captain Henry King, sailing aboard the Elizabeth, landed on the island to find the king's colours already flying. His crew scratched the name of their ship into a tree, and for some years the island's name was Elizabeth or Henderson. Oeno Island was discovered on 26 January 1824 by U.S. Captain George Worth aboard the whaler Oeno.
British colony
Pitcairn Island became a British colony in 1838 and was among the first territories to extend voting rights to women. By the mid-1850s the Pitcairn community was outgrowing the island and its leaders appealed to the British government for assistance. They were offered Norfolk Island and on 3 May 1856, the entire community of 193 people set sail for Norfolk on board the Morayshire, arriving on 8 June after a miserable five-week trip. But after eighteen months on Norfolk, seventeen of the Pitcairners returned to their home island; five years later another twenty-seven did the same.
In 1902 Henderson, Oeno and Ducie islands were annexed by Britain, Henderson on 1 July, Oeno on 10 July and Ducie on 19 December.[13] In 1938 the three islands along with Pitcairn were formally incorporated into a single administrative unit called the "Pitcairn Group of Islands".
Since a population peak of 233 in 1937, the island has been suffering from emigration, primarily to New Zealand, leaving some fifty people living on Pitcairn (December 2009: 45 islanders on Electoral Roll)
In 2004 charges were laid against seven men living on Pitcairn and six living abroad after extensive trials, the men were convicted, some with multiple counts of having sexual relations with children.(Marks)[citation needed] On 25 October 2004, six men were convicted, including Steve Christian, the island's mayor at the time. After the six men lost their final appeal, the British government set up a prison on the island at Bob's Valley (Pitkern: Walley). The men began serving their sentences in late 2006. By 2010 all had served their sentences or been granted home detention status (Pitcairn News, 2010)[citation needed].
In 2010 the island received a new and updated constitution.[14]
Politics
Politics of the Pitcairn Islands takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic dependency, whereby the Mayor is the head of government. The territory's constitution is the Local Government Ordinance of 1964. In terms of population, the Pitcairn Islands is the smallest democracy in the world.
The government's administrative offices are in Auckland, New Zealand.[15]
Military
The Pitcairn Islands are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom, meaning defence is the responsibility of the Ministry of Defence and Her Majesty's Armed Forces.[citation needed]
Geography
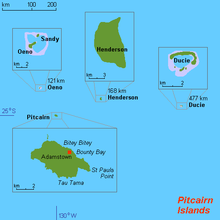
The Pitcairn Islands form the southeasternmost extension of the geological archipelago of the Tuamotus of French Polynesia, and consist of four islands: Pitcairn Island, Oeno Island (atoll with five islets, one of which is Sandy Island), Henderson Island and Ducie Island (atoll with four islets).
The only permanently inhabited island, Pitcairn, is accessible only by boat through Bounty Bay.
Henderson Island, covering about 86% of the territory's total land area and supporting a rich variety of animals in its nearly inaccessible interior, is also capable of supporting a small human population, but access is difficult, owing to its outer shores' being steep limestone cliffs covered by sharp coral.
The Pitcairn Islands were formed by a centre of upwelling magma called the Pitcairn hotspot.
The other islands are at a distance of more than 100 km (62 mi) and are not habitable.
Island or atoll Type Land area
(km²)Total area
(km²)Pop.
July 2008Coordinates Ducie Island Atoll 0.7 3.9* – 24°40′09″S 124°47′11″W / 24.66917°S 124.78639°W Henderson Island Uplifted coral island 37.3 37.3 – 24°22′01″S 128°18′57″W / 24.36694°S 128.31583°W Oeno Island Atoll 0.65 16.65* – 23°55′26″S 130°44′03″W / 23.92389°S 130.73417°W Pitcairn Island Volcanic island 4.6 4.6 50 25°04′00″S 130°06′00″W / 25.0666667°S 130.1°W Pitcairn Islands
(all islands)– 43.25 62.45 50 23°55′26″ to 25°04′00″S,
124°47′11″ to 130°44′03″W* Includes reef flat and lagoon of the atolls.
Flora and fauna
About nine plant species are thought to occur only on Pitcairn. These include tapau, formerly an important timber resource, and the giant nehe fern (Angiopteris chauliodonta). Some, such as red berry (Coprosma rapensis var. Benefica), are perilously close to extinction. The Pitcairn Islands are one of two places (the other being Mangareva) in the world in which the plant species Glochidion pitcairnense occurs.[16]
In terms of fauna, an interesting and rare introduction is the Galapagos giant tortoise (Testudo elephantopus). The sole surviving tortoise, Ms T (also known as Turpen), was one of five, which arrived on Pitcairn between 1937 and 1951, brought to the island by Irving Johnson, skipper of the 96-foot (29 m) Brigantine Yankee. Turpen usually resides at Tedside by Western Harbour. A protection order makes it an offence should anyone kill, injure, capture, maim or cause harm or distress to the tortoise.[17]
The birds of Pitcairn fall into several groups. These include seabirds, wading birds and a small number of resident land bird species. Of 20 breeding species, Henderson Island has 16, including the unique flightless Henderson Crake (Porzana atra); Oeno 12; Ducie 13 and Pitcairn six. Of the birds breeding on Pitcairn the best known are the Fairy Tern (Gygis alba), the Common Noddy (Anous stolidus) and the Red-tailed Tropic Bird (Phaethon rubricauda). The Pitcairn Island Warbler (Acrocephalus vaughani), known by Pitcairners as a "Sparrow", is a native species, dark-brown above and yellowish to buff below. It used to be common throughout the island but was placed on the endangered status list in 2008.
Economy
The fertile soil of the Pitcairn valleys, such as Isaac's Valley on the gentle slopes south-east of Adamstown, produces a wide variety of fruits: including bananas (Pitkern: plun), papaya (paw paws), pineapples, mangoes, watermelons, rockmelons, passionfruit, breadfruit, coconuts, avocadoes, and citrus (including oranges, mandarins, grapefruit, lemons and limes); and vegetables include: sweet potatoes (kumura), carrots, sweet corn, tomatoes, taro, yams, peas, and beans. Arrowroot (Tacca leontopetaloides) and sugarcane are grown and harvested to produce arrowroot flour and molasses. Pitcairn Island is remarkably productive and its benign climate allows a wide range of tropical and temperate crops to be grown.[18]
Fish are plentiful in the seas around Pitcairn. Spiny lobster and a large variety of fish are caught for meals and for trading aboard passing ships. Almost every day someone will go fishing, whether it is from the rocks, from a longboat or diving with a spear gun. There are numerous types of fish around the island. Fish such as Nanwee, White Fish, Moi and Opapa are caught in shallow water, while Snapper, Big Eye and Cod are caught in deep water and Yellow Tail and Wahoo are caught by trolling. A range of minerals have been discovered within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), which extends 370 km offshore and comprises 880,000 km2, including manganese, iron, copper, gold, silver and zinc.[19]
Souvenirs
The Pitcairners are involved in creating crafts and curios (made out of wood from Henderson). Typical wood carvings include sharks, fish, whales, dolphins, turtles, vases, birds, walking sticks, book boxes and the famous models of the Bounty. Miro (Thespesia populnea), a dark, durable and beautifully grained wood, is preferred for carving. Islanders also produce exquisite tapa cloth and painted hattie leaves.[20]
Coins and stamps
The major sources of revenue, until recently, have been the sale of coins and postage stamps to collectors, .pn domain names, and the sale of handicrafts to passing ships, most of which are plying the United Kingdom to New Zealand route via the Panama Canal.[21] Trade is restricted by the jagged geography of the island, which lacks a harbour or airstrip, forcing all trade to be made by longboat to visiting ships. Occasionally, passengers from expedition-type cruise ships will come ashore for a day, weather permitting.[22] Tourism is the main focus for building the future economy focusing on small groups coming by charter vessel and staying at "home stays". Providing accommodation is a growing source of revenue and some have invested in building separate self contained units adjacent to their homes.
Honey production
In 1998, the UK Government aid agency, the Department for International Development, funded an apiculture programme for Pitcairn which included training for Pitcairn's beekeepers and a detailed analysis of Pitcairn's bees and honey with particular regard to the presence or not of disease. Pitcairn, it was discovered, has one of the best examples of disease-free bee populations anywhere in the world and the honey produced was and remains exceptionally high in quality. Pitcairn bees were also found to be a particularly placid variety and, within a short time, the beekeepers were able to work with them wearing minimal protection (The Telegraph, 9 January 2010). As a result, Pitcairn today exports its renowned honey to New Zealand and to the United Kingdom, where it is stocked in London by Fortnum and Mason and Partridges in Sloane Square. The honey has become a favourite of Her Majesty, Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Charles.[23] The Pitcairn Islanders, under the "Bounty Products" and "Delectable Bounty" brands, also export dried fruit including bananas, papayas, pineapples and mangoes to New Zealand.[24]
Tourism
Tourism plays a major role on Pitcairn providing the locals 80% of their annual income. Since 2009, the Government has been operating the MV Claymore II as the island's only dedicated passenger/cargo vessel providing tourists with adventure tourism holidays to Pitcairn for three- or ten-day visits. Tourists stay with local families and get to experience the island's history while contributing to the local economy. Some families have invested in private self-contained units for tourists to rent. Each year approximately ten cruise ships call at the island for a few hours generating income for the locals from the sale of souvenirs, landing fees and the stamping of passports. Children under the age of 16 years require a completed entry clearance application in order to visit the island.[25]
Electricity
Electricity on the island is provided by diesel generators operating ten hours per day (from 8 am to 1 pm, and from 5 pm to 10 pm). A wind power plant is planned to be installed in the next year or two, to help reduce the high cost of power generation currently associated with the import of diesel, and provide 24-hour electricity to the islanders at 70 cents per unit with no government subsidy.
Culture
Language
Main article: Languages of the Pitcairn IslandsThe majority of the resident Pitcairn Islanders are the descendants of the Bounty Mutineers and Tahitians (or Polynesians). Pitkern is a creole language derived from 18th century English, with elements of the Tahitian language. It is spoken as a first language by the population and is taught alongside standard English at the island's only school. It is closely related to the creole language Norfuk, spoken on Norfolk Island, because Norfolk was repopulated in the mid-19th century by Pitcairners.
Demographics
In September 2003, a baby was born on the island for the first time in 17 years (Pitcairn Miscellany, 2003). Another child, Adrianna Tracey Christian, was born on Pitcairn on 3 March 2007 (Miscellany, 2007). In February 2005, Shirley and Simon Young became the first married outsider couple in recorded history to obtain citizenship on Pitcairn (Miscellany, March 2005). Since 2001, a significant proportion of the Pitcairn population (21 people) has been given a Personal Public Service Number in Ireland, which is required for work, taxes and social benefits.[26]
Religion
A successful Seventh-day Adventist mission in the 1890s was important in shaping Pitcairn society. In recent years, the church has declined, with only about eight islanders worshipping regularly, but most of them still attend church on special occasions.[27] The Sabbath is observed as a day of rest and as a mark of respect for observant Adventists.
The church which was built in 1954, is run by the Church board and resident pastor, who usually serves a two year term. The Sabbath School meets at 10 am on Saturday mornings and is followed by Divine Service an hour later. On Tuesday evenings there is a further service in the form of a prayer meeting.
Society
The once-strict moral codes, which prohibited dancing, public displays of affection, smoking, and consumption of alcohol, have been relaxed in recent years. Islanders and visitors no longer require a six-month licence to purchase, import, and consume alcohol (Pitcairn Island Government Ordinance). There is now one licensed cafe and bar on the island, and the Government Store sells alcohol and cigarettes.
The unique cuisine and rich cultural heritage of the Pitcairn Islanders is detailed in a cookbook: "A Taste of Pitcairn: The First Pitcairn Island Cookbook", by Pitcairn resident Meralda Warren (updated ed. 2005).
Fishing and swimming are two popular recreational activities. A birthday celebration or the arrival of a ship or yacht will involve the entire Pitcairn community in a public dinner in the Square, Adamstown. Tables are covered in a variety of foods, including fish, meat, chicken, philhi, baked rice, boiled plun (banana), breadfruit, vegetable dishes, an assortment of pies, bread, breadsticks, an array of desserts, pineapple, watermelon and more.
Public work, which by law is required of all men and women between the ages of 16 and 65, ensures the ongoing maintenance of the island's numerous roads and paths. The island has a labour force of only 15 men and women (as of 2004).[28]
Education
Education is free and compulsory between the ages of five and 16.[29] All of Pitcairn's seven children were enrolled in school in 2000.[29] The island's children have produced a book in Pitkern and English called "Mi Bas Side orn Pitcairn=My Favourite Place on Pitcairn" (National Library of New Zealand Catalogue).
The school at Pulau provides pre-school and primary education based on the New Zealand syllabus. The teacher is appointed by the Governor from suitable qualified applicants who are New Zealand registered teachers. The contract includes the role of Editor of the Pitcairn Miscellany.
Historical population
Pitcairn's population has drastically decreased since its peak of over 250 in 1936 to 60 in 2011.
Year Population Year Population Year Population Year Population Year Population 1790 27 1880 112 1970 96 1992 54 2002 48 1800 34 1890 136 1975 74 1993 57 2003 59 1810 50 1900 136 1980 61 1994 54 2004 65 1820 66 1910 140 1985 58 1995 55 2005 63 1830 70 1920 163 1986 68 1996 43 2006 65 1840 119 1930 190 1987 59 1997 40 2007 64 1850 146 1936 250 1988 55 1998 66 2008 66 1856* 193 1940 163 1989 55 1999 46 2009 70 1859** 16 1950 161 1990 59 2000 51 2010 64 1870 70 1960 126 1991 66 2001 44 2011 60 - 1856 Emigration to Norfolk Island leaves Pitcairn uninhabited.
- 1859 First group returns from Norfolk Island.
Media and communications
- Telephones: Pitcairn uses New Zealand's international dialling code, +64.
- Radio: There is no broadcast station. Marine band walkie-talkie radios are used to maintain contact among people in different areas of the island. Foreign stations can be picked up on shortwave radio.
- Amateur Radio: QRZ.COM lists seven amateur radio operators on the island.
- Television: There are 2 live English TV channels from satellite, CNN, and Turner Classic Movies. Free-To-Air satellite dishes can be used to watch foreign TV.
- Internet: There is one Government-sponsored satellite internet connection, with networking provided to the inhabitants of the island. Pitcairn's country code (top level domain) is .pn. Residents pay NZ$100 (about USD$75) for 2 GB of data per month, at a rate of 256 kbit/s.[30]
Transport
The settlers of the Pitcairns all arrived by some form of boat or ship.
Pitcairn Island does not have an airport or seaport; the islanders rely on longboats to ferry people and goods between ship and shore through Bounty Bay. The island has one small harbour and launch ramp that is used to dock and load long-boats. Because it is small and the water is shallow, only small-craft can fit (Pitkern Ilan, David Evans, 2007).
A dedicated passenger/cargo supply ship chartered by the Pitcairn Island Government, the MV Claymore II, is the principal transport from Mangareva, Gambier Islands, French Polynesia.
Mangareva is reachable by air from the French Polynesian capital Papeete (Lonely Planet South Pacific, 3rd ed. 2006, "Pitcairn Getting There" pp. 429–30).
There is one 6.4-kilometre (4 mi) paved road leading up from Bounty Bay through Adamstown.
The main mode of transport on Pitcairn islands is by four-wheel-drive quad bikes. There are also two cars on the island.
Climate
Pitcairn is located just under the Tropic of Capricorn and enjoys year round warm weather. Summer temperatures average 25–35 degrees Celsius from the months of October through to April, while the winter months range from 17 degrees to 25. The average humidity in summer can exceed 95%. The rainy season is from November through to March.
Gallery
See also
- Outline of the Pitcairn Islands
- Bibliography of Pitcairn Islands
- Bounty Day
- British Overseas Territories
- Climate of the Pitcairn Islands
- Island Council (Pitcairn)
- Thursday October Christian I
References
- ^ Oxford English Dictionary
- ^ "Pitcairn Islands: UK's most remote territory". YouTube. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZwhWwVWYmPQ&feature=related. Retrieved 31 July 2011.
- ^ [1]|date=July 2011}}
- ^ "United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories". United Nations. 14 December 1960. http://www.un.org/Depts/dpi/decolonization/trust3.htm. Retrieved 31 July 2011.
- ^ Diamond, Jared M (2005). Collapse: how societies choose to fail or succeed. New York: Penguin. p. 132. ISBN 9780143036555. OCLC 62868295. "But by A.D. 1606 ... Henderson’s population had ceased to exist. Pitcairn’s own population had disappeared at least by 1790 ... and probably disappeared much earlier."
- ^ Pitcairn Islands, "History of Government and Laws, Part 15" 30 September 2006
- ^ Hooker, Brian. "Down with Bligh – hurrah for Tahiti". Finding New Zealand. http://www.findingnz.co.nz/al/gal1_bounty.htm.
- ^ Winthrop, Mark. "The Story of the Bounty Chronometer". Lareau Web Parlour. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070927005607/http://www.lareau.org/chrono.html. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ "Mutineers of the Bounty". The European Magazine, and London Review (Philological Society of London,) 69: 134. January–June 1816. http://books.google.com/?id=mOwRAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA62#PPA134,M1.
- ^ Staff. The Annual Biography and Obituary for the Year ..., Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown, 1831, Volume 15 "Chapter X Sir Thomas Staines" pp. 366–367
- ^ History of Pitcairn Island, Pitcairn Study Centre. Retrieved 15 September 2008.
- ^ "Pitcairn descendants of the ''Bounty'' Mutineers". Janesoceania.com. 29 April 2009. http://www.janesoceania.com/oceania_pitcairn_descendants/index.htm. Retrieved 31 July 2011.
- ^ Cahoon, Ben. "Pitcairn Island". worldstatesmen.org. http://www.worldstatesmen.org/Pitcairn.htm. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ Presenter: Paul Allen Speaker: Pitcairn Island Governor, George Fergusson. Pitcairn Island proclaims new constitution. Radio Australia, 11 March 2010
- ^ "Home." Government of the Pitcairn Islands. Retrieved on October 31, 2011.
- ^ Pitcairn Islands Environment Management Plan, 2008.
- ^ Endangered Species Protection Ordinance, 2004 revised edition.
- ^ Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC): Pitcairn Islands-Joint Country Strategy, 2008.
- ^ Commonwealth Secretariat Yearbook 2010: Pitcairn Economy.
- ^ Foreign and Commonwealth Office, Profile on Pitcairn Islands, British Overseas Territory, 11 February 2010.
- ^ Pitcairn Island Report prepared by Jaques and Associates, 2003 p. 18.
- ^ Jaques, p. 21.
- ^ "I'll let you off, Mr Christian: you make honey fit for a queen", Evening Standard, 8 January 2010.
- ^ Pitcairn Islands Study Center, News Release: Products from Pitcairn, 7 November 1999.
- ^ Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Travel Advice: Pitcairn (British Overseas Territory)
- ^ "Personal Public Service Numbers -Allocation By Nationality-All Countries 2000–2009 » PPSN » Topics » Department of Social Protection". Welfare.ie. 6 January 2010. http://www.welfare.ie/EN/Topics/PPSN/Pages/ppsn_all_years.aspx. Retrieved 31 July 2011.
- ^ "Turning Point for Historic Adventist Community on Pitcairn Island" 30 September 2006
- ^ "CIA World Factbook – Pitcairn Islands". The World Factbook. U.S. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/pc.html. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- ^ a b "Territories and Non-Independent Countries". 2001 Findings on the Worst Forms of Child Labor. Bureau of International Labor Affairs, U.S. Department of Labor (2002). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "iPad Makes Its Way to the Farthest Reaches of the Earth" MacRumors.com, retrieved 3 November 2010
Further reading
The Mutiny on the Bounty
- The Bounty: The True Story of the Mutiny on the Bounty by Caroline Alexander (Harper Perennial, London, 2003 pp.491)
- The Discovery of Fletcher Christian: a Travel Book by Glynn Christian, a descendant of Fletcher Christian, Bounty Mutineer (Guild Press, London, 2005 pp.448)
After the Mutiny
- The Pitcairners by Robert B. Nicolson (Pasifika Press, Auckland, 1997 pp.260)
- After the Bounty: The aftermath of the infamous Mutiny on the HMS Bounty-an insight to the plight of the mutineers by Cal Adams, a descendant of John Adams, Bounty Mutineer (Self-published, Sydney, 2008 pp.184)
Pitcairn Island Today
- The Guide to Pitcairn produced by Pitcairn Island Government (Pitcairn Island Administration, Auckland, 1999 pp.68)
- Pitkern Ilan=Pitcairn Island by David H. Evans (Self-published, Auckland, 2007 pp.46)
- "Lost Paradise From Mutiny of the bounty to a Modern-Day Legacy of Sexual mayhem the Dark Secrets of Pitcairn island Revealed", (Free Press, 2009).
External links
Travel to Pitcairn
- Pitcairn Islands travel guide from Wikitravel
- Pitcairn Island Tourism Official tourism site of the Pitcairn Islands.
Government of the Pitcairn Islands
- Pitcairn Government
- Pitcairn Islands from the British Foreign and Commonwealth Office
- Wikimedia Atlas of Pitcairn Islands
News from Pitcairn Island
- Pitcairn Miscellany News from Pitcairn Island. The Editor is Pulau school teacher.
- Pitcairn News information from Chris Double, a Bounty descendant based in Auckland NZ
- Uklun Tul Un Dem Tul Pitcairn news by Kari Young, a Pitcairn resident.
Pitcairn Island Study Groups on the Internet
Coordinates: 25°04′S 130°06′W / 25.067°S 130.1°W
 Pitcairn Islands topics
Pitcairn Islands topicsIslands and settlement 
Culture Main topics British Overseas Territories and Crown dependencies Overseas territories Anguilla · Bermuda · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Gibraltar · Montserrat · Pitcairn Islands · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha1 · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands · Turks and Caicos Islands
Crown dependencies Sovereign base areas 1 includes Saint Helena · Ascension Island · Tristan da Cunha
² includes Alderney · SarkCountries and territories of Oceania Sovereign states Australia · Chile (Easter Island · Juan Fernández Islands) · East Timor (Timor-Leste) · Fiji · Indonesia · Kiribati · Marshall Islands · Federated States of Micronesia · Japan (Bonin Islands) · Nauru · New Zealand · Palau · Papua New Guinea · Samoa · Solomon Islands · Tonga · Tuvalu · United States (Hawaii · Palmyra Atoll) · Vanuatu
Dependencies and other territories AustraliaFranceNew ZealandUnited KingdomPitcairn IslandsUnited StatesList of resources about traditional arts and culture of Oceania Art ahu · Australia · Austronesia · Cook Islands · Hawaiʻi · kapa (Hawaiʻi) · lei (Hawaii) · magimagi · Māori · moai · New Zealand · nguzu nguzu · Oceania · Papua New Guinea · reimiro · tā moko · tapa ["masi" (Fiji), "ngatu" (Tonga), "siapo" (Sāmoa), " ʻuha" (Rotuma)] · tabua · ta'ovala · tattoo · tēfui · tivaivaiBroad culture Geo-specific, general Australia · Australian Aboriginal astronomy · Austronesia · Caroline Islands, -Pwo · Chatham Islands · Cook Islands · Easter Island · Fiji, -Lau Islands, -traditions and ceremonies · Guam · Hawaiʻi, -Lomilomi massage · Kiribati · French Polynesia's Marquesas Islands · Marshall Islands, -Stick charts of · Federated States of Micronesia · Nauru · New Caledonia · New Zealand · Niue · Norfolk Island · Palau · Papua New Guinea · Pitcairn Islands · Sāmoa · Solomon Islands · Tonga · Torres Strait Islands · Tuvalu · Vanuatu · Wallis and Futuna · Yap, -navigation, -Weriyeng navigation schoolCanoes Aboriginal Dugout · Alingano Maisu · Drua · Dugout (boat) · Hawaiʻiloa · Hōkūleʻa · Modern Hawaiian outrigger · Māori migration · Outrigger · Polynesian sailing · Proa · Waka,-List of · WalapDance Festivals Australia's Garma Festival · Hawaiʻi's Aloha Festivals, Merrie Monarch Festival, and World Invitational Hula Festival · Fiji · New Zealand's Pasifika Festival · The Pacific Community's Festival of Pacific Arts · Festivals in Papua New GuineaLanguages by areaLanguages of Oceania Sovereign states - Australia
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Fiji
- Indonesia
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
by categoryLiterature Literature of Oceania Sovereign states - Australia
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Fiji
- Indonesia
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
Music Austral Islands (French Polynesia) · Australia · Austronesia · Cook Islands · Easter Island · Fiji · Guam · Hawaiʻi · Kiribati · Lali · Māori · Melanesia · Northern Mariana Islands · Micronesia · Federated States of Micronesia · Nauru · New Caledonia · New Zealand · Niue · Palau · Papua New Guinea · Polynesia · Sāmoa · Slit drum · Solomon Islands · Tahiti · Tokelau · Tonga · Tuvalu · Vanuatu · Wallis and FutunaMythology Australian Aboriginal · Fijian · Māori · Melanesian · Menehune · Micronesian · Oceanian legendary creatures · Polynesian · Rapa Nui · VanuatuPeople Indigneous Australian · Austronesian · Chamorro · Chatham Islander (Moriori or Rekohu) · Fijian · Hawaiian (kānaka maoli) · Māori · Marshallese · Melanesian · Micronesian · Negrito · Norfolk Islander · Papuan · Polynesian · Indigenous Polynesian (Mā’ohi) · Rapanui · Rotuman · Samoan · Tahitian · Tongan · Torres Strait IslanderReligion Religion in Oceania Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
Not included: Oceanian: cinema, (indigenous) currency, dress, folkore, cuisine. Also see Category:Oceanian culture. Polynesia Polynesian triangle Austral Islands · Cook Islands · Easter Island · Gambier Islands · Hawaiian Islands · Marquesas · New Zealand · Pitcairn Islands · Sala y Gómez · Samoan Islands · Society Islands · Tokelau · Tonga · Tuamotus · Tuvalu · Wallis and Futuna IslandsPolynesian outliers Anuta · Emae · Futuna · Kapingamarangi · Loyalty Islands · Mele · Nuguria · Nukumanu · Nukuoro · Ontong Java · Ouvéa · Pileni · Rennell · Sikaiana · Takuu · TikopiaPolynesian-influenced World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom England Bath · Blenheim Palace · Canterbury Cathedral, St. Augustine's Abbey and St. Martin's Church · Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape · Derwent Valley Mills · Durham Castle and Cathedral · Frontiers of the Roman Empire (Hadrian's Wall) · Ironbridge Gorge · Jurassic Coast · Kew Gardens · Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City · Maritime Greenwich · Saltaire · Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites · Studley Royal Park and Fountains Abbey · Tower of London · Westminster Palace, Westminster Abbey and St. Margaret's Church
Scotland Wales Northern Ireland British Overseas Territories Gough Island and Inaccessible Island, Tristan da Cunha · Henderson Island, Pitcairn Islands · Town of St George and Related Fortifications
British Empire and Commonwealth of Nations Legend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of NationsEurope18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1763–1782 Minorca
1798–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands20th century
1921-1937 Irish Free StateNorth America17th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
1607–1776 Virginia
since 1619 Bermuda
1620–1691 Plymouth Colony
1629–1691 Massachusetts Bay Colony
1632–1776 Maryland
1636–1776 Connecticut
1636–1776 Rhode Island
1637–1662 New Haven Colony
1663–1712 Carolina
1664–1776 New York
1665–1674 and 1702-1776 New Jersey
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
1674–1702 East Jersey
1674–1702 West Jersey
1680–1776 New Hampshire
1681–1776 Pennsylvania
1686–1689 Dominion of New England
1691–1776 Massachusetts18th century
1701–1776 Delaware
1712–1776 North Carolina
1712–1776 South Carolina
1713–1867 Nova Scotia
1733–1776 Georgia
1763–1873 Prince Edward Island
1763–1791 Quebec
1763–1783 East Florida
1763–1783 West Florida
1784–1867 New Brunswick
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
1818–1846 Columbia District / Oregon Country1
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1853–1863 Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands
1858–1866 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
1866–1871 Vancouver Island and British Columbia
1867–1931 *Dominion of Canada2
20th century
1907–1949 Dominion of Newfoundland31Occupied jointly with the United States
2In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. see Canada's name.
3Gave up self-rule in 1934, but remained a de jure Dominion until it joined Canada in 1949.Latin America and the Caribbean17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *Saint Kitts.2C 1623 to 1700|St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago
20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation4Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
AfricaAsiaOceania18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land/Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands7
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony/Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1841–1907 Colony of New Zealand
1851–1901 Victoria
1874–1970 Fiji8
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands7
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)7
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands9
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands1020th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue7
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1942 Nauru
1945–1968 Nauru
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea117Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
8Suspended member
9Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
10Now the *Solomon Islands
11Now *Papua New GuineaAntarctica and South Atlantic17th century
since 1659 St. Helena1219th century
since 1815 Ascension Island12
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha12
since 1833 Falkland Islands1320th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory14
since 1908 South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands13, 1412Since 2009 part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Ascension Island (1922—) and Tristan da Cunha (1938—) were previously dependencies of St Helena
13Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982
14Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands)Categories:- Pitcairn Islands
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Island countries
- Islands of the Pitcairn Islands
- Mutiny on the Bounty
- Polynesia
- Special territories of the European Union
- States and territories established in 1838
- Volcanoes of the United Kingdom
- 1856 Emigration to Norfolk Island leaves Pitcairn uninhabited.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.