- Antonine Wall
-
For the Military Way associated with Hadrian's Wall, see Military Way (Hadrian's Wall).
 Location of the Antonine Wall and Hadrian's Wall in Scotland and Northern England
Location of the Antonine Wall and Hadrian's Wall in Scotland and Northern England

This article is part of the series on:
Military of ancient Rome (portal)
753 BC – AD 476Structural history Roman army (unit types and ranks, legions, auxiliaries, generals) Roman navy (fleets, admirals) Campaign history Lists of wars and battles Decorations and punishments Technological history Military engineering (castra, siege engines, arches, roads) Political history Strategy and tactics Infantry tactics Frontiers and fortifications (limes, Hadrian's Wall) The Antonine Wall is a stone and turf fortification built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Forth and the Firth of Clyde. Representing the northernmost frontier barrier of the Roman Empire, it spanned approximately 39 miles (63 km) and was about ten feet (3 m) high and fifteen feet (5 m) wide. Security was bolstered by a deep ditch on the north side. The barrier was the second of two "great walls" created by the Romans in Caledonia. Its ruins are less evident than the better known Hadrian's Wall to the south.
Construction began in AD 142 at the order of Roman Emperor Antoninus Pius, and took about twelve years to complete. Pressure from the Caledonians may have led Antoninus to send the empire's troops farther north. The wall was protected by sixteen forts with a number of small fortlets between them; troop movement was facilitated by a road linking all the sites known as the Military Way. The soldiers who built the wall commemorated the construction and their struggles with the Caledonians in a number of decorative slabs, twenty of which still survive. Despite this auspicious start the wall was abandoned after only twenty years, and the garrisons relocated back to Hadrian's Wall. In 208 Emperor Septimius Severus re-established legions at the wall and ordered repairs; this has led to the wall being referred to as the Severan Wall. However, the occupation ended only a few years later, and the wall was never fortified again. Most of the wall and its associated fortifications have been destroyed over time, but some remains are still visible. Many of these have come under the care of Historic Scotland and the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
Contents
Location and construction
Roman Emperor Antoninus Pius ordered the construction of the Antonine Wall around AD 142.[1] Quintus Lollius Urbicus, governor of Roman Britain at the time, initially supervised the effort, which took about twelve years to complete.[2] The wall stretches 39 miles (63 km) from Old Kilpatrick in West Dunbartonshire on the Firth of Clyde to Carriden near Bo'ness on the Firth of Forth. The wall was intended to extend Roman territory and dominance by replacing Hadrian's Wall 100 miles (160 km) to the south, as the frontier of Britannia. But while the Romans did establish many forts and temporary camps further north of the wall in order to protect their routes to the north of Scotland, they did not conquer the Caledonians, and the Antonine Wall suffered many attacks. The Romans called the land north of the wall Caledonia, though in some contexts the term may refer to the whole area north of Hadrian's Wall.
The Antonine Wall, looking east, from Barr Hill between Twechar and Croy
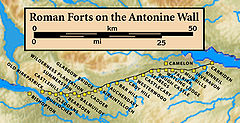
The Antonine Wall was shorter than Hadrian's Wall and built of turf on a stone foundation rather than of stone, but it was still an impressive achievement. The stone foundations and wing walls of the original forts demonstrate that the original plan was to build a stone wall similar to Hadrian's Wall, but this was quickly amended. As built, the wall was typically a bank, about four metres (13 feet) high, made of layered turves and occasionally earth with a wide ditch on the north side, and a military way on the south. The Romans initially planned to build forts every six miles (10 km), but this was soon revised to every two miles (3.3 km), resulting in a total of nineteen forts along the wall. The best preserved but also one of the smallest forts is Rough Castle Fort. In addition to the forts, there are at least 9 smaller fortlets, very likely on roman mile spacings, which formed part of the original scheme, some of which were later replaced by forts.[3] The most visible fortlet is Kinneil, at the eastern end of the Wall, near Bo'ness.[4]
In addition to the line of the Wall itself there are a number of coastal forts both in the East (e.g. Inveresk) and West (Outerwards and Lurg Moor), which should be considered as outposts and/or supply bases to the Wall itself. In addition a number of forts farther north were brought back into service in the Gask Ridge area, including Ardoch, Strageath, Bertha[3] and probably Dalginross and Cargill.[5]
Abandonment
The wall was abandoned after only twenty years, when the Roman legions withdrew to Hadrian's Wall in AD 162 (although there is evidence to suggest that they left the wall in AD 158/60, its reliability is unclear), and over time reached an accommodation with the Brythonic tribes of the area who they fostered as the buffer states which would later become "The Old North". After a series of attacks in AD 197, Emperor Septimius Severus arrived in Scotland in AD 208 to secure the frontier, and repaired parts of the wall. Although this re-occupation only lasted a few years, the wall is sometimes referred to by later Roman historians as the Severan Wall. This led to later scholars like Bede mistaking references to the Antonine Wall for ones to Hadrian's Wall.
Post-Roman history
Grim's Dyke
In medieval histories, such as the chronicles of John of Fordun, the wall is called Gryme's dyke. Fordun says that the name came from the grandfather of the imaginary king Eugenius son of Farquahar. This was corrupted into Graham's dyke – a name still found in Bo'ness at the wall's eastern end – and then linked with Clan Graham. Of note is that Graeme in some parts of Scotland is a nickname for the devil, and Gryme's Dyke would thus be the Devil's Dyke, mirroring the name of the Roman Limes in Southern Germany often called 'Teufelsmauer'. Grímr and Grim are bynames for Odin or Wodan, who might be credited with the wish to build earthworks in unreasonably short periods of time. This name is the same one found as Grim's Ditch several times in England in connection with early ramparts: for example, near Wallingford, Oxfordshire or between Berkhamsted (Herts) and Bradenham (Bucks). Other names used by antiquarians include the Wall of Pius and the Antonine Vallum, after Antoninus Pius.[6][7]
World Heritage Status
The UK government's nomination of the Antonine Wall for World Heritage status to the international conservation body UNESCO was first officially announced in 2003.[8] It has been backed by the Scottish Government since 2005[9] and by Scotland's then Culture Minister Patricia Ferguson since 2006.[10] It became the UK's official nomination in late January 2007,[11] and MSPs were called to support the bid anew in May 2007.[12] The Antonine Wall was listed as an extension to the World Heritage Site "Frontiers of the Roman Empire" on 7 July 2008.[13][14] Though the Antonine is mentioned in text, it makes no appearance on the map of UNESCO's map of world heritage properties.[15]
Historic Scotland
Several individual sites along the line of the wall are in the care of Historic Scotland. These are:
- Bar Hill Fort
- Bearsden Bath House
- Castlecary
- Croy Hill
- Dullatur
- Rough Castle
- Seabegs Wood
- Watling Lodge
- Westerwood
All sites are unmanned and open at all reasonable times.[16]
Mapping the wall
The first capable effort to systematically map the Antonine Wall was undertaken in 1764 by William Roy,[17] of Ordnance Survey fame. He provided accurate and detailed drawings of its remains, and where the wall has been destroyed by later development, his maps and drawings are now the only reliable record of it.
In fiction
The Northern Wall is depicted in some of Rosemary Sutcliff's historical fiction novels; as a fully functioning outpost of Roman power in The Mark of the Horse Lord, and as an abandoned ruin in Frontier Wolf.
In Max Brooks's post-apocalyptic novel World War Z, the Antonine Wall marks the line at which the British establish their defense against the zombies and the beginning of their free zone.
See also
- Hadrian's Wall
- Gask Ridge
- Trimontium
- Scotland during the Roman Empire
- World Heritage Sites in Scotland
- National Museums of Scotland
References
- ^ Robertson, Anne S. (1960) The Antonine Wall. Glasgow Archaeological Society. p. 7.
- ^ Breeze, David J. (2006) The Antonine Wall. Edinburgh. John Donald. ISBN 0859766551 p. 167.
- ^ a b L.Keppie, Scotland's Roman Remains. Edinburgh 1986)
- ^ Kinneil Estate Feature Page on Undiscovered Scotland
- ^ D.J.Woolliscroft & B.Hoffmann, Romes First Frontier. The Flavian occupation of Northern Scotland (Stroud: Tempus 2006)
- ^ Earthwork of England: prehistoric, Roman, Saxon, Danish, Norman and mediæval - Page 496, by Arthur Hadrian Allcroft
- ^ 'Transactions of the Woolhope Naturalists' Field Club - Page 255, by Woolhope Naturalists' Field Club, Hereford, England, G. H. Jack, 1905
- ^ "Roman wall builds heritage claim". BBC News. 22 February 2003. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/2789239.stm. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
- ^ "Roman wall heritage bid backing". BBC News. 14 June 2005. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/4090692.stm. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
- ^ "World Heritage bid hope for wall". BBC News. 20 June 2006. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/5100616.stm. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
- ^ "World Heritage support for wall". BBC News. 23 January 2007. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/tayside_and_central/6290053.stm. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
- ^ "MSPs called to support Roman wall". BBC News. 23 May 2007. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/scotland/tayside_and_central/6683339.stm. Retrieved 2007-05-24.
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre. New Inscribed Properties
- ^ "Wall gains World Heritage status'" BBC News. Retrieved 8 July 2008.
- ^ Frontiers of the Roman Empire - UNESCO World Heritage Centre
- ^ Historic Scotland - Antonine Wall: Overview Property Detail
- ^ Hübner, Emil (1886). "The Roman Annexation of Britain". In Hodgkin, Thomas. Archaeologia Aeliana. New. XI. Newcastle-Upon-Tyne: Society of Antiquaries of Newcastle upon Tyne. pp. 82–116. http://books.google.com/?id=4_4RAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA82.
External links
- Antonine Wall - site information from Historic Scotland
- http://www.antoninewall.org/
- http://www.antonineway.co.uk
- http://www.historic-scotland.gov.uk/antoninewall
- [1][dead link]
- http://www.kinneil.org.uk/attractions
- http://www.athenapub.com/antwall1.htm
- http://www.athenapub.com/britsite/hillfoot.htm
- http://www.theromangaskproject.org.uk/
- http://www.roman-britain.org/frontiers/antonine.htm
- http://www.almac.co.uk/FalkirkTCM/Rome.htm
- The Antonine Wall and Barr Hill
- Richard Stillwell, ed. Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites, 1976: "Antonine Wall, Scotland"
- Museum news
- Information on the Antonine Wall - Clyde Waterfront Heritage
World Heritage Sites in the United Kingdom England Bath · Blenheim Palace · Canterbury Cathedral, St. Augustine's Abbey and St. Martin's Church · Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape · Derwent Valley Mills · Durham Castle and Cathedral · Frontiers of the Roman Empire (Hadrian's Wall) · Ironbridge Gorge · Jurassic Coast · Kew Gardens · Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City · Maritime Greenwich · Saltaire · Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites · Studley Royal Park and Fountains Abbey · Tower of London · Westminster Palace, Westminster Abbey and St. Margaret's Church
Scotland Edinburgh Old Town and New Town · Frontiers of the Roman Empire (Antonine Wall) · Heart of Neolithic Orkney · New Lanark · St. Kilda
Wales Northern Ireland British Overseas Territories Categories:- Historic Scotland properties
- Antonine Wall
- 2nd-century architecture
- Archaeological sites in East Dunbartonshire
- Archaeological sites in North Lanarkshire
- Archaeological sites in Falkirk
- Fortification
- Nerva-Antonine Dynasty
- Separation barriers
- Walls in Scotland
- Roman frontiers
- Roman military architecture
- World Heritage Sites in Scotland
- Roman sites in Scotland
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.