- Plazas de soberanía
-
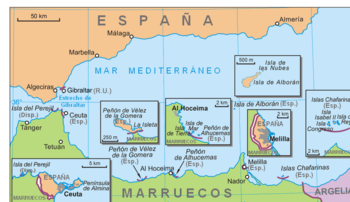
The plazas de soberanía (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈplaθaz ðe soβeɾaˈni.a]) or sovereign territories, referred to in English as Spanish North Africa or simply Spanish Africa, are the current Spanish territories in continental North Africa bordering Morocco, except the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla.
After the Reconquista, forces of the Spanish and Portuguese Kingdoms conquered and maintained numerous posts in North Africa for trade and as a defence against piracy. Many of them, such as Oran, have been lost, and nowadays, with an approximate population of 145,000 people (with Ceuta and Melilla), only the Islas Chafarinas, the Peñón de Alhucemas and the Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera are still part of Spain.
Contents
Physical geography
 Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, seen from the Moroccan coast.
Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, seen from the Moroccan coast.
There are historically three sovereign territories: the Islas Chafarinas, Peñón de Alhucemas, and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera.
Apart from those, Isla Perejil, a small uninhabited islet close to Ceuta that was the subject of a confrontation with Morocco in 2002, has been lately defined[who?] as an extra sovereign territory. It is not a sovereign territory in itself but, rather, no-man's land.[citation needed] The Isla de Alborán, another small island in the western Mediterranean, about 50 kilometres from the Moroccan coast and 90 kilometres from Spain, is attached to the municipality of Almería.
Political geography
The sovereign territories are tiny islets or peninsulas on the coast of Morocco which have no civilian population. They are guarded by military garrisons and administered directly by the Spanish government. As part of Spain, they are also part of the European Union, and their currency is the euro.
History
In 1481 the Papal bull Æterni regis had granted all land south of the Canary Islands to Portugal. Only this archipelago and the possessions of Santa Cruz de la Mar Pequeña (1476–1524), Melilla (conquered by Pedro de Estopiñán in 1497), Villa Cisneros (founded in 1502 in current Western Sahara), Mazalquivir (1505), Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera (1508), Oran (1509–1790), Algiers (1510–29), Bugia (1510–54), Tripoli (1511–51), Tunis (1535–69) and Ceuta (ceded by Portugal in 1668) remained as Spanish territory in Africa.
In 1848, Spanish troops conquered the Islas Chafarinas.
When Spain relinquished its protectorate over the North of Morocco, Spanish Morocco, and recognized Morocco's independence in 1956, it did not give up the sovereign territories, since Spain had held them since before the establishment of its protectorate.
On July 11, 2002, Morocco stationed six navy cadets on Isla Perejil to tackle illegal immigration which was at the time a source of complaint by Spain. The Spanish Armed Forces responded by launching a military operation code-named Operation Romeo-Sierra. The attack was carried out by Spanish commandos of Grupo de Operaciones Especiales. The Spanish Navy and Spanish Air Force provided support, the six Moroccan navy cadets did not offer any resistance and were captured and evicted from the island, which has since been evacuated by both countries.
See also
References
 Spain topics
Spain topicsHistory Prehistoric Iberia · Roman Hispania · Medieval Spain · Union · Expansion · Enlightenment · Reaction and revolution · First Spanish Republic · Restoration · Second Spanish Republic · Civil War · Spain under Franco · Transition to democracy · Modern SpainGeography Autonomous communities · Autonomous cities · Sovereign territories · Provinces · Comarcas · Municipalities · Islands · Extreme points · National Parks · Forests · ClimateGovernance Constitution · Monarch · Government · General Courts · Human rights · Foreign relations · Military · LGBT rightsPolitics Economy Society Culture Architecture · Art · Languages · Literature · Cuisine · Tapas · Wines · Music · Bullfighting · Cinema · Myths and legends · Public holidays · International Fiestas · National Fiestas · Toro de Osborne · Nationalisms and regionalisms · SportPortal Autonomies of Spain Autonomous communities 
Autonomous cities Plazas de soberanía Outlying territories of European countries Territories under European sovereignty but closer to or on continents other than Europe (see inclusion criteria for further information) Denmark France Italy Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain Canary Islands · Ceuta · Melilla · Plazas de soberanía (Islas Chafarinas • Peñón de Alhucemas • Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera)United
KingdomAnguilla · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsCategories:- Plazas de soberanía
- Spanish Africa
- Subdivisions of Spain
- Mediterranean
- Territorial disputes of Spain
- Territorial disputes of Morocco
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.