- North Borneo
-
North Borneo
Borneo UtaraColony of the United Kingdom
(Protectorate until 1946)
←
1882–1963  →
→
 →
→

Flag Badge Motto
Pergo et Perago
(Latin: "I undertake and I achieve”)Capital Sandakan (pre war); Jesselton (post war) Language(s) English, Malay Government Protectorate, Crown Colony Governor - 1896–1901 Robert Scott (North Borneo) Historical era New Imperialism - North Borneo Company May 1882 - British protectorate 1888 - Japanese invasion 1 January 1942 - Australian liberation June 1946 - Restored as colony 15 July 1946 - Independence 31 August 1963 - Formation of Malaysia 16 September 1963 Area - 1936 76,115 km2 (29,388 sq mi) Population - 1936 est. 285,000 Density 3.7 /km2 (9.7 /sq mi) Currency North Borneo dollar, until 1953
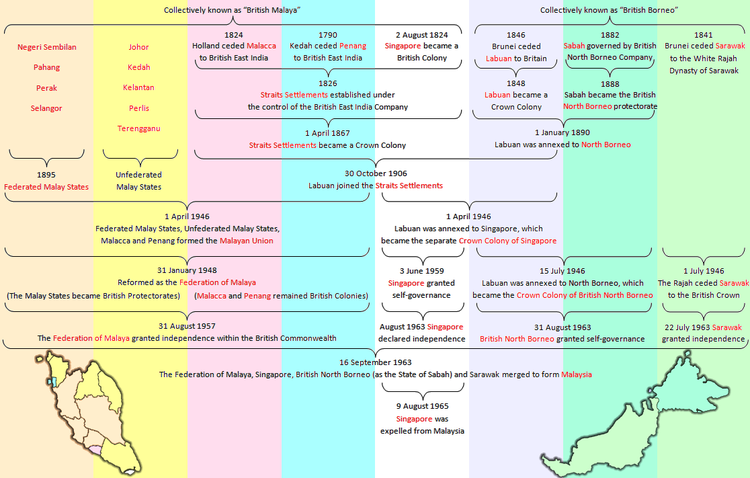
Malaya and Borneo dollar, after 1953North Borneo was a British protectorate under the sovereign North Borneo Chartered Company from 1882 to 1946. After the war it became a crown colony of Great Britain from 1946 to 1963, known in this time as British North Borneo. It is located on the northeastern end of the island of Borneo. It is now the state of Sabah, East Malaysia. The last Governor of North Borneo was William Allmond Codrington Goode who held office from 1959 to 1963.
Contents
History
State of North Borneo
In 1865, the United States Consul to Brunei, Charles Lee Moses, obtained a 10-year lease for the territory of North Borneo from the Sultan of Brunei. However, the post-Civil War United States wanted nothing to do with Asian colonies, so Moses sold his rights to the Hong Kong-based American Trading Company of Borneo owned by Joseph William Torrey, Thomas Bradley Harris, Tat Cheong and possibly other Chinese merchants. Torrey began a settlement at the Kimanis River mouth, which he named Ellena. Attempts to find financial backing for the settlement were futile, and disease, death and desertion by the immigrant labourers led to the abandonment of the settlement towards the end of 1866. Harris died in 1866 and Torrey returned to America in 1877, he died in Boston, Massachusetts, in March 1884.
With the imminent termination of the lease at hand in January 1875, Torrey managed to sell his rights to the Consul of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in Hong Kong, Baron Von Overbeck. Von Overbeck managed to get a 10-year renewal of the lease from the Temenggong of Brunei, and a similar treaty from the Sultan of Sulu on 22 January 1878. To finance his plans for North Borneo, Overbeck found financial backing from the Dent brothers (Alfred and Edward). However, he was unable to interest his government in the territory. After efforts to sell the territory to Italy for use as a penal colony, Von Overbeck withdrew in 1880, leaving Alfred Dent in control. Dent was supported by Sir Rutherford Alcock, and Admiral Sir Harry Keppel.
In July 1881, Alfred Dent and his brother formed the British North Borneo Provisional Association Ltd and obtained an official Royal Charter 1 November the same year. In May 1882, the North Borneo Chartered Company replaced the Provisional Association. Sir Rutherford Alcock became the first President, and Alfred Dent became Managing Director. In spite of some diplomatic protests by the Dutch, Spanish and Sarawak governments, the North Borneo Chartered Company proceeded to organize settlement and administration of the territory. The company subsequently acquired further sovereign and territorial rights from the sultan of Brunei, expanding the territory under control to the Putatan river (May 1884), the Padas district (November 1884), the Kawang river (February 1885), the Mantanani Islands (April 1885), and additional minor Padas territories (March 1898).
The Company established a foundation for economic growth in North Borneo by restoring peace to a land where piracy and tribal feuds had grown rampant. It abolished slavery and set up transport, health and education services for the people. Chinese immigrants were wooed to boost the small population of less than 100,000. Through the combined effort of the locals and immigrants, towns, farms, a timber industry, tobacco and rubber plantations began to thrive.
Protectorate of Britain
In 1888, North Borneo became a protectorate of Great Britain, but its administration remained entirely in the hands of the North Borneo Chartered Company, with the crown reserving only control of foreign relations.
From 1890 to 1905 the British government placed the colony of Labuan under the administration of North Borneo.
The Company's rule in North Borneo had great impact on the development of the region. Although was generally peaceful, the local population occasionally resented the imposition of taxes and the loss of land to European plantations. The most serious resistance was the Mat Salleh (Mahomet Saleh) War from 1894 to 1900, and the Rundum Uprising by the Murut in 1915.
The Chartered Company's system of administration was based on standard British colonial administration structures, with the land divided into Residencies, and sub-divided into Districts. Initially, there were only two Residencies: East Coast and West Coast, with Residents based at Sandakan and Jesselton respectively. Each Residency was divided into Provinces, later known as Districts, which were run by District Officers. By 1922, there were five Residencies to accommodate new areas that were opened up for development. These were the West Coast, Kudat, Tawau, Interior and East Coast Residencies. These Residencies were in turn divided into 17 Districts.
Under this system, British held top posts, while native chiefs managed the people at grassroots level. This was not a conscious attempt by the British to instil indirect rule but a convenient arrangement for the District Officers who were unfamiliar with local customs and politics.
The North Borneo Chartered Company effectively ruled until 1 January 1942. Japanese forces occupied North Borneo from 1942 to 1945. The North Borneo Armed Constabulary with only 650 men hardly provided any resistance to slow down the Japanese invasion. During Japanese military occupation, the Europeans were interned, public services ceased to exist, and there were widespread poverty, disease and malnutrition.
In June 1945 the Australian 9th Division landed in Brunei and liberated much of North Borneo before the end of the war. North Borneo was placed under British Military Administration until restoration of civil government on 15 July 1946.
Crown Colony of British North Borneo
The North Borneo Chartered Company did not have the financial resources to reconstruct North Borneo after the destruction of World War II. The major towns had been razed to the ground by allied bombing, and the infrastructure of North Borneo was in total devastation. The North Borneo Chartered Company decided to sell its interests to the British government. The territory was placed under control of the colonial office, and became a British crown colony on 15 July 1946 together with islands of Labuan. The destruction of the former capital Sandakan was so complete that Jesselton was chosen as the new post-war capital. The colonial system of administration was in most ways similar to rule during the Company era, retaining the same Residency and District structure; however, as a result of this change in status, North Borneo had access to British government funds for reconstruction.
A Governor and Commander-in-Chief was appointed to administer the colony of North Borneo with the assistance of an Advisory Council consisting of three ex-officio members: a Chief Secretary, the Attorney-General, and the Financial Secretary, together with other members both official and unofficial whom the Governor chose to appoint. In 1950, the Advisory Council was replaced by the Executive and Legislative Councils.
The Executive Council functioned as a Cabinet and was headed by the Chief Secretary. In addition to the Attorney General and the Financial Secretary, it consisted of two officials and four nominated members. The Governor presided at the Executive Council meetings and he alone was entitled to submit questions to the Council.
The Legislative Council consisted of the Governor as President, the usual three ex-officio members, nine official members and ten nominated members.
The high-ranking administrative posts continued to be held by the British, and in fact, it was only in 1957 that the first non-European filled an administrative officer's post.
The British North Borneo was granted self-government on 31 August 1963 in Keningau. A little over two weeks later, on 16 September 1963, the state united with Malaya, Sarawak and Singapore, forming the Federation of Malaysia.
The First Natives Paramount Leader was Pehin Orang Kaya-Kaya Koroh bin Santulan of Keningau "The father of former Sabah State Minister Tan Sri Stephen (Suffian) Koroh, and Sabah's fifth State Governor Tun Thomas (Ahmad) Koroh (the elder brother of Suffian)". Santulan which also a Pengeran, the father to Pehin Orang Kaya-Kaya Koroh was a Murut descendant of Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin, the 25th Sultan of Brunei.
Postage stamps
Initially, mail from North Borneo was sent via Labuan or Singapore, using postage stamps of the Straits Settlements. The company issued its own stamps in March 1883, using a design incorporating the coat of arms (a dhow and a lion), inscribed "NORTH BORNEO", and with the value written in English, Jawi, and Chinese. Initial values included 2c, 4c, and 8c, followed by large 50c and $1 stamps of a more elaborate design with the arms flanked by two natives.
In 1886 ½c, 1c, and 10c values were added, and there was a demand for 3c and 5c stamps, resolved by overprinting existing types. At the same time, the printers (Blades, East, and Blades of London) produced a new design, largely the same but inscribed "BRITISH NORTH BORNEO", and joined by 25c and $2 values, also with elaborate frames. The stamps were redesigned again in 1888, to say "POSTAGE & REVENUE" instead of just "POSTAGE", at which time the 25c to $2 values also received minor changes. These were followed up in 1889 by even larger and more elaborate $5 and $10 stamps.
Shortages in 1890, 1891, and 1892 necessitated more surcharges.
In 1894, the protectorate issued a new definitive series engraved by Waterlow and Sons, comprising nine pictorials featuring natives plants, animals, and scenes, and inscribed "STATE OF NORTH BORNEO".
See also
- Governor of North Borneo
- History of Sabah
- British North Borneo dollar
- Malaya and British Borneo dollar
- Manila Accord
British Empire and Commonwealth of Nations Legend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of NationsEurope18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1763–1782 Minorca
1798–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands20th century
1921-1937 Irish Free StateNorth America17th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
1607–1776 Virginia
since 1619 Bermuda
1620–1691 Plymouth Colony
1629–1691 Massachusetts Bay Colony
1632–1776 Maryland
1636–1776 Connecticut
1636–1776 Rhode Island
1637–1662 New Haven Colony
1663–1712 Carolina
1664–1776 New York
1665–1674 and 1702-1776 New Jersey
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
1674–1702 East Jersey
1674–1702 West Jersey
1680–1776 New Hampshire
1681–1776 Pennsylvania
1686–1689 Dominion of New England
1691–1776 Massachusetts18th century
1701–1776 Delaware
1712–1776 North Carolina
1712–1776 South Carolina
1713–1867 Nova Scotia
1733–1776 Georgia
1763–1873 Prince Edward Island
1763–1791 Quebec
1763–1783 East Florida
1763–1783 West Florida
1784–1867 New Brunswick
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
1818–1846 Columbia District / Oregon Country1
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1853–1863 Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands
1858–1866 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
1866–1871 Vancouver Island and British Columbia
1867–1931 *Dominion of Canada2
20th century
1907–1949 Dominion of Newfoundland31Occupied jointly with the United States
2In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. see Canada's name.
3Gave up self-rule in 1934, but remained a de jure Dominion until it joined Canada in 1949.Latin America and the Caribbean17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *Saint Kitts.2C 1623 to 1700|St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago
20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation4Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
AfricaAsiaOceania18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land/Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands7
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony/Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1841–1907 Colony of New Zealand
1851–1901 Victoria
1874–1970 Fiji8
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands7
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)7
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands9
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands1020th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue7
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1942 Nauru
1945–1968 Nauru
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea117Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
8Suspended member
9Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
10Now the *Solomon Islands
11Now *Papua New GuineaAntarctica and South Atlantic17th century
since 1659 St. Helena1219th century
since 1815 Ascension Island12
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha12
since 1833 Falkland Islands1320th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory14
since 1908 South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands13, 1412Since 2009 part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Ascension Island (1922—) and Tristan da Cunha (1938—) were previously dependencies of St Helena
13Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982
14Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands) Sabah
SabahDivisions Cities Towns Beaufort • Beluran • Bingkor • Bongawan • Donggongon • Inanam • Kalabakan • Keningau • Kimanis • Kinabatangan • Kinarut • Kota Belud • Kota Marudu • Kuala Penyu • Kudat • Kunak • Kundasang • Lahad Datu • Membakut • Menggatal • Nabawan • Papar • Pensiangan • Pitas • Putatan • Ranau • Sapulut • Semporna • Sepanggar • Sindumin • Sipitang • Sook • Tambunan • Tamparuli • Telipok • Telupid • Tenom • Tongod • Tuaran • WestonIslands Balambangan Island • Banggi Island • Berhala Island • Gaya Island • Manukan Island • Jambongan Island • Kapalai Island • Lankayan Island • Layang Layang Island • Libaran Island • Ligitan Island • Mabul Island • Malawali Island • Mantanani Islands • Sebatik Island • Selingan Island • Sipadan Island • Tabawan Island • Tiga Island • Timbun Mata IslandTerritorial disputes of the Philippines Current Macclesfield Bank · Sabah (North Borneo dispute) · Scarborough Shoal · Spratly Islands (Spratly Islands dispute; Philippines and the Spratly Islands)Former Palmas Island (Miangas) · Sangihe IslandsCategories:- Former countries in Southeast Asia
- Former British protectorates
- States and territories established in 1882
- States and territories disestablished in 1963
- Territorial disputes of the Philippines
- 1963 disestablishments
- Borneo
- British North Borneo
- Former countries in Borneo
- Former countries in Malaysian history
- Disputed territories in Asia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.