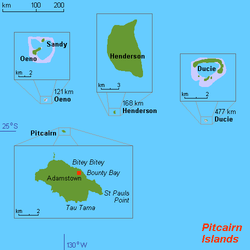
- Geography of the Pitcairn Islands
-
The Pitcairn Islands consist of four islands: Pitcairn Island, Oeno Island, Henderson Island and Ducie Island:
Pitcairn Islands as a group of islands (25°04′00″S 130°05′00″W / 25.0666667°S 130.0833333°WCoordinates: 25°04′00″S 130°05′00″W / 25.0666667°S 130.0833333°W)
- Pitcairn Island (main island) (25°04′S 130°06′W / 25.067°S 130.1°W)
- Henderson Island (24°22′01″S 128°18′57″W / 24.36694°S 128.31583°W)
- Ducie Island (24°40′09″S 124°47′11″W / 24.66917°S 124.78639°W)
- Oeno Island (23°55′26″S 130°44′03″W / 23.92389°S 130.73417°W)
Pitcairn Island is a volcanic high island. Henderson Island is an uplifted coral island. Ducie and Oeno are coral atolls.
The only inhabited island, Pitcairn, has an area of 5 km2 (1.9 sq mi) and a population density of 10/km²; it is only accessible by boat through Bounty Bay.
The other islands are at a distance of more than 100 km (62 mi). Wikimedia Atlas of the Pitcairn Islands
Contents
Location
Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about one-half of the way from Peru to New Zealand, one of the most remote sites of human habitation on Earth.[1][2]
The inhabited island, Pitcairn, is at 25.04 south, 130.06 west. Pitcairn is about 2,170 kilometres (1,350 mi) southeast of Tahiti, 5,310 kilometres (3,300 mi) from Auckland, New Zealand, and over 6,600 kilometres (4,100 mi) from Panama.[3]
Area
Total: 47 km²
Land: 47 km²
Water: 0 km²Pitcairn Island is about 3.2 kilometres (2.0 mi) long and {{convert|1.6|km|mi]} wide.[3]
Area - comparative
About 0.3 times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries
0 km
Coastline
51 km
Maritime claims
Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi
Territorial sea: 3 nmiClimate
Tropical, hot, humid; modified by southeast trade winds; rainy season (November to March)
Terrain
Rugged volcanic formation; rocky coastline with cliffs
Elevation extremes
Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Highest point: Pawala Valley Ridge 347 m (1,138 ft)Natural resources
Miro trees (used for handicrafts), fish
Note: manganese, iron, copper, gold, silver, and zinc have been discovered offshoreNatural hazards
Typhoons (especially November to March)
Environment - current issues
Deforestation (only a small portion of the original forest remains because of burning and clearing for settlement)
See also
Maps
Worldwide map services show very little detail of the islands, and are even of limited use to show the location of them with respect to each other and to other islands, because they are so small and far apart. However, Mapquest zoom level 1 is a suitable map to see the location between Peru and New Zealand. See also map showing location of the Pitcairn Islands with respect to other island groups and to continents
For the location with respect to French Polynesia, see the inset of Image:French Polynesia map.jpg.
References
- ^ Shadle, Robert (1996). Historical Dictionary of the British Empire. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 890. ISBN 978-0-313-29367-2. http://books.google.com/books?id=f0VnzMelzm8C&pg=PA890. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Ntumy, Michael A. (1993). South Pacific islands legal systems. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 252. ISBN 978-0-8248-1438-0. http://books.google.com/books?id=AwTIfVhFA2gC&pg=PA252. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ a b "Home." Government of the Pitcairn Islands. Retrieved on October 31, 2011.
 Pitcairn Islands topics
Pitcairn Islands topicsIslands and settlement 
Culture Main topics Geography of Oceania Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.