- Lisbon
-
For other uses, see Lisbon (disambiguation).
Lisbon (Lisboa) Settlement From top to right: Panoramic view of Lisbon from the Ponte 25 de Abril; the Castelo de São Jorge; the Baixa Pombalina de Lisboa; a Lisbon trolley; Praça do Comércio at Christmas; Palácio de São Bento; Torre de Belém; Parque das Nações; the triumphal arch in the Praça do Comércio; Estádio da Luz; Sé de Lisboa; Gare do Oriente; the 25 de Abril bridge over the Rio Tejo; Eduardo VII Park and the Marquês de Pombal square; view of Lisbon from the Castelo de São Jorge; Aeroporto da Portela.FlagCoat of armsOfficial name: Concelho de Lisboa Name origin: lisboa, Portuguese derivative of the Phoenician Allis Ubbo for safe harbour; Latin Ulyssippo after Ulysses; and/or Roman Olissipona, for the name of the Tagus Nickname: A Cidade das Sete Colinas (The City of Seven Hills) Country  Portugal
PortugalRegion Lisboa Subregion Greater Lisbon District Lisbon Municipality Lisbon Civil Parishes (see text) River Tagus River Center Lisbon - elevation 2 m (7 ft) - coordinates 38°42′49.72″N 9°8′21.79″W / 38.7138111°N 9.1393861°W Highest point 227 m - location Serra de Monsanto, Benfica, Lisbon - elevation 199 m (653 ft) - coordinates 38°43′42.97″N 9°11′4.80″W / 38.7286028°N 9.184667°W Lowest point Sea level - location Atlantic Ocean - elevation 0 m (0 ft) Area 84.8 km2 (33 sq mi) - urban 958 km2 (370 sq mi) - metro 2,957 km2 (1,142 sq mi) Population 545,245 (2011) - metro 2,815,851 Density 6,429 / km2 (16,651 / sq mi) Settlement fl. 719 - City c. 1256 LAU Concelho/Câmara Municipal - location Praça do Município, Lisbon, Grande Lisboa - elevation 33 m (108 ft) - coordinates 38°42′29″N 9°8′18″W / 38.70806°N 9.13833°W President António Costa (PS) Municipal Chair Maria Simonetta Bianchi Aires de Carvalho Luz Afonso (PS) Timezone WET (UTC0) - summer (DST) WEST (UTC+1) ISO 3166-2 code PT- Postal Zone 1149-014 Lisboa Area Code & Prefix (+351) 21 XXX-XXXX Demonym Lisboeta or Alfacinha Patron Saint São Vicente Municipal Address Praça do Município, 1
1149-014 LisboaLocation of the municipality of Lisbon in PortugalWikimedia Commons: Lisbon Website: http://www.cm-lisboa.pt/ Lisbon (/ˈlɪzbən/; Portuguese: Lisboa, IPA: [liʒˈβoɐ]) is the capital city and largest city of Portugal with a population of 545,245 within its administrative limits[1] on a land area of 84.8 km2 (33 sq mi). The urban area of Lisbon extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of 3 million[2] on an area of 958 km2 (370 sq mi),[2] making it the 9th most populous urban area in the European Union. About 2,831,000[3][4] people live in the Lisbon Metropolitan Area (which represents approximately 27% of the population of the country). Lisbon is the westernmost large city located in Europe, as well as its westernmost capital city and the only one along the Atlantic coast. It lies in the western Iberian Peninsula on the Atlantic Ocean and the Tagus River.
Lisbon is recognised as an alpha- city because of its importance in finance, commerce, media, entertainment, arts, international trade, education, and tourism.[5][6] It is one of the major economic centres on the continent, with a growing financial centre and the largest/second largest container port in the "Europe's Atlantic coast",[7] Lisbon Portela Airport serves about 13 million passengers per year, motorway network and hub of high-speed rail (Alfa Pendular) linking main cities in Portugal, and in 2013 will have a rail's high-speed connection to Spain.[8] Lisbon is the 25th most livable city in the World according to lifestyle magazine Monocle.[9] The city is the seventh-most-visited city in Southern Europe, after Istanbul, Rome, Barcelona, Madrid, Athens, and Milan, with 1,740,000 tourists in 2009.[10] The Lisbon region is the wealthiest region in Portugal, GDP PPP per capita is 26,100 euros (4.7% higher than the average European Union's GDP PPP per capita). It is the tenth richest metropolitan area by GDP on the continent amounting to 98 billion euros and thus €34,850 per capita.[11] This is 40% higher than the average European Union's GDP per capita. The city occupies 32nd place of highest gross earnings in the world.[12] Most of the headquarters of multinationals in the country are located in the Lisbon area and it is the ninth city in the world in terms of quantity of international conferences.[13] It is also the political centre of the country, as seat of Government and residence of the Head of State. The seat of the district of Lisbon and the centre of the Lisbon region.
Lisbon is one of the oldest cities in the world, predating other modern European capitals such as London, Paris and Rome by hundreds of years. Julius Caesar made it a municipium called Felicitas Julia, adding to the name Olissipo. Ruled by a series of Germanic tribes from the fifth century, it was captured by the Moors in the eighth century. In 1147, the Crusaders under Afonso Henriques reconquered the city for the Christians and since then it has been a major political, economic, and cultural centre of Portugal. Unlike most capital cities, Lisbon's status as the capital of Portugal has never been granted or confirmed officially – by statute or in written form. Its position as the capital has formed through constitutional convention, making its position as de facto capital a part of the Constitution of Portugal.
Lisbon hosts two agencies of the European Union: the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) and the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA). The Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP) is also headquartered in Lisbon.
Lisbon has two sites listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site: Belém Tower and Jerónimos Monastery. Furthermore, in 1994, Lisbon was the European Capital of Culture and in 1998 organised an Expo '98 (1998 Lisbon World Exposition).
Lisbon enjoys a Mediterranean climate. Among all the metropolises in Europe, it has the warmest winters, with average temperatures 15 °C (59 °F) during the day and 8 °C (46 °F) at night in the period from December to February. The typical summer's season lasts about six months, from May to October, although also in November, March and April temperatures sometimes reach around 20 °C (68.0 °F).
Contents
History
Main article: History of LisbonDuring the Neolithic, the region was inhabited by Iberian tribes, who built religious and funerary monuments, megaliths, Dolmens and menhirs, which still survive in areas on the periphery of Lisbon. The Indo-European Celts invaded after the first millennium BC, mixing with the Pre-Indo-European population, giving a rise to Celtic-speaking local tribes such as the Cempsi.
Archaeological findings suggest that there was Phoenician influences dating back to the 1200 BC, leading some historians to believe that a Phoenician trading post might have occupied the centre of the present city (on the southern slope of the Castle hill). The sheltered harbour in the Tagus River estuary, was an ideal spot for a settlement and provided a secure port for provisioning of Phoenician ships travelling to the Islands of Tin (modern Isles of Scilly) and Cornwall. The new city might have been named Allis Ubbo, Phoenician for "safe harbour", according to one of several theories on the origin of Lisbon's toponymy.[14] Another theory suggests that the settlement took the name of the pre-Roman word for the Tagus (Lisso or Lucio). The Tagus settlement was also an important output on commercial trade with inland tribes who collected valuable metals, salt, salted-fish, and the Lusitanian horses (that were renowned in antiquity). Although Phoenician remains from the 8th century BC were found beneath the Mediaeval Sé Cathedral, modern historians[15] however, believe that Lisbon was an ancient autochthonous settlement (Roman oppidum) and that, at most, it maintained commercial relations with the Phoenicians (accounting Phoenician pottery and artefacts).
Lisbon's name was written Ulyssippo in Latin by the geographer Pomponius Mela, a native of Hispania. It was later referenced as "Olisippo" by Pliny the Elder, and to the Greeks as Olissipo (Ολισσιπο) and Olissipona (Ολισσιπόνα).[16] According to legend, the location was named for Ulysses, who founded the settlement after he left Troy to escape the Greek coalition.[17][18] Later, the Greek name was corrupted in vulgar Latin to Olissipona.
Some of the native gods worshipped in Lisbon were Aracus, Carneus, Bandiarbariaicus, and Coniumbricenses.
Roman era
Following the defeat of Hannibal, during the Punic wars, the Romans determined to deprive Carthage of its most valuable possession: Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula). The defeat of Carthaginians forces by Scipio Africanus in Eastern Hispania, allowed the pacification of the west was led by Consul Decimus Junius Brutus Callaicus. Decimus obtained the alliance of Olissipo (which sent men to fight alongside the Roman Legions against the northwestern Celtic tribes) by integrating it into the Empire, as the Municipium Cives Romanorum Felicitas Julia. Local authorities were granted self-rule over a territory that extended 50 kilometres (31 mi), exempt from taxes, its citizens were given the privileges of Roman citizenship, and it was integrated within the Roman province of Lusitania (whose capital was Emerita Augusta).
Lusitanians raids and rebellions during Roman occupation necessitated the construction of a wall around the settlement. During Augustus' reign, the Romans also built a great theatre; the Cassian Baths (underneath Rua da Prata); temples to Jupiter, Diana, Cybele, Tethys, and Idea Phrygiae (an uncommon cult from Asia Minor), in addition to temples to the Emperor; a large necropolis under Praça da Figueira; a large forum and other buildings such as insulae (multi-storied apartment buildings) in the area between the Castle Hill and the historic downtown.[19]
The city prospered as piracy was eliminated, technological advances were introduced and as Felicitas Julia became the a centre of trade with the Roman provinces of Britannia (particularly Cornwall) and the Rhine. Economically strong, Olissipo was known for its garum (fish sauce highly prized by the elites of the Empire and exported in Amphorae to Rome), wine, salt and horse-breeding, while Roman culture permeated into the hinterland. The city was connected by a broad road to Western Hispania's two other large cities, Bracara Augusta in the province of Tarraconensis (Portuguese Braga), and Emerita Augusta, the capital of Lusitania (Mérida in Spain). The city was ruled by an oligarchical council dominated by two families, the Julii and the Cassiae, although regional authority was administered by the Roman Governor of Emerita or directly to Emperor Tiberius. Among the majority of Latin speakers lived a large minority of Greek traders and slaves.
Around 80 BCE, the Roman Quintus Sertorius led a rebellion against the dictator Sulla. During this period, he organized the tribes of Lusitania (and Hispania) and was on the verge of forming an independent province in the Sertorian War when he died.
Olissipo, like most great cities in the Western Empire, was a centre for the dissemination of Christianity. Its first attested Bishop was Potamius (c. 356), and there were several martyrs during the period of Christina persecutions: Maxima, Verissimus and Eulalia of Mérida are the most significant examples. By the Fall of Rome, Olissipo was one of the first Christian centres.
Following Roman disintegration and barbarian invasions, between 409 and 429 the centre was occupied by Sarmatian Alans and Germanic Vandals. The Germanic Suebi, who established a kingdom in Gallaecia (modern Galicia and northern Portugal), with capital in Bracara Augusta, also controlled the region of Lisbon from until 585. In 585, the Suebi Kingdom was integrated into the Germanic Visigothic Kingdom of Toledo, that comprised all of the Iberian Peninsula: Lisbon was then called Ulishbona.
 The Castelo de São Jorge, a fortified citadel reconquered by King Afonso Henriques's forces with assistance from knights from the Second Crusade, and its old and historical neighbourhoods.
The Castelo de São Jorge, a fortified citadel reconquered by King Afonso Henriques's forces with assistance from knights from the Second Crusade, and its old and historical neighbourhoods.
Muslim invasion period
The Lisbon Cathedral
On 6 August 711, Lisbon was taken by Muslim forces. These conquerors, who were mostly Berbers and Arabs from North Africa and the Middle East, built many mosques and houses, rebuilt the city wall (known as the Cerca Moura) and established administrative control, while permitting the diverse population (Christians, Berbers, Arabs, Jews, and Saqalibas) to maintain their socio-cultural lifestyles. Mozarabic was the mother language spoken by most of the Christian population. Islam was the official religion practised by the Arabs and Muladi (muwallad); the Christians were allowed to keep their religion, but under a second-class (Dhimmi) status and were required to pay the jizyah (in return for paying this surtax, Christians and Jews were not required to join the Islamic army, as their security was guaranteed by the Islamic state, as long as they accepted their submittal to the country rules).
The Muslim influence is still present in the Alfama, an old quarter of Lisbon that survived the 1755 Lisbon earthquake: many place-names are derived from Arabic and the Alfama (the oldest existing district of Lisbon) was derived from the Arabic "al-hamma".
For a brief time, Lisbon was the central town in the Regulo Eslavo of the Taifa of Badajoz, and then as an independent Taifa.
Reconquista - Return to Christian rule
In 1108 the city was conquered by Norwegian crusaders led by Sigurd I on their way to the Holy Land as part of the Norwegian Crusade.
In 1147, as part of the Reconquista, crusader knights led by Afonso I of Portugal, besieged and reconquered Lisbon. The city, with around 154,000 residents at the time, returned to Christian rule. The reconquest of Portugal and re-establishment of Christianity is one of the most significant events in Lisbon's history, described through the chronicle Expugnatione Lyxbonensi, telling that the local bishop was killed by the crusaders and that its residents were praying to the Virgin Mary. As Arabic lost its place in the everyday life of the city, many of the remaining Muslim residents were converted to Roman Catholicism by force, or were expelled, and the mosques were either destroyed or converted into churches.
Middle Ages
Although, Lisbon received its first foral (charter) in 1179, periodically, raiders from Al-Andalus were sent, or challenged, the control of the Iberian Christian kingdoms (capturing slaves and taking local treasures). In a raid against Lisbon in 1189, the Almohad caliph Yaqub al-Mansur took 3,000 female and child captives.[20] Due to its central location, Lisbon became the capital city of the new Portuguese territory in 1255. The first Portuguese university was founded in Lisbon in 1290 by King Denis I; for many years the Studium Generale (General Study) was transferred several times to Coimbra, where it was installed definitively in the 16th century (University of Coimbra).
During the last centuries of the Middle Ages, the city expanded substantially and became an important trading post with both northern Europe and Mediterranean cities.
Most of the Portuguese expeditions of the Age of Discovery left from Lisbon during the 15th to 17th centuries, including Vasco da Gama's expedition to India in 1497. In 1506, thousands of "New Christians" (converted Jews) were massacred in Lisbon.[21] The 16th century was Lisbon's golden era: the city was the European hub of commerce between Africa, India, the Far East and, later, Brazil, exploiting the riches from trade in spices, slaves, sugar, textiles, and other goods. This was the time of the exuberant Manueline-style, which left its mark in many 16th century monuments (including Lisbon's Belém Tower and Jerónimos Monastery, which were declared World Heritage Sites by UNESCO). A description of Lisbon in the 16th century was written by Damião de Góis and published in 1554.[22]
Portugal lost its independence to Spain in 1580 after a succession crisis, and the 1640 revolt that restored the Portuguese independence took place in Lisbon.
Kingdom
In the early 18th century, gold from Brazil allowed King John V to sponsor the building of several Baroque churches and theatres in the city.
1755 Earthquake
Main article: 1755 Lisbon earthquakePrior to the 18th century, Lisbon had experienced several significant earthquakes – eight in the 14th century, five in the 16th century (including the 1531 earthquake that destroyed 1,500 houses, and the 1597 earthquake when three streets vanished), and three in the 17th century. On 1 November 1755, the city was destroyed by another earthquake, which killed an estimated 30,000 to 40,000 Lisbon residents[23] and destroyed 85 percent of the city.[24] With a population estimated at between 200,000 and 275,000 residents,[25][26] Among several important structures of the city, the Ribeira Palace and the Hospital Real de Todos os Santos were lost. In coastal areas, such as Peniche, situated about 80 km (50 mi) north of Lisbon, many people were killed by the tsunami. In Setúbal, 30 km (19 mi) south of Lisbon, the water reached the first floor (second floor, in U.S. terms) of buildings. The destruction was also great in the Algarve, southern Portugal, where the tsunami dismantled some coastal fortresses and, in the lower levels, razed houses. In some places the waves crested at more than 30 m (98.43 ft). Almost all the coastal towns and villages of Algarve were heavily damaged, except Faro, which was protected by sandy banks. In Lagos, the waves reached the top of the city walls. For many Portuguese coastal regions, the destructive effects of the tsunami were more disastrous than those of the earthquake proper.
By 1755, Lisbon was one of the largest cities in Europe: the event shocked the whole of Europe. In southwestern Spain, the tsunami caused damage to Cadiz and Huelva, and the waves penetrated the Guadalquivir River, reaching Seville. In Gibraltar, the sea rose suddenly by about two metres. In Ceuta the tsunami was strong, but in the Mediterranean Sea, it decreased rapidly. On the other hand, it caused great damage and casualties to the western coast of Morocco, from Tangier, where the waves reached the walled fortifications of the town, to Agadir, where the waters passed over the walls, killing many. The tsunami also reached Cornwall, in the United Kingdom, at a height of three metres. Along the coast of Cornwall, the sea rose rapidly in vast waves, and then ebbed equally rapidly. A two metre tsunami also hit Galway in Ireland, and did some considerable damage to the Spanish Arch section of the city wall. Voltaire wrote a long poem, "Poême sur le désastre de Lisbonne", shortly after the quake, and mentioned it in his 1759 novel Candide (indeed, many argue that this critique of optimism was inspired by that earthquake). Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. also mentions it in his 1857 poem, The Deacon's Masterpiece, or The Wonderful One-Hoss Shay. In the town of Cascais, some 30 km (19 mi) west of Lisbon, the waves wrecked several boats and when the water withdrew, large stretches of sea bottom were left uncovered.
After the 1755 earthquake, the city was rebuilt largely according to the plans of Prime Minister Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, the 1st Marquess of Pombal; the lower town began to be known as the Baixa Pombalina (Pombaline Downtown). Instead of rebuilding the medieval town, Pombal decided to demolish the remains of the earthquake and rebuild the downtown in accordance with modern urban rules. It was reconstructed in a open rectangular plan with two great squares: the Praça do Rossio and the Praça do Comércio. The first, the central commercial district, is the traditional gathering place, and location of the older cafés, theatres and restaurants; the second, became the city's main access to the Tagus, point of departure and arrival, with its triumphal arch (1873) and monument to King Joseph I.
19th century
In the first years of the 19th century, Portugal was invaded by the troops of Napoléon Bonaparte, forcing Queen Maria I and Prince-Regent John (future John VI) to flee temporarily to Brazil. By the time the new King returned to Lisbon, many of the buildings and properties were pillaged, sacked or destroyed by the invaders.
During the 19th century, the Liberal movement introduced new changes into the urban landscape. The principal areas were in the Baixa and along the Chiado district, where shops, tobacconists shops, cafés, bookstores, clubs and theatres proliferated. The development of industry and commerce determined the growth of the city, extending north along the Avenida da Liberdade (1879), distanciing itself from the Tagus River.
20th century
 The Treaty of Lisbon, which amended the two treaties which comprise the constitutional basis of European Union, was signed by members of the EU in 2009, initiating a new chapter in the history of the European Union
The Treaty of Lisbon, which amended the two treaties which comprise the constitutional basis of European Union, was signed by members of the EU in 2009, initiating a new chapter in the history of the European Union
Lisbon was the stage of the regicide of Carlos I of Portugal (1908), which culminated two years later in the First Republic.
The city refounded its university in 1911 after centuries of inactivity in Lisbon, incorporating reformed former colleges and other non-university higher education schools of the city (such as the Escola Politécnica – now Faculdade de Ciências). Today there are 3 public universities in the city (University of Lisbon, Technical University of Lisbon and New University of Lisbon), a public university institute (ISCTE - Lisbon University Institute) and a polytechnic institute (IPL – Instituto Politécnico de Lisboa). See list of universities in Portugal.
During World War II Lisbon was one of the very few neutral, open European Atlantic ports, a major gateway for refugees to the U.S. and a spy nest. More than 100,000 refugees were able to flee Nazi Germany via Lisbon.[27]
During the Estado Novo regime (1926–1974), Lisbon was expanded at the cost of other districts within the country, resulting in nationalist and monumental projects. New residential and public developments were constructed; the zone of Belém was modified for the 1940 Portuguese Exhibition, while in along the periphery new neighborhoods appeared to house the growing populations. The inauguration of the bridge over the Tagus, allowed the rapid connect between the two margins of the river.
Lisbon was the centre of the republican coup of 5 October 1910 which established the democratic Portuguese Republic. The period following the Carnation Revolution resulted in a euphoria and modernization of Lisbon. In the 1990s, many of the neighborhoods were renovated and projects in the historic quarters were established to modernize the areas; architectural and patrimonial buildings were recuperated; the northern margin of the Tagus was re-purposed for leisure and residential use; the Vasco da Gama bridge was constructed; and the eastern part of the municipality was re-purposed for Expo '98 (intended to commemorate the 500th anniversary of Vasco da Gama's sea voyage to India).
In 1988, a fire near the historical centre of Chiado greatly disrupted normal life in the area for about 10 years.
In 1994, Lisbon was the European Capital of Culture.
21st century
The Lisbon Agenda was a European Union agreement on measures to revitalize the EU economy, signed in Lisbon in March 2000. In October 2007 Lisbon hosted the 2007 EU Summit, where agreement was reached regarding a new EU governance model. The resulting Treaty of Lisbon was signed on the 13 December 2007 and came into force on 1 December 2009.
On the 3 November 2005, Lisbon hosted the MTV European Music Awards. The show was opened by a leotard-clad Madonna, who exploded from a shiny disco ball to the tune "Hung Up".
On the 7 July 2007, Lisbon held the ceremony of the "New 7 Wonders Of The World"[28] election, in Luz stadium, with live transmission for millions of people all over the world.
It is the host city for the Portuguese editions of Rock in Rio, the largest rock festival in the world.
It hosted the NATO summit (19–20 November 2010), a summit meeting that is regarded as a periodic opportunity for Heads of State and Heads of Government of NATO member countries to evaluate and provide strategic direction for Alliance activities.[29]
Geography
Physical geography
 A orthophotograph from a SPOT Satellite, showing the extent of the urbanized area of the city of Lisbon
A orthophotograph from a SPOT Satellite, showing the extent of the urbanized area of the city of Lisbon
Lisbon is located at 38°42′49.75″N 9°8′21.79″W / 38.7138194°N 9.1393861°W, situated at the mouth of the Tagus River and is the westernmost capital of a mainland European country.
The westernmost part of Lisbon, is occupied by the Parque Florestal de Monsanto (English: Monsanto Forest Park), an 10 km2 (4 sq mi) urban park, that occupies 10% of the municipality of Lisbon, considered[who?] one the largest in Europe.
The city occupies an area of 84.94 km2 (33 sq mi), and its city boundaries, unlike those of most major cities, are narrowly defined by historical center.[30] The rest of the urbanized area of the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, known generically as Greater Lisbon (Portuguese: Grande Lisboa), are actually several administratively defined cities and municipalities, such as Amadora, Queluz, Agualva-Cacém, Odivelas, Loures, Sacavém, Almada, Barreiro, Seixal and Oeiras
Climate
Lisbon has a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa)[31] with mild winters and warm to hot summers. The average annual temperature is 17 °C (63 °F): 21 °C (70 °F) during the day and 13 °C (55 °F) at night. Average annual temperature of the sea is 17.5 °C (63.5 °F). In the coldest month – January – the temperature typically ranges from8 to 17 °C (46 to 63 °F) during the day, 4 to 12 °C (39 to 54 °F) at night and the average sea temperature is 15 °C (59 °F).[32] In the warmest month – August – the temperature typically ranges from26 to 32 °C (79 to 90 °F) during the day (sometimes there are higher temperatures), around 18 °C (64 °F) at night and the average sea temperature is 20 °C (68 °F).[32] Generally – typical summer's season lasts about 6 months, from May to October. Three months – November, March and April – are transitional, at times the temperature exceeds20 °C (68 °F), with an average temperature of these three months amounting 18.5 °C (65 °F) during the day and 11.2 °C (52.2 °F) at night. December, January and February are the coldest months, with an average temperature of these three months amounting 15.2 °C (59.4 °F) during the day and 8.9 °C (48.0 °F) at night. Among all metropolises in Europe continent, Lisbon has the warmest winters. Also, are here one of the mildest nights in Europe: one of the warmest in the winter - from average 8 °C (46 °F) in the coldest month and comfortable in the summer - to average 18 °C (64 °F) in the warmest month. Rain occurs mainly in winters, the summers being generally dry. Sunshine hours are about 2,800 per year, from an average of 4.6 hours of sunshine / day in December to an average of 11.4 hours of sunshine / day in July.
Climate data for Lisbon Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Record high °C (°F) 20.6
(69.1)24.8
(76.6)28.3
(82.9)29.4
(84.9)35.0
(95.0)41.5
(106.7)40.6
(105.1)37.9
(100.2)37.1
(98.8)32.6
(90.7)25.0
(77.0)25.1
(77.2)41.5
(106.7)Average high °C (°F) 14.5
(58.1)15.9
(60.6)18.2
(64.8)19.2
(66.6)21.4
(70.5)24.8
(76.6)27.5
(81.5)27.8
(82.0)26.2
(79.2)22.1
(71.8)18.0
(64.4)15.2
(59.4)20.9 Daily mean °C (°F) 11.3
(52.3)12.6
(54.7)14.3
(57.7)15.4
(59.7)17.4
(63.3)20.4
(68.7)22.7
(72.9)23.0
(73.4)21.8
(71.2)18.4
(65.1)14.8
(58.6)12.4
(54.3)17.0 Average low °C (°F) 8.1
(46.6)9.2
(48.6)10.4
(50.7)11.5
(52.7)13.3
(55.9)15.9
(60.6)17.9
(64.2)18.1
(64.6)17.3
(63.1)14.6
(58.3)11.5
(52.7)9.5
(49.1)13.1 Record low °C (°F) 0.4
(32.7)1.2
(34.2)2.9
(37.2)5.5
(41.9)6.9
(44.4)10.3
(50.5)13.1
(55.6)13.8
(56.8)10.7
(51.3)8.0
(46.4)3.9
(39.0)2.4
(36.3)0.4
(32.7)Rainfall mm (inches) 96.8
(3.811)90.2
(3.551)51.2
(2.016)64.7
(2.547)55.6
(2.189)17.2
(0.677)6.1
(0.24)6.8
(0.268)28.5
(1.122)79.8
(3.142)107.1
(4.217)121.8
(4.795)725.8
(28.575)Avg. rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) 15.0 15.0 13.0 12.0 8.0 5.0 2.0 2.0 6.0 11.0 14.0 14.0 117.0 Sunshine hours 142.6 156.6 207.7 234.0 291.4 303.0 353.4 344.1 261.0 213.9 156.0 142.6 2,806.3 Source: Instituto de Meteorologia[33], Hong Kong Observatory[34] for data of avg. precipitation days & sunshine hours Human geography
Demographics
Population of the
City of Lisbon
(1801 - 2011)Year Pop. ±% 1801 203,999 — 1849 174,900 −14.3% 1900 350,919 +100.6% 1930 591,939 +68.7% 1960 801,155 +35.3% 1981 807,937 +0.8% 1991 663,394 −17.9% 2001 564,657 −14.9% 2011 545,245 −3.4% The population of the city proper is, as of 2011, 545,245 and the metropolitan area (Lisbon Metropolitan Area) more than 2,800,000 according to the Instituto Nacional de Estatística[4] (English: National Institute of Statistics). The Lisbon Metropolitan Area incorporates two NUTS II (European statistical subdivisions): Grande Lisboa (English: Greater Lisbon), along the northern bank of the Tagus River, and Península de Setúbal (English: Setúbal Peninsula), along the southern bank (which represents the Portuguese sub-regions of Região Lisboa (English: Lisbon Region). The population density of the city itself is 6,429 inhabitants per square kilometre (16,650 /sq mi).
Like most metropolitan cities, Lisbon is surrounded by many satellite cities or suburbs, and it is estimated that more than one million people enter Lisbon every day for business or employment from these communities. Cascais and Estoril are among the most neighbouring towns for night life. Beautiful palaces, landscapes and historical sites can be found in Sintra and Mafra. Other major municipalities around Lisbon include Amadora, Oeiras, Odivelas, Loures, Vila Franca de Xira and, in the south bank of the Tagus river estuary, Almada, Barreiro and Seixal.
In terms of Portuguese cities, Lisbon was considered the most livable in a survey of living conditions published yearly by Expresso.[35]
Civil parishes
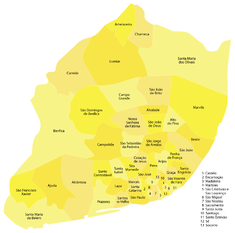
The municipality of Lisbon includes 53 freguesias (English: civil parishes), including:
- Ajuda
- Alcântara
- Alto do Pina
- Alvalade
- Ameixoeira
- Anjos
- Beato
- Benfica
- Campo Grande
- Campolide
- Carnide
- Castelo
- Charneca
- Coração de Jesus
- Encarnação
- Graça
- Lapa
- Lumiar
- Madalena
- Mártires
- Marvila
- Mercês
- Nossa Senhora de Fátima
- Pena
- Penha de França
- Prazeres
- Sacramento
- Santa Catarina
- Santa Engrácia
- Santa Isabel
- Santa Justa
- Santa Maria de Belém
- Santa Maria dos Olivais
- Santiago
- Santo Condestável
- Santo Estevão
- Santos-o-Velho
- São Cristóvão e São Lourenço
- São Domingos de Benfica
- São Francisco Xavier
- São João
- São João de Brito
- São João de Deus
- São Jorge de Arroios
- São José
- São Mamede
- São Miguel
- São Nicolau
- São Paulo
- São Sebastião da Pedreira
- São Vicente de Fora
- Sé
- Socorro
But, locally, their inhabitants may more commonly refer the spaces of Lisbon in terms of historic bairros (English: neighborhoods). These communities have no clearly defined boundaries and represent special quarters with a common historical culture, identifiable architectural landmarks, livings standards and/or local personality, such as Amoreiras, Bairro Alto,Bica, Alfama, Mouraria, Avenidas Novas, Intendente, Chelas and Lapa.
International relations
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in PortugalTwin towns – Sister cities
Lisbon is twinned with:
 Bethlehem, Palestinian Authority [36]
Bethlehem, Palestinian Authority [36] Budapest, Hungary[37]
Budapest, Hungary[37] Fairfield, California, United States
Fairfield, California, United States Madrid, Spain [38]
Madrid, Spain [38] Bissau, Guinea-Bissau
Bissau, Guinea-Bissau Cacheu, Guinea-Bissau
Cacheu, Guinea-Bissau Malacca, Malaysia
Malacca, Malaysia Mexico City, Mexico
Mexico City, Mexico Pontelandolfo, Italy
Pontelandolfo, Italy La Paz, Bolivia
La Paz, Bolivia San Diego, United States
San Diego, United States Luanda, Angola
Luanda, Angola Paris, France
Paris, France Maputo, Mozambique
Maputo, Mozambique São Paulo, Brazil[39][40]
São Paulo, Brazil[39][40] Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Brasília, Brazil
Brasília, Brazil Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
Salvador, Bahia, Brazil Buenos Aires, Argentina
Buenos Aires, Argentina Praia, Cape Verde
Praia, Cape Verde Tunis, Tunisia
Tunis, Tunisia Waterbury, Connecticut, United States
Waterbury, Connecticut, United States Zagreb, Croatia[41]
Zagreb, Croatia[41] Beijing, People's Republic of China[42]
Beijing, People's Republic of China[42] Ruse, Bulgaria
Ruse, Bulgaria Macau, People's Republic of China
Macau, People's Republic of China Damascus, Syria
Damascus, Syria
Culture
The city of Lisbon is rich in architecture; Romanesque, Gothic, Manueline, Baroque, Modern and Post-Modern constructions can be found all over Lisbon. The city is also crossed by historical boulevards and monuments along the main thoroughfares, particularly in the upper districts; notable among these are the Avenida da Liberdade (Avenue of Liberty), Avenida Fontes Pereira de Melo, Avenida Almirante Reis and Avenida da República (Avenue of the Republic).
There are several Museums one can enjoy. The most famous ones are the Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga (National Museum of Ancient Art), the Museu do Azulejo (Museum of Portuguese-style Tile Mosaics), the Museu Calouste Gulbenkian (Calouste Gulbenkian Museum), containing varied collections of ancient and modern art, the Museu Nacional do Traje e da Moda (National Museum of Costume and Fashion), the Berardo Collection Museum (Modern Art) at the Belém Cultural Center, the Museu da Electricidade (English: Electricity Museum), the Museu Nacional dos Coches (National Coach Museum, containing the largest collection of royal coaches in the world), the Museu da Farmácia (Pharmacy Museum), Museum of the Orient, the Museu do Teatro Romano (The Roman Theatre Museum), and the Museu da Cidade (the City Museum).
Lisbon's Opera House, the Teatro Nacional de São Carlos, hosts a relatively active cultural agenda, mainly in autumn and winter. Other important theatres and musical houses are the Centro Cultural de Belém, the Teatro Nacional D. Maria II, the Gulbenkian Foundation, and the Teatro Camões.
The monument to Christ the King (Portuguese: Cristo Rei) stands on the southern bank of the Tagus River, in Almada. With open arms, overlooking the whole city, it resembles the Corcovado monument in Rio de Janeiro, and was built after World War II, as work of thanksgiving for Portugal's being spared the horrors and destruction of the war.
On June 13 is Lisbon´s holiday in honour of the city´s saint Anthony of Lisbon (Portuguese: Santo António). Saint Anthony, also known as Saint Anthony of Padua, was a wealthy Portuguese bohemian who was canonised and made Doctor of the Church after a life preaching to the poor. Ironically, although Lisbon’s patron saint is Saint Vincent of Saragossa, whose remains are housed in the Sé Cathedral, there are no festivities associated with this saint.
Parque Eduardo VII, the second largest park in the city following the Parque Florestal de Monsanto (Monsanto Forest Park), extends down the main avenue (Avenida da Liberdade), with many flowering plants and greenspaces, that includes the permanent collection of subtropical and tropical plants in the winter garden (Portuguese: Estufa Fria). Originally named Parque da Liberdade, it was renamed in honour of Edward VII of England who visited Lisbon in 1903.
Lisbon is home every year to the Lisbon Gay & Lesbian Film Festival,[43] the Lisboarte, the DocLisboa – Lisbon International Documentary Film Festival,[44] the Arte Lisboa – Contemporary Art Fair,[45] the Festival of the Oceans,[46] the International Organ Festival of Lisbon,[47] the MOTELx – Lisbon International Horror Film Festival,[48] the Lisbon Village Festival,[49] the Festival Internacional de Máscaras e Comediantes, the Lisboa Mágica – Street Magic World Festival, the Monstra – Animated Film Festival, the Lisbon Book Fair,[50] the Peixe em Lisboa – Lisbon Fish and Flavours,[51] the Lisbon International Handicraft Exhibition,[52] the Lisbon Photo Marathon, the IndieLisboa – International Independent Film Festival,[53] the Alkantara Festival,[54] the Temps d´Images Festival[55] and the Jazz in August festival.[56]
Lisbon has been home four times (in 2004, 2006, 2008, and 2010) to Rock in Rio, one of the world's largest pop-rock festivals. Annual popular music events within the metropolitan area include the Optimus Alive! and Super Bock Super Rock festivals.
Lisbon is also home to the Lisbon Architecture Triennial,[57] the Moda Lisboa (Fashion Lisbon),[58] ExperimentaDesign – Biennial of Design[59] and LuzBoa – Biennial of Light.[60]
Alcântara
Although today it is quite central, it was once a mere suburb of Lisbon, comprising mostly farms and palaces. In the 16th century, there was a brook there which the nobles used to promenade in their boats. Through the late 19th century, Alcântara became a popular industrial area, with lots of small factories and warehouses. Through the centuries, this area has lost all of its charm and old buildings, as well as its brook (where the women of the village would do their laundry).
In the early 1990s, Alcântara began to attract youth because of the number of pubs and discothèques. This was mainly due its outer area of mostly commercial buildings, which acted as barriers to the noise-generating nightlife (which acted as a buffer to the residential communities surrounding it). In the meantime, some of these areas began to become gentrified, attracting loft developments and new apartments, which have profited from its river views and central location.
Alfama
 View of the Alfama district, on one of the many hilltops along the river (highlighted by the churches of Santa Engrácia and São Vicent da Fora
View of the Alfama district, on one of the many hilltops along the river (highlighted by the churches of Santa Engrácia and São Vicent da Fora
The oldest district of Lisbon, it spreads down the southern slope from the Castle of São Jorge to the Tagus river. Its name, derived from the Arabic Al-hamma, means fountains or baths. During the Islamic invasion of Iberia, the Alfama constituted the largest part of the city, extending west to the Baixa neighbourhood. Increasingly, the Alfama became inhabited by fishermen and the poor: its fame as a poor neighbourhood continues to this day. While the 1755 Lisbon Earthquake caused considerable damage throughout the capital, the Alfama survived with little damage, due to its compact labyrinth of narrow streets and small squares. It is a historical quarter of mixed-used buildings of homes with small shops, Fado bars and restaurants. Modernizing trends have invigorated the district: old houses have been re-purposed or remodelled, while new buildings have been constructed. Fado, the typically Portuguese-style of melancholy music, is common (but not obligatory) in the restaurants of the district. Among the many architectural vestiges of the area:
- Castle of São Jorge - the Moorish castle conquered by Afonso Henriques and Crusader forces, was once a home of the Portuguese royal family, with a complex of buildings within its walls. Since the Portuguese revolution, the abandoned castle decayed into ruin, and many of the buildings were destroyed. In the late 20th century many of the archaeologically significant foundations of the Moorish structure were recuperated;
- Sé Cathedral of Santa Maria Maior;
- Monastery of São Vicente de Fora;
- Santo António Church;
- Santa Luzia Belvedere;
- Largo das Portas ao Sol
Bairro Alto
Main article: Bairro AltoBairro Alto (literally the upper quarter in Portuguese) is an area of central Lisbon. It functions as a residential, shopping and entertainment district: it is the heart of the Portuguese capital's nightlife, attracting its youth. Lisbon's Punk, Gay, Metal, Goth, Hip Hop and Reggae scenes, all count the Bairro as their home, due to the specialization of its clubs and bars. Although fado, Portugal's national music still survives in the new nightlife, the crowds in the Bairro Alto area is a multicultural mix of cultures and entertainment.
Baixa
 Statue of King José I in the Praça do Comércio, erected after the 1775 Lisbon Earthquake disaster and subsequent reconstruction
Statue of King José I in the Praça do Comércio, erected after the 1775 Lisbon Earthquake disaster and subsequent reconstruction
The heart of the city is the Baixa (Downtown) or city centre; the Pombaline Baixa is an elegant district, primarily constructed after the 1755 Lisbon earthquake, taking its name from its benefactor, 1st Marquess of Pombal, Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo (Joseph I's Prime Minister (1750–1777) and key figure during the Portuguese Enlightenment. Following the 1755 disaster, Pombal took the lead in rebuilding Lisbon, imposing strict conditions and guidelines on the construction of the city, and transforming the organic street plan, that characterised the district before the earthquake, into its current grid pattern. As a result, the Pombaline Baixa is one of the first examples of earthquake-resistant construction. Architectural models were tested by having troops march around them to simulate an earthquake. Notable features of Pombaline structures include the Pombaline cage, a symmetrical wood-lattice framework aimed at distributing earthquake force, and inter-terrace walls that were built higher than roof timbers to reduce fire contagion.
It was placed on Portugal's tentative list of potential World Heritage Sites on 7 December 2004. Other important monuments in this area include:
- Praça do Comércio (Commerce Square)
- Rossio - the oldest and historically most important squares in Lisbon
- Church of Nossa Senhora da Conceição Velha which has a beautiful manueline façade
- Church of São Domingos
- Restauradores Square
- Elevador de Santa Justa, an elevator (lift) in Gothic revival style, built around 1900 to connect the Baixa and Chiado.
Belém
 The Praça do Império with the Jerónimos Monastery in the background in the Santa Maria de Belem parish. (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
The Praça do Império with the Jerónimos Monastery in the background in the Santa Maria de Belem parish. (UNESCO World Heritage Site) Main article: Belém
Main article: BelémSanta Maria de Belém, or just Belém (Portuguese pronunciation: [ˈsɐ̃tɐ mɐˈɾiɐ dɨ bɨˈlɐ̃ȷ̃]) is a parish of Lisbon, Portugal, located 6 km (4 mi) west of the present city centre and 2 km (1 mi) west of Ponte 25 de Abril (25 April Bridge). Its name is derived from the Portuguese for Bethlehem.
Belém is famous as the place from which many of the great Portuguese explorers set off on their voyages of discovery. In particular, it is the place from which Vasco da Gama departed for India in 1497. It is also a former royal residence and features the 17th–18th century Belém Palace, former royal residence and now occupied by the President of Portugal, and the Ajuda Palace, begun in 1802 but never completed.
Perhaps Belém's most famous feature is its tower, Torre de Belém, whose image is much used by Lisbon's tourist board. The tower was built as a fortified lighthouse late in the reign of Dom Manuel (1515–1520) to guard the entrance to the port at Belém. It stood on a little island in right side of the Tagus, surrounded by water.
Belém's other major historical building is the Mosteiro dos Jerónimos (Jerónimos Monastery), which the Torre de Belém was built partly to defend. The building of the monastery, an example of Manueline architecture, was begun in 1502 on the instructions of Manuel I and took 50 years to complete. It was built as a monument to Vasco da Gama's successful voyage to India and was funded by a tax on eastern spices. The monastery contains the tomb of Vasco da Gama. Located in the wings of the monastery are the Museu Nacional de Arqueologia (National Archaeological Museum) and the Museu da Marinha(Maritime Museum).
Belém's most notable modern feature is the Padrão dos Descobrimentos (Monument to the Discoveries). This is a 52 m (170.60 ft) high slab of concrete, erected in 1960 to commemorate the 500th anniversary of the death of Henry the Navigator. The monument is carved into the shape of the prow of a ship in which stand statues of various explorers, as well as a statue of Henry himself. Adjacent to the monument is a square into whose surface is set a map showing the routes of various Portuguese explorers.
 A view of Belém Tower, a World Heritage Site, which is a typical example of Portugal's unique Manueline architecture.
A view of Belém Tower, a World Heritage Site, which is a typical example of Portugal's unique Manueline architecture.
In the heart of Belém is the Praça do Império: gardens centred upon a large fountain, laid out during World War II. To the west of the gardens lies the Centro Cultural de Belém. This was built for Portugal's 1992 presidency of the EU. It is now an arts complex, containing Belém's Museu do Design (Design Museum). To the southeast of the gardens is the Belém Palace (1770), the official residence of the Portuguese President. Five hundred metres to the east of Praça do Império lies Belém's other major squarePraça Afonso de Albuquerque.
Belém is home to a number of other museums, many of which were established by Salazar for the 1940 Belém Expo: Museu da Electricidade (Electricity Museum), Museu do Centro Científico e Cultural de Macau (Macau Cultural Museum), Museu de Arte Popular (Folk Art Museum) and Museu Nacional dos Coches (National Coach Museum).
Belenenses, a renowned sports club from Lisbon is based in Belém.
Belém's main street is Rua de Belém, in which there is a 160-year-old pastry shop, at which can be purchased one of the famous pastel de Belém (plural: pastéis de Belém) – custard tarts made with flaky pastry. Other attractions within the area are:
- Padrão dos Descobrimentos (Monument of the Discoveries), built in mid-20th century, during Estado Novo dictatorial regime
- Belem Cultural Centre, example of Portuguese contemporary architecture, finished in 1994
- Belem Tower, an ex-libris of the city, built in the 16th century
- Belem Palace, 18th century palace, which is now the official residence of the President of the Republic
- Coach Museum, displaying most relevant and spectacular carriages from 17th to 19th century.
Chiado
 The Praça de Luís de Camões in the Chiado neighbourhood
The Praça de Luís de Camões in the Chiado neighbourhood
The Chiado is a traditional shopping area that mixes old and modern commercial establishments, concentrated specially in the Carmo's and Garrett's streets. Locals as well as tourists visit the Chiado to buy books, garments, pottery as well as to have a cup of coffee. The most famous café of Chiado is A Brasileira, famous for having had poet Fernando Pessoa among its customers. The Chiado is also an important cultural area, with several museums and theatres. Several buildings of the Chiado were destroyed in a fire in 1988, an event that deeply shocked the country. Thanks to a renovation project that lasted more than 10 years, coordinated by celebrated architect Siza Vieira, the affected area is now recovered.
Attractions include:
- Basilica dos Mártires
- Brasileira Cafe
- Carmo Convent
- Church of Corpo Santo
- Church of Nossa Senhora do Loreto
- Museu do Chiado, which houses most important works of Portuguese contemporary art
- The richly decorated Church of São Roque is located nearby.
Estrela
The Baroque-Neoclassical Estrela Basilica is the main attraction of this district. The huge church has a giant dome, and is located in a hill in what was at the time the western part of Lisbon and can be viewed from far away. The style is similar to the Mafra National Palace, in late baroque and neoclassical. The front has two twin bell towers and includes statues of saints and some allegoric figures. The Parliament, housed in Sao Bento Palace, is in this district. Nearby is the official residence of Portugal’s Prime Minister. and the Prazeres Cemetery is nearby as well.
Parque das Nações
Parque das Nações is the newest district in Lisbon, having emerged from an urban regeneration programmed that led to the World Exhibition of Lisbon 1998. A long lasting legacy of the same, the area has become another commercial and higher end residential area for the city.
 View of main entrance of Gare do Oriente Station
View of main entrance of Gare do Oriente Station Main article: Gare do Oriente
Main article: Gare do OrienteCentral to this is the Gare do Oriente (Orient Station), one of the main transportation hubs of Lisbon, for trains, metro, buses and taxis. Its glass and steel columns are inspired in Gothic Architecture, making the whole structure fascinating to look at (especially in sunlight or when illuminated at night). It was designed by the architect Santiago Calatrava from Valencia (Spain). Across the street, through Vasco da Gama Mall, is Parque das Nações (Park of the Nations), site of the 1998 World Expo.
Walking around to see the new buildings, restaurants, gardens, the Lisbon Casino, the FIL building (International Exhibition and Fair), the Camões Theatre, as well as a must see the Oceanário de Lisboa (Lisbon Oceanarium), the second largest in the world.Economy
The Lisbon region is the wealthiest region in Portugal and it is well above the European Union's GDP per capita average – it produces 45% of the Portuguese GDP. Lisbon's economy is based primarily on the tertiary sector. Most of the headquarters of multinationals operating in Portugal are concentrated in the Grande Lisboa Subregion, specially in the Oeiras municipality. The Lisbon Metropolitan Area is heavily industrialized, especially the south bank of the Tagus river (Rio Tejo).
The Lisbon region is rapidly growing, each year are higher Gross Domestic Product (GDP) PPP per capita: € 22,745 (2004)[61] – € 23,816 (2005)[62] – € 25,200 (2006)[63] – € 26,100 (2007).[64]
The country's chief seaport, featuring one of the largest and most sophisticated regional markets on the Iberian Peninsula, Lisbon and its heavily populated surroundings are also developing as an important financial centre and a dynamic technological hub.
Lisbon has the largest and most developed mass media sector of Portugal, and is home to several related companies ranging from leading television networks and radio stations to major newspapers.
The Euronext Lisbon stock exchange, part of the pan-European Euronext system together with the stock exchanges of Amsterdam, Brussels and Paris, is tied with the New York Stock Exchange since 2007, forming the multinational NYSE Euronext group of stock exchanges.
The main industries consist of oil refineries, textile mills, shipyards, steel and fishing.
For the decade of 2010, Lisbon is preparing to receive many investments, including building a new airport, a new bridge, an expansion of 30 km (18.64 mi) underground, the construction of a mega-hospital (or central hospital), the creation two lines of the TGV will join Madrid, Porto, Vigo and the rest of Europe, the restoration of the main part of town (between the Marquês de Pombal roundabout and Terreiro do Paço), the creation of a large number of bike lanes, as well as modernization and renovation of various facilities.[65]
Transport
Lisbon's public transport network is extremely far-reaching and reliable and has its metro as its main artery, connecting the city centre with the upper and eastern districts, and now reaching the suburbs. Ambitious expansion projects will increase the network by almost one third, connecting the airport, and the northern and western districts. Bus, funicular and tram services have been supplied by the Companhia de Carris de Ferro de Lisboa (Carris), for over a century.
A traditional form of public transport in Lisbon is the tram. Introduced in the 19th century, the trams were originally imported from the USA and called americanos. The earliest trams can still be seen in the Museu da Carris (the Public Transport Museum) (Carris). Other than on the modern Line 15, the Lisbon tramway system still employs small (four wheel) vehicles of a design dating from the early part of the twentieth century. These distinctive yellow trams are one of the tourist icons of modern Lisbon, and their size is well suited to the steep hills and narrow streets of the central city.[66][67]
There are other commuter bus services from the city: Vimeca,[68] Rodoviaria de Lisboa,[69] Transportes Sul do Tejo,[70] Boa Viagem,[71] Barraqueiro[72] are the main ones, operating from different terminals in the city.
There are four commuter train lines departing from Lisbon: the Cascais, Sintra and Azambuja lines (operated by CP - Comboios de Portugal), as well as a fourth line to Setúbal (operated by Fertagus) crossing the Tagus river, over the 25 de Abril Bridge. The major railway stations are Santa Apolónia, Rossio, Gare do Oriente, Entrecampos, and Cais do Sodré. The city does not offer a light rail service (tram line 15, although running with new and faster trams does not fall onto this category), but there are plans to build light rail lines to provide service along the city's periphery.
Lisbon is connected to its suburbs as well as throughout Portugal by an extensive motorway network. There are three circular motorways around the city; the 2ª Circular, the CRIL, and the CREL. The city is connected to the far side of the Tagus by two important bridges:
- The 25 de Abril Bridge, inaugurated (as Ponte Salazar) on August 6, 1966, and later renamed after the date of the Carnation Revolution, was the longest suspension bridge in Europe. Because of its similar coloring, it is often compared to the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco, USA. In fact, it was built by the same company (American Bridge Company) that constructed the San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge and not the Golden Gate, also explaining its similarity in design to the former.
- The Vasco da Gama Bridge, inaugurated on May 1998 is, at 17.2 km (10.7 mi), the longest bridge in Europe.
Another way of crossing the river is by taking the ferry. The company is Transtejo-Soflusa,[73] which operates from different points in the city to Cacilhas, Seixal, Montijo, Porto Brandão and Trafaria under the brand Transtejo and to Barreiro under the brand Soflusa.
The Portela Airport is located within the city limits, with the national (TAP), regional or low-cost services that connects Lisbon to major cities in Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
Panoramic Views
Panoramic view of Lisbon from the top of Sanctuary of Christ the King, with 25 de Abril Bridge in the foreground.
Education
 One of the principal buildings at the Universidade Nova de Lisboa
One of the principal buildings at the Universidade Nova de Lisboa
The city has several private and public secondary schools, primary schools as well as Kindergärten. In Greater Lisbon area there are also international schools such as Saint Julian's School, the Carlucci American International School of Lisbon, Saint Dominic's International School, Deutsche Schule Lissabon, Instituto Español de Lisboa (Lisbon Spanish Institute), and Lycée Français Charles Lepierre.
There are three major public universities in Lisbon: the University of Lisbon (Lisbon's oldest university in operation, founded in 1911, also called the Classic University of Lisbon), the Technical University of Lisbon (founded in 1930) and the New University of Lisbon (founded in 1973), providing degrees in all academic disciplines. There is also one state-run university institute – the ISCTE - Lisbon University Institute, and a polytechnic institute – the Polytechnical Institute of Lisbon.
Major private institutions of higher education include the Portuguese Catholic University, as well as the Lusíada University, the Universidade Lusófona, and the Universidade Autónoma de Lisboa, among others.
The total number of enrolled students in higher education in Lisbon was, for the 2007–2008 school year, of 125,867 students, of whom 81,507 in the Lisbon's public institutions.[74]
Sports
 The "Estádio José Alvalade", home to Sporting Clube de Portugal, commonly shortened to "Sporting Lisbon"
The "Estádio José Alvalade", home to Sporting Clube de Portugal, commonly shortened to "Sporting Lisbon"
Lisbon has a long sporting tradition. It was one of the Portuguese cities that hosted the UEFA Euro 2004 Championship. The city also played host to the final of the 2001 IAAF World Indoor Championships and 1983, 1992 European Fencing Championships, 2003 World Men's Handball Championship, 2008 European Judo Championships. In 2006 and 2007, the city provided the starting point for the Dakar Rally.
Sport Lisboa e Benfica (commonly known as "Benfica") is a sports club best known worldwide for its football team, one of the major clubs in Portugal, one of the Big Three, two-times winner and five-times runners-up of the European Cup, one-time runners-up of the UEFA Cup and one-time runners-up of the Intercontinental Cup. Sporting Clube de Portugal (commonly known as "Sporting") is one of the major clubs in Portugal, one of the Big Three, having won the UEFA Cup Winners' Cup (1964) and was runners-up of the UEFA Cup (2005). The third most important club is C.F. Os Belenenses (commonly "Belenenses" also "Belenenses Lisbon"). Other sports, such as indoor football, handball, basketball and roller hockey are also popular. There are many other sport facilities in Lisbon, ranging from athletics to sailing to golf to mountain-biking. Every March the city hosts the Lisbon Half Marathon, while in September - Portugal Half Marathon.
Lisbon has two UEFA elite stadiums (




 ): Estádio da Luz (Stadium of Light), with a capacity of over 65,000 and the Estádio José Alvalade, with a capacity of over 50,000. There is also – Estádio do Restelo, with a capacity of over 30,000. In the neighborhood exist Estádio Nacional, with a capacity of over 37,000 (in Oeiras) and Estádio do Bonfim, with a capacity of nearly 20,000 (in Setúbal).
): Estádio da Luz (Stadium of Light), with a capacity of over 65,000 and the Estádio José Alvalade, with a capacity of over 50,000. There is also – Estádio do Restelo, with a capacity of over 30,000. In the neighborhood exist Estádio Nacional, with a capacity of over 37,000 (in Oeiras) and Estádio do Bonfim, with a capacity of nearly 20,000 (in Setúbal).Notable citizens
- Verissimo, Maxima and Julia according to tradition were the first three martyrs of Olisipo, considered native and later also as Romans in the city (3th and 4th centuries A.D.);
- São Gens was a legendary bishop-martyr who, according to tradition, has been one of the first bishops of Lisbon, even during the Roman domination of Lusitania;
- Fernando Martins de Bulhões, later Saint Anthony of Lisbon (c.1195 [75] – 13 June 1231) is a Catholic saint;
- Pedro Julião, ordained Pope John XXI, (c. 1215 – May 20, 1277), was the only Portuguese-born Pope;
- Fernão Lopes (c. 1385 – after 1459) was a chronicler appointed by King Edward of Portugal. Fernão Lopes wrote the history of Portugal, but only a part of his work remained. His way of writing was based on oral discourse, and, on every page, it revealed his roots among the common people. He is one of the fathers of the European historiography, or a precursor of the scientific historiography, basing his works always on the documental proof, and, has he said, on his pages "one cannot find the beauty of words but the nudity of the truth." He was an autodidact;
- Duarte Pacheco Pereira, called "the Great", was a 15th century sea captain, soldier, explorer and cartographer. He travelled particularly in the central Atlantic Ocean west of the Cape Verde islands, near Brazil, in 1498 and before; also along the coast of West Africa and to India. His accomplishments in strategic warfare, exploration, mathematics and astronomy were of an exceptional level. With the anticipation of more than two centuries, he was responsible for calculating the value of the degree of the meridian arc with a margin of error of only 4%;
- Francisco de Almeida, (c. 1450 – 1 March 1510), was a nobleman, soldier and explorer, counsellor to King John II of Portugal and the first Viceroy of Portuguese India. Almeida is credited with establishing Portuguese hegemony in the Indian Ocean, with his decisive victory at the naval Battle of Diu in 1509;
- João de Castro (February 7, 1500 – June 6, 1548), was a naval officer, notable scientist, writer and cartographer. He was also the fourth viceroy of Portuguese India. He was called Castro Forte ("Strong Castro") by poet Luís de Camões. He undertook many observations and can in a way be considered as one of the discoverers of crustal magnetism. He also discovered spatial variations of Declination in some points of the globe (as in Baçaim, India), which he attributed to the disturbing effects of underwater rock masses. Castro was one of the most important representative of scientific maritime investigations of the time;
- Francisco de Holanda (originally Francisco d'Olanda), (c. 1517 – 1585) was a humanist and painter. Considered to be one of the most important figures of the Portuguese Renaissance, he was also an essayist, architect, and historian. He was a maternal nephew of Pope Adrian VI and a remote uncle of Deodoro da Fonseca, Sérgio Buarque de Holanda and his namesake Chico Buarque;
- António Ferreira (1528 – November 29, 1569), was a poet and the foremost representative of the classical school, founded by Francisco de Sá de Miranda. His most considerable work, Castro, is the first tragedy in Portuguese, and the second in modern European literature. known as the Portuguese Horace, he was an ardent defender of the Portuguese language.
- António Vieira (6 February 1608 – 18 July 1697), Jesuit and writer, considered the "prince" of pulpit-orators in his time. The honorable and great poet Fernando Pessoa crowned Vieira with the magnificent title of "Emperor of the Portuguese Language";
- João Pinto Ribeiro was a celebrated conjurado and one of the conspirators and planners of the revolution of December 1, 1640.
- Catherine of Braganza (25 November 1638 – 31 December 1705), Queen Consort of King Charles II of England;
- José da Silva Pais (October 25, 1679 — November 14, 1760) was a soldier and colony administrator. He organized the support for the Sacramento Colony during the Spanish–Portuguese War, 1735–1737. For the purpose of maintaining the South of Brazil in the hands of Portugal, Pais was charged with the colonization and construction of many villages and Fortresses like the Jesus Maria e José and others in Rio Grande do Sul and Santa Catarina;
- Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, 1st Count of Oeiras, 1st Marquess of Pombal (Marquês de Pombal,; 13 May 1699–8 May 1782) was an 18th century statesman in the Age of Enlightenment. He was Minister of the Kingdom in the government of Joseph I of Portugal from 1750 to 1777. Undoubtedly the most prominent minister in the government, he is considered today to have been the de facto head of government. Pombal is notable for his swift and competent leadership in the aftermath of the 1755 Lisbon earthquake;
- Leonor de Almeida Portugal (1750–1839) - Marchioness of Alorna, 8th Countess of Assumar, one of the greatest figures of Portuguese literature, known as Alcippe, and the most famous holder of the title;
- António José de Souza Manoel de Menezes Severim de Noronha (March 18, 1792, - April 26, 1860), 7th Count of Vila Flor, 1st Marquis of Vila Flor and 1st Duke of Terceira, was a military officer, statesman and a leader of the Constitutionalist side in the Liberal Wars, as well as a Prime Minister of Portugal;
- Alexandre Herculano (Alexandre Herculano de Carvalho e Araújo; born March 28, 1810; died September 13, 1877 in Santarém), was a novelist and historian;
- Camilo Castelo Branco (Camilo Ferreira Botelho Castelo-Branco,1st Viscount de Correia Botelho; March 16, 1825 – June 1, 1890), was a prolific and notable writer, having authored over 260 books (mainly novels, plays and essays). His writing is, overall, considered original in that it combines the dramatic and sentimental spirit of Romanticism with a highly personal combination of bitterness, dark humour of sarcasm;
- Cesário Verde (February 25, 1855 – July 19, 1886) Poet. His work, while mostly ignored during his lifetime, is generally considered to be amongst the most important in Portuguese poetry and is widely taught in schools. This is partly due to his being championed by many other authors after his death, notably Fernando Pessoa;
- Henrique Mitchell de Paiva Couceiro ( December 30, 1861 - February 11, 1944), son of a Portuguese father and an Irish mother, was a soldier, colonial governor, monarchist politician and counter-revolutionary; he was notable for his role during the colonial occupation of Angola and Mozambique and for his dedication to the monarchist cause during the period of the First Portuguese Republic;
- Gago Coutinho or Carlos Viegas Gago Coutinho (17 February 1869 – 18 February 1959) was a aviation pioneer who, together with Sacadura Cabral (1881–1924), was the first to cross the South Atlantic Ocean by air, from March to June 1922 (some sources wrongly claim 1919), from Lisbon to Rio de Janeiro. Gago Coutinho invented a type of sextant incorporating two spirit levels to provide an artificial horizon. This adaptation of the traditional marine sextant allowed navigation without visual reference to the real horizon.
- Fernando Pessoa (13 June 1888 – 30 November 1935 ), poet, writer, literary critic and translator, considered one of the most significant literary figures of the 20th century;
- Mário de Sá-Carneiro (May 19, 1890 — April 26, 1916) was a poet and writer. He is one of the most well known of the "Geração D'Orpheu" and friend of Fernando Pessoa and Almada Negreiros;
- Amália Rodrigues (23 July 1920 – 6 October 1999), the Rainha do Fado (English: Queen of Fado), influential in popularizing the fado worldwide;
- Jorge Ferreira Chaves (22 February 1920 – 22 August 1982), architect;
- Mário Cesariny (9 August 1923 – 26 November 2006), surrealist poet, a minor painter;
- Alexandre O'Neill (19 December 1924 – 21 August 1986), poet/writer;
- Mário Soares (born 7 December 1924), politician, 17th President and 53rd/60th Prime-Ministers of Portugal;
- Jaime Montestrela (12 June 1925 - 8 November 1975), writer, poet and psychiatrist;
- Paula Rego (born c.1935), painter, illustrator and printmaker;
- Jorge Sampaio (born 18 September 1939), politician, United Nations High Commissioner for the Alliance of Civilizations, former Mayor of Lisbon and 18th President of Portugal;
- Gonçalo Byrne (born c.1941), architect;
- António Damásio, (born c.1944), neuroscientist;
- António Guterres (born 30 April 1949), United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, 62nd Prime-Minister of Portugal;
- José Manuel Durão Barroso (born 23 March 1956), President of the European Commission, 63rd Prime-Minister of Portugal;
- Joaquim de Almeida (born 15 March 1957), actor.
- Panda Bear (musician) (born July 17, 1978), musician.
See also
The Lisbon Treaty
References
- ^ Censos 2011 - Resultados Preliminares
- ^ a b Demographia: World Urban Areas, March 2010
- ^ United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, World Urbanization Prospects (2009 revision), (United Nations, 2010), Table A.12. Data for 2007.
- ^ a b ITDS, Rui Campos, Pedro Senos (2009-06-30). "Statistics Portugal". Ine.pt. http://www.ine.pt/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "The World According to GaWC 2008". Globalization and World Cities Study Group and Network, Loughborough University. http://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/world2008t.html. Retrieved 3 March 2009.
- ^ "Inventory of World Cities". Globalization and World Cities (GaWC) Study Group and Network. http://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/citylist.html. Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ^ "Avance del Plan Territorial Sectorial de la Red Intermodal y Logística del Transporte de la Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco" – Eusko Jaurlaritza – Gobierno Vasco
- ^ "Alta Velocidade em Síntese". Rave.pt. http://www.rave.pt/tabid/233/Default.aspx. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ^ "Monocle, Issue June 2009". Monocle.com. 2009-06-11. http://www.monocle.com/sections/affairs/Magazine-Articles/The-Worlds-top-25-most-liveable-cities/. Retrieved 2010-06-26.
- ^ Bremner, Caroline (10 January 2011). "Euromonitor International's Top City Destination Ranking". Euromonitor International. http://www.euromonitor.com/euromonitor-internationals-top-city-destinations-ranking/article. Retrieved 10 January 2011.
- ^ "Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025". Pricewaterhouse Coopers. https://www.ukmediacentre.pwc.com/Content/Detail.asp?ReleaseID=3421&NewsAreaID=2. Retrieved 16 December 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Ranking: The richest cities in the world" – City Mayors.com
- ^ "Lisboa é 9ª cidade que mais recebe congressos internacionais" – Agência LUSA
- ^ Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (5 November 2008). "Lisbon, Portugal – Where the Land Ends and the Sea Begins". http://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/en/imgdata/topics/2008/tp081105.html. Retrieved 7 December 09.
- ^ José Mattoso, ed. (1992) (in Portuguese), História de Portugal. Primeiro Volume: Antes de Portugal, 1, Círculo de Leitores
- ^ Smith, William (1854), Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography, illustrated by numerous engravings on wood, London, England: Walton and Maberly
- ^ Cailleux, Théophile (1879) (in French), Pays atlantiques décrits par Homère, Ibérie, Gaule, Bretagne, Archipels, Amériques: Théorie nouvelle, Paris, France: Maisonneuve et cie
- ^ If all of Odysseus' travels were in the Atlantic as Cailleux argued, then this could mean that Odysseus founded the city coming from the north, before trying to round Cape Malea, (which Cailleux located at Cabo de São Vicente), in a southeasterly direction, to reach his homeland of Ithaca, supposedly present Cadiz.
- ^ Many of these ruins were first unearthed during the middle 18th century (when the recent discovery of Pompeii made Roman archaeology fashionable among Europe's upper classes).
- ^ Brodman, James William. "Ransoming Captives in Crusader Spain: The Order of Merced on the Christian-Islamic Frontier". Libro.uca.edu. http://libro.uca.edu/rc/rc1.htm. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ Rabbi Jules Harlow (2011), "A 500-Year-Old Memory – Another tragic date in Jewish history" (in Portuguese), Jewish Week, Lisbon, Portugal: Comunidade Judaica Masorti – Lisboa
- ^ Jeffrey S. Ruth, ed. (1996) [1554], "Urbis Olisiponis descriptio", Lisbon in the Renaissance, New York, New York
- ^ Pereira, A.S. (March 2006). "The Opportunity of a Disaster: The Economic Impact of the Lisbon 1755 Earthquake" (PDF). Centre for Historical Economics and Related Research at York, York University. http://www.york.ac.uk/res/cherry/docs/Alvaro3.pdf. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ^ "Historical Depictions of the 1755 Lisbon Earthquake". Nisee.berkeley.edu. 1998-11-12. http://nisee.berkeley.edu/lisbon/index.html. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ^ "The Economic Impact of the Lisbon 1755 Earthquake - p. 8, estimates a population of 200,000" (PDF). March 2006. http://www.york.ac.uk/res/cherry/docs/Alvaro3.pdf. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ^ "Historical Depictions of the 1755 Lisbon Earthquake, citing an unreferenced estimate of 275,000". Nisee.berkeley.edu. 1998-11-12. http://nisee.berkeley.edu/lisbon/index.html. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ^ "Portugal". The Virtual Jewish History Tour.
- ^ "Welcome to the official global voting platform of". New7Wonders. http://www.new7wonders.com/index.php?id=315&L=0. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ NATO, NATO Summit Meetings, December 4, 2006
- ^ IGP, ed. (2011) (in Portuguese), Carta Administrativa Oficial de Portugal, Lisbon, Portugal: Instituto Geográfico Português
- ^ "World Map of Köppen−Geiger Climate Classification". http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/.
- ^ a b "Weather2Travel.com: Lisbon Climate Guide". http://www.weather2travel.com/climate-guides/portugal/lisbon.php.
- ^ "Monthly Averages for Lisbon, Portugal (1971-2000)". Instituto de Meteorologia. http://www.meteo.pt/pt/oclima/normais/. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
- ^ "Climatological Information for Lisbon, Portugal" (1961-1990) - Hong Kong Observatory
- ^ Classificação Expresso das melhores cidades portuguesas para viver em 2007, Expresso
- ^ "::Bethlehem Municipality::". www.bethlehem-city.org. http://www.bethlehem-city.org/Twining.php. Retrieved 2009-10-10.
- ^ "Sister cities of Budapest" (in Hungarian). Official Website of Budapest. http://www.budapest.hu/engine.aspx?page=20030224-cikk-testvervarosok. Retrieved 2009-07-01.
- ^ city council webpage "Mapa Mundi de las ciudades hermanadas". Ayuntamiento de Madrid. http://www.munimadrid.es/portal/site/munimadrid/menuitem.dbd5147a4ba1b0aa7d245f019fc08a0c/?vgnextoid=4e84399a03003110VgnVCM2000000c205a0aRCRD&vgnextchannel=4e98823d3a37a010VgnVCM100000d90ca8c0RCRD&vgnextfmt=especial1&idContenido=1da69a4192b5b010VgnVCM100000d90ca8c0RCRDMadrid city council webpage.
- ^ Prefeitura.Sp – Descentralized Cooperation[dead link]
- ^ "International Relations – São Paulo City Hall – Official Sister Cities". Prefeitura.sp.gov.br. http://www.prefeitura.sp.gov.br/cidade/secretarias/relacoes_internacionais/cidadesirmas/index.php?p=1066. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ^ "Intercity and International Cooperation of the City of Zagreb". © 2006–2009 City of Zagreb. http://www1.zagreb.hr/mms/en/index.html. Retrieved 2009-06-23.
- ^ "Sister cities of Beijing". Official Website of Beijing. http://www.ebeijing.gov.cn/Sister_Cities/Sister_City/. Retrieved 2009-07-11.
- ^ "Official web-site.". Lisbon Gay and Lesbian Film Festival. http://www.lisbonfilmfest.org/. Retrieved 2006-11-06.
- ^ "::: doclisboa 2009 :::". Doclisboa.org. http://www.doclisboa.org/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "ARTE LISBOA 2009 – Feira de Arte Contemporânea". Artelisboa.fil.pt. http://www.artelisboa.fil.pt/. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ^ Webcomum. "Festival Dos Oceanos". Festival Dos Oceanos. http://www.festivaldosoceanos.com/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Juventude Musical Portuguesa". Jmp.pt. http://www.jmp.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ two. "MOTELx – Festival Internacional de Cinema de Terror de Lisboa = {LISBON INTERNATIONAL HORROR FILM FESTIVAL}". Motelx.org. http://www.motelx.org. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "lisbon village festival". lisbon village festival. http://lisbon.villagefestival.net/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Feira do Livro de Lisboa". Feiradolivrodelisboa.pt. http://www.feiradolivrodelisboa.pt. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ^ "Peixe em Lisboa". Peixemlisboa.com. http://www.peixemlisboa.com. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Feira Internacional do Artesanato". Artesanato.fil.pt. http://www.artesanato.fil.pt/. Retrieved 2010-04-30.
- ^ "Festival IndieLisboa". Indielisboa.com. http://www.indielisboa.com. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "alkantara". Alkantara.pt. http://www.alkantara.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Festival Temps d'Images Portugal". Tempsdimages-portugal.com. http://www.tempsdimages-portugal.com/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation / Music Department". Musica.gulbenkian.pt. http://www.musica.gulbenkian.pt/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Trienal de Arquitectura de Lisboa". www.trienaldelisboa.com. http://www.trienaldelisboa.com. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "ModaLisboa – LisboaFashionWeek – Semana oficial da moda portuguesa". Modalisboa.pt. http://www.modalisboa.pt/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Experimentadesign". Experimentadesign.pt. http://www.experimentadesign.pt/. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Luzboa 2008". Luzboa.com. http://www.luzboa.com. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "GDP per inhabitant in 2004". Eurostat. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/pls/portal/docs/PAGE/PGP_PRD_CAT_PREREL/PGE_CAT_PREREL_YEAR_2007/PGE_CAT_PREREL_YEAR_2007_MONTH_02/1-19022007-EN-AP.PDF.
- ^ "GDP per inhabitant in 2005". Eurostat. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/pls/portal/docs/PAGE/PGP_PRD_CAT_PREREL/PGE_CAT_PREREL_YEAR_2008/PGE_CAT_PREREL_YEAR_2008_MONTH_02/1-12022008-EN-AP.PDF.
- ^ "GDP per inhabitant in 2006". Eurostat. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/pls/portal/docs/PAGE/PGP_PRD_CAT_PREREL/PGE_CAT_PREREL_YEAR_2009/PGE_CAT_PREREL_YEAR_2009_MONTH_02/1-19022009-EN-AP.PDF.
- ^ "GDP per inhabitant in 2007". Eurostat. http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/1-18022010-AP/EN/1-18022010-AP-EN.PDF.
- ^ "Pequeno Resumo Histórico de Lisboa" – Câmara Municipal de Lisboa
- ^ [1] Information from Carris, Lisbon transportation company.
- ^ [2] Details of Lisbon's trams, from Luso Pages
- ^ "vimeca". Vimeca.pt. http://www.vimeca.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Bem vindo ao site da Rodoviária de Lisboa". Rodoviariadelisboa.pt. http://www.rodoviariadelisboa.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "TST – Transportes Sul do Tejo". Tsuldotejo.pt. http://www.tsuldotejo.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Boa Viagem". Boa-viagem.pt. http://www.boa-viagem.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Barraqueiro Transportes". Barraqueirotransportes.pt. http://www.barraqueirotransportes.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Transtejo e Soflusa". Transtejo.pt. http://www.transtejo.pt. Retrieved 2009-07-08.
- ^ [3] Statistics on enrollment from GPEARI/Ministry of Science, Technology and Higher Education (MCES) (Excel spreadsheet, 2007/08 school year)
- ^ Purcell, Mary (1960). Saint Anthony and His Times. Garden City, New York: Hanover House. pp. 19, 275–6.
External links
- Lisbon travel guide from Wikitravel
- Visit Portugal: Lisbon Past and Present – Official page by the Government of Portugal
- Associação de Turismo de Lisboa – Official site of the Lisbon Tourism Association
- OTLIS – Official site of the Lisbon Region Transport Operators Consortium
- Portal das Nações Official site of Parque das Nações in Lisbon
Categories:- Lisbon
- Capitals in Europe
- Cities in Portugal
- European Capitals of Culture
- Municipalities of Portugal
- Phoenician colonies
- Roman towns and cities in Portugal
- Populated coastal places in Portugal
- Port cities and towns in Portugal
- Marinas in Portugal
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.