- Geography of Slovenia
-
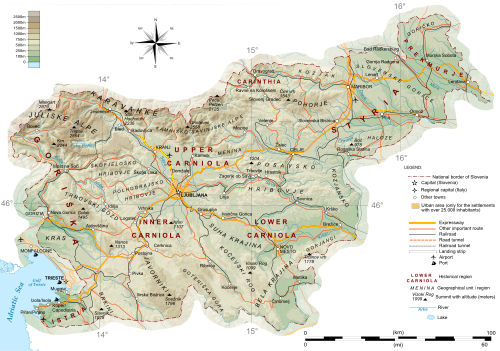
Slovenia is situated in Central Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. The Alps — including the Julian Alps, the Kamnik-Savinja Alps and the Karavanke chain, as well as the Pohorje massif — dominate Northern Slovenia along its long border to Austria. Slovenia's Adriatic coastline stretches approximately 43 km (27 mi)[1] from Italy to Croatia. Its part south of Sava river belongs to Balkan peninsula - Balkans.
The term "Karst" originated in southwestern Slovenia's Karst Plateau (Slovene: Kras), a limestone region of underground rivers, gorges, and caves, between Ljubljana and the Mediterranean.
On the Pannonian plain to the East and Northeast, toward the Croatian and Hungarian borders, the landscape is essentially flat. However, the majority of Slovenian terrain is hilly or mountainous, with around 90% of the surface 200 meters or more above sea level.
Contents
Location
Southeastern or Central Europe, Eastern Alps bordering the Adriatic Sea, between Austria and Croatia. The 15th meridian east almost corresponds to the middle line of the country in the direction west-east.[2]
Geographic coordinates
 Aerial view of Lake Bled
Aerial view of Lake Bled
Extreme geographical points of Slovenia:
- North: 46°52′36″N 16°13′59″E / 46.87667°N 16.23306°E, Municipality of Šalovci,
- South: 45°25′19″N 15°10′0″E / 45.42194°N 15.166667°E, Municipality of Črnomelj,
- East: 46°28′11″N 16°36′38″E / 46.46972°N 16.61056°E, Municipality of Lendava,
- West: 46°17′53″N 13°22′32″E / 46.29806°N 13.37556°E, Municipality of Kobarid.
The maximum north-south distance is 1°28' or 163 km (101 mi).
The maximum east-west distance is 3°13' or 248 km (154 mi).The geometric centre of Slovenia (GEOSS) is located at 46°07′11.8″N 14°48′55.2″E / 46.119944°N 14.815333°E.
Map references
Area
 Triglav Peak
Triglav Peak
- Total: 20,273 km²
- Land: 20,273 km²
- Water: 0 km²
- Comparison: slightly smaller than New Jersey
Borders
The entire Slovenian coastline is located on the Gulf of Trieste. Towns along the coastline include:
Regions
Historical Regions
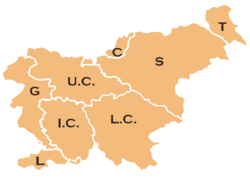
The traditional Slovenian regions, based on the former division of Slovenia into the four Habsburg crown lands of (Carniola, Carinthia, Styria, and the Littoral) and their parts, are:
- Upper Carniola (Gorenjska) (denoted on the map by U.C.)
- Styria (Štajerska) (S)
- Prekmurje (T)
- Carinthia (Koroška) (C)
- Inner Carniola (Notranjska) (I.C.)
- Lower Carniola (Dolenjska) (L.C.)
- Gorizia (Goriška) (G)
- Slovenian Istria (Slovenska Istra) (L)
The last two are usually considered together as the Littoral Region (Primorska). White Carniola (Bela krajina), otherwise part of Lower Carniola, is usually considered a separate region, as is the Central Sava Valley (Zasavje), which is otherwise a part of Upper and Lower Carniola and Styria.
Slovenian Littoral has no natural island, but there is a plan on building an artificial one.
Climate
Submediterranean climate on the coast, continental climate with mild to hot summers and cold winters on the plateaus and in the valleys to the east. Precipitation is high away from the coast, with the spring being particularly prone to rainfall. Slovenia's Alps have frequent snowfalls during the winter. [4]
Terrain
A short coastal strip on the Adriatic, an alpine mountain region adjacent to Italy and Austria, mixed mountain and valleys with numerous rivers to the east.
There is only one natural island in Slovenia: Bled Island in Lake Bled in the country's northwest.
Elevation extremes
- Lowest point: Adriatic Sea 0 m
- Highest point: Triglav 2,864 m (9,396 ft)
Natural resources
Lignite coal, lead, zinc, mercury, uranium, silver, hydropower
Land use
- Arable land: 12%
- Permanent crops: 3%
- Permanent pastures: 24%
- Forests and woodland: 60%
- Other: 7% (1996 est.)
- Irrigated land: 20 km² (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards: flooding and earthquakes
Environment
Current issues
The Sava River polluted with domestic and industrial waste; pollution of coastal waters with heavy metals and toxic chemicals; forest damage near Koper from air pollution (originating at metallurgical and chemical plants) and resulting acid rain.
International agreements
- Party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78), Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
See also
- Slovenian Riviera (Slovenska obala)
- List of national parks of Slovenia
- Mountains of Slovenia
References
- ^ a b Boštjan Burger web-site about Slovenia
- ^ Jenko, Marjan (2005). "O pomenu meridiana 15° vzhodno od Greenwicha [About the Significance of the 15th Degree to the East of Greenwich Meridian]" (in Slovene). Geodetski vestnik 49 (4): pp. 637-638. http://www.geodetski-vestnik.com/49/4/gv49-4_637-638.pdf. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ^ The World Factbook by CIA (retrieved 2008-02-12)
- ^ http://www.geckogo.com/Guide/Slovenia/Natural-Environment/Climate/
External links
- http://www.geopedia.si/ - Geodesic Institute of Slovenia – Detailed Topographic and Ortophoto maps of Slovenia
Geography of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognitionDependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Climate of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territoriesOther entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.