- Madeira
-
Madeira Autonomous Region (Região Autonoma) The fireworks celebrations ringing in the New Year; Madeira is known for its annual New Year's fireworks displayFlagSymbolOfficial name: Região Autonoma da Madeira Name origin: madeira, Portuguese for wood Motto: Das ilhas, as mais belas e livres
(Of all islands, the most beautiful and free)Nickname: Pérola do Atlântico
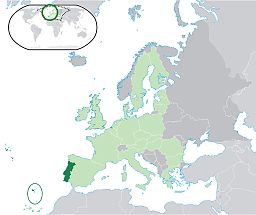
(Pearl of the Atlantic)Country  Portugal
PortugalAutonomous Region  Madeira
MadeiraRegion Atlantic Ocean Subregion Tore-Madeira Ridge Position Madeira Platform,
Savage Islands submarine mountIslands Madeira, Porto Santo, Desertas, Selvagem Municipalities Calheta, Câmara de Lobos, Funchal, Machico, Ponta do Sol, Porto Moniz, Porto Santo, Ribeira Brava, Santa Cruz, Santana, São Vicente Capital Funchal Largest city Funchal - coordinates 32°39′4″N 16°54′35″W / 32.65111°N 16.90972°W Highest point Pico Ruivo - location Paul da Serra, Santana, Madeira - elevation 1,862 m (6,109 ft) Lowest point Sea level - location Atlantic Ocean, Madeira - elevation 0 m (0 ft) Area 801 km2 (309 sq mi) Population 267,938 (2011) Estimate[1] 
Density 308.5 / km2 (799 / sq mi) Settlement c. 1420 - Administrative autonomy c. 1895 - Political autonomy 4 September 1976 Discovery c. 1415 Management - location Assembleia Regional, Sé, Funchal - elevation 16 m (52 ft) - coordinates 32°38′49.96″N 16°54′29.59″W / 32.6472111°N 16.9082194°W Government - location Quinta Vigia, Sé, Funchal - elevation 51 m (167 ft) - coordinates 32°38′42.39″N 16°54′57.16″W / 32.6451083°N 16.9158778°W President (Government) Alberto João Jardim (PPD-PSD) - President (Assembleia) José Miguel Jardim d´Olival de Mendonça (PPD-PSD) Timezone WET (UTC0) - summer (DST) WEST (UTC+1) ISO 3166-2 code PT-30 Postal code 9XXX-XXX Area code (+351) 291 XXX XXX ccTLD .pt Date format dd-mm-yyyy Drive right-side Demonym Madeiran; Madeirense Patron Saint Nossa Senhora do Monte Holiday 1 July Anthem A Portuguesa (national)
Hino da Madeira (regional)Currency Euro (€)[2] Gross domestic product (PPP) € 6,361 billion[3]  (2008)
(2008)Per capita GDP € 25,800-$35,589[3] 
Wikimedia Commons: Madeira Statistics: Instituto Nacional de Estatística[4] Website: www.gov-madeira.pt Geographic detail from CAOP (2010)[5] produced by Instituto Geográfico Português (IGP) Madeira (
 /məˈdɪərə/ mə-deer-ə or /məˈdɛərə/ mə-dair-ə; Portuguese: [mɐˈðejɾɐ] or [mɐˈðɐjɾɐ]) is a Portuguese archipelago that lies between 32°22.3′N 16°16.5′W / 32.3717°N 16.275°W and 33°7.8′N 17°16.65′W / 33.13°N 17.2775°W, just under 400 km north of Tenerife, Canary Islands, in the north Atlantic Ocean and an outermost region of the European Union.[6] The archipelago comprises the major part of one of the two Autonomous regions of Portugal (the other being the Azores located to the northwest), that includes the islands of Madeira, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands.
/məˈdɪərə/ mə-deer-ə or /məˈdɛərə/ mə-dair-ə; Portuguese: [mɐˈðejɾɐ] or [mɐˈðɐjɾɐ]) is a Portuguese archipelago that lies between 32°22.3′N 16°16.5′W / 32.3717°N 16.275°W and 33°7.8′N 17°16.65′W / 33.13°N 17.2775°W, just under 400 km north of Tenerife, Canary Islands, in the north Atlantic Ocean and an outermost region of the European Union.[6] The archipelago comprises the major part of one of the two Autonomous regions of Portugal (the other being the Azores located to the northwest), that includes the islands of Madeira, Porto Santo, and the Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands.Madeira was re-discovered by Portuguese sailors in the service of Infante D. Henrique (Henry the Navigator) in 1419, and settled after 1420. The archipelago is considered to be the first territorial discovery of the exploratory period of the Portuguese Age of Discovery.
Today, it is a popular year-round resort, being visited every year by about one million tourists,[7] noted for its Madeira wine, flowers, landscapes and embroidery artisans, as well as for its annual New Year celebrations that feature the largest fireworks show in the world, as officially recognized by the Guinness World Records, in 2006.[8][9] The main harbour in Funchal is the leading Portuguese port in cruise liner dockings,[10] being an important stopover for commercial and trans-Atlantic passenger cruises between Europe, the Caribbean and North America.
Madeira is currently the second richest region in Portugal, after Lisbon, with a GDP per capita of 103% of the European average.[11]
Contents
History
 The Santa Maria de Colombo, a replica of the types of ship typical during the re-Discovery, built by craftsmen from Câmara de Lobos
The Santa Maria de Colombo, a replica of the types of ship typical during the re-Discovery, built by craftsmen from Câmara de Lobos
Exploration
Pliny mentioned certain "Purple Islands", their position corresponding to the location of the Fortunate Isles (or Canary Islands), that may have referred to islands of Madeira. Plutarch (Sertorius, 75 AD) referring to the military commander Quintus Sertorius (d. 72 BC), relates that after his return to Cádiz:
- "...The islands are said to be two in number separated by a very narrow strait and lie 10,000 furlongs from Africa. They are called the Isles of the Blessed"
The estimated distance from Africa (2,000 kilometres/1,250 miles), and the closeness of the two islands, seem to describe the similar position of the islands of Madeira and Porto Santo.
Legend
There is also a romantic tale of two lovers, Robert Machim and Anna d'Arfet, during the reign of King Edward III of England, who, fleeing from England to France in 1346, were driven off their course by a violent storm. Their ship crashed along the coast of an island, that may have been Madeira; later, this story would be used in the naming of Machico, whose name was transliterated from the name of the boy in the tale, in memory of the young lovers.[12]
Discovery
Much like the Azores, it is clear that some knowledge of Atlantic islands, such as Madeira, existed before the discovery and settlement of these lands, as the islands appear on maps as early as 1339.[13] From a portolan dating to 1351, and preserved in Florence, Italy, it would appear that the islands of Madeira had been discovered, long before Portuguese vessels rediscovered them in the "official" timeline. In Libro del Conocimiento (1348–1349), a Spanish monk also identified the location of the islands in its present location, with the names Leiname, Diserta and Puerto Santo.
Officially, in 1418, two captains under service to Prince Henry the Navigator, João Gonçalves Zarco and Tristão Vaz Teixeira, were driven off-course by a storm to an island which they named Porto Santo (English: holy harbour); the name was bestowed for their gratitude and divine deliverance from a possible shipwreck by the protected anchorage. The following year, an organized expedition, under the captaincy of Zarco and Vaz Teixeira, was sent to this new land, and along with captain Bartolomeu Perestrello, to take possession of the island on behalf of the Portuguese crown. Consequently, the new settlers discovered "a heavy black cloud suspended to the southwest",[14] which when explored they discovered the larger island of Madeira.[15]
Settlement
The first settlers began colonizing the islands around 1420 or 1425; the three Captains-major had led the first settlement, along with their respective families, a small group of minor nobility, people of modest conditions and some prisoners, who could be trusted to work the lands. To gain the minimum conditions for the development of agriculture, they had to rough-hew a part of the dense forest of laurisilva and to construct a large number of canals (levadas), since in some parts of the island there was excess water, while in others water was scarce. During this period, fish constituted about half of the settlers' diet, together with vegetables and fruits cultivated from small cleared parcels of land. Initially, these colonists produced wheat for their own subsistence, but later the quantity cultivated was sufficient to begin exporting wheat to continental Portugal.
In 23 September 1433, the name Ilha da Madeira (English: Madeira Island, or literally island of wood) began to appear in the first documents and maps. The name given to the islands corresponded to the large dense forests of native laurisilva trees that populated the island during the settlement.
However, when grain production began to fall, the ensuing crisis forced Henry the Navigator, as principal benefactor of the islands, to plant other commercial crops. The planting of sugarcane, and later Sicilian sugar beet, allowed the introduction of the "sweet salt" (as sugar was known) into Europe, where it was a rare and popular spice. These specialized plants, and their associated industrial technology, created one of the major revolutions on the islands and fueled Portuguese industry. The expansion of sugar plantations in Madeira began in 1455, using advisers from Sicily and financed by Genoese capital (it would become an integral part of the island economy until the 17th century). The accessibility of Madeira attracted Genoese and Flemish traders who were keen to bypass Venetian monopolies.
- "By 1480 Antwerp had some seventy ships engaged in the Madeira sugar trade, with the refining and distribution concentrated in Antwerp. By the 1490s Madeira had overtaken Cyprus as a producer of sugar."[16]
Sugarcane production was the primary engine of the island's economy, increasing the demand for labour. Slaves were used during portions of the island's history to cultivate sugar cane, and the proportion of imported slaves reached 10% of the total population of Madeira by the 16th century.[17]
In 1617, Algerian pirates, having long enslaved Christians along the Mediterranean coasts, captured 1,200 men and women in Porto Santo.[18][19] After the 17th century, as sugar production shifted to Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe and elsewhere, Madeira's most important product became its wine. The British occupied Madeira as a result of the Napoleonic Wars, a friendly occupation starting in 1807 and concluding in 1814 when the island was returned to Portugal.[20]
When, after the death of King John VI of Portugal, his usurper son Miguel of Portugal seized power from the rightful heir, his niece Maria II, and proclaimed himself 'Absolute King', Madeira held out for the queen under the governor José Travassos Valdez until Miguel sent an expeditionary force and the defence of the island was overwhelmed by crushing force. Valdez was forced to flee to England under the protection of the Royal Navy (September 1828).
World War I
The effect on Portugal in World War I was first felt in Madeira on December 3, 1916 when the German U-boat, SM U-38, captained by Max Valentiner went into Funchal harbour on Madeira and torpedoed and sank 3 ships, CS Dacia (1,856 tons),[21] Kanguroo (2,493 tons)[22] and Surprise (680 tons).[23] The commander of the French Gunboat Surprise and 34 of her crew (7 Portuguese) died in the attack. The Dacia, a British cable laying vessel,[24] had previously undertaken war work off the coast of Casablanca and Dakar, was in the process of diverting the German South American cable into Brest, France. Following the attack on the ships, the Germans proceeded to bombard Funchal for two hours from a range of about 2 miles. Batteries on Madeira returned fire and eventually forced the Germans to withdraw.
In 1917 on December 12, 2 German U-boats, SM U-156 and SM U-157 (captained by Max Valentiner) again bombarded Funchal, Madeira. This time the attack lasted around 30 minutes. Forty, 4.7-inch (120 mm) and 5.9-inch (150 mm) shells were fired. There were 3 fatalities and 17 wounded, In addition, a number of houses and Santa Clara church were hit.
Charles I the last Emperor of the Austro-Hungarian Empire went into exile in Madeira, after his second unsuccessful coup d'état in Hungary. He died there on April 1, 1922 and is buried in Monte. Charles I had tried in 1917, to secretly enter into peace negotiations with France. Although his foreign minister, Ottokar Czernin, was only interested in negotiating a general peace which would include Germany as well, Charles himself, in negotiations with the French with his brother-in-law, Prince Sixtus of Bourbon-Parma, an officer in the Belgian Army, as intermediary, went much further in suggesting his willingness to make a separate peace. When news of the overture leaked in April 1918, Charles denied involvement until the French Prime Minister Georges Clemenceau published letters signed by him. This led to Czernin's resignation, forcing Austria-Hungary into an even more dependent position with respect to its seemingly-wronged German ally. Determined to prevent a restoration attempt, the Council of Allied Powers had agreed on Madeira because it was isolated in the Atlantic and easily guarded.[25]
Autonomy
On 1 July 1976, following the democratic revolution of 1974, Portugal granted political autonomy to Madeira, celebrated on Madeira Day. The region now has its own government and legislative assembly.
Geography
Physical geography
Madeira Island (Ilha) Official name: Ilha de Madeira Name origin: madeira, Portuguese for the wood Country  Portugal
PortugalAutonomous Region  Madeira
MadeiraLocation Tore-Madeira Ridge, African Tectonic Plate, Atlantic Ocean Archipelago Madeira Municipalities Calheta, Câmara de Lobos, Funchal, Machico, Ponta do Sol, Porto Moniz, Porto Santo, Ribeira Brava, Santa Cruz, Santana, São Vicente Highest point Pico Ruivo - location Pico Ruivo, [(Santana)], Santana - elevation 1,862 m (6,109 ft) Lowest point Sea level - location Atlantic Ocean - elevation 0 m (0 ft) Length 57 km (35 mi), West-East Width 22 km (14 mi), North-South Area 740.7 km2 (286 sq mi) Biomes Temperate, Mediterranean Geology Alkali basalt, Tephra, Trachyte, Trachybasalt Orogeny Volcanism Period Miocene Demonym Madeirense; Madeiran Ethnic groups Portuguese Wikimedia Commons: Madeira Website: http://www.gov-madeira.pt Statistics from INE (2001); geographic detail from Instituto Geográfico Português (2010) The archipelago of Madeira is located 520 km (323.11 mi) from the African coast and 1,000 km (621.37 mi) from the European continent (approximately an one-and-a-half hour flight from the Portuguese capital of Lisbon[26]). It is found in the extreme south of the Tore-Madeira Ridge, a bathymetric structure of great dimensions oriented along a north-northeast to south-southwest axis that extends for 1000 kilometres. This submarine structure consists of long geomorphological relief that extends from the abyssal plain to 3500 meters; its highest submersed point is at a depth of about 150 meters (around latitude 36ºN). The origins of the Tore-Madeira Ridge are not clearly established, but may have resulted from a morphological buckling of the lithosphere.[27][28]
The archipelago itself is a series of oceanic volcanic islands that date back to the Miocene (about 20 million years ago), and constructed from a hotspot in the Earth's crust of the African Tectonic Plate. Madeira, and the smaller Desertas Islands, are the youngest of these islands (dating from 4.6 to 0.7 million years), while Porto Santo, the smaller of the main islands, is the oldest (approximately 14 million years). Since their immersion, there have been five phases related to the volcanism of the group, and they are particularly visible on the island of Madeira, which include:
- Base formation - characterised by large eruptions and ejecta which terminated about three million years ago;
- Peripheral formation - where there is a diminishing level of the projectiles, causing the formation of several dykes and platforms, that terminated about 740,000 years ago;
- High altitude formation - marked by a continuation of projectiles, pyroclastic materials and the formation of faults along the northern and southern coasts (between 400–900 meters);
- Paul da Serra - formation that travelled along the Bica da Cana around 550,000 years ago;
- Recent eruptions, associated with minor island formations; the magma fields discovered on the islands (which terminated about 6500 years ago) are associated with this phase.
These basaltic islands have not seen any volcanic activity within the last 6000 years.
Islands and islets
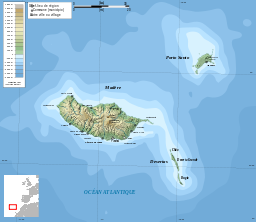
- Madeira (740.7 km²), including Ilhéu de Agostinho, Ilhéu de São Lourenço, Ilhéu Mole (northwest);
- Porto Santo (42.5 km²), including Ilhéu de Baixo ou da Cal, Ilhéu de Ferro, Ilhéu das Cenouras, Ilhéu de Fora, Ilhéu de Cima;
- Desertas Islands (14.2 km²), including the three uninhabited islands: Deserta Grande Island, Bugio Island and Ilhéu de Chão;
- Savage Islands (3.6 km²), including three main islands and 16 uninhabited islets) in two groups: the Northwest Group (Selvagem Grande Island, Ilhéu de Palheiro da Terra, Ilhéu de Palheiro do Mar) and the Southeast Group (Selvagem Pequena Island, Ilhéu Grande, Ilhéu Sul, Ilhéu Pequeno, Ilhéu Fora, Ilhéu Alto, Ilhéu Comprido, Ilhéu Redondo, Ilhéu Norte).
Madeira Island
The island of Madeira is at the top of a massive shield volcano that rises about 6 km (3.7 mi) from the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, on the Tore underwater mountain range. The volcano formed atop an east-west rift[29][30] in the oceanic crust along the African Plate, beginning during the Miocene epoch over 5 million years ago, continuing into the Pleistocene until about 700,000 years ago.[31] This was followed by extensive erosion, producing two large amphitheatres open to south in the central part of the island. Volcanic activity later resumed, producing scoria cones and lava flows atop the older eroded shield. The most recent volcanic eruptions were on the west-central part of the island only 6,500 years ago, creating more cinder cones and lava flows.[31]
Madeira Island represents 93% of the archipelago's area, with 90% of the landmass above 500 m. It is the largest island of the group with an area of 741 km2 (286 sq mi), a length of 57 km (35 mi) (from Ponte de São Lourenço to Ponte do Pargo), while approximately 22 km (14 mi) at its widest point (from Ponte da Cruz to Ponte São Jorge), with a coastline of 150 km (93.21 mi). It has a mountain ridge that extends along the center of the island, reaching 1862 meters (6,107 ft) at its highest point (Pico Ruivo), while much lower (below 200 meters) along its eastern extent. The primitive volcanic foci responsible for the central mountainous area, consisted of the peaks: Ruivo (1862 meter), Torres (1851 meter), Areeiro (1818 meter), Cidrão (1802 meter), Cedro (1759 meter), Casado (1725 meter), Grande (1657 meter), Ferreiro (1582 meter). At the end of this eruptive phase, an island circled by reefs was formed, its marine vistiges are evident in a calcierous layer in the area of Lameiros, in São Vicente (which was later explored for calcium oxide production). Sea cliffs, such as Cabo Girão, valleys and ravines extend from this central spine, making the interior generally inaccessible.[32] Daily life has concentrated in the many villages at the mouths of the ravines, through which the heavy rains of autumn and winter usually travel to the sea.[33] A long, narrow, and comparatively low rocky promontory forms (Paul da Serra) the eastern extremity of the island, on which lies a tract of calcareous sand known (1300-1500 meter). It is a fossil bed, that contains shells and numerous bodies resembling the roots of trees, probably produced by infiltration.
The island was formed from a base volcanic complex, forming to two massifs:
- The Base Volcanic Complex - was formed during the Miocene period from submarine and sub-aerial eruptions in the central part of the island, and is associated with some of the deeper valleys (São Vicente, Boaventura, Socorridos). The complex extends to the east into the (Porto da Cruz and Machico) ravines until Ponta de São Lourenço and consists of accumulated block pyroclasts, lapilli and ash, layered with basaltic lava. The volcanic material is essentially effusive, of non-viscous compact basalts; the lava formed flows that were not dense which covered the topography and substrata. These first flows were extensive, occupying a large part of the plateau, filling many of the valleys and ending at the sea. More recent episodes were confined into the valley of the São Vicente, Seixal and Porto Moniz ravines. The basaltic flows correspond to the last period of volcanic activity on Madeira (around .5-.2 millions of years). The flows were boxed into the valleys, and fossilized, sometimes, such as in the valley of São Vicente, forming morphological terraces. The island is covered in faults, and easily identifiable in the area around Ribeira Brava, near Encumeada. The spatial distribution of these faults is varied and their align is also diverse, although it is common to encounter some faults from west-northwest to east-south-southeast to northwest to southeast (coincident with the direction of some volcanic cones). Between many of pyroclastic cliffs, there exists a great variability in materials, from large blocks to fine ash, and a intermediary layer referred to locally as feijoco, or lapilli, of a consistency that is more porous. The material is normally dark to black rocks, yellow and reddish materials, and is used in some construction for their refractive characteristics (as well as used in the construction of blast ovens).
- Central Massif - which occupies the central region of the island, consisting of explosive material (large blocks, Lapilli and ash) and deposited chaotically around volcanic centres of the eruptions, but today mostly hidden and unrecognisable. This massif is crossed by several dense faults, basaltic and trachyte, oriented in many directions, converging on Pico Ruivo. The peak which includes many dykes, has resisted erosion, in contrast to many of the surrounding deposits; the weak cohesion of pyroclastic materials permitted the easy carving of the terrain in this area, constituting the morphology of many of the ravines: Brava, Socorridos, Machico, São Vicente, Porco (Boaventura) and Faial.
- The Paul da Serra Massif - corresponds to a similar structural platform of basaltic flows oriented towards the southwest.
Climate
Madeira has been classified as a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csb),[34] but based on differences in sun exposure, humidity, and annual mean temperature there are clear variations between north- and south-facing regions, as well as between some islands. The islands are strongly influenced by the Gulf Stream, giving it mild year-round temperatures; the average annual temperature along the coastline is between 15 to 22 °C (59 to 72 °F) at lower altitudes, and between 5 to 15 °C (41 to 59 °F) at the highest altitudes. Average annual sea temperatures are approximately 20 °C (68 °F), from 18 °C (64.4 °F) in the winter to 23 °C (73 °F) during the summer. Coastal temperatures usually persist year-round, although between December and April temperatures often fall below 20 °C (68 °F).
Climate data for Funchal, capital of Madeira Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 19.1
(66.4)19.1
(66.4)19.5
(67.1)19.6
(67.3)20.9
(69.6)22.3
(72.1)24.3
(75.7)25.6
(78.1)25.7
(78.3)24.2
(75.6)22.0
(71.6)20.0
(68.0)21.8 Daily mean °C (°F) 16.1
(61.0)16.0
(60.8)16.3
(61.3)16.5
(61.7)17.8
(64.0)19.4
(66.9)21.2
(70.2)22.3
(72.1)22.3
(72.1)20.9
(69.6)18.8
(65.8)17.0
(62.6)18.6 Average low °C (°F) 13.1
(55.6)12.8
(55.0)13.0
(55.4)13.4
(56.1)14.6
(58.3)16.5
(61.7)18.0
(64.4)18.9
(66.0)18.9
(66.0)17.6
(63.7)15.6
(60.1)13.9
(57.0)15.5 Precipitation mm (inches) 102.7
(4.043)87.2
(3.433)63.6
(2.504)38.9
(1.531)18.9
(0.744)11.9
(0.469)25
(0.98)31
(1.22)36.7
(1.445)75.0
(2.953)100.8
(3.969)99.9
(3.933)641.2
(25.244)Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) 12 11 10 8 5 3 1 2 6 9 11 13 91 Sunshine hours 167.4 171.1 204.6 225.0 213.9 198.0 244.9 260.4 225.0 204.6 168.0 164.3 2,447.2 Source: World Meteorological Organization (UN),[35] Climatetemp.info[36] for Sunshine hours data Biome
In the south, there is very little left of the indigenous laurisilva subtropical rainforest which once covered the whole island (the original settlers set fire to the island to clear the land for farming) and gave it the name it now bears (Madeira means "wood" in Portuguese). However, in the north, the valleys contain native trees of fine growth. These laurisilva forests, notably the forests on the northern slopes of Madeira Island, are designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
Madeira has three endemic bird species: Zino's Petrel, the Trocaz Pigeon and the Madeira Firecrest, while the Madeiran Chaffinch is an endemic subspecies. It is also important for breeding seabirds, including the Madeiran Storm-petrel, North Atlantic Little Shearwater and Cory's Shearwater.
The Macaronesia region harbours an important floral diversity. In fact, the archipelago's forest composition and maturity are quite similar to the forests found in the Tertiary period that covered Southern Europe and Northern Africa millions of years ago. The great biodiversity of Madeira is phytogeographically linked to the Mediterranean region, Africa, America and Australia, and interest in this phytogeography has been increasing in recent years due to the discovery of some epiphytic bryophyte species with non-adjacent distribution.
Madeira also has many endemic species of fauna – mostly invertebrates which include the extremely rare Madeiran Large White but also some vertebrates such as the native bat, some lizards species, and some birds as already mentioned. The biggest tarantula of Europe is found on Desertas islands of Madeira and can be as wide as a man's hand. These islands have more than 250 species of land molluscs (snails and slugs), some with very unusual shell shape and colours, most of which are endemic and vulnerable.
Levadas
The island of Madeira is wet in the northwest but dry in the southeast. In the 16th century the Portuguese started building levadas or aqueducts to carry water to the agricultural regions in the south. The most recent were built in the 1940s. Madeira is very mountainous, and building the levadas was difficult and often sentenced criminals or slaves were used. Many are cut into the sides of mountains, and it was also necessary to dig 25 miles (40 km) of tunnels, some of which are still accessible.
Today the levadas not only supply water to the southern parts of the island but provide hydro-electric power. There are over 1,350 miles (2,170 km) of levadas and they provide a remarkable network of walking paths. Some provide easy and relaxing walks through beautiful countryside, but others are narrow, crumbling ledges where a slip could result in serious injury or death.
Two of the most popular levadas to hike are the Levada do Caldeirão Verde and the Levada do Caldeirão do Inferno which should not be attempted by hikers prone to vertigo or without torches and helmets. The Levada do Caniçal is a much easier walk, running 7.1 miles (11.4 km) from Maroços to the Caniçal Tunnel. It is known as the mimosa levada because mimosa trees are found all along the route.
Human geography
Administratively, Madeira (with a population of 244,286 inhabitants in 2009) and covering an area of 768.0 km2 (296.5 sq mi) is organized into eleven municipalities:[37]
Municipality Population
(2006)[38]Area Main settlement Parishes Funchal[39] 100,847 75.7 km2 (29.2 sq mi) Funchal 10 Câmara de Lobos 35,150 52.6 km2 (20.3 sq mi) Câmara de Lobos 5 Santa Cruz[40] 32,696 68.0 km2 (26.3 sq mi) Santa Cruz 5 Machico 21,321 67.6 km2 (26.1 sq mi) Machico 5 Ribeira Brava 12,523 64.9 km2 (25.1 sq mi) Ribeira Brava 4 Calheta 11,856 110.3 km2 (42.6 sq mi) Calheta 8 Santana 8,491 93.1 km2 (35.9 sq mi) Santana 6 Ponta do Sol 8,189 46.8 km2 (18.1 sq mi) Ponta do Sol 3 São Vicente 6,063 80.8 km2 (31.2 sq mi) São Vicente 3 Porto Santo[41] 4,388 42.4 km2 (16.4 sq mi) Vila Baleira 1 Porto Moniz 2,762 82.6 km2 (31.9 sq mi) Porto Moniz 4 Funchal
Funchal, is the capital and principal city of the Madeira Autonomous Region, located along the southern coast of the island of Madeira. It is a modern city, located within a natural geological "amphitheater" composed of volcanological structure and fluvial hydrological forces. Beginning at the harbor (Porto de Funchal), the neighborhoods and streets rise almost 1,200 metres (3,900 ft), along gentle slopes that helped to provide a natural shelter to the early settlers.
With five centuries of populated history, Funchal was named by the early discoverers and settlers, for the abundance of fennel (funcho) that was found in this heavily forested area. The natural harbor and climate, combined with an excellent geographical position, allowed Funchal to rapidly grow. Its Sé Cathedral, built between 1493 and 1514 (by Pêro Annes in Manueline-style), was one of the main centers of activity during its formative period, and represents one of Madeira's numerous historical treasures.
Demographics
When the Portuguese discovered the island of Madeira in 1419, it was uninhabited by humans, with no aboriginal population. The island was settled by Portuguese people, especially farmers from the Minho region,[42] meaning that Madeirans (Portuguese: Madeirenses), as they are called, are ethnic Portuguese, though they have developed their own distinct regional identity and cultural traits.
The region has a total population of just under 250,000 inhabitants, the majority of whom live on the main island of Madeira where the population density is 337/km²; meanwhile only around 4,500 live on the Porto Santo Island where the population density is 112/km².
Population genetics
As in continental Portugal, the most frequent mtDNA haplogroup in Madeira is H (36.2%), followed by U (19.4% including 3.9% of North African Berber U6), T (7.7%), pre-HVclades (7.1%) and K (6.5%). Two haplogroups, H and U5 alone account for more than 50% of the individuals. The relatively high frequency of sub-Saharan L and M1 haplogroups (14.8%) in Madeira is also consistent with the historical records of slaves being introduced in both the south of Portugal and in Madeira.[43]
Sample H I J K T U (except U6) Pre-V W X U6 M1 L1 L2 L3 155 36.2 1.3 2.6 6.5 7.7 15.5 7.1 1.9 0.6 3.9 1.9 4.5 2.6 5.8 Concerning the males Y-Dna haplogroups, R1b (particularly R1b3) was found to be the most dominant Y chromosomal lineage in Madeira, covering about 53% of the Y chromosomal lineages. The high frequency of this haplogroup is typical in all West European populations, reflecting a cline and likely continuity of the Palaeolithic gene pool in Europe. Haplogroups I and G, also characteristic markers for many different West European populations, were found in Madeira at frequencies above 5%. Together with R1b, haplogroups J (12%) and E1b1b (14%) comprise about 80% of the Y-chromosomal gene pool of Madeira individuals. Haplogroups J and E1b1b consist of lineages with differential distribution within Middle East, North Africa and Europe. The typical Berber haplogroup E1b1b1b (M81) was found as in continental Portugal at a frequency of 5–6%.[44]
Sample A E1b1b1 E1b1b1a E1b1b1b E1b1b1c G I J* J2 T L N1c R1* R1a R1b 129 0.8 1.6 5.4 5.4 1.6 3.1 7.0 0.8 10.9 3.1 1.6 2.3 1.6 2.3 52.7 Diaspora
Madeiran immigrants in the United States mostly clustered in the New England and mid-Atlantic states, Northern California, and Hawaii. They also settled in Rhode Island and Massachusetts to participate in the flourishing American whaling industry. By 1980, the U.S. Census registered more than a million Americans of Portuguese descent, a large portion Madeirans.
In 1846 when a famine struck Madeira over 6,000 of the inhabitants migrated to British Guiana. In 1891 they numbered 4.3% of the population.[45] In 1902 in Honolulu, Hawaii there were 5,000 Portuguese people mostly Madeirans. In 1910 this grew to 21,000. South Africa and Venezuela were also both important historically host countries for Madeirans.
There are several large Madeiran communities around the world, such is the great number in the UK, including Jersey,[46] the Portuguese British community mostly made up of Madeirans celebrate Madeira Day.
Economy
The setting-up of the Free trade zone has led to the installation, under more favourable conditions, of infrastructure, production shops and essential services for small and medium-sized industrial enterprises. The Free Zone of Madeira, also called the Madeira International Business Centre, being a tax-privileged economic area, provides an incentive for companies, offering them financial and tax advantages via a whole range of activities exercised in the Industrial Free Zone, the Off-Shore Financial Centre, the International Shipping Register organisation, and the International Service Centre.
The services sector makes the largest contribution to the formation of the regional gross value added as opposed to the agricultural sector, for which the share has continuously declined in the regional economy.
Over the last few years, the regional economy has managed to open up and establish more internal and external competitiveness, so that its companies have become competitive internationally. The largest industries are by sector food, beverages (especially Madeira wine), and construction.
Tourism
 The manufactured coastal beach of Calheta: replacing the dark rock/sand of the volcanic island with beach sand.
The manufactured coastal beach of Calheta: replacing the dark rock/sand of the volcanic island with beach sand.
Tourism is an important sector in the region's economy since it contributes 20%[citation needed] to the region's GDP, providing support throughout the year for commercial, transport and other activities and constituting a significant market for local products. The share in Gross Value Added of hotels and restaurants (9%) also highlights this phenomenon. The island of Porto Santo, with its 9 km (5.6 mi) long beach and its climate, is entirely devoted to tourism. Over the past decade it has recorded a substantial increase in its hotel accommodation capacity.
Development in Madeira is considered to have future potential since the necessary infrastructure has been established and adequate investment incentives have been introduced for expanding its hotel and catering structure in a controlled manner. Nature conservation is seen as important because it is a major draw for tourists to Madeira.
Visitors are mainly from the European Union, with German, British, Scandinavian and Portuguese tourists providing the main contingents. The average annual occupancy rate was 60.3% in 2008,[47] reaching its maximum in March and April, when it exceeds 70%.
Transport
European Union citizens of the Schengen Treaty area can enter the islands freely, while those from other regions need identification.
There were in 2009, 7,105 legal immigrants living in Madeira Islands. They come mostly from Brazil (1.300), the UK (912), Venezuela (732) and Ukraine (682), according to SEF.[48]
The Islands have two airports, Funchal Airport on the Island of Madeira and the other in the island of Porto Santo. Flights to the islands are mostly made from Lisbon and Porto, but there are also direct flights from other major European cities and other countries, like Brazil, Venezuela, and South Africa.
Transport between the two main islands is by plane or ferries, the latter also carrying vehicles. Visiting the interior of the islands is now easy thanks to construction of the Vias Rápidas, major roads built during Portugal's economic boom. Modern roads reach all points of interest on the islands. The old, curving mountain roads are still an excellent way to tour the island. Funchal has an extensive public transportation system. Bus companies, including Horários do Funchal which has been operating for over a hundred years, have regularly scheduled routes to all points of interest on the island.
Gastronomy
Food
Fish
Due to the geographic situation of Madeira, the island enjoys an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that are consumed the most are Black scabbardfish, Blue Fin Tuna, White Marlin, Blue Marlin, Albacore, Big Eye Tuna, Wahoo, Spearfish, skipjack tuna and many others are found in the local dishes as they are found up and down the coast of Madeira
Espada (Black scabbardfish) is often served with banana. Bacalhau also being popular as it is in Portugal.
Meat
There are many meat dishes on Madeira, one of the most popular being Espetada.[49] The Espetada is traditionally made of large chunks of beef rubbed in garlic, salt and bay leaf and marinated for 4 to 6 hours in Madeira wine, red wine vinegar and olive oil then skewered onto a Bay laurel stick and left to grill over smouldering wood chips. Portuguese Americans use California Bay Laurel sticks as skewers as they are more readily available in the USA.[50] In Madeira they are so integral a part of traditional eating habits that a special iron stand was developed with a T-shaped end, each branch of the "T" having a slot in the middle to hold a brochette. A small plate is then placed underneath to collect the juices. The brochettes are very long and have a V-shaped blade in order to more easily pierce the meat.
Carne de Vinha d' Alhos is another popular dish in Madeira and in Portugal.
Pastries
Traditional pastries in Madeira usually contain local ingredients, one of the most common being mel de cana, literally “sugarcane honey” (molasses). The traditional cake of Madeira is called Bolo de Mel, which translates as (Sugarcane) "Honey Cake" and according to custom is never cut with a knife but broken into pieces by hand. It is a rich and heavy cake. Malasada's are a Madeira creation which were taken around the world by Madeiran Emigrants to places such as Hawaii. In Madeira Malasada's are mainly consumed during the Carnival of Madeira. Pastel de nata's as in the rest of Portugal are also very popular.
Other
Milho Frito is a very popular dish in Madeira which is very similar to the Italian dish Polenta.
Beverages
Wine
Madeira is a fortified Portuguese wine, produced in the Madeira Islands; varieties may be sweet or dry. It has a history dating back to the Age of Exploration when Madeira was a standard port of call for ships heading to the New World or East Indies. To prevent the wine from spoiling, neutral grape spirits were added. However, wine producers of Madeira discovered, when an unsold shipment of wine returned to the islands after a round trip, that the flavour of the wine had been transformed by exposure to heat and movement. Today, Madeira is noted for its unique winemaking process which involves heating the wine and deliberately exposing the wine to some levels of oxidation.[51] Most countries limit the use of the term Madeira or Madère to only those wines that come from the Madeira Islands, to which the European Union grants Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status.[52]
Beer
 Coral Beer
Coral Beer
The local Beer called Coral is produced by the Madeira Brewery, which has been around since 1872. Other Portuguese beers are also popular on Madeira to a much lesser extent.
Soft Drinks
Laranjada is a type of carbonated soft drink with an orange flavour, which is 14 years older than Coca-Cola drink. Launched in 1872 it was the first soft drink to be produced in Portugal and therefore the oldest, remaining very popular to the present day. Brisa drinks are also very popular and come in a range of flavours.
Coffee
There is also a huge coffee culture in Madeira where, like the rest of Portugal, Portuguese coffees are more popular such as Garoto, Galão, Bica, Chinesa and many more
Madeira Gourmet Festival
To promote Madeiran gastronomy worldwide, every November the Madeira Gourmet Festival is organized. The festival brings international chefs to the island, mixing their know-how with local young chefs and preparing new recipes using Madeiran traditional products, like Madeira wine, local fish and other products.
Sports
In Madeira a large number of sports are practiced, both outdoors and indoors in the various facilities available throughout the island. However the main professional sports that Madeira competes in are listed below:-
Football
Monument in Camacha, celebrating the first ever organised football game in Portugal, that took place in 1875.
The first organised game of football took place in 1875 in Camacha, organised by the Madeira born Harry Hinton. This being the first organised game of football anywhere in Portugal
Madeira has two football teams in the Portuguese Liga (Portugal's top league), C.S. Marítimo and Nacional. There would have been three but União da Madeira were relegated from the top league in 1995 and have never been able to gain promotion back to the top league.
The Real Madrid and Portugal footballer Cristiano Ronaldo was born in Madeira and played for Nacional before going to Sporting Lisbon.[53]
C.S. Marítimo is considered as the biggest club of Madeira and have enjoyed various campaigns in the UEFA Cup having recorded famous results against teams such as Juventus, Leeds[citation needed] and Rangers. Having finished 5th in the league in the 2009/2010 season, C.S. Marítimo qualified for the Europa League for the 2010/2011 season[54]
C.S. Marítimo has nurtured great players such as Pepe, now at Real Madrid, Tonel, now at Sporting, Danny, now at Zenit, Jorge Costa, retired (F.C. Porto), Tarik Sektioui, left F.C. Porto at the start of 2009/2010 league, Nuno Valente, retired, Makukula, now at Manisaspor, among others.
In 2003–04 Nacional achieved 4th place in the Portuguese League, their best classification ever.
Outside the Portuguese top league, there are two other Maderian teams U.D. Santana and A.D. Pontassolense. U.D. Santana was relegated from the Portuguese Second Division so they now play the football in the Portuguese Third Division, while A.D. Pontassolense plays in the Portuguese Second Division.
Basketball
In recent years, Madeira has had a considerable amount of success in professional basketball, with CAB Madeira having won numerous titles, especially their female team. CAB are often seen competing in European competitions such as the FIBA EuroCup, and former stars include Filipe da Silva and ex-Los Angeles Lakers player Ike Nwankwo.
Surfing
Paul do Mar: this surfspot according to surf experts[55] has the best barreling waves (also known as tubular, tunnel waves) on Madeira. Both stand-up surfing and bodyboarding are practised at this spot.
In 2001 the World Surfing Championships were held in Madeira at Surfspots including Paul do Mar, Ponta Pequena and Jardim do Mar (see Surfing in Madeira).
Handball
Madeira Andebol SAD, the island's only professional handball team is one of the most successful in the country.
Rugby
Rugby union is also played on the island to a minor degree.[56]
Walking and hiking
With around 600 miles of walks, many alongside the Levadas, one of the islands greatest attractions providing stunning walks some of which are quite challenging.[57]
Fishing
Due to the geographic situation of Madeira, the island enjoys an abundance of fish of various kinds. The species that can be caught are Black scabbardfish, Blue Fin Tuna, White Marlin, Blue Marlin, Albacore, Big Eye Tuna, Wahoo, Spearfish, skipjack tuna and many others are found up and down the coast of Madeira.
Dolphin (Common dolphin, Bridled dolphin, Striped dolphin, Bottle-nose Dolphin) and Whale (Short-finned Pilot Whale, Sperm whale, Fin whale) watching is also very popular.[58]
Other Sports
While rally car racing (Rali Vinho da Madeira), Karting and golf are other popular sports played on the island. The island lies in an ideal location for water sports such as fishing, Sailing and diving due to its climate and location. Jogo do Pau, a Portuguese martial art is still practised in the rural areas of the island but has declined since its peak in the early part of the 20th century.
Postage stamps
Portugal has issued postage stamps for Madeira during several periods, beginning in 1868.
Notable residents
The following people were either born or have lived part of their lives in Madeira:
- António de Abreu, naval officer and navigator
- Nadia Almada, a winner of the British reality show Big Brother
- Menasseh Ben Israel, a notable Jewish Rabbi.
- Joe Berardo, Portuguese millionaire, and art collector
- Pedro Macedo Camacho, Composer
- Charles I of Austria, deposed monarch, died in exile on Madeira in 1922
- Catarina Fagundes, Olympic athlete for windsurf
- Vânia Fernandes, Portuguese singer who represented Portugal in Eurovision 2008
- José Vicente de Freitas, military and politician
- Vasco da Gama Rodrigues, Poet, born in Paul do Mar
- Teodósio Clemente de Gouveia, Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church
- Herberto Hélder, Poet
- Moisés Henriques, former Australian Under-19 Captain and current NSW Blues cricketer
- Alberto João Jardim, President of the Regional Government
- Luís Jardim, Producer of music
- Paul Langerhans, German pathologist and biologist
- Fátima Lopes, Fashion designer
- Jaime Ornelas Camacho, first and former President of the Regional Government
- Aires de Ornelas e Vasconcelos, former Archbishop of the former Portuguese colonial enclave Goa (in India)
- Sir Lloyd William Matthews, British naval officer, politician and abolitionist
- Dionísio Pestana, president of the Pestana Group
- Rigo 23, Artist
- João Rodrigues, Olympic windsurfer
- Cristiano Ronaldo, Real Madrid, Portugal and former Manchester United football player
- John Santos, Photographer
- Ana da Silva, founding member of the post-punk band The Raincoats
- Manoel Dias Soeyro or Menasseh Ben Israel (1604–1657), Sephardi Rabbi and publisher
- Artur de Sousa Pinga, former CS Marítimo and FC Porto football player
- Maximiano de Sousa (Max), popular singer, born in Funchal
- Virgílio Teixeira, actor
- José Travassos Valdez, 1st Count of Bonfim, governor in 1827–1828
See also
- History of Portuguese Nationality
- Madeira Island Open, an annual European Tour golf tournament.
- Surfing in Madeira
- University of Madeira
References
- Notes
- ^ http://www.ine.pt/scripts/flex_v10/Main.html
- ^ Until 2002, the Portuguese escudo was used in financial transactions, and until 1910 the Portuguese real was the currency used by the monarchy of Portugal.
- ^ a b "GDP per inhabitant in 2008". Eurostat. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/1-24022011-AP/EN/1-24022011-AP-EN.PDF. Retrieved 2011-03-29.
- ^ INE, ed. (2010) (in Portuguese), Censos 2011 - Resultadas Preliminares [2011 Census - Preliminary Results], Lisbon, Portugal: Instituto Nacional de Estatística, http://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_publicacoes&PUBLICACOESpub_boui=122114780&PUBLICACOESmodo=2, retrieved 1 July 2011
- ^ IGP, ed. (2010) (in Portuguese), Carta Administrativa Oficial de Portugal, Lisbon, Portugal: Instituto Geográfico Português, http://www.igeo.pt/produtos/cadastro/caop/download/Areas_Freg_Mun_Dist_CAOP2010.zip, retrieved 1 July 2011
- ^ "EUROPA - Glossary - Outermost regions". Europa.eu. 2008-07-17. http://europa.eu/scadplus/glossary/outermost_regions_en.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ [http://www.presstur.com/site/news.asp?news=29046 "Hotelaria da Madeira suaviza quebras em 2010 apesar de impacto devastador dos temporais"]. presstur.com. 08-02-2001. http://www.presstur.com/site/news.asp?news=29046. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "A Guinness World Record Fireworks Show – Madeira Island, 2006-2007 New Year Eve at Wayfaring Travel Guide". Wayfaring.info. http://www.wayfaring.info/2007/01/12/a-guinness-world-record-fireworks-show-madeira-island-2006-2007-new-year-eve/. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ "><". <PressTur. http://www.presstur.com/site/news.asp?news=28572. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ "Regional GDP per inhabitant in 2008 GDP per inhabitant ranged from 28% of the EU27 average in Severozapaden in Bulgaria to 343% in Inner London" (PDF). Eurostat. February 24, 2011. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/1-24022011-AP/EN/1-24022011-AP-EN.PDF. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ Nicholas Cayetano de Bettencourt Pitta, 1812, p.11-17
- ^ Fernández-Armesto, Felipe (2004). "Machim (supp. fl. 14th cent.)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/17535.
- ^ Nicholas Cayetano de Bettencourt Pitta, 1812, p.20
- ^ The discoveries of Porto Santo and Madeira were first described by Gomes Eanes de Zurara in Chronica da Descoberta e Conquista da Guiné. (Eng. version by Edgar Prestage in 2 vols. issued by the Hakluyt Society, London, 1896–1899: The Chronicle of Discovery and Conquest of Guinea.) Arkan Simaan relates these discoveries in French in his novel based on Azurara's Chronicle: L’Écuyer d’Henri le Navigateur, published by Éditions l’Harmattan, Paris.
- ^ Ponting, Clive (2000) [2000]. World history: a new perspective. London: Chatto & Windus. p. 482. ISBN 0-701-16834-X.
- ^ Godinho, V. M. Os Descobrimentos e a Economia Mundial, Arcádia, 1965, Vol 1 and 2, Lisboa
- ^ Fernando Augusto da Silva & Carlos Azevedo de Menezes, "Porto Santo", Elucidário Madeirense, vol. 3 (O-Z), Funchal, DRAC, p. 124.
- ^ "Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast and Italy, 1500–1800". Robert Davis (2004). p.7. ISBN 1-4039-4551-9.
- ^ "The Map Room: Africa: Madeira". British Empire. http://www.britishempire.co.uk/maproom/madeira.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "uboat.net". uboat.net. 2010-11-13. http://uboat.net/wwi/ships_hit/1531.html. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ^ "uboat.net". uboat.net. 2010-11-13. http://uboat.net/wwi/ships_hit/3247.html. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ^ "uboat.net". uboat.net. 2010-11-13. http://uboat.net/wwi/ships_hit/5841.html. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ^ "www.atlantic-cable.com". uboat.net. 2010-11-13. http://www.atlantic-cable.com/Cableships/Dacia/index.htm. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ^ The New York Times, Nov. 6, 1921 (accessed 4 May 2009)
- ^ "Madeira Islands Tourism". Madeiraislands.travel. http://www.madeiraislands.travel/pls/madeira/wsmwdet0.detalhe_conteudo?p_cot_id=59&p_lingua=en&p_sub=1. Retrieved 2010-07-30.[dead link]
- ^ Ribeiro et al., 1996
- ^ Kullberg & Kullberg, 2000
- ^ Geldemacher et. al., 2000
- ^ Ribeiro, 2001
- ^ a b "Madeira". Global Volcanism Program, Smithsonian Institution. http://www.volcano.si.edu/world/volcano.cfm?vnum=1802-12-.
- ^ "MadeiraHelp.com". MadeiraHelp.com. 1999-02-22. http://www.madeirahelp.com/madeira_geography. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ Robert White, 1851, p.4
- ^ "World Map of Köppen−Geiger Climate Classification". http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/.
- ^ "Weather Information for Funchal". June 2011. http://www.worldweather.org/003/c00005.htm. Retrieved 2011-03-29.
- ^ "Funchal, Madeira Climate, Temperature, Average Weather History, Rainfall/Precipitation, Sunshine". http://www.climatetemp.info/portugal/madeira.html.
- ^ Map of municipalities at FreguesiasDePortugas l.com
- ^ Associação Nacional de Municípios Portugueses
- ^ Statistics include Savage Islands, which are administered by the parish of Sé
- ^ Statistics include the mainland parish of Santa Cruz and the islands of the Desertas
- ^ Statistics represent island population; Porto Santo is the second largest island in the archipelago of Madeira
- ^ "Alberto Vieira, ''O Infante e a Madeira: dúvidas e certezas, Centro Estudos História Atlântico". Ceha-madeira.net. http://www.ceha-madeira.net/livros/infante.html. Retrieved 2010-07-30.[dead link]
- ^ "The relatively high proportion of African lineage clusters L1–L3, U6, and M1 in Madeira (18.7%) and only 5.1% in the Açores agrees well with previous estimates of African admixture based on HLA and STR markers (Spínola et al. 2002; Fernandes et al. 2003)". Mitochondrial portraits of the Madeira and Açores archipelagos witness different genetic pools of its settlers, Brehm et al. 2003
- ^ Y-chromosome lineages from Portugal, Madeira and Açores record elements of Sephardim and Berber ancestry, Goncalves et al. 2005
- ^ "Portuguese emigration from Madeira to British Guiana"
- ^ "BBC – Jersey Voices"
- ^ "Statistics from DRE of Madeira tourism (2008)" (PDF). http://estatistica.gov-madeira.pt/DRE_SRPC/EmFoco/Servicos/Turismo/emfoco.pdf. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "SEFSTAT – Portal de Estatística". Sefstat.sef.pt. http://sefstat.sef.pt/distritos.aspx. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "Madeira Espetada". theworldwidegourmet.com. http://www.theworldwidegourmet.com/recipes/espetada-beef-brochettes/. Retrieved 2010-08-30.
- ^ "Portuguese American Espetada". Bay Area Bites. http://blogs.kqed.org/bayareabites/2009/08/07/espetada-meat-on-a-stick-the-portuguese-way/. Retrieved 2011-10-10.
- ^ T. Stevenson "The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia" pg 340-341 Dorling Kindersley 2005 ISBN 0-7566-1324-8
- ^ Labelling of wine and certain other wine sector products
- ^ "Cristiano Ronaldo". Diariodigital.sapo.pt. http://diariodigital.sapo.pt/news.asp?section_id=126&id_news=282895. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "Cristiano Ronaldo". Portugoal.net. 2010-05-10. http://www.portugoal.net/index.php/more-maritimo-news/10249-maritimo-snatch-europa-league-berth. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ "Rugby Madeira". Rugbymadeira.blogspot.com. 2010-05-29. http://rugbymadeira.blogspot.com/. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "Levadas of Madeira". Walkingmadeira.com. http://www.walkingmadeira.com/levadas. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ "Madeira whale and Dolphin watching". www.madeirawindbirds.com. 2010-08-30. http://www.madeirawindbirds.com/en/tours/madeira_half_day_dolphin_watching.html. Retrieved 2010-12-10.
- Sources
- Pitta, Nicholas Cayetano de Bettencourt (1812). Account of the Island of Madeira. London, England: C.Stewart Printer.
External links
- Madeira's Government Website
- Madeira Tourism Official Website
- Wikimedia Atlas of Madeira
- Madeira travel guide from Wikitravel
- Madeira at the Open Directory Project
Geographic locale  NUTS 2 regions, NUTS 3 subregions and Districts of Portugal
NUTS 2 regions, NUTS 3 subregions and Districts of PortugalNorte Region Subregions: Alto Trás-os-Montes · Ave · Cávado · Douro · Entre Douro e Vouga · Grande Porto · Minho-Lima · Tâmega · Districts: Braga · Bragança · Porto · Viana do Castelo · Vila Real · Aveiro * · Guarda * · Viseu *Centro Region Subregions: Baixo Mondego · Baixo Vouga · Beira Interior Norte · Beira Interior Sul · Cova da Beira · Dão-Lafões · Médio Tejo · Oeste · Pinhal Interior Norte · Pinhal Interior Sul · Pinhal Litoral · Serra da Estrela · Districts: Castelo Branco · Coimbra · Leiria · Aveiro * · Guarda* · Santarém * · Viseu *Lisboa Region Alentejo Region Algarve Region Subregions: Algarve · Districts: FaroAzores Subregions: AzoresMadeira Subregions: Madeira(*) Situated in more than one Region. NOTE: The Azores and Madeira are Autonomous Regions: districts have been discontinued in these areas and local government replaced by LAU1 and LAU2 authorityDistricts and Autonomous regions of Portugal Districts 
Autonomous regions International membership Outlying territories of European countries Territories under European sovereignty but closer to or on continents other than Europe (see inclusion criteria for further information) Denmark France Italy Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain United
KingdomAnguilla · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsPortuguese Empire North Africa15th century
1415–1640 Ceuta
1458–1550 Alcácer Ceguer (El Qsar es Seghir)
1471–1550 Arzila (Asilah)
1471–1662 Tangier
1485–1550 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1487– middle 16th century Ouadane
1488–1541 Safim (Safi)
1489 Graciosa16th century
1505–1769 Santa Cruz do Cabo
de Gué (Agadir)
1506–1525 Mogador (Essaouira)
1506–1525 Aguz (Souira Guedima)
1506–1769 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1513–1541 Azamor (Azemmour)
1515 São João da Mamora (Mehdya)
1577–1589 Arzila (Asilah)Sub-Saharan Africa15th century
1455–1633 Arguin
1470–1975 Portuguese São Tomé1
1474–1778 Annobón
1478–1778 Fernando Poo (Bioko)
1482–1637 Elmina (São Jorge
da Mina)
1482–1642 Portuguese Gold Coast
1496–1550 Madagascar (part)
1498–1540 Mascarene Islands16th century
1500–1630 Malindi
1500–1975 Portuguese Príncipe1
1501–1975 Portuguese E. Africa
(Mozambique)
1502–1659 St. Helena
1503–1698 Zanzibar
1505–1512 Quíloa (Kilwa)
1506–1511 Socotra
1557–1578 Portuguese Accra
1575–1975 Portuguese W. Africa
(Angola)
1588–1974 Cacheu2
1593–1698 Mombassa (Mombasa)17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Cape Verde
1645–1888 Ziguinchor
1680–1961 São João Baptista de Ajudá
1687–1974 Portuguese Bissau2
18th century
1728–1729 Mombassa (Mombasa)
1753–1975 Portuguese São Tomé and Príncipe
19th century
1879–1974 Portuguese Guinea
1885–1975 Portuguese Congo1 Part of São Tomé and Príncipe from 1753. 2 Part of Portuguese Guinea from 1879. Southwest Asia16th century
1506–1615 Gamru (Bandar-Abbas)
1507–1643 Sohar
1515–1622 Hormuz (Ormus)
1515–1648 Quriyat
1515–? Qalhat
1515–1650 Muscat
1515?–? Barka
1515–1633? Julfar (Ras al-Khaimah)
1521–1602 Bahrain (Muharraq and Manama)
1521–1529? Qatif
1521?–1551? Tarut Island
1550–1551 Qatif
1588–1648 Matrah17th century
1620–? Khor Fakkan
1621?–? As Sib
1621–1622 Qeshm
1623–? Khasab
1623–? Libedia
1624–? Kalba
1624–? Madha
1624–1648 Dibba Al-Hisn
1624?–? Bandar-e KongIndian subcontinent15th century
1498–1545 Laccadive Islands
(Lakshadweep)16th century
Portuguese India
· 1500–1663 Cochim (Kochi)
· 1502–1661 Quilon (Coulão/Kollam)
· 1502–1663 Cannanore (Kannur)
· 1507–1657 Negapatam (Nagapatnam)
· 1510–1962 Goa
· 1512–1525 Calicut (Kozhikode)
· 1518–1619 Chaul
· 1523–1662 Mylapore
· 1528–1666 Chittagong
· 1531–1571 Chalium
· 1534–1601 Salsette Island
· 1534–1661 Bombay (Mumbai)
· 1535–1739 Baçaím (Vasai-Virar)
· 1536–1662 Cranganore (Kodungallur)
· 1540–1612 Surat
· 1548–1658 Tuticorin (Thoothukudi)16th century (continued)
Portuguese India (continued)
· 1559–1962 Daman and Diu
· 1568–1659 Mangalore
· 1579–1632 Hugli
· 1598–1610 Masulipatnam (Machilipatnam)
1518–1521 Maldives
1518–1658 Portuguese Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1558–1573 Maldives
17th century
Portuguese India
· 1687–1749 Mylapore
18th century
Portuguese India
· 1779–1954 Dadra and Nagar HaveliEast Asia and Oceania16th century
1511–1641 Portuguese Malacca
1512–1621 Ternate
· 1576–1605 Ambon
· 1578–1650 Tidore
1512–1665 Makassar
1553–1999 Portuguese Macau
1571–1639 Decima (Dejima, Nagasaki)17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Timor (East Timor)1
19th century
Portuguese Macau
· 1864–1999 Coloane
· 1849–1999 Portas do Cerco
· 1851–1999 Taipa
· 1890–1999 Ilha Verde
20th century
Portuguese Macau
· 1938–1941 Lapa and Montanha (Hengqin)1 1975 is the year of East Timor's Declaration of Independence and subsequent invasion by Indonesia. In 2002, East Timor's independence was recognized by Portugal & the world.
North America and the North Atlantic Ocean15th century
1420 Madeira
1432 Azores16th century
1500–1579? Terra Nova (Newfoundland)
1500–1579? Labrador
1516–1579? Nova ScotiaCentral and South America16th century
1500–1822 Brazil
1536–1620 Portuguese Barbados17th century
1680–1777 Nova Colônia do Sacramento
19th century
1808–1822 Cisplatina (Uruguay)Outermost regions of European Union states Portugal Azores • Madeira
Spain France French Guiana • Guadeloupe • Martinique • Réunion • Saint Barthélemy • Saint-Martin
Geography of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognitionDependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Climate of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territoriesOther entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Categories:- Madeira Island
- Islands of Macaronesia
- Autonomous regions of Portugal
- NUTS 2 statistical regions of Portugal
- Outermost regions of the European Union
- Volcanoes of Portugal
- Volcanoes of the Atlantic Ocean
- Wine regions of Portugal
- Autonomous Region of Madeira
- Archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.