- Dejima
-
This article is about the artificial island. For the sumo wrestler, see Dejima Takeharu.
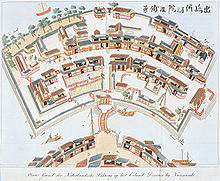
Dejima (出島, literally "exit island"; Dutch: also Desjima or Deshima, sometimes latinised as Decima or Dezima) was a small fan-shaped artificial island built in the bay of Nagasaki in 1634. This island, which was formed by digging a canal through a small peninsula, remained as the single place of direct trade and exchange between Japan and the outside world during the Edo period. Dejima was built to constrain foreign traders as part of sakoku, the self-imposed isolationist policy. Originally built to house Portuguese traders, it was used by the Chinese and Dutch as a trading post from 1641 until 1853. Covering an area of 120 m x 75 m (9000 square meters, or 0.9 hectares), it later was integrated into the city.
"Dejima Dutch Trading Post" has been designated a Japanese national historic site.
Contents
History
A Fujianese worker and an official, Malaysia, 1880. A Chinese official and a woman from Macao, 1880.
A Chinese official and a woman from Macao, 1880.
In 1543 Portuguese traders were the first to land in Japan, on Tanegashima. Six years later the Jesuit missionary Francis Xavier landed in Kagoshima. At first Portuguese traders were based in Hirado, but they moved in search of a better port. In 1570 daimyo Ōmura Sumitada converted to Catholicism (choosing Bartolomeu as his Christian name) and made a deal with the Portuguese to develop Nagasaki; soon the port was open for trade. In 1580 Sumitada gave the jurisdiction of Nagasaki to the Jesuits, and the Portuguese obtained the de facto monopoly on the silk trade with China through Macau.
The shogun Iemitsu ordered the construction of the artificial island in 1634, to constrain the Portuguese merchants living in Nagasaki. But after an uprising of the predominantly Christian population in the Shimabara-Amakusa region, the Tokugawa government decided to expel all Western nationals except the Dutch employees of the Dutch East India Company (Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie, VOC).
Since 1609 the Dutch had run a trading post on the island of Hirado. At its maximum the Hirado trading post covered a large area.[quantify][1] In 1637 and 1639 stone warehouses were constructed within the ambit of this Hirado trading post. Christian-era year dates were used on the stonework of the new warehouses.
Without the annual trading with Portuguese ships from Macau, the economy of Nagasaki suffered greatly. Government officials, who were looking for means to relocate the Dutch trading post, forced the Dutch to move from Hirado to Dejima.[2]
From 1641 on, only Chinese and Dutch ships were allowed to come to Japan.
Organization
On the administrative level, the island of Dejima was part of the city of Nagasaki. The 25 local Japanese families who owned the real estate received an annual rent from the Dutch. Dejima was a small island, 120 by 75 meters,[3] linked to the mainland by a small bridge, guarded on both sides, and with a gate on the Dutch side. It contained houses for about twenty Dutchmen, warehouses, and accommodation for Japanese officials. The Dutch were watched by a number of Japanese officials, gatekeepers, night watchmen, and a supervisor (otona) with about fifty subordinates. Numerous merchants supplied goods and catering, and about 150 tsūji ("interpreters") served. They all had to be paid by the VOC. Like the city of Nagasaki, Dejima was under direct supervision of Edo by a governor (Nagasaki bugyō).
Every ship that arrived in Dejima was inspected. Its sails were held by the Japanese until they released the ship to leave. They confiscated religious books and weapons. The Dutch were not allowed to hold any religious services on the island.
Despite the financial burden of maintaining the isolated outpost on Dejima, the trade with Japan was very profitable for the VOC, initially yielding profits of 50% or more. Trade declined in the 18th century, as only two ships per year were allowed to dock at Dejima. After the bankruptcy of the VOC in 1795, the Dutch government took over exchange with Japan. Times were especially hard when the Netherlands (then called the Batavian Republic) was under French Napoleonic rule. All the ties with the homeland were severed at Dejima, and for a while, it was the only place in the world where the Dutch flag was flown.
The chief VOC official in Japan was called the Opperhoofd by the Dutch, or Kapitan (from Portuguese capitão) by the Japanese. This descriptive title did not change when the island's trading fell under Dutch state authority. Throughout these years, the plan was to have one incumbent per year—but sometimes plans needed to be flexible.
Trade
Originally, the Dutch mainly traded in silk, cotton, and materia medica from China and India, but sugar became more important later. Also, deer pelts and shark skin were transported to Japan from Taiwan, as well as books, scientific instruments and many other rarities from Europe. In return, the Dutch traders bought Japanese copper, silver, camphor, porcelain, lacquer ware and rice.
To this was added the personal trade of VOC employees on Dejima, which was an important source of income for them. They sold more than 10,000 foreign books on various scientific subjects to the Japanese from the end of the 18th to the early 19th century. These became the basis of knowledge and a factor in the Rangaku movement, or Dutch studies.
Ship arrivals
In all, 606 Dutch ships arrived at Dejima during its two centuries of settlement, from 1641 to 1847.
- The first period, from 1641 to 1671, was rather free, and saw an average of 7 Dutch ships every year (12 sank during this period).
- From 1671 to 1715, about 5 Dutch ships were allowed to visit Dejima every year.
- From 1715, only 2 ships were permitted every year, which was reduced to 1 ship in 1790, and again increased to 2 ships in 1799.
- During the Napoleonic wars, in which the Netherlands was occupied by (and a satellite of) France, Dutch ships could not safely reach Japan in the face of British opposition. They relied on "neutral" American and Danish ships. (When the Netherlands was made a province by France (1811–1814), and Britain conquered Dutch colonial possessions in Asia, Dejima for four years was the only place in the world where the free Dutch flag flew, as ordered by Hendrik Doeff.)
- After the liberation of the Netherlands in 1815, regular Dutch trading traffic was reestablished.
Sakoku policy
For two hundred years, Dutch merchants were generally not allowed to cross from Dejima to Nagasaki. The Japanese were likewise banned from entering Dejima, except for prostitutes from Nagasaki teahouses. These yūjo were handpicked from 1642 by the Japanese, often against their will. From the 18th century, there were some exceptions to this rule, especially following Tokugawa Yoshimune's doctrine of promoting European practical sciences. A few Oranda-yuki ("those who stay with the Dutch") were allowed to stay for longer periods, but they had to report regularly to the Japanese guard post. European scholars such as Engelbert Kaempfer, Carl Peter Thunberg, Isaac Titsingh and Philipp Franz von Siebold were allowed to enter the mainland with the shogunate's permission.[4] Starting in the 18th century, Dejima became known throughout Japan as a center of medicine, military science, and astronomy. Many samurai travelled there for "Dutch studies" (Rangaku).
 The Vinegar Tasters: Laozi, Buddha, and Confucius. Dejima was a center for the trade of products and ideas. At the same time that Japanese intellectuals studied scientific developments in Europe, they sought to remain in touch with the political and social philosophy of Neo-Confucianism, which flourished in Japan during the Edo period.
The Vinegar Tasters: Laozi, Buddha, and Confucius. Dejima was a center for the trade of products and ideas. At the same time that Japanese intellectuals studied scientific developments in Europe, they sought to remain in touch with the political and social philosophy of Neo-Confucianism, which flourished in Japan during the Edo period.
In addition, the Opperhoofd was treated like the head of a tributary state, which meant that he had to pay a visit of homage to the Shogun in Edo. The Dutch delegation traveled to Edo yearly between 1660 and 1790, and once every four years thereafter. This prerogative was denied to the Chinese traders. The lengthy travel to the imperial court broke the boredom of the Dutch stay, but it was a costly affair. The shōgun told them in advance and in detail which (expensive) gifts he expected, such as astrolabes, a pair of glasses, telescopes, globes, medical instruments, medical books, or exotic animals and tropical birds. In return, the Dutch delegation received some gifts from the shogun. On arrival in Edo, the Opperhoofd and his retinue (usually his scribe and the factory doctor) had to wait in the Nagasakiya, their mandatory residence, until they were summoned at the court. After their official audience, they were expected, according to Engelbert Kaempfer, to perform Dutch dances and songs etc. for the amusement of the shogunate. But they also used the opportunity of their stay of about two to three weeks in the capital to exchange knowledge with learned Japanese and, under escort, to visit the town.
New introductions to Japan
- Badminton, a sport that originated in India, was introduced by the Dutch during the 18th century; it is mentioned in the Sayings of the Dutch.
- Billiards were introduced in Japan on Dejima in 1794; it is noted as "Ball striking table" (玉突の場) in the paintings of Kawahara Keika (川原慶賀).
- Beer seems to have been introduced as imports during the period of isolation. The Dutch governor Doeff made his own beer in Nagasaki, following the disruption of trade during the Napoleonic wars. Local production of beer started in Japan in 1880.
- Clover was introduced in Japan by the Dutch as packing material for fragile cargo. The Japanese called it "White packing herb" (シロツメクサ), in reference to its white flowers.
- Coffee was introduced in Japan by the Dutch under the name Moka. Siebold refers to Japanese coffee amateurs in Nagasaki around 1823.
- Piano. Japan's oldest piano was introduced by Siebold in 1823, and later given to a tradesperson in the name of Kumatani (熊谷). The piano is today on display in the Kumatani Museum (萩市の熊谷美術館).
- Paint, used for ships, was introduced by the Dutch. The original Dutch name (pek) was also adopted in Japanese (Penki/ペンキ).
- Cabbage and tomatoes were introduced in the 17th century by the Dutch.
- Chocolate was introduced between 1789 and 1801; it is mentioned as a drink in the pleasure houses of Maruyama.
 The Nagasaki Training Center, in Nagasaki, next to Dejima (in the background).
The Nagasaki Training Center, in Nagasaki, next to Dejima (in the background).
Following the forced opening of Japan by US Navy Commodore Perry in 1854, the Bakufu suddenly increased its interactions with Dejima in an effort to build up knowledge of Western shipping methods. The Nagasaki Naval Training Center (長崎海軍伝習所 Nagasaki Kaigun Denshūsho), a naval training institute, was established in 1855 by the government of the Shogun at the entrance of Dejima, to enable maximum interaction with Dutch naval know-how. The center was equipped with Japan's first steamship, the Kankō Maru, given by the government of the Netherlands the same year. The future Admiral Enomoto Takeaki was one of the students of the Training Center.
Reconstruction
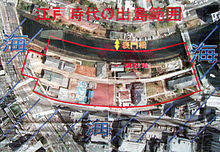
The Dutch East India Company's trading post at Dejima was closed in 1857, after Dutch merchants were allowed to trade in Nagasaki City. Since then, the island has been expanded by reclaimed land and merged into Nagasaki. Extensive redesigning of Nagasaki Harbor in 1904 has obscured its original location.[5] The original footprint of Dejima Island has been marked by rivets; but as restoration progresses, the ambit of the island will be easier to see at a glance.
Dejima today is a work in progress. The island was designated a national historical site in 1922, but further steps were slow to follow. Restoration work was started in 1953, but that project languished.[5] In 1996, restoration of Dejima began with plans for reconstructing 25 buildings in their early 19th-century state. To better display Dejima's fan-shaped form, the project anticipated rebuilding only parts of the surrounding embankment wall that had once enclosed the island. Buildings that remained from the Meiji Period were to be used.
In 2000, five buildings including the Deputy Factor's Quarters were completed and opened to the public. In the spring of 2006, the finishing touches were put on the Chief Factor's Residence, the Japanese Officials' Office, the Head Clerk's Quarters, the No. 3 Warehouse, and the Sea Gate.
The long-term planning intends that Dejima will be surrounded by water on all four sides; its characteristic fan-shaped form and all of its embankment walls will be fully restored. This long-term plan will include large-scale urban redevelopment in the area. To make Dejima an island again will require rerouting the Nakashima River and moving a part of Route 499.
Chronology
 Two Chinese men depicted by Utagawa Yoshitora on a print of the Bakumatsu era, c. 1859-1863.
Two Chinese men depicted by Utagawa Yoshitora on a print of the Bakumatsu era, c. 1859-1863.
- 1550: Portuguese ships visit Hirado.
- 1561: Following the murder of foreigners in the area of the Hirado clan, Portuguese began to look for other ports to trade.
- 1570: Christian daimyo Ōmura Sumitada make a deal with the Portuguese to develop Nagasaki, six town blocks are built.
- 1571: Nagasaki Harbor is opened for trade, the first Portuguese ships enter.
- 1580: Omura Sumitada cedes jurisdiction over Nagasaki and Mogi to the Jesuits.
- 1588: Toyotomi Hideyoshi exerts direct control over Nagasaki, Mogi, and Urakami from the Jesuits.
- 1609: The Dutch East India Company opens a factory in Hirado. It closes in 1641 when it is moved to Deshima.
- 1612: Japan's feudal government decrees that Christian proselytizing on Bakufu lands is forbidden.
- 1616: All trade with foreigners except that with China is confined to Hirado and Nagasaki.
- 1634: The construction of Dejima begins.
- 1636: Dejima is completed; the Portuguese are interned on Dejima (Fourth National Isolation Edict).
- 1638: Shimabara Rebellion of Christian peasants is repressed with Dutch support, Christianity in Japan is repressed.
- 1639: Portuguese ships are prohibited from entering Japan. Consequently, the Portuguese are banished from Dejima.
- 1641: The Dutch East India Company Trading Post in Hirado is moved to Nagasaki.
- 1649: German surgeon Caspar Schamberger comes to Japan.
- 1662: A shop is opened on Dejima to sell Imari porcelain.
- 1673: The English ship "Return" enters Nagasaki, but the Shogunate refuses its request for trade.
- 1678: A bridge connecting Dejima with the shore is replaced with a stone bridge.
- 1690: The German physician Engelbert Kaempfer comes to Dejima.
- 1696: Warehouses for secondary cargo reach completion on Dejima.
- 1698: The Nagasaki Kaisho (trade association) is founded.
- 1699: The Sea Gate is built at Dejima.
- 1707: Water pipes are installed on Dejima.
- 1775: Carl Thunberg starts his term as physician on Dejima.
- 1779: Surgeon Isaac Titsingh arrives for his first tour of duty as "Opperhoofd".
- 1798: Many buildings, including the Chief Factor's Residence, are destroyed by the Great Kansei Fire of Dejima.
- 1804: Russian Ambassador N.P. Rezanov visits Nagasaki to request an exchange of trade between Japan and Imperial Russia.
- 1808: The Phaeton Incident occurs.
VOC outpost
-
-
- See more at VOC Opperhoofden in Japan
-
 The last of the Dejima-based Opperhoofden handled the 1855 delivery of the Kankō Maru (観光丸), Japan's first modern steam warship – a gift from the Dutch King Willem III to the Tokugawa Shogunate.
The last of the Dejima-based Opperhoofden handled the 1855 delivery of the Kankō Maru (観光丸), Japan's first modern steam warship – a gift from the Dutch King Willem III to the Tokugawa Shogunate.
Opperhoofd is a Dutch word (plural Opperhoofden) which literally means 'supreme head[man]'. In its historical usage, the word is a gubernatorial title, comparable to the English Chief factor, for the chief executive officer of a Dutch factory in the sense of trading post, as led by a Factor, i.e. agent.
At Hirado
- François Caron: 3.2.1639 - 13.2.1641 [Caron was last Opperhoofd at Hirado.]
At Dejima
- François Caron: 3.2.1639 - 13.2.1641 [Caron was the first Opperhoofd in Dejima following the forced move from Hirado.]
- Zacharias Wagenaer [Wagener]: 1.11.1656 - 27.10.1657
- Zacharias Wagenaer [Wagener]: 22.10.1658 - 4.11.1659
- Andreas Cleyer [Andries]: 20.10.1682 - 8.11.1683
- Andreas Cleyer: 17.10.1685 - 5.11.1686
- Hendrik Godfried Duurkoop: 23.11.1776 - 11.11.1777
- Isaac Titsingh: 29.11.1779 - 5.11.1780
- Isaac Titsingh: 24.11.1781 - 26.10.1783
- Isaac Titsingh: _.8.1784 - 30.11.1784
- Hendrik Doeff: 14.11.1803 - 6.12.1817
- Jan Cock Blomhoff: 6.12.1817 - 20.11.1823
- Janus Henricus Donker Curtius: 2.11.1852 - 28.2.1860 [Donker Curtius became the last in a long list of hardy Dutch Opperhoofden who were stationed at Dejima; and fortuitously, Curtius also became the first of many Dutch diplomatic and trade representatives in Japan during the burgeoning pre-Meiji years.][citation needed]
Image gallery
 A bird's-eye view of Nagasaki harbor, in the Illustrated London News (March 23, 1853). In the center – the fan-shape of the Dutch traders' Dejima island compound; the Chinese compound is to the left, separated by a narrow stretch of water. Bakufu supervision of the foreigners was controlled by the Governor of Nagasaki (the Nagasaki bugyō.
A bird's-eye view of Nagasaki harbor, in the Illustrated London News (March 23, 1853). In the center – the fan-shape of the Dutch traders' Dejima island compound; the Chinese compound is to the left, separated by a narrow stretch of water. Bakufu supervision of the foreigners was controlled by the Governor of Nagasaki (the Nagasaki bugyō.
 The Chinese traders at Nagasaki were confined to a walled compound located near Dejima island. The Chinese were closely monitored by the Nagasaki bugyō.
The Chinese traders at Nagasaki were confined to a walled compound located near Dejima island. The Chinese were closely monitored by the Nagasaki bugyō.
 Hendrik Doeff and a Balinese servant in Dejima, Japanese painting, c. early 19th century.
Hendrik Doeff and a Balinese servant in Dejima, Japanese painting, c. early 19th century.
 Monument erected in Dejima by Siebold to honor Kaempfer and Thunberg
Monument erected in Dejima by Siebold to honor Kaempfer and Thunberg
See also
- Nanban trade
- Dutch missions to Edo
- VOC Opperhoofden in Japan
- Neo-Confucianism
- Rangaku
- Sakoku
- China-Japan relations
- Japan–Netherlands relations
- The Thousand Autumns of Jacob de Zoet - Historical novel set in Dejima
Notes
- ^ Edo-Tokyo Museum exhibition catalog. (2000). A Very Unique Collection of Historical Significance: The Kapitan (the Dutch Chief) Collection from the Edo Period – The Dutch Fascination with Japan, p. 206.
- ^ Edo-Tokyo Museum exhibition catalog, p. 207.
- ^ Ken Vos - The article "Dejima als venster en doorgeefluik" in the catalog (Brussels, 5 October 1989 - 16 December 1989) of the exhibition Europalia 1989 : "Oranda : De Nederlanden in Japan (1600-1868)
- ^ In the context of Commodore Perry's "opening" of Japan in 1853, American naval expedition planners incorporated reference material written by men whose published accounts of Japan were based on first-hand experience. J.W. Spaulding brought with him books by Japanologists Engelbert Kaempfer, Carl Peter Thunberg, and Isaac Titsingh. Screech, T. (2006). Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779-1822, p.73.
- ^ a b Edo-Tokyo Museum exhibition catalog, p. 47.
References
- Blomhoff, J.C. (2000). The Court Journey to the Shogun of Japan: From a Private Account by Jan Cock Blomhoff. Amsterdam
- Blussé, L. et al., eds. (1995–2001) The Deshima [sic] Dagregisters: Their Original Tables of Content. Leiden.
- Blussé, L. et al., eds. (2004). The Deshima Diaries Marginalia 1740-1800. Tokyo.
- Boxer. C.R. (1950). Jan Compagnie in Japan, 1600-1850: An Essay on the Cultural, Aristic, and Scientific Influence Exercised by the Hollanders in Japan from the Seventeenth to the Nineteenth Centuries. Den Haag.
- Caron, François. (1671). A True Description of the Mighty Kingdoms of Japan and Siam. London.
- Doeff, Hendrik. (1633). Herinneringen uit Japan. Amsterdam. [Doeff, H. "Recollections of Japan" (ISBN 1-55395-849-7)]
- Edo-Tokyo Museum exhibition catalog. (2000). A Very Unique Collection of Historical Significance: The Kapitan (the Dutch Chief) Collection from the Edo Period—The Dutch Fascination with Japan. Catalog of "400th Anniversary Exhibition Regarding Relations between Japan and the Netherlands," a joint project of the Edo-Tokyo Museum, the City of Nagasaki, the National Museum of Ethnology, the National Natuurhistorisch Museum and the National Herbarium of the Netherlands in Leiden, the Netherlands. Tokyo.
- Leguin, F. (2002). Isaac Titsingh (1745–1812): Een passie voor Japan, leven en werk van de grondlegger van de Europese Japanologie. Leiden.
- Nederland's Patriciaat, Vol. 13 (1923). Den Haag.
- Screech, Timon. (2006). Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779-1822. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 0-7007-1720-X
- Siebold, P.F.v. (1897). Nippon. Würzburg e Leipzig.Click link for full text in modern German
- Titsingh, I. (1820). Mémoires et Anecdotes sur la Dynastie régnante des Djogouns, Souverains du Japon. Paris: Nepveau.
- Titsingh, I. (1822). Illustrations of Japan; consisting of Private Memoirs and Anecdotes of the reigning dynasty of The Djogouns, or Sovereigns of Japan. London: Ackerman.
External links
- Dejima: The Island Comes Back to Life
- Hendrick Hamel in Japan: Deshima, layout and building placement
- WorldStatesmen - Japan
- New York Public Library Digital Gallery:
- NYPL ID 481279, Engelbert Kaempfer's map of Nagasaki harbor, 1727: Deshima location
Coordinates: 32°44′37″N 129°52′23″E / 32.74352°N 129.87302°E
Links to related articles Portuguese Empire North Africa15th century
1415–1640 Ceuta
1458–1550 Alcácer Ceguer (El Qsar es Seghir)
1471–1550 Arzila (Asilah)
1471–1662 Tangier
1485–1550 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1487– middle 16th century Ouadane
1488–1541 Safim (Safi)
1489 Graciosa16th century
1505–1769 Santa Cruz do Cabo
de Gué (Agadir)
1506–1525 Mogador (Essaouira)
1506–1525 Aguz (Souira Guedima)
1506–1769 Mazagan (El Jadida)
1513–1541 Azamor (Azemmour)
1515 São João da Mamora (Mehdya)
1577–1589 Arzila (Asilah)Sub-Saharan Africa15th century
1455–1633 Arguin
1470–1975 Portuguese São Tomé1
1474–1778 Annobón
1478–1778 Fernando Poo (Bioko)
1482–1637 Elmina (São Jorge
da Mina)
1482–1642 Portuguese Gold Coast
1496–1550 Portuguese Madagascar
1498–1540 Mascarene Islands16th century
1500–1630 Malindi
1500–1975 Portuguese Príncipe1
1501–1975 Portuguese E. Africa
(Mozambique)
1502–1659 Portuguese Saint Helena
1503–1698 Zanzibar
1505–1512 Quíloa (Kilwa)
1506–1511 Socotra
1557–1578 Portuguese Accra
1575–1975 Portuguese W. Africa
(Angola)
1588–1974 Cacheu2
1593–1698 Mombassa (Mombasa)17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Cape Verde
1645–1888 Ziguinchor
1680–1961 São João Baptista de Ajudá
1687–1974 Portuguese Bissau2
18th century
1728–1729 Mombassa (Mombasa)
1753–1975 Portuguese São Tomé and Príncipe
19th century
1879–1974 Portuguese Guinea
1885–1975 Portuguese Congo1 Part of São Tomé and Príncipe from 1753. 2 Part of Portuguese Guinea from 1879. Southwest Asia16th century
1506–1615 Gamru (Bandar-Abbas)
1507–1643 Sohar
1515–1622 Hormuz (Ormus)
1515–1648 Quriyat
1515–? Qalhat
1515–1650 Muscat
1515?–? Barka
1515–1633? Julfar (Ras al-Khaimah)
1521–1602 Bahrain (Muharraq and Manama)
1521–1529? Qatif
1521?–1551? Tarut Island
1550–1551 Qatif
1588–1648 Matrah17th century
1620–? Khor Fakkan
1621?–? As Sib
1621–1622 Qeshm
1623–? Khasab
1623–? Libedia
1624–? Kalba
1624–? Madha
1624–1648 Dibba Al-Hisn
1624?–? Bandar-e KongIndian subcontinent15th century
1498–1545 Laccadive Islands
(Lakshadweep)16th century
Portuguese India
· 1500–1663 Cochim (Kochi)
· 1502–1661 Quilon (Coulão/Kollam)
· 1502–1663 Cannanore (Kannur)
· 1507–1657 Negapatam (Nagapatnam)
· 1510–1962 Goa
· 1512–1525 Calicut (Kozhikode)
· 1518–1619 Portuguese Paliacate trading outpost (Pulicat)
· 1521–1740 Chaul
· 1523–1662 Mylapore
· 1528–1666 Chittagong
· 1531–1571 Chaul
· 1534–1601 Salsette Island
· 1534–1661 Bombay (Mumbai)
· 1535–1739 Baçaím (Vasai-Virar)
· 1536–1662 Cranganore (Kodungallur)
· 1540–1612 Surat
· 1548–1658 Tuticorin (Thoothukudi)16th century (continued)
Portuguese India (continued)
· 1559–1962 Daman and Diu
· 1568–1659 Mangalore
· 1579–1632 Hugli
· 1598–1610 Masulipatnam (Machilipatnam)
1518–1521 Maldives
1518–1658 Portuguese Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1558–1573 Maldives
17th century
Portuguese India
· 1687–1749 Mylapore
18th century
Portuguese India
· 1779–1954 Dadra and Nagar HaveliEast Asia and Oceania16th century
1511–1641 Portuguese Malacca
1512–1621 Portuguese Maluku Islands
· 1522–1575 Ternate
· 1576–1605 Ambon
· 1578–1650 Tidore
1512–1665 Makassar
1553–1999 Portuguese Macau
1571–1639 Decima (Dejima, Nagasaki)17th century
1642–1975 Portuguese Timor (East Timor)1
19th century
Portuguese Macau
· 1864–1999 Coloane
· 1849–1999 Portas do Cerco
· 1851–1999 Taipa
· 1890–1999 Ilha Verde
20th century
Portuguese Macau
· 1938–1941 Lapa and Montanha (Hengqin)1 1975 is the year of East Timor's Declaration of Independence and subsequent invasion by Indonesia. In 2002, East Timor's independence was recognized by Portugal & the world.
North America and the North Atlantic Ocean16th century
1500–1579? Terra Nova (Newfoundland)
1500–1579? Labrador
1516–1579? Nova ScotiaCentral and South America16th century
1500–1822 Brazil
1536–1620 Portuguese Barbados17th century
1680–1777 Nova Colónia do Sacramento
19th century
1808–1822 Cisplatina (Uruguay)
1809–1817 Portuguese Guiana
1822 Upper PeruDutch Empire Colonies and trading posts of the Dutch East India Company (1602-1798) GovernoratesAmbon · Banda · Batavia · Cape Colony · Ceylon · Coromandel · Formosa · Northeast coast of Java · Makassar · Malacca · MoluccasDirectoratesCommandmentsResidenciesSettlements with an opperhoofdColonies and trading posts of the Dutch West India Company (1621-1792) Colonies in the AmericasAcadia · Berbice† · Cayenne · Curaçao and Dependencies · Demerara · Essequibo · Brazil · New Netherland · Pomeroon · Sint Eustatius and Dependencies · Suriname‡ · Tobago · Virgin IslandsTrading posts in Africa† Governed by the Society of Berbice · ‡ Governed by the Society of SurinameSettlements of the Noordsche Compagnie (1614-1642) SettlementsColonies of the Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815-1962) Until 1825Until 1853DejimaUntil 1872Until 1945Until 1954Until 1962† Became constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands; Suriname gained full independence in 1975, Curaçao and Dependencies was renamed to the Netherlands Antilles, which was eventually dissolved in 2010.Kingdom of the Netherlands (1954-Present) Constituent countriesPublic bodies of the NetherlandsCategories:- Dutch East India Company
- Artificial islands of Japan
- Edo period
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.