- Military of Slovenia
-
Slovenian Army
Slovenska vojska
Founded 1991 Service branches Slovenian Navy
Slovenian Air Force
Slovenian Ground ArmyHeadquarters Ljubljana Leadership Commander-in-Chief Danilo Türk (president of Slovenia) Minister of Defense Ljubica Jelušič Chief of staff Alojz Šteiner (Major General) Manpower Military age 18 Conscription Abolished in 2003 Available for
military service496,929, age 17 (voluntary) (2005 est.) Fit for
military service405,593, age 17 (voluntary) (2005 est.) Active personnel 7,600 (professional soldiers) (ranked 123rd) Reserve personnel 1,700 (contract reserve soldiers) Deployed personnel  Kosovo -321
Kosovo -321
 Afghanistan -90
Afghanistan -90 Lebanon-14
Lebanon-14 Serbia-3
Serbia-3 Syria-2
Syria-2 Somalia -2
Somalia -2Expenditures Budget € 507,780,067 (2010)[1] Percent of GDP 1.6% (2009)[2] Related articles History Slovenian War of Independence
Slovenian Territorial DefenceRanks Slovenian military ranks The Military of Slovenia consists of the Slovenian Armed Forces (also Slovenian Army; officially Slovene Slovenska vojska; SAF/SV). The SAF are the armed forces of Slovenia. Since 2003, it is organized as a fully professional standing army. The Commander-in-Chief of the SAF is the President of the Republic of Slovenia (Danilo Türk), while operational command is in the domain of the Chief of the General Staff of the Slovenian Armed Forces, the position being held since 2009 by Alojz Šteiner.
Contents
History
The military history of Slovenia spans less than a hundred years. Following the disintegration of the Austrian-Hungarian Empire at the end of World War I, the Duchy of Styria was divided between the newly established states of German Austria and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. Rudolf Maister, a Slovene major of the former Austro-Hungarian Army, liberated the town of Maribor in November 1918 and claimed it to the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. After a short fight with German Austrian provisional units, the current border was established, which mostly followed the ethnic-linguistic division between Slovenes and ethnic Germans in Styria.
The current Slovenian Armed Forces are descended from the Slovenian Territorial Defence (Teritorialna Obramba Republike Slovenije; or Slovene TO), formed in 1991 by fusion of Territorial Defence (formed in 1968 as a paramilitary complement to the regular army of the former Yugoslav within the territory of Slovenia) with secret alternative command structure, known as the Manoeuvre Structures of National Protection (Manevrska struktura narodne zaščite, or MSNZ), which was an existing but antiquated institution, (unique to Slovenia), intended to enable the republic to form an ad hoc defence structure, akin to a Home Guard. It was of negligible importance prior to 1990, with antiquated weapons and few members.
When Slovenia declared independence at the onset of the Yugoslav Wars in 1991, the Slovenian Territorial Defence and the Slovenian police comprised the majority of forces engaging the Yugoslav People's Army during the Ten-Day War. The Slovenian Armed Forces were formally established in 1993 as a reorganization of the Slovenia Territorial Defence.
Current status
A major reorganization of the Slovenian Armed Forces is currently underway, with the goal of changing it from a territorial defense force into a deployable force primarily aimed at peacekeeping. After 1993, the Slovenian Armed Forces had relied on mandatory military service, with conscripts receiving 6–7 months of training. In 2003, the Slovenian Government abolished conscription and as of July 2004, the Slovenian Armed Forces had been almost completely reorganised into a professional army now based on volunteers. Currently there are approximately 7,600 active troops and approximately 1,700 in reserve, reduced from 55,000 personnel during conscription. The operational units now consist of three brigades, the 1st, 72nd and an Air Defense and Aviation Brigade; all three are subordinated to the Forces Command.
During a press conference on July 18, 2008,[3] the Slovenian defense minister confirmed plans for the acquisition of a Russian Svetlyak class (Project 10412) patrol boat. Displacing 355 (full 395) tons and measuring 49.5 x 9.2 x 2.6 m, the vessel will have a maximum speed of 30 knots and a complement of 24. Armaments include one 30mm AK-630m cannon, two side-mounted 14.5mm MTPU machine guns, 9M120 anti-ship missile system and 16 air-defense missiles type Igla. The ship will be built by Almaz Shipbuilding[4] of Saint Petersburg; delivery is expected in 2010. Total cost of the purchase is said to be $39.4 million, two-thirds of which will be covered by existing Russian debt.[5]
NATO membership
As part of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Slovenia was never a member of the Warsaw Pact. Today, the foreign policy priority of NATO membership drives Slovenia's defense reorganization. Once many countries lifted the arms embargo on Slovenia in 1996, the country embarked on a military procurement program to bolster its status as a NATO candidate and to aid its transformation into a mobile force. Active in the SFOR deployment in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia is also a charter member of Partnership for Peace and a regular participant in PfP exercises. The United States provides bilateral military assistance to Slovenia, including through the International Military Education and Training (IMET) program, the State Partnership Program (aligned with Colorado), and the EUCOM Joint Contact Team Program.
Slovenia formally joined NATO in March 2004.[6] The transition of its armed forces from a primarily conscript-based territorial defense organization to a professional force structure have the ultimate goal of creating NATO-interoperable combat units able to operate on an even par with units from other NATO armies. Implementation of interoperability objectives as determined by the Planning and Review Process (PARP) and the Individual Partnership Program (IPP) as part of Slovenia's PfP participation proceeds. Slovenia's elite units already train with and are integrated into international units including NATO members—for example as part of SFOR and on Cyprus. Its elite mountain troops will be assigned to the Multinational Land Force peacekeeping battalion with Italy, Hungary, and Croatia. Slovenia hosted its first PfP exercise in 1998--"Cooperative Adventure Exchange"--a multinational disaster-preparedness command post exercise involving almost 6,000 troops from 19 NATO and PfP member nations.
Slovenian soldiers are a part of international forces serving in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Afghanistan,[7] Iraq, Chad, Lebanon. They have also served in Cyprus and the Golan Heights as a part of UNFICYP and UNDOF respectively.
Organization
The Slovenian Armed Forces are organized as single-branch armed forces with the army as their primary component. The personnel is divided into three categories:
- professional soldiers (full-time soldiers)
- contract reserve soldiers (serve up to 30 days per year)
- voluntary recruits (basic training)
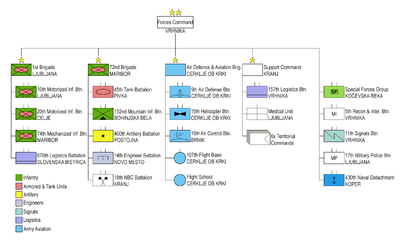
Commands and units
-
-
-
- 10th Motorized Battalion
- 20th Motorized Battalion
- 74th Motorized Battalion
- 670th Command-Logistics Battalion
-
- 45th Armoured Battalion
- 132nd Mountain Battalion
- 460th Artillery Battalion
- 14th Engineer Battalion
- 18th NBC-Defence Battalion
- Air Defence and Aviation Brigade
-
- 9th Air Defence Battalion
- 15th Helicopter Battalion
- 16th Air Control Battalion
- 107th Flight Base
- Flight school
-
- 157th Logistics Battalion
- Medical Unit
-
-
Military airports (Slovenian army)
The Slovenian army currently maintains one military airport Cerklje ob Krki near town of Brežice. The airport's official name is Cerklje ob Krki Airbase.
The others that are partially military are:
- Ljubljana Airbase shares the airport with Ljubljana International Airport
- Lesce Airbase 2x helicopters Bell 412 are stationed there for mountain rescue
Barracks
Main article: List of Barracks of the Slovenian Armed ForcesInternational cooperation
Slovenia is part of NATO and the European Union. The Slovenian Armed Forces have participate and presently participate in many aspects of both organizations.
Current Mission Organization Country Nr. of personnel ALTHEA EUFOR Bosnia and Herzegovina 25 Joint Enterprise NATO Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Joint Enterprise NATO Kosovo 387 CENTCOM NATO U.S. 1 UNTSO United Nations Syria 2 ISAF NATO Afghanistan 88 UNIFIL UN Lebanon 14 Joint Enterprise NATO Serbia 3 Former Mission Operation Country Organization Nr. of personnel Time ALBA Operation Sunrise Albania OSCE 21 May–July 1997 UNFICYP / Cyprus United Nations 29 September 1997-June 2001 ALBA Operation Allied Harbour Albania NATO 26 May–July 1999 UNMIK / Kosovo United Nations 1 October 1999-December 2001 OHR / Bosnia and Herzegovina United Nations 1 July 2001-January 2003 ? Operation Concordia Republic of Macedonia European Union 1 March 2003 Kosovo Force Operation Joint Guardian Kosovo NATO 11 November 2003-May 2004 / Nato support to Pakistan Pakistan NATO 2 November 2005-January 2006 International military exercises Country Organization Nr. of personnel Time Cooperative Nugget 1997 Fort Polk, U.S. Partnership for Peace/NATO 1997 Cooperative Adventure Exchange '98 Slovenia NATO 1998 Cooperative Key 2002 2002 Cunning Wassel 2002 2002 Clever Ferret 2003 2003 Elite 2003 2003 Data
Military branches: Slovenian Army (includes Air and Naval Forces)
Military manpower - military age: 19 years of age
Military manpower - availability:
males age 15-49: 525,031 (2000 est.)Military manpower - fit for military service:
males age 15-49: 417,726 (2000 est.)Military manpower - reaching military age annually:
males: 14,958 (2000 est.)Military expenditures - dollar figure: $335 million (FY99)
Military expenditures - percent of GDP: 1.6% (FY99)
Gallery
-
Slovenian MAN Army Truck
References
- ^ [1]
- ^ Defence Expenditures of NATO Countries (1985-2009)
- ^ RTV Slovenija: Slovensko obalo bo varovala "Kresnica"
- ^ Homepage of ALMAZ Shipbuilding company
- ^ Slovensko obalo bo varovala "Kresnica" :: Prvi interaktivni multimedijski portal, MMC RTV Slovenija
- ^ http://www.nato.int/docu/update/2004/03-march/e0329a.htm
- ^ The Slovenia Times - Daily News
External links
- Official page (English)
- Slovenian Ministry of Defence official site (English)
- Slovenian Air Force
- Slovenian Armed Forces/Slovenska vojska
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) History 
Structure Members Militaries of the member states of the European Union Military of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Other entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Categories:- Military of Slovenia
- Military units and formations established in 1991
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.