- Overseas region
-

(incl. overseas regions)
(incl. overseas departments)
Urban communities
Agglomeration communities
Commune communities
Syndicates of New AgglomerationOverseas collectivities
Sui generis collectivity
Overseas country
Overseas territory
Clipperton IslandOverseas region (French: Région d'outre-mer) is a recent designation given to the Overseas departments which have similar powers to those of the regions of metropolitan France. They have had these powers since 1982, when France's decentralisation policy dictated that they be given elected regional councils along with other regional powers. It was not until the 2003 constitutional change that these regions are now to be called overseas regions; indeed the new wording of the Constitution aims to give no precedence to either appellation overseas department or overseas region, though the second one is still virtually unused by French media.
The following have overseas region status:
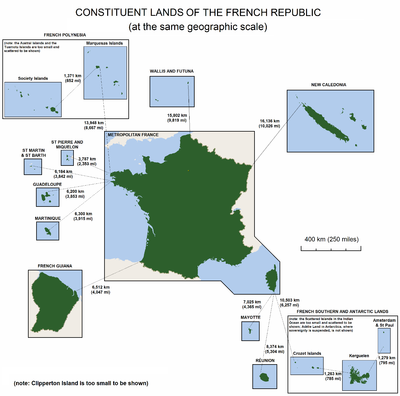
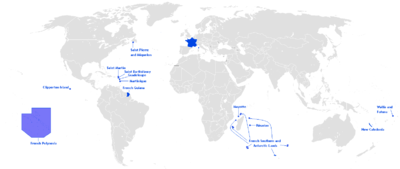
- French Guiana in South America
- Guadeloupe in North America (the Caribbean)
- Martinique in North America (the Caribbean)
- Réunion in Africa (the Indian Ocean)
- Mayotte in Africa (the Indian Ocean)
Saint Pierre and Miquelon were once an overseas department, but were demoted to a territorial collectivity in 1985, before the French regions were created.
Powers
As integral parts of the French Republic, they are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council, elect a Member of the European Parliament (MEP), and also use the Euro as their currency.
See also
- Administrative divisions of France
- French overseas departments and territories
- Colonialism
External links
Categories:- France geography stubs
- Subdivisions of France
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.