- Geography of Cuba
-
Cuba Nickname: La Isla Grande 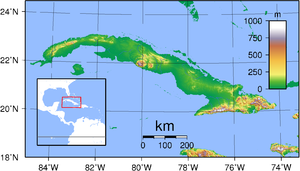
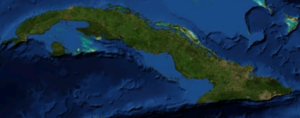
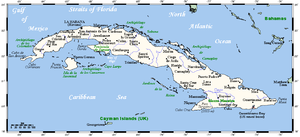
Map of CubaGeography Location Caribbean Sea Coordinates 21°30′N 80°00′W / 21.5°N 80°W Archipelago Greater Antilles Area 110,860 km2 (42,803 sq mi) Area rank 17th Length 1,199 km (745 mi) Width 200 km (120 mi) Coastline 3,735 km (2,320.8 mi) Highest elevation 2,005 m (6,578 ft) Highest point Pico Turquino Country CubaLargest city Havana (pop. 2,400,000) Demographics Population 11,451,652 (as of 2007) Density 102.79 /km2 (266.22 /sq mi) Ethnic groups White: 37%, Mulatto / Mestizo: 51%, Black: 11%, Chinese: 1% Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea. Cuba has a total land area of 110,860 km2 (42,800 sq mi). It has 3,735 km (2,321 mi) of coastline and 29 km (18 mi) of land borders — all figures including the United States territory at Guantánamo Bay, where the U.S. Navy's Guantanamo Bay Naval Base is located.
Cuba lies west of the North Atlantic Ocean, east of the Gulf of Mexico, south of the Straits of Florida, northwest of the Windward Passage, and northeast of the Yucatan Channel. The main island (Cuba) makes up most of the land area 105,006 km2 (40,543 sq mi).[1] The island is 1,199 km (745 mi) long and 200 km (120 mi) across its widest points and 35 km (22 mi) across its narrowest points.[1] The largest island outside the main island is the Isla de la Juventud (Isle of Youth) in the southwest, with an area of 3,056 km2 (1,180 sq mi).[1]
Contents
Physical geography
This short video shows the cloudy island of Cuba and the Bahamas as the ISS flies from the Caribbean Sea north-east to the Atlantic Ocean. In the video, you can see Cuba is mostly covered by clouds, but the reefs in the Bahamas stand out quite nicely.
Cuba is located 80 km (50 mi) west of Haiti across the Windward Passage, 140 km (87 mi) south of the Bahamas, 145 km (90 mi) south of Florida, 210 km (130 mi) east of Mexico, and 146 km (91 mi) north of Jamaica.
Cuba is the largest country by land area in the Caribbean. Its main island is the seventeenth-largest island in the world by land area. The island rises between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. It is bordered on the north by the Straits of Florida, on the northeast by Nicholas Channel and the Old Bahamas Channel. The southern part is bounded by the Windward Passage and the Cayman Trench, while the southwest lies in the Caribbean Sea. To the west, it reaches to the Yucatan Channel, and the northwest is open to the Gulf of Mexico.
More than 4,000 islands and cays are found in the surrounding sea and bays. The southern coast includes such archipelagos as Jardines de la Reina and the Canarreos. The northeastern shore is lined by the Sabana-Camagüey Archipelago, which includes Jardines del Rey and is composed of approximately 2,517 cays and islands.[2] The Colorados Archipelago is developed on the north-western coast.
See also: Islands of CubaTerrain
 Beach on Cayo Largo del Sur
Beach on Cayo Largo del Sur
Terrain is mostly flat to rolling plains, with rugged hills and mountains in the southeast. The lowest point is the Caribbean Sea at 0 m (sea level) and the highest point is Pico Turquino at 2,005 m (6,578 ft), part of the Sierra Maestra mountain range, located in the southeast of the island. Other significant mountain ranges are Sierra Cristal in the southeast, Escambray Mountains in the center of the island, and Sierra del Rosario in the northwest. White sand beaches (most notably in Varadero[3]), as well as mangroves and marshes can be found in the coastal area. The largest is the Zapata Swamp, with over 4,520 km2 (1,750 sq mi).
Cuba has negligible inland water area. The largest natural water mirror is Laguna de Leche at 67.2 km2 (25.9 sq mi), while the man-made Zaza Reservoir, at 113.5 km2 (43.8 sq mi), is the largest inland water surface by area in the country.
Maritime claims
Cuba makes maritime claims that include a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi) and an exclusive economic zone of 200 nautical miles (370.4 km; 230.2 mi).
Extreme points
Extreme points in Cuba are:
Point Name Location Remarks North (on-shore) Punta Hicacos 23°12′23″N 81°08′44″W / 23.20639°N 81.14556°W On Hicacos Peninsula North (off-shore) Cayo Cruz del Padre 23°16′34″N 80°54′38″W / 23.27611°N 80.91056°W Part of Sabana-Camaguey Archipelago East Punta Maisi 20°12′32″N 74°08′01″W / 20.20889°N 74.13361°W Near Maisí West siders Cape San Antonio 21°51′39″N 84°57′25″W / 21.86083°N 84.95694°W On Guanahacabibes Peninsula South siders Cape Cruz 19°49′37″N 77°40′30″W / 19.82694°N 77.675°W Near Niquero Highest point Pico Turquino 19°59′22″N 76°50′09″W / 19.98944°N 76.83583°W Part of Sierra Maestra, 1,975 m (6,480 ft) Lowest point sea level Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean Largest city Havana 23°08′00″N 82°23′00″W / 23.1333333°N 82.3833333°W National capital, population 2,328,000 Oldest city Baracoa 20°20′55″N 74°30′38″W / 20.34861°N 74.51056°W Founded in 1511 Natural resources
Main article: Economy of CubaNatural resources include cobalt, nickel, iron ore, copper, manganese, salt, timber, silica, and petroleum. At one time, the whole island was covered with forests and there are still many cedar (Cedrela odorata), chechem (Metopium brownei), mahogany (Swietenia mahagoni), and other valuable trees. Large areas were cleared to grow more sugarcane, and so few trees remained that timber had to be imported.
The most important Cuban mineral economic resource is nickel. Cuba has the second largest nickel reserves in the world after Russia.[4] Sherritt International, a Canadian energy company, operates a large nickel mining facility in Moa, Cuba. Another leading mineral resource is cobalt, a byproduct of nickel mining operations. Cuba ranks as the fifth largest producer of refined cobalt in the world.
Petroleum is extracted on Cuba's northern shore, in the provinces of La Habana and Matanzas. Recent petroleum exploration has revealed that the North Cuba Basin could produce approximately 4.6 billion barrels (730,000,000 m3) to 9.3 billion barrels (1.48×109 m3) of petroleum. As of 2006, Cuba has now started to test-drill these locations for possible exploitation.[5][6][7] The petroleum is of low quality, and used for energy generation only.
Sugarcane was the most important part of the economy in Cuba's history, and is still grown on large areas. Extensive irrigation systems are developed in the south of Sancti Spíritus Province. Tobacco, used for some of the world's best cigars, is grown especially in the Pinar del Río Province.
See also: Agriculture of CubaClimate
Cuba's climate is tropical and moderated by trade winds. The dry season lasts from November to April and the rainy season from May to October.
Casa Blanca, Havana Climate chart (explanation) J F M A M J J A S O N D 64261969261946282054292198302218231231063124100322414431241812923882821582720Average max. and min. temperatures in °C Precipitation totals in mm Source: Climate Charts[8] Imperial conversion J F M A M J J A S O N D 2.579662.779661.882682.184703.986727.288734.288753.990755.788757.184733.582702.38168Average max. and min. temperatures in °F Precipitation totals in inches Cuba is an archipelago of islands located in the Caribbean Sea, with the geographic coordinates 21°3N, 80°00W. Cuba is the principal island, which is surrounded by four main groups of islands. These are the Colorados, the Sabana-Camagüey, the Jardines de la Reina and the Canarreos. The main island of Cuba constitutes most of the nation's land area or 105,006 km2 (40,543 sq mi) and is the seventeenth-largest island in the world by land area. The second largest island in Cuba is the Isla de la Juventud (Isle of Youth) in the southwest, with an area of 3,056 km2 (1,180 sq mi). Cuba has a total land area of 110,860 km2 (42,800 sq mi).
The main island consists mostly of flat to rolling plains. At the southeastern end is the Sierra Maestra, a range of steep mountains whose highest point is the Pico Real del Turquino at 1,975 metres (6,480 ft). The local climate is tropical, though moderated by trade winds. In general (with local variations), there is a drier season from November to April, and a rainier season from May to October. The average temperature is 23.1 °C (73.6 °F) in January and 27 °C (80.6 °F) in July. Cuba lies in the path of hurricanes, and these destructive storms are most common in September and October. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. Better known smaller towns include Baracoa which was the first Spanish settlement on Cuba, Trinidad, a UNESCO world heritage site, and Bayamo.
Administrative subdivisions
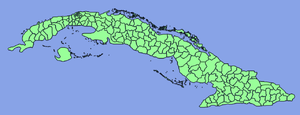
Main article: Provinces of CubaCuba is divided into 15 Provinces and one special municipality (Isla de la Juventud). The provinces are further subdivided into level 3 subdivisions, called municipalities (Spanish: Municipios), of which there are 169 following the 1976 administrative redistribution.[9]
See also: Municipalities of Cuba and List of places in CubaReferences
- ^ a b c Stoner, K. Lynn. "Cuba" Encarta Online Encyclopedia. 2005. Archived 2009-10-31.
- ^ Mapping Interactivo (March 2005). "Mangroves variability in the Sabana-Camaguay Archipellago". http://www.mappinginteractivo.com/plantilla-ante.asp?id_articulo=874. Retrieved 2007-10-16.
- ^ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CVvZCNcBy_Y&feature=related
- ^ http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/country/1997/9509097.pdf The Mineral Resources of Cuba 1997
- ^ Cuban Oil, Gas Output Grow - Prensa Latina - Cuba Business News - Havana Journal
- ^ theTrumpet.com
- ^ Smith, Wayne S (2006-11-01). "After 46 years of failure, we must change course on Cuba". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/comment/story/0,,1936186,00.html. Retrieved 2010-05-03.
- ^ Cuba Climate data
- ^ Fifth United Nations Conference on the Standardization of Geographical Names, Vol. II, published by the United Nations, New York, 1991
Sovereign states Antigua and Barbuda · Bahamas · Barbados · Belize · Canada · Costa Rica · Cuba · Dominica · Dominican Republic · El Salvador · Grenada · Guatemala · Haiti · Honduras · Jamaica · Mexico · Nicaragua · Panama · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Trinidad and Tobago · United States
Dependencies and
other territoriesAnguilla · Aruba · Bermuda · Bonaire · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Curaçao · Greenland · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Montserrat · Navassa Island · Puerto Rico · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States Virgin Islands
Climate of North America Sovereign states Antigua and Barbuda · Bahamas · Barbados · Belize · Canada · Costa Rica · Cuba · Dominica · Dominican Republic · El Salvador · Grenada · Guatemala · Haiti · Honduras · Jamaica · Mexico · Nicaragua · Panama · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Trinidad and Tobago · United States
Dependencies and
other territoriesAnguilla · Aruba · Bermuda · Bonaire · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Curaçao · Greenland · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Montserrat · Puerto Rico · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States Virgin Islands
 Provinces of Cuba
Provinces of CubaCurrent Artemisa · Camagüey · Ciego de Ávila · Cienfuegos · Ciudad de La Habana · Granma · Guantánamo · Holguín · Isla de la Juventud · Las Tunas · Matanzas · Mayabeque · Pinar del Río · Sancti Spíritus · Santiago de Cuba · Villa Clara
Historical Provincial capitals Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.