- Collectivity of Saint Martin
-
"Saint-Martin" redirects here. For other uses, see St. Martin (disambiguation).
Collectivity of Saint Martin Collectivité de Saint-Martin

Flag Coat of arms Anthem: La Marseillaise Capital
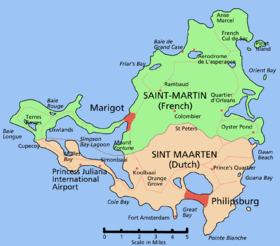
(and largest city)Marigot Official language(s) French Ethnic groups Mulatto, West African, Mestizo (French-East Asia), European, East Indian[1] Government Dependent territory - President of France Nicolas Sarkozy - Prefect Jacques Simonnet - President of the Territorial Council Frantz Gumbs Overseas collectivity of France - Island divided between France and the Netherlands 23 March 1648 - as separate Collectivity 15 July 2007 Area - Total 53.2 km2 (not ranked)
20.5 sq mi- Water (%) negligible Population - Jan. 1, 2008 census 36,661[2] - Density 675/km2 (not ranked)
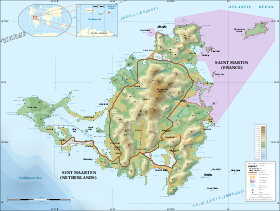
1,749/sq miHDI (2003) n/a (unranked) (n/a) Currency Euro (€) ( EUR)Time zone (UTC-4) Internet TLD .mf assigned but not in use, .fr and .gp in use Calling code 590 Saint Martin (French: Saint-Martin), officially the Collectivity of Saint Martin (French: Collectivité de Saint-Martin) is an overseas collectivity of France located in the Caribbean. It came into being on 15 July 2007,[3] encompassing the northern parts of Saint Martin island and neighbouring islets, the largest of which is Île Tintamarre. The southern part of the island, Sint Maarten, is one of the four constituent countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
Contents
Politics and government
Saint Martin was for many years a French commune forming part of Guadeloupe, which is an overseas région and département of France and is therefore in the European Union. In 2003 the population of the French part of the island voted in favour of secession from Guadeloupe in order to form a separate overseas collectivity (COM) of France.[4] On 9 February 2007, the French Parliament passed a bill granting COM status to both the French part of Saint Martin and (separately) the neighbouring Saint Barthélemy.[5] The new status took effect once the local assembly was elected on 15 February 2007.[6] Saint Martin remains part of the European Union.[7]
The new governance structure befitting an overseas collectivity took effect on 15 July 2007 with the first session of the Territorial Council (French: Conseil territorial) and the election of Louis-Constant Fleming as president of the Territorial Council. On 25 July 2008 Fleming resigned after being sanctioned by the Conseil d'État for one year over problems with his 2007 election campaign.[8] On 7 August, Frantz Gumbs was elected as President of the Territorial Council.[9] However, his election was declared invalid on 10 April 2009 and Daniel Gibbs appointed as Acting President of the Territorial Council on 14 April 2009.[10] However, Gumbs was reelected on 5 May 2009.[11]
Before 2007, Saint Martin was coded as GP (Guadeloupe) in ISO 3166-1. In October 2007, it received the ISO 3166-1 code MF (alpha-2 code), MAF (alpha-3 code), and 663 (numeric code).[12]
Summary of the 1 July and 8 July 2007 Saint Martin Territorial Council election results Parties 1st round 2nd round Seats Votes % Votes % Union for Progress/UMP (Union pour le Progrès, Louis Constant-Fleming) 2,829 40.35 3,753 48.96 16 Rally Responsibility Success (Rassemblement responsabilité réussite, Alain Richardson) 2,237 31.90 3,231 42.15 6 Succeed Saint Martin (Réussir Saint-Martin, Jean-Luc Hamlet) 767 10.94 681 8.89 1 Alliance (Alliance, Dominique Riboud) 635 9.05 — — — Democratic Alliance for Saint Martin (Alliance démocratique pour Saint-Martin, Wendel Cocks) 544 7.76 — — — Total 7,012 100.00 7,665 100.00 23 Source: RFO1, RFO2 Coat of arms
The coat of arms of the French overseas collectivity Saint-Martin features a ship, a palm and a sun, and reads "Collectivité de Saint Martin".[13] The comune that existed until February 22, 2007, used similar arms but with the legend "Ville de Saint Martin".[14] [15]
Demographics
The French part of the island has a land area of 53.20 square kilometres (20.5 sq mi). A local English-based dialect is spoken in informal situations on both the French and Dutch sides of the island.[16] At the January 2007 French census, the population in the French part of the island was 35,925 (up from only 8,072 inhabitants at the 1982 census), which means a population density of 675 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,750 /sq mi) in 2007.
Historical population 1885 1961 1967 1974 1982 1990 1999 2006 2007 3,400 4,502 5,061 6,191 8,072 28,518 29,078 35,263 35,925 Official figures from French censuses. Economy
The official currency of Saint Martin is the euro, though the US dollar is also widely accepted. Tourism is the main economic activity.
INSEE estimated that the total GDP of Saint Martin amounted to 421 million euros in 1999 (US$449 million at 1999 exchanges rates; US$599 million at Oct. 2007 exchange rates).[17] In that same year the GDP per capita of Saint Martin was 14,500 euros (US$15,500 at 1999 exchanges rates; US$20,600 at Oct. 2007 exchange rates), which was 39% lower than the average GDP per capita of metropolitan France in 1999.[17] In comparison, the GDP per capita on the Dutch side of the island, Sint Maarten, was 14,430 euros in 2004.[18]
More information at Economy of Saint Martin (collectivity)
Maps
 Map showing the former constituent parts of the Guadeloupe region/department among the Leeward Islands, including Saint-Martin, before February 2007.
Map showing the former constituent parts of the Guadeloupe region/department among the Leeward Islands, including Saint-Martin, before February 2007.
See also
- Caribbean
- Leeward Islands
- Saint Martin
- Collectivity of Saint Martin
- France
- Overseas departments and territories of France
- Région Guadeloupe et Saint Martin (Scouting)
- Overseas departments and territories of France
- France
- Sint Maarten
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- List of Sint Maarten governors
- Princess Juliana International Airport
- Maho Beach, famous viewing area for airport takeoffs and landings.
- Collectivity of Saint Martin
- Culture of St. Martin
- O sweet Saint-Martin's Land (bi-national song/anthem of Saint-Martin/Sint-Maarten)
- History of St. Martin
- Saint Martin
- Leeward Islands
- List of divided islands
References
- ^ World factbook Saint Martin
- ^ INSEE, Government of France. "Populations légales 2008 pour les départements et les collectivités d'outre-mer". http://www.insee.fr/fr/ppp/bases-de-donnees/recensement/populations-legales/france-departements.asp?annee=2008. Retrieved 31 December 2010. (French)
- ^ The French law was passed in February 2007, but the new status came in force once the local assemblies elected, with second leg of the vote on 15th July 2007. See J. P. Thiellay, Droit des outre-mers, Paris:Dalloz, 2007.
- ^ "French Caribbean voters reject change". Caribbean Net News. 9 December 2003. http://www.caribbeannetnews.com/2003/12/09/voters.htm. Retrieved 9 February 2007. "However voters on the two tiny French dependencies of Saint-Barthelemy and Saint-Martin, which have been administratively attached to Guadeloupe, approved the referendum and are set to acquire the new status of "overseas collectivity"."
- ^ "Saint-Barth To Become An Overseas Collectivity" (PDF). St. Barth Weekly. 9 February 2007. p. 2. http://www.st-barths.com/jsb/pdf_files/weekly107.pdf. Retrieved 9 February 2007.
- ^ Les élections du futur conseil territorial font débat - Politique - Nouvelles sur Newmedia.fr - New Media : Infos Guadeloupe, Martinique, Guyane, Saint-Martin, Saint-Barthelémy, Caraïbes - Infos Newmedia.fr
- ^ The Treaty of Lisbon states that Saint-Martin is a part of the EU. See: "Treaty of Lisbon, Article 349 and 355". http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:C:2008:115:0047:0199:EN:PDF. Retrieved 18 March 2010..
- ^ "Louis-Constant Fleming démissionné par le conseil d’Etat" (in french). fxgpariscaraibe. 28 July 2008. http://www.fxgpariscaraibe.com/article-21561959.html. Retrieved 17 August 2008.
- ^ "Frantz Gumbs elected new president of Collectivité". The Daily Herald. 8 August 2008. http://news.caribseek.com/Sint_Maarten/The_Daily_Herald/article_68029.shtml. Retrieved 17 August 2008. "Frantz Gumbs, formerly president of Union Pour le Progrès (UPP) party, swept into power as new president of the Collectivité at an extraordinary meeting of the Territorial Council on Thursday after winning the 23-councillor vote with a clear majority over Marthe Ogoundélé-Tessi."
- ^ http://www.thedailyherald.com/news/daily/l278/shamel278.html
- ^ http://rulers.org/2009-05.html
- ^ ISO 3166-1 Newsletter. Assignment of code elements for Saint Barthélemy and Saint Martin and update of France and other French Territories
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ [3]
- ^ Holm (1989) Pidgins and Creoles, vol. 2
- ^ a b (French) INSEE, CEROM. "Estimation du PIB de Saint-Barthélemy et de Saint-Martin" (PDF). http://www.insee.fr/fr/insee_regions/guyane/publi/PIB_IDN.pdf. Retrieved 13 November 2007.
- ^ Total 2004 GDP of Sint Maarten ([4]) divided by the number of inhabitants in 2004 ([5]), then converted from Netherlands Antillean gulden to euro by using the 2004 exchange rate.
External links
- Official website of the Collectivity of Saint Martin
- Official website of the Tourist Office of Saint Martin
- Wikimedia Atlas of Saint Martin (France)
- Saint Martin (France) travel guide from Wikitravel
- Saint Martin entry at The World Factbook
Countries and territories of the Caribbean Sovereign states Other republicsDependencies and other areas by parent state United KingdomNetherlandsAruba · Bonaire · Curaçao · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint MaartenFranceGuadeloupe · Martinique · St. Barthélemy · St. MartinUnited StatesCountries and dependencies of North America Sovereign states - Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Canada
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- France (Guadeloupe · Martinique)
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Netherlands (Bonaire · Saba · Sint Eustatius)
- Panama
- St. Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- St. Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
Dependencies DenmarkFranceNetherlandsUnited KingdomUnited States Overseas departments and territories of France
Overseas departments and territories of FranceInhabited areas  Special status
Special statusUninhabited areas Pacific Ocean French Southern and
Antarctic LandsBanc du Geyser4 · Bassas da India4 · Europa Island4 · Glorioso Islands3, 4, 5 · Juan de Nova Island4 · Tromelin Island4, 51 Also known as overseas regions. 2 Claimed by Comoros. 3 Claimed by Madagascar. 4 Claimed by Seychelles. 5 Claimed by Mauritius.Dependencies of European Union states 
Denmark France United Kingdom Anguilla · Bermuda · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Gibraltar · Montserrat · Pitcairn Islands · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands · Turks and Caicos IslandsOutlying territories of European countries Territories under European sovereignty but closer to or on continents other than Europe (see inclusion criteria for further information)Denmark France Clipperton Island · French Guiana · French Polynesia · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Mayotte · New Caledonia · Réunion · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Wallis and FutunaItaly Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain United
KingdomAnguilla · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Navassa Island
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
Climate of North America Sovereign states - Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Canada
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
Categories:- Collectivity of Saint Martin
- Caribbean countries
- Overseas departments, collectivities and territories of France
- Dependent territories in North America
- Special territories of the European Union
- States and territories established in 2007
- Caribbean
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.