- Geography of Guatemala
-
Guatemala Continent North America Subregion Central America Geographic coordinates 15°30′N 90°15′W / 15.5°N 90.25°W Area
- Total
- WaterRanked 106th
108,890 km²
approx. 950 km²[1]Coastline 400 km Land boundaries 1,687 km Countries bordered Mexico, 962 km
Belize, 266 km
El Salvador, 203 km
Honduras, 256 kmMaritime claims 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi) Highest point Tajumulco volcano, 4,220 m Lowest point Pacific Ocean, 0 m Longest river Motagua River, 486 km Largest inland body of water Lake Izabal 589.6 km² Land Use
- Arable land
- Permanent
crops
- Permanent
pastures
- Forests and
woodlands
- Other
12 %
5 %
24 %
54 %
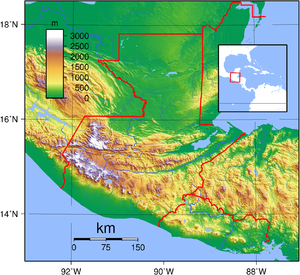
5 % (1993 est.)Climate: Tropical to temperate Terrain: plains, mountains Natural resources petroleum, nickel, rare woods, fish, wildlife, hydropower Natural hazards earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floodings, landslides Environmental issues deforestation, air and water pollution Guatemala is mountainous, except for the south coastal area and the northern vast lowlands of Petén department. Two mountain chains enter Guatemala from west to east, dividing the country into three major regions: the highlands, where the mountains are located; the Pacific coast, south of the mountains; and the Petén region, north of the mountains. These areas vary in climate, elevation, and landscape, providing dramatic contrasts between hot and humid tropical lowlands and highland peaks and valleys.
Contents
Overview
The southern edge of the western highlands is marked by the Sierra Madre, which stretches from the Mexican border south and east, and continues at lower elevations toward El Salvador. The mountain chain is characterized by steep volcanic cones, including Tajumulco Volcano (4,220 m/13,845 ft, the highest point in the country and Central America. All of Guatemala’s 37 volcanoes (4 of them active Pacaya, Santiaguito, Fuego and Tacaná), are in this mountain chain, and are frequent in the highlands.
The northern chain of mountains begins near the Mexican border with the Cuchumatanes range, then stretches east through the Chuacús and Chamá sierras, down to the Santa Cruz and Minas sierras, near the Caribbean Sea. The northern and southern mountains are separated by the Motagua valley, where the Motagua river and its tributaries drains from the highlands into the Caribbean being navigable in its lower end, where it forms the boundary with Honduras.
Its climate is hot and humid in the Pacific and Petén Lowlands – more temperate in the highlands, to freezing cold at the high of the Cuchumatanes range, and hot/drier in the easternmost departments.
The rivers are short and shallow in the Pacific vertient, larger and deeper, such as the Polochic which drains in Lake Izabal, Río Dulce, Motagua and Sarstún that forms the boundary with Belize in the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico vertient (Usumacinta, which forms the boundary between Chiapas, Mexico and Petén and its tributaries such as La Pasión and San Pedro.
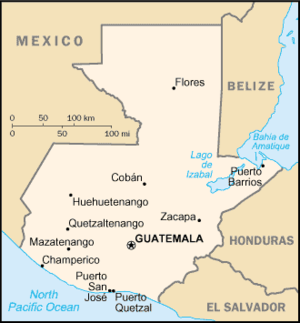
All major cities are in the Highlands and the Pacific Lowlands. Major cities are the capital Guatemala City, elevation 1,600 m (Central Highlands), Antigua Guatemala, elevation 1,533 m (Central Highlands), Quetzaltenango elevation 2,350 m (Western Highlands), Escuintla elevation 300 m, Mazatenango elevation 220 m and Coatepeque elevation 515 m, (Pacific Lowlands). The largest lake Lago de Izabal (589.6 km²), is close to the Caribbean coast. Volcán Tajumulco, 4,220 m, the highest point in Central America, is located in the western department of San Marcos.
Guatemala's location on the Caribbean Sea and Pacific Ocean makes it a target for hurricanes, including Hurricane Mitch in 1998 and Hurricane Stan in October 2005, which killed more than 1,500 people. (The damage was not wind related, but caused by flooding and landslides). The last major earthquake was on February 4, 1976, killing more than 23,000 in the Central Highlands (see also: Earthquakes in Guatemala).
Climate
Tropical; hot, humid in lowlands; cooler in highlands
Geographic data
- Location
- Central America, bordering the Caribbean Sea, between Honduras and Belize and bordering the North Pacific Ocean, between El Salvador and Mexico
- Geographic coordinates
- 15°30′N 90°15′W / 15.5°N 90.25°W
- Map references
- Central America and the Caribbean
- Area
-
- Total: 108,890 km²
- Land: 107,940 km²
- Land boundaries
-
- Total: 1,687 km
- Border countries: Belize 266 km, El Salvador 203 km, Honduras 256 km, Mexico 962 km
- Coastline
- 400 km
- Maritime claims
-
- Continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
- Exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370 km)
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22 km)
- Terrain
- Mostly mountains with narrow coastal plains and rolling limestone plateau (Peten)
- Elevation extremes
-
- Lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
- Highest point: Volcán Tajumulco 4,220 m
- Natural resources
- Petroleum, nickel, rare woods, fish, chicle, hydropower
- Land use
-
- Arable land: 12%
- Permanent crops: 5%
- Permanent pastures: 24%
- Forests and woodland: 54%
- Other: 5% (1993 est.)
- Irrigated land
- 1,250 km² (1993 est.)
- Natural hazards
- Several active volcanoes, occasional violent earthquakes; Caribbean coast subject to hurricanes and other tropical storms, causing flooding, mudflows and landslides
- Environment—current issues
- Deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution
- Environment—international agreements
-
- Party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78), Wetlands
- Signed, but not ratified: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol
- Geography—note
- No natural harbors on west coast
See also
Notes
- ^ INSIVUMEH. "Indice de lagos". http://www.insivumeh.gob.gt/hidrologia/lagos.htm. Retrieved 2008.
Sovereign states Antigua and Barbuda · Bahamas · Barbados · Belize · Canada · Costa Rica · Cuba · Dominica · Dominican Republic · El Salvador · Grenada · Guatemala · Haiti · Honduras · Jamaica · Mexico · Nicaragua · Panama · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Trinidad and Tobago · United States
Dependencies and
other territoriesAnguilla · Aruba · Bermuda · Bonaire · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Curaçao · Greenland · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Montserrat · Navassa Island · Puerto Rico · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States Virgin Islands
Climate of North America Sovereign states Antigua and Barbuda · Bahamas · Barbados · Belize · Canada · Costa Rica · Cuba · Dominica · Dominican Republic · El Salvador · Grenada · Guatemala · Haiti · Honduras · Jamaica · Mexico · Nicaragua · Panama · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Trinidad and Tobago · United States
Dependencies and
other territoriesAnguilla · Aruba · Bermuda · Bonaire · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Curaçao · Greenland · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Montserrat · Puerto Rico · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States Virgin Islands
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.