- Åland Islands
-
"Åland" redirects here. For other uses, see Åland (disambiguation).
Åland Islands Landskapet Åland
(Ahvenanmaan maakunta)

Flag Coat of arms Motto: "Islands of Peace"[1] Anthem: Ålänningens sång Capital
(and largest city)Mariehamn
60°07′N 019°54′E / 60.117°N 19.9°EOfficial language(s) Swedish Demonym Ålänning/Åländare (swedish), Ålandish, Ålandic Government Autonomous region of Finland - Governor Peter Lindbäck - Premier Viveka Eriksson Autonomy - Declared 1920 - Recognized 19212 Area - Total 13,517 km2 (unranked)
5,219 sq mi- Water (%) 88 Population - 2010 estimate 28,007 - Density 18.14/km2
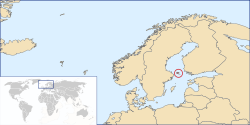
46.98/sq miGDP (PPP) 2007 estimate - Total $1.563 billion[2] - Per capita $55,829 HDI (2007) 0.967[3] (very high) Currency Euro (€)4 6 ( EUR)Time zone EET (UTC+2) - Summer (DST) EEST (UTC+3) Internet TLD .ax5 Calling code +358 (area code 18) 1 The governor is an administrative post appointed by the Government of Finland, and does not have any authority over the autonomous Government of Åland. 2 Settled by the League of Nations following the Åland crisis. 3 Åland held a separate referendum and then joined at the same time as the rest of Finland. 4 Until 1999, the Finnish markka. 5 Replacing .aland.fi from August 2006. The .eu domain is also used, as it is shared with Finland and the rest of European Union member states. 6 Swedish krona (SEK) is also widely used. The Åland Islands (Swedish pronunciation: [ˈoːland], Finnish: Ahvenanmaa) form an archipelago in the Baltic Sea. They are situated at the entrance to the Gulf of Bothnia and form an autonomous, demilitarised, monolingually Swedish-speaking region of Finland. The islands collectively constitute the smallest region of Finland, with only 0.49% of its land area, and 0.50% of its population.
Åland comprises Fasta Åland (the "Main Island," with 90% of the population),[4] together with an archipelago to the east that comprises over 6,500 skerries and islands. Fasta Åland is separated from the coast of Sweden by 38 kilometres (24 mi) of open water to the west. In the east, the Åland archipelago is contiguous with the Finnish Archipelago Sea. Åland's only land border is located on the uninhabited skerry of Märket,[5] which it shares with Sweden.
Because of the autonomous status of the Åland Islands, the powers exercised at the provincial level by representatives of the central state administration in the rest of Finland are largely exercised by the Government of Åland in Åland.
Contents
Autonomy of Åland
See also: Special member state territories and their relations with the EUThe autonomous status of the islands was affirmed by a decision made by the League of Nations in 1921 following the Åland crisis. It was reaffirmed within the treaty admitting Finland to the European Union. By law, Åland is politically neutral and entirely demilitarised, and residents are exempt from conscription to the Finnish Defence Forces. The islands were granted extensive autonomy by the Parliament of Finland in the Act on the Autonomy of Åland of 1920, which was later replaced by new legislation by the same name in 1951 and 1991. Åland remains exclusively Swedish-speaking by law.
In connection with Finland's admission to the European Union, a protocol was signed concerning the Åland Islands that stipulates, among other things, that provisions of the European Community Treaty shall not force a change of the existing restrictions for foreigners (i.e., persons who do not enjoy "home region rights" (hembygdsrätt) in Åland) to acquire and hold real property or to provide certain services, implying a recognition of a separate nationality.
Etymology
Åland's original name was Germanic *Ahvaland which means "Land of Water". In Swedish, this first developed into Áland and eventually into Åland, literally "river land"—even though rivers are not a prominent feature of Åland's geography. The Finnish name of the island, Ahvenanmaa ("perch land"), is seen to preserve another form of the old name.[6]
Another theory suggests that the Finnish Ahvenanmaa would be the original name of the archipelago, from which the Swedish Åland derives.[7]
History
Main article: History of ÅlandThe Åland Islands were part of the territory ceded to Russia by Sweden under the Treaty of Fredrikshamn in September 1809. As a result, along with all other parts of Finland, they became part of the semi-autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland.
During this process, Sweden was unable to secure a provision that the islands not be fortified. The issue was important not only for Sweden but also for the United Kingdom, which was concerned that a military presence on the islands could threaten Britain's military and commercial interests.
In 1832, Russia started to fortify the islands with the great fortress of Bomarsund. This was captured and destroyed by a combined British and French force of warships and marines in 1854 as part of the campaign in the Baltic during the Crimean War. In the Treaty of Paris (1856), the entire Åland Islands were demilitarized.
During the Finnish Civil War, in 1918, Swedish troops intervened as a peacekeeping force between the Russian troops stationed on the islands and "White" and "Red" Finnish troops that came from Finland over the frozen sea. Historians, however, point out that Sweden may have in reality planned to occupy the islands. Within weeks, the Swedish troops gave way to German troops that occupied Åland by request of the "White" (conservative) Finnish Senate.
After 1917, the residents of the islands worked towards having them ceded to Sweden. A petition for secession from Finland was signed by 96.2% of the Åland Islands' native adults (those working or living abroad excluded), although serious questions were later raised regarding this extraordinarily high figure. Swedish nationalist sentiments had grown strong particularly as a result of the following issues: anti-Swedish tendencies in Finland, Finnish nationalism fuelled by Finland's struggle to retain its autonomy, and the Finnish resistance against Russification. In addition, the conflict between the Swedish-speaking minority and the Finnish-speaking majority (on the mainland), which since the 1840s had been prominent in Finland's political life, contributed to the Åland population's apprehension about its future in Finland.
Finland was, however, not willing to cede the islands and instead offered them an autonomous status. Nevertheless the residents did not approve the offer, and the dispute over the islands was submitted to the League of Nations. The latter decided that Finland should retain sovereignty over the province but that the Åland Islands should be made an autonomous territory. Thus Finland was obliged to ensure the residents of the Åland Islands the right to maintain the Swedish language, as well as their own culture and local traditions. At the same time, an international treaty established the neutral status of Åland, whereby it was prohibited to place military installations or forces on the islands.
In the course of the 20th century, increasing numbers of the islanders have perceived Finnish sovereignty as benevolent and even beneficial.[citation needed] The combination of disappointment about insufficient support from Sweden in the League of Nations, Swedish disrespect for Åland's demilitarized status in the 1930s, and some feelings of a shared destiny with Finland during and after World War II has changed the islanders' perception of Åland's relation to Finland from "a Swedish province in Finnish possession" to "an autonomous part of Finland". The islanders enjoyed safety at sea during WWII as their merchant fleet sailed for both the allied countries and the Germans. Consequently Åland shipping was not generally attacked as each side rarely knew which cargo was being carried to whom.
The 150th Anniversary of Demilitarisation of Åland Islands was celebrated in Finland by issuing a high value commemorative coin, the €5 150th Anniversary of Demilitarisation of Åland Islands commemorative coin, minted in 2006. The obverse depicts a pine tree, very typical in the Åland Islands. The reverse design features a boat's stern and rudder, with a dove perched on the tiller, a symbol of 150 years of peace.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Åland The Åland Islands during the Crimean War
The Åland Islands during the Crimean War
The Åland Islands are governed according to the Act on the Autonomy of Åland and international treaties. These laws guarantee the islands' autonomy from Finland, which has ultimate sovereignty over them, as well as a demilitarized status. The Government of Åland, or Landskapsregering, answers to the Parliament of Åland, or Lagting, in accordance with the principles of parliamentarism.
Åland has its own flag, has issued its own postage stamps since 1984, runs its own police force, and is a member of the Nordic Council. Since 2005 the Åland Islands also have had their own airline, Air Åland. The islands are demilitarised, and the population is exempt from conscription. Although Åland's autonomy preceded the creation of the regions of Finland, the autonomous government of Åland also has responsibility for the functions undertaken by Finland's regional councils. Åland is a member of the Small European Postal Administration Cooperation.
The Åland Islands are guaranteed representation in the Finnish parliament, to which they elect one representative. Åland also has a different system of political parties from the mainland (see List of political parties in Finland).
Administration
The State Department of Åland represents the Finnish central government and performs many administrative duties. It has a somewhat different function from the other Regional Administrative Agencies, owing to its autonomy. Prior to 2010, the state administration was handled by the Åland State Provincial Office.
Åland has its own postal administration but still uses the Finnish five-digit postal code system, using the number range 22000-22999, with the prefix AX. The lowest numbered postal code is for the capital Mariehamn, AX 22100, and the highest AX 22950 for Jurmo.
Municipalities
Main article: Municipalities of ÅlandGeography
Main article: Geography of ÅlandThe Åland Islands occupy a position of great strategic importance, as they command one of the entrances to the port of Stockholm, as well as the approaches to the Gulf of Bothnia, in addition to being situated near the Gulf of Finland.
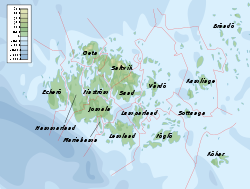
The Åland archipelago consists of nearly three hundred habitable islands, of which about eighty are inhabited; the remainder are merely some 6,000 skerries and desolate rocks. The archipelago is connected to Åboland archipelago in the east (Finnish: Turunmaan saaristo, Swedish: Åbolands skärgård) — the archipelago adjacent to the southwest coast of Finland. Together they form the Archipelago Sea. To West from Åland is Sea of Åland and to North the Bothnian Sea.
The surface of the islands is generally rocky and the soil thin. There are several excellent harbours.
The islands' landmass occupies a total area of 1,527 square kilometres (590 sq mi). Ninety per cent of the population live on Fasta Åland (the Main Island), which is also the site of the capital town of Mariehamn. Fasta Åland is the largest island in the archipelago, extending over 1,010 square kilometres, more than 66% of the province's land area. It measures approximately 47 kilometres (29 mi) from north to south and 34 kilometres (21 mi) from east to west.
During the Åland Crisis, the parties sought support from different maps of the islands. On the Swedish map, the most densely populated main island dominated, and many skerries were left out. On the Finnish map, a lot of smaller islands or skerries were, for technical reasons, given a slightly exaggerated size. The Swedish map made the islands appear to be closer to the mainland of Sweden than to Finland; the Finnish map stressed the continuity of the archipelago between the main island and mainland Finland, while a greater gap appeared between the islands and the archipelago on the Swedish side. Although both Finns and Swedes of course argued for their respective interpretations, in retrospect it is hard to say that one is more correct than the other. One consequence is the oft-repeated number of "over 6,000" skerries that was given authority by the outcome of the arbitration.
Economy
Åland's economy is heavily dominated by shipping, trade and tourism. Shipping represents about 40% of the economy, with several international carriers owned and operated off Åland. Most companies aside from shipping are small, with fewer than ten employees. Farming and fishing are important in combination with the food industry. A few high-profile technology companies contribute to a prosperous economy.
The main ports are Mariehamn (south), Berghamn (west) and Långnäs on the eastern shore of the Main Island.
Mariehamn was the base for the last large oceanic commercial sailing ships in the world. Their final tasks were bringing Australian wheat to Great Britain, on which Åland shipowner Erikson kept going until after WW2, 1947 being his last year. The ships latterly made only one round-trip from South Australia to Britain per year, after each marathon voyage going back to Mariehamn to lay up for a few months. The ship Pommern, now a museum in Mariehamn, was one of these last vessels.
The abolition of tax-free sales on ferry boats travelling between destinations within the European Union made Finland demand an exception for the Åland Islands on EU's VAT rules. The exception allows for maintained tax-free sales on the ferries between Sweden and Finland (provided they stop at Mariehamn or Långnäs) and at the airport, but has also made Åland a different tax-zone, meaning that tariffs must be levied on goods brought to the islands.
Unemployment is well below that of surrounding regions, 1.8% in 2004.
The Finnish State collects taxes, duties and fees also in Åland. In return, the Finnish Government places a sum of money at the disposal of the Åland Parliament. The sum is 0.45 per cent of total Government income, excluding Government loans. In 2006, the sum was about 182 million EUR.[8]
According to Eurostat, in 2006 Åland was the 20th wealthiest of the EU's 268 regions, and the wealthiest in Finland, with a GDP per inhabitant 47 percent above the EU mean.[9][10] Åland enjoys the largest state subsidies of any Finnish region (maakunta/landskap), totalling annually about 4,000 EUR per inhabitant more than the Ålanders pay in state taxes (2006 figures).[11]
While the official currency is the euro, the Swedish krona also circulates freely in Åland.
Demographics
 A mock wedding in Jomala. This event is held annually, mostly as a tourist attraction. It is a reenactment of an 1800s farmer's wedding (bondbröllop).
A mock wedding in Jomala. This event is held annually, mostly as a tourist attraction. It is a reenactment of an 1800s farmer's wedding (bondbröllop).
Births and deaths [12]
Average population Live births Deaths Natural change Crude birth rate (per 1000) Crude death rate (per 1000) Natural change (per 1000) 1951 340 279 61 1952 362 221 141 1953 382 260 122 1954 331 244 87 1955 303 200 103 1956 330 209 121 1957 327 248 79 1958 330 217 113 1959 313 226 87 1960 328 250 78 1961 317 237 80 1962 297 229 68 1963 293 222 71 1964 315 264 51 1965 331 229 102 1966 324 226 98 1967 338 223 115 1968 314 244 70 1969 298 262 36 1970 283 225 58 1971 302 228 74 1972 296 219 77 1973 299 229 70 1974 283 255 28 1975 296 219 77 13.3 9.9 3.4 1976 275 203 72 1977 247 202 45 1978 268 215 53 1979 262 192 70 1980 22 700 300 236 64 13.2 10.4 2.8 1981 22 900 267 214 53 11.7 9.4 2.3 1982 23 100 287 214 73 12.4 9.3 3.2 1983 23 300 281 246 35 12.0 10.5 1.5 1984 23 500 273 230 43 11.6 9.8 1.8 1985 23 600 287 241 46 12.2 10.2 1.9 1986 23 600 272 213 59 11.5 9.0 2.5 1987 23 700 276 220 56 11.6 9.3 2.4 1988 23 900 345 216 129 14.4 9.0 5.4 1989 24 100 323 297 26 13.4 12.3 1.1 1990 24 400 362 226 136 14.8 9.3 5.6 1991 24 700 324 256 68 13.1 10.4 2.8 1992 24 900 325 278 47 13.0 11.2 1.9 1993 25 000 329 241 88 13.1 9.6 3.5 1994 25 100 303 261 42 12.1 10.4 1.7 1995 25 200 338 258 80 13.4 10.2 3.2 1996 25 200 290 281 9 11.5 11.1 0.4 1997 25 300 286 241 45 11.3 9.5 1.8 1998 25 500 311 237 74 12.2 9.3 2.9 1999 25 700 287 297 - 10 11.2 11.6 -0.4 2000 25 700 258 247 11 10.0 9.6 0.4 2001 25 900 283 228 55 10.9 8.8 2.1 2002 26 100 269 236 33 10.3 9.0 1.3 2003 26 300 262 268 - 6 10.0 10.2 -0.2 2004 26 400 281 262 19 10.6 9.9 0.7 2005 26 600 268 259 9 10.1 9.7 0.3 2006 26 800 295 257 38 11.0 9.6 1.4 2007 27 000 286 249 37 10.6 9.2 1.4 2008 27 300 294 250 44 10.8 9.2 1.6 2009 27 600 267 247 20 9.7 9.0 0.7 2010 Ethnicity and language
See also: Languages of ÅlandMost inhabitants have Swedish (the sole official language) as their first language: 90.2% in 2009, and 5.0% speak Finnish. The language of instruction in publicly financed schools is Swedish, but an Ålandic municipality is free to provide teaching of Finnish. (In the rest of Finland, bilingual municipalities provide schooling both in Finnish and in Swedish.) See Åland Swedish for information about the dialect. The issue of the ethnicity of the Ålanders, and the correct linguistic classification of their language, remains somewhat sensitive and controversial. They may be considered either ethnic Swedes or Swedish-speaking Finns, but their language is closer to the adjacent dialects in Sweden, i.e. Uppländska, than to adjacent dialects of Finland Swedish. See Languages of Sweden.
Regional citizenship or the right of domicile (hembygdsrätt) is a prerequisite for the right to vote or stand as a candidate in elections to the Legislative Assembly, to own and hold real estate in Åland or to exercise without restriction a trade or profession in Åland.
Religion
The vast majority of the population, 94.8%, belongs to the Evangelical Lutheran Church.[citation needed] The Åland islands are home to some of the oldest churches in Finland.
Sport
- Åland competes in the biennial Island Games, which it hosted in 1991 and 2009.
- Åland United and IFK Mariehamn are the leading football clubs.
See also
- Outline of the Åland Islands
- Bibliography of the Åland Islands
- Index of Åland Islands-related articles
- Åland crisis
- Åland Islands national football team
- Åland Swedish & languages of Åland
- Flag of Åland
- Government of Åland
- Heraldry of Åland
- Provincial Governors of Finland
- Public holidays in Åland
- Transport on the Åland Islands
References
- ^ http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qn4188/is_20040718/ai_n11466101%7C Deseret News (Salt Lake City), Jul 18, 2004 by Tim Vickery Associated Press
- ^ http://www.asub.ax/text.con?iPage=227
- ^ "Human Development Report 2007". 2007. http://www.asub.ax/text.con?iPage=251.
- ^ The Åland Islands
- ^ an account of the border on Märket, and how it was redrawn in 1985, appears in Hidden Europe Magazine, 11 (November 2006) pp. 26-29 ISSN 1860-6318
- ^ Virrankoski, Pauli. Suomen historia. Ensimmäinen osa. SKS 2001. ISBN 951-746321-9. Page 59.
- ^ Lars Hulden: Finlandssvenska bebyggelsenamn, 2001, ISBN 951-583-071-0.
- ^ Budget för landskapet Åland 2008, page 308
- ^ Europe's Regions
- ^ "Ahvenanmaa on EU:n 20. vaurain alue". Helsingin Sanomat. February 19, 2009. http://www.hs.fi/talous/artikkeli/Ahvenanmaa+on+EUn+20+vaurain+alue/1135243664753. Retrieved July 19, 2009.
- ^ "Pääkaupunkiseutu elättää suuren osan Suomea". Helsingin Sanomat. January 17, 2009. http://www.hs.fi/kotimaa/artikkeli/P%C3%A4%C3%A4kaupunkiseutu+el%C3%A4tt%C3%A4%C3%A4+suuren+osan+Suomea/1135242814280. Retrieved July 19, 2009.
- ^ Alands Statistik
External links
- Åland – Official Site (mainly in Swedish)
- Tourist guide to Åland
- Åland in Brief
- Government of Åland ((Swedish))
- Parliament of Åland
- Act on the Autonomy of Åland
- B7 Baltic Islands Network
- The example of Åland, autonomy as a minor protector
- Åland Tourist Gateway
- Åland Official Tourist Gateway
- Ålandsbanken
- Posten Åland – the Post Office of Åland
- Ålandstidningen – Local Newspaper
Historical provinces of Finland Finland Proper · Karelia · Laponia · Ostrobothnia · Satakunta · Savonia · Tavastia · Uusimaa · ÅlandRegions of Finland Regions Åland · Central Finland · Central Ostrobothnia · Finland Proper · Kainuu · Kymenlaakso · Lapland · North Karelia · Northern Ostrobothnia · Northern Savonia · Ostrobothnia · Päijänne Tavastia · Pirkanmaa · Satakunta · South Karelia · Southern Ostrobothnia · Southern Savonia · Tavastia Proper · UusimaaFormer regions Nordic Council Members 
Associates  Åland Islands
Åland Islands Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands Greenland
Greenland
Former provinces of Finland 1997–2009 Eastern Finland • Lapland • Oulu • Southern Finland • Western Finland • Åland1917–1997 Central Finland (1960–1997) • Häme • Kuopio • Kymi (1947–1997) • Lapland • Mikkeli • Northern Karelia (1960–1997) • Oulu • Petsamo (1921) • Turku and Pori • Uusimaa • Vaasa • Viipuri (1917–1947) • ÅlandInhabited islands in the Baltic Sea Denmark Estonia Finland Archipelago Sea Islands (Åland Islands) · Hailuoto · Kimitoön · Laajasalo · Lauttasaari · Replot · SuomenlinnaGermany Poland Russia Sweden
Categories:- Åland
- Archipelagoes of the Baltic Sea
- Finnish islands in the Baltic
- Historical provinces of Finland
- Provinces of Finland (1917–1997)
- Provinces of Finland (1997–2009)
- Regions of Finland
- NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union
- NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
- Special territories of the European Union
- States and territories established in 1920
- Autonomous regions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.