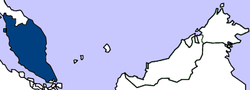
- Malayan Union
-
Malayan Union British colony ↓ 1946–1948  →
→

Flag Coat of arms Capital Kuala Lumpur Language(s) Malay, English Political structure Colony King George VI Governor Sir Edward Gent Historical era Decolonization - Established April 1, 1946 - Disestablished January 31, 1948 Area - 1948 132,364 km2 (51,106 sq mi) Currency Malayan dollar Preceded by Succeeded by 
Federated Malay States 
Straits Settlements 
Johor 
Kedah 
Perlis 
Kelantan 
Terengganu Federation of Malaya 
1 - FMS consisted of Selangor, Perak, Negeri Sembilan and Pahang
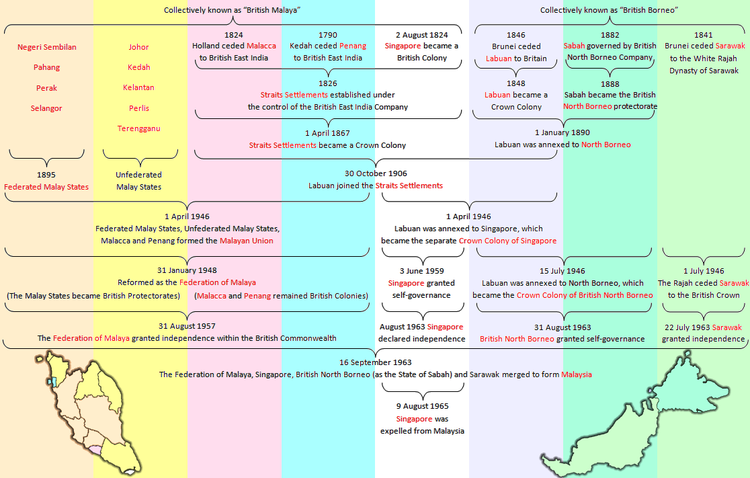
2 - Singapore taken out of the Straits Settlements and made a Crown Colony of its ownThe Malayan Union was a federation of the Malay states and the Straits Settlements of Penang and Malacca. It was the successor to British Malaya and was conceived to unify the Malay Peninsula under a single government so as to simplify administration. The Malayan Union later became the independent Federation of Malaya in 1948. The Federation of Malaya became the Federation of Malaysia in 1963, following the admission of Singapore, Sabah (North Borneo) and Sarawakto the new federation. Singapore left the federation and became independent in 1965.
Contents
Formation of the Malayan Union
On April 1, 1946, the Malayan Union officially came into existence with Sir Edward Gent as its governor. The capital of the Union was Kuala Lumpur.
The idea of the Union was first expressed by the British on October 1945 (plans had been presented to the War Cabinet as early as May 1944)[1] in the aftermath of the Second World War by the British Military Administration. Sir Harold MacMichael was assigned the task of gathering the Malay state rulers' approval for the Malayan Union in the same month. In a short period of time, he managed to obtain all the Malay rulers’ approval. The reasons for their agreement, despite the loss of political power that it entailed for the Malay rulers, has been much debated; the consensus appears to be that the main reasons were that as the Malay rulers were of course resident during the Japanese occupation, they were open to the accusation of collaboration, and that they were threatened with dethronement.[2] Hence the approval was given, though it was with utmost reluctance.
The Malayan Union gave equal rights to people who wished to apply for citizenship. It was automatically granted to people who were born in any state in British Malaya or Singapore and were living there before 15 February 1942, born outside British Malaya or the Straits Settlements only if their fathers were citizens of the Malayan Union and those who reached 18 years old and who had lived in British Malaya or Singapore "10 out of 15 years before 15 February 1942". The group of people eligible for application of citizenship had to live in Singapore or British Malaya "for 5 out of 8 years preceding the application", had to be of good character, understand and speak the English or Malay language and "had to take an oath of allegiance to the Malayan Union".
The Sultans, the traditional rulers of the Malay states, conceded all their powers to the British Crown except in religious matters. The Malayan Union was placed under the jurisdiction of a British Governor, signalling the formal inauguration of British colonial rule in the Malay peninsula. Moreover, even though State Councils were still kept functioning in the former Federated Malay States, it lost the limited autonomy that they enjoyed as they administered some local and less important aspects of government and the Federal government in Kuala Lumpur controlling vital aspects. State Councils became an extended hand of the Federal government that had to do its bidding. Also, British Residents replacing the Sultans as the head of the State Councils meant that the political status of the Sultans were greatly reduced.[3]
Opposition, dissolution of the Malayan Union and the creation of the Federation of Malaya
The Malays generally opposed the creation of the Union. The opposition was due to the methods Sir Harold MacMichael used to acquire the Sultans' approval, the reduction of the Sultans' powers, and the granting of citizenship to non-Malay immigrants and their descendants-especially the ethnic Chinese, not only because of their racial and religious difference but also because their economic dominance was seen as a threat to the Malays. The United Malays National Organization or UMNO, a Malay political association formed by Dato' Onn bin Ja'afar on March 1, 1946, led the opposition against the Malayan Union. Malays also wore white bands around their heads, signifying their mourning for the loss of the Sultans' political rights. However, ex-Malayan government officials criticised the way these constitutional reforms were brought about in Malaya, even saying that it went against the principles of the Atlantic Charter. They also encouraged Malay opposition to the Malayan Union. The fact that people were allowed to hold dual nationalities meant there was a possibility that the Chinese and Indians would be loyal to their home country, rather than Malaya.
After the inauguration of the Malayan Union, the Malays, under UMNO, continued opposing the Malayan Union. They utilised civil disobedience as a means of protest by refusing to attend the installation ceremonies of the British governors. They had also refused to participate in the meetings of the Advisory Councils, hence Malay participation in the government bureaucracy and the political process had totally stopped. The British had recognised this problem and took measures to consider the opinions of the major races in Malaya before making amendments to the constitution. The Malayan Union ceased to exist in January, 1948. It was replaced by the Federation of Malaya.
Evolution towards Malaysia
Gallery
See also
- Bumiputra
Notes
- ^ CAB 66/50 'Policy in Regard to Malaya and Borneo'
- ^ Ariffin Omar, Bangsa Melayu: Malay Concepts of Democracy and Community, 1945-1950 (Kuala Lumpur: Oxford University Press, 1993), p. 46. Cited in Ken'ichi Goto, Tensions of Empire: Japan and Southeast Asia in the Colonial and Postcolonial World (Athens: Ohio University Press, 2003), p. 222
- ^ [1]
References
- Zakaria Haji Ahmad. Government and Politics (1940-2006). p.p 30-21. ISBN 981-3018-55-0.
- Marissa Champion. Odyssey: Perspectives on Southeast Asia - Malaysia and Singapore 1870-1971. ISBN 9971-0-7213-0
- Sejarah Malaysia[2]
British Empire and Commonwealth of Nations Legend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of NationsEurope18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1763–1782 Minorca
1798–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands20th century
1921-1937 Irish Free StateNorth America17th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
1607–1776 Virginia
since 1619 Bermuda
1620–1691 Plymouth Colony
1629–1691 Massachusetts Bay Colony
1632–1776 Maryland
1636–1776 Connecticut
1636–1776 Rhode Island
1637–1662 New Haven Colony
1663–1712 Carolina
1664–1776 New York
1665–1674 and 1702-1776 New Jersey
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
1674–1702 East Jersey
1674–1702 West Jersey
1680–1776 New Hampshire
1681–1776 Pennsylvania
1686–1689 Dominion of New England
1691–1776 Massachusetts18th century
1701–1776 Delaware
1712–1776 North Carolina
1712–1776 South Carolina
1713–1867 Nova Scotia
1733–1776 Georgia
1763–1873 Prince Edward Island
1763–1791 Quebec
1763–1783 East Florida
1763–1783 West Florida
1784–1867 New Brunswick
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
1818–1846 Columbia District / Oregon Country1
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1853–1863 Colony of the Queen Charlotte Islands
1858–1866 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
1866–1871 Vancouver Island and British Columbia
1867–1931 *Dominion of Canada2
20th century
1907–1949 Dominion of Newfoundland31Occupied jointly with the United States
2In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. see Canada's name.
3Gave up self-rule in 1934, but remained a de jure Dominion until it joined Canada in 1949.Latin America and the Caribbean17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands4
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *Saint Kitts.2C 1623 to 1700|St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago
20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation4Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
AfricaAsiaOceania18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land/Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands7
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony/Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1841–1907 Colony of New Zealand
1851–1901 Victoria
1874–1970 Fiji8
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands7
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)7
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands9
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands1020th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue7
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1942 Nauru
1945–1968 Nauru
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea117Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
8Suspended member
9Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
10Now the *Solomon Islands
11Now *Papua New GuineaAntarctica and South Atlantic17th century
since 1659 St. Helena1219th century
since 1815 Ascension Island12
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha12
since 1833 Falkland Islands1320th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory14
since 1908 South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands13, 1412Since 2009 part of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Ascension Island (1922—) and Tristan da Cunha (1938—) were previously dependencies of St Helena
13Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982
14Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands)Categories:- Former countries in Southeast Asia
- Former British colonies
- States and territories established in 1946
- States and territories disestablished in 1948
- 1948 disestablishments
- Former countries in Malaysian history
- British Malaya
- 1946 in Malaya
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.