- Cinder cone
-
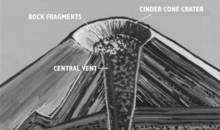
A cinder cone or scoria cone is a steep conical hill of volcanic fragments that accumulate around and downwind from a volcanic vent.[1] The rock fragments, often called cinders or scoria, are glassy and contain numerous gas bubbles "frozen" into place as magma exploded into the air and then cooled quickly.[1] Cinder cones range in size from tens to hundreds of metres tall.[1] Cinder cones are made of pyroclastic material.
Many cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. Lava flows are usually erupted by cinder cones, either through a breach on one side of the crater or from a vent located on a flank.[1] If the crater is fully breached, the remaining walls form an amphitheatre or horseshoe shape around the vent. Lava rarely issues from the top (except as a fountain) because the loose, uncemented cinders are too weak to support the pressure exerted by molten rock as it rises toward the surface through the central vent.[1]
Cinder cones are commonly found on the flanks of shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, and calderas.[1] For example, geologists have identified nearly 100 cinder cones on the flanks of Mauna Kea, a shield volcano located on the island of Hawaii.[1] These cones are also referred to as 'scoria cones' and 'cinder and spatter cones.'[1]
Perhaps the most famous cinder cone, Paricutin, grew out of a corn field in Mexico in 1943 from a new vent.[1] Eruptions continued for 9 years, built the cone to a height of 424 metres, and produced lava flows that covered 25 km².[1]
The Earth's most historically active cinder cone is Cerro Negro in Nicaragua.[1] It is part of a group of four young cinder cones NW of Las Pilas volcano.[1] Since it was born in 1850, it has erupted more than 20 times, most recently in 1992 and 1995.[1]
See also
- List of cinder cones
- Volcanic cone
- Capulin Volcano National Monument
References
Categories:- Cinder cones
- Volcanic cones
- Volcanic landforms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.