- History of the Gambia
-
The modern-day Gambia was once part of the Ghana, Mali and Songhai Empires.
Contents
Early history
The first written accounts of the region come from records of Arab traders in the 9th and 10th centuries AD. In medieval times the area was dominated by the trans-Saharan trade. The reign of the Mali Empire, most renowned for the Mandinka ruler Mansa Kankan Musa, brought world wide recognition to the region due to its enormous wealth, scholarship, and civility. The North African scholar and traveler Ibn Battuta visited the area in 1352 AD and said this about its inhabitants:
The negroes possess some admirable qualities. They are seldom unjust, and have a greater abhorrence of injustice than any other people. There is complete security in their country. Neither traveler nor inhabitant in it has anything to fear from robbers or men of violence.[1]
Since the early 13th century, the Kouroukan Fouga, Mali's constitution, was the law of the land. The Songhai Empire, named after the Soninke people whose king assumed official control of the Empire, came to dominate the region in the 16th century. As time went on the area began to suffer from continuous Moroccan and Portuguese invasion and looting. By the end of the 16th century, as the raids continued, the empire collapsed and was conquered and claimed by Portugal.
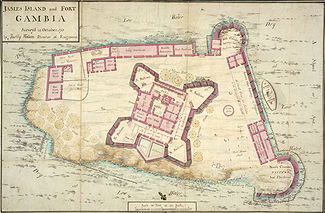
In 1588, the claimant to the Portuguese throne, Antonio, Prior of Crato, sold exclusive trade rights on The Gambia River to English merchants; this grant was confirmed by letters patent from Queen Elizabeth I. In 1618, King James I granted a charter to an English company for trade with The Gambia and the Gold Coast (now Ghana). Between 1651 and 1661 part of Gambia was (indirectly) a colony of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth; it was purchased by the Courlandish duke Jakub Kettler. At that time Courland, in modern-day Latvia, was a fiefdom of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Courlanders settled on James Island, which they called St. Andrews Island and used as a trade base from 1651 until its capture by the English in 1661.
Colonial competition
During the late 17th and throughout the 18th century, Great Britain and France constantly struggled for political and commercial supremacy in the regions of the Senegal and Gambia Rivers. The 1783 Treaty of Paris gave Great Britain possession of The Gambia, but the French retained a tiny enclave at Albreda on the north bank of the river, which was ceded to the British in 1857.
As many as 3 million slaves may have been taken from the region during the three centuries that the transatlantic slave trade operated. It is not known how many slaves were taken by Arab traders prior to and simultaneous with the transatlantic slave trade. Most of those taken were sold to Europeans by other Africans; some were prisoners of intertribal wars; some were sold because of unpaid debts, while others were kidnapped. Slaves were initially sent to Europe to work as servants until the market for labor expanded in the West Indies and North America in the 18th century. In 1807, slave trading was abolished throughout the British Empire, and the British tried unsuccessfully to end the slave trade in The Gambia. They established the military post of Bathurst (now Banjul) in 1816. In the ensuing years, Banjul was at times under the jurisdiction of the British Governor General in Sierra Leone. In 1888, The Gambia became a separate colonial entity.
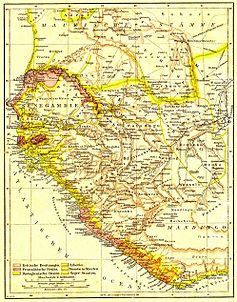
An 1889 agreement with France established the present boundaries, and The Gambia became a British Crown Colony, divided for administrative purposes into the colony (city of Banjul and the surrounding area) and the protectorate (remainder of the territory).
20th century on
The Gambia received its own executive and legislative councils in 1901 and gradually progressed toward self-government. A 1906 ordinance abolished slavery.
During the Second World War, Gambian troops fought with the Allies in Burma. Banjul served as an air stop for the U.S. Army Air Corps and a port of call for Allied naval convoys. U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt stopped overnight in Banjul en route to and from the Casablanca Conference in 1943, marking the first visit to the African Continent by an American president while in office.
After the Second World War, the pace of constitutional reform increased. Following general elections in 1962, full internal self-governance was granted in the following year. The Gambia achieved independence on February 18, 1965 as a constitutional monarchy within the Commonwealth. Shortly thereafter, the government held a referendum proposing that an elected president replace the Gambian monarch as head of state. The referendum failed to receive the two-thirds majority required to amend the constitution, but the results won widespread attention abroad as testimony to The Gambia's observance of secret balloting, honest elections, and civil rights and liberties. On April 24, 1970, The Gambia became a republic within the Commonwealth, following a second referendum, with Prime Minister Sir Dawda Kairaba Jawara, as head of state.
Until a military coup in July 1994, The Gambia was led by President Jawara, who was re-elected five times. The relative stability of the Jawara era was shattered first by a coup attempt in 1981. The coup was led by Kukoi Samba Sanyang, who, on two occasions, had unsuccessfully sought election to Parliament. After a week of violence which left several hundred people dead, Jawara, in London when the attack began, appealed to Senegal for help. Senegalese troops defeated the rebel force.
In the aftermath of the attempted coup, Senegal and The Gambia signed the 1982 Treaty of Confederation. The Senegambia Confederation came into existence; it aimed eventually to combine the armed forces of the two states and to unify their economies and currencies. The Gambia withdrew from the confederation in 1989.
In July 1994, Yahya A.J.J. Jammeh led a coup d'état that deposed the Jawara government. Between 1994 and 1996, Jammeh ruled as head of the Armed Forces Provisional Ruling Council (AFPRC) and banned opposition political activity. The AFPRC announced a transition plan for a return to democratic civilian rule, establishing the Provisional Independent Electoral Commission (PIEC) in 1996 to conduct national elections. After a constitutional referendum (in August), presidential and parliamentary elections were held. Jammeh was sworn into office as president on November 6, 1996. The following year, the PIEC transformed into the Independent Electoral Commission (IEC) on April 17.
Jammeh has won both the 2001 and 2006 elections. He is up for re-election in 2011.
The People's Republic of China cut ties with The Gambia in 1995 after the latter established diplomatic links with the Republic of China.
The Gambia accepted a non-permanent seat on the UN Security Council from 1998 to 1999.
See also
- History of Africa
- History of West Africa
- List of heads of government of the Gambia
- List of heads of state of the Gambia
- Politics of Gambia
Notes
- ^ Ibn Battuta: Travels in Asia and Africa 1325-1354 pg323-335
External links
History of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
British Empire and Commonwealth of Nations Legend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of NationsEurope18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1763–1782 Minorca
1798–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands20th century
1921-1937 Irish Free StateNorth America17th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
1607–1776 Virginia
since 1619 Bermuda
1620–1691 Plymouth Colony
1629–1691 Massachusetts Bay Colony
1632–1776 Maryland
1636–1776 Connecticut
1636–1776 Rhode Island
1637–1662 New Haven Colony
1663–1712 Carolina
1664–1776 New York
1665–1674 and 1702-1776 New Jersey
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
1674–1702 East Jersey
1674–1702 West Jersey
1680–1776 New Hampshire
1681–1776 Pennsylvania
1686–1689 Dominion of New England
1691–1776 Massachusetts18th century
1701–1776 Delaware
1712–1776 North Carolina
1712–1776 South Carolina
1713–1867 Nova Scotia
1733–1776 Georgia
1763–1873 Prince Edward Island
1763–1791 Quebec
1763–1783 East Florida
1763–1783 West Florida
1784–1867 New Brunswick
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
1818–1846 Columbia District / Oregon Country1
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1853–1863 Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands
1858–1866 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
1866–1871 Vancouver Island and British Columbia
1867–1931 *Dominion of Canada2
20th century
1907–1949 Dominion of Newfoundland31Occupied jointly with the United States
2In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. see Canada's name.
3Gave up self-rule in 1934, but remained a de jure Dominion until it joined Canada in 1949.Latin America and the Caribbean17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *Saint Kitts.2C 1623 to 1700|St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago
20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation4Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
AfricaAsiaOceania18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land/Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands7
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony/Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1841–1907 Colony of New Zealand
1851–1901 Victoria
1874–1970 Fiji8
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands7
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)7
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands9
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands1020th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue7
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1942 Nauru
1945–1968 Nauru
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea117Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
8Suspended member
9Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
10Now the *Solomon Islands
11Now *Papua New GuineaAntarctica and South Atlantic17th century
since 1659 St. Helena1219th century
since 1815 Ascension Island12
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha12
since 1833 Falkland Islands1320th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory14
since 1908 South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands13, 1412Since 2009 part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Ascension Island (1922—) and Tristan da Cunha (1938—) were previously dependencies of St Helena
13Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982
14Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands)Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.