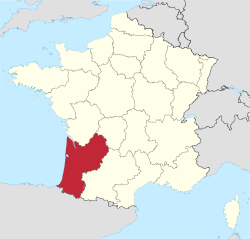
- Aquitaine
-
Aquitaine — Region of France — 
Flag
LogoCountry  France
FrancePrefecture Bordeaux Departments Government – President Alain Rousset (PS) Area – Total 41,308 km2 (15,949.1 sq mi) Population (2008)INSEE – Total 3,150,890 – Density 76.3/km2 (197.6/sq mi) Time zone CET (UTC+1) – Summer (DST) CEST (UTC+2) ISO 3166 code FR-B GDP/ Nominal € 85.9 billion (2007)[1] NUTS Region FR61 Website aquitaine.fr Aquitaine (French pronunciation: [a.ki.tɛn], English /ˌækwɪˈteɪn/; Occitan: Aquitània; Basque: Akitania), archaic Guyenne/Guienne (Occitan: Guiana), is one of the 27 regions of France, in the south-western part of metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain. It comprises the 5 departments of Dordogne, Lot et Garonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes and Gironde. In the Middle Ages Aquitaine was a kingdom and a duchy, whose boundaries fluctuated considerably.
Contents
History
Ancient Age
There are traces of human settlement by prehistoric peoples, especially in the Périgord, but the earliest attested inhabitants in the south-west were the Aquitani, who were not proper Celtic people, but more akin to the Iberians (see Gallia Aquitania). Although a number of different languages and dialects were in use in the area during ancient times, it is most likely that the prevailing language of Aquitaine during the late pre-historic to Roman period was an early form of the Basque language. This has been demonstrated by various Aquitanian names and words that were recorded by the Romans, and which are currently easily readable as Basque. Whether this Aquitanian language (Proto-Basque) was a remnant of a Vasconic language group that once extended much farther, or whether it was generally limited to the Aquitaine/Basque region is not currently known. One reason the language of Aquitaine is important is because Basque is the last surviving non-Indo-European language in western Europe and it has had some effect on the languages around it, including Spanish and, to a lesser extent, French.
The original Aquitania (named after the inhabitants) at the time of Caesar's conquest of Gaul included the area bounded by the Garonne River, the Pyrenees and the Atlantic ocean. The name may stem from Latin 'aqua', maybe derived from the town "Aquae Augustae", "Aquae Tarbellicae" or just "Aquis" (Dax, Akize in modern Basque) or as a more general geographical feature.
Under Augustus' Roman rule, since 27 BC the province of Aquitania was further stretched to the north till the River Loire, so including proper Gaul tribes along with old Aquitani south of the Garonne (cf. Novempopulania and Gascony) within the same region. In 392, the Roman imperial provinces were restructured and Aquitania Prima, Aquitania Secunda and Aquitania Tertia (or Novempopulania) were established in south-western Gaul.
Early Middle Ages
Accounts on Aquitania during the Early Middle Ages are blurry, lacking precision, but there was much unrest. The Visigoths were called into Gaul as foederati, but eventually established themselves as the de-facto rulers in south-west Gaul as central Roman rule collapsed. The Visigoths established their capital in Toulouse, but their actual tenure on Aquitaine was feeble. Furthermore, in 507 they were expelled south to Hispania after their defeat in the Battle of Vouillé by the Franks, who became the new rulers in the area. Two regions come to be distinguished after the Frank expansion to the south, Vasconia/Gascony and Aquitaine, with the former comprising the previous Novempopulania and the latter the territory lying between the Loire and Garonne rivers.
The Franks likewise had difficulty controlling their south-western marches, i.e. Vasconia, in turn setting up a Duchy as of AD 602 to hold a grip on the area, appointing a duke in charge. These dukes were quite detached from central Frank overlordship, sometimes governing as independent rulers with strong ties to their Vascon kinsmen south of the Pyrenees. As of 660, the duchies of Aquitaine and Vasconia were united under the rule of Felix of Aquitaine to form an independent polity. Despite its nominal submission to the Merovingians, the ethnic make-up of new realm Aquitaine wasn´t Frankish, but Gallo-Roman north of the Garonne and main towns and Basque, especially south of the Garonne.
A united Vascon-Aquitanian realm reached its heyday under Odo the Great's rule. The independent status of the realm might have continued but for an attack by the Muslim troops who had just invaded the Visigoth Hispania. After successfully fending them off in Toulouse in 719 he was defeated close to Bordeaux, with the hosts under Abd-al-Raḥmân al-Ghafiqi command ransacking the lands south of the Garonne. Odo was required to pledge allegiance to the Frankish Charles Martel in exchange for help against the Muslim forces, and Vascon-Aquitanian self-rule first came to an end by 742, and definitely in 768 after the assassination of Waifer. In the period previous and after the Muslim thrust, the Basques are often cited in several accounts stirring against Frankish attempts to subdue Aquitaine (stretching up to Toulouse) and Vasconia, pointing to a not preponderant but clearly significant Basque presence in the former. 'Romans' are also cited as living in the cities of Aquitaine, as opposed to the Franks.
In 781, Charlemagne decided to proclaim his son Louis King of Aquitaine within the Carolingian Empire, ruling over a realm comprising the Duchy of Aquitaine and the Duchy of Vasconia (Et 3 Calend Augusti habuit concilium magnum in Aquis, et constituit duos filius sans reges Pippinum et Clotarium, Pippinum super Aquitaniam et Wasconiam). He suppressed various Vascon uprisings, even venturing into the lands of Pamplona past the Pyrenees after ravaging the Gascony, with a view to imposing his authority in the Vasconia south of Pyrenees too. According to his biography, he achieved everything he wanted and after staying overnight in Pamplona, on his way back his army was attacked in Roncesvaux in 812, but didn't suffer defeat thanks to the precautions he had taken.
Seguin (Sihiminus, Semen...), count of Bordeaux and Duke of Vasconia, seemed to have attempted a detachment from the Frankish central authority on Charlemagne's death. The new emperor Louis the Pious reacted by removing him from his capacity, which stirred the Vascons into rebellion. The king in turn sent his troops over to the territory, submitting them in two campaigns and even killing the duke, while his family crossed the Pyrenees and kept raising against the Frankish power. In 824, the 3rd Battle of Roncesvaux took place, where counts Aeblus and Aznar, Frankish vassals from the Duchy of Vasconia sent by the new King of Aquitaine Pepin, were captured by the joint forces of Iñigo Arista and the Banu Qasi.
Before Pepin's death, emperor Louis had appointed a new king in 832, his son Charles the Bald, while the Aquitanian lords elected king Pepin II. This contest for the head of the kingdom led to a constant period of war among Charles, loyal to his father and the Carolingian power, and Pepin II, who relied more on the support of Vascon and Aquitanian lords.
The title "Duke of Aquitaine" was held by the counts of Poitiers from the 10th to the 12th century.
It passed to France in 1137 when the duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine married Louis VII of France, but their marriage was annulled in 1152 and when Eleanor's new husband became Henry II of England in 1154, the area became an English possession.
Links between Aquitaine and England were strengthened, with large quantities of wine produced in southwestern France being exported to London, Southampton, and other English ports.
Aquitaine remained English until the end of the Hundred Years’ War in 1453, when it was annexed by France. From the 13th century until the French Revolution, Aquitaine was usually known as Guyenne.
The region served as a stronghold for the Protestant Huguenots during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, who suffered persecution at the hands of the Roman Catholic Church. The Huguenots called upon the English crown for assistance against the Catholic Cardinal Richelieu.
Demographics
Aquitaine consists of 3,150,890 inhabitants equivalent to 6% of the total French population.
Sport
The region is home to many successful sports teams. In particular worth mentioning are:
Football
- FC Girondins de Bordeaux, one of France's most successful association football teams.
- Pau FC
- FC Libourne-Saint-Seurin
Rugby Union is particularly popular in the region. Clubs include:
- Aviron Bayonnais
- Biarritz Olympique, runners-up in the 2005-6 Heineken Cup.
- Union Bordeaux-Bègles
- Section Paloise
- US Dax
Basketball
- Élan Béarnais Pau-Orthez one of the most successful French basketball clubs
Bull-fighting is also popular in the region.
Major Surfing championships regularly take place on Aquitaine's coast.
See also
- Aquitania
- Basque people
- Basque Country (historical territory)
- Bordeaux wine regions
- Gascony
- Occitania
Notes
External links
- (French) Regional Council of Aquitaine
- (English) Aquitaine at the Open Directory Project
- (English) Short guide to Aquitaine with main tourist attractions
- CSfrance.amb-usa.fr
Bordeaux (Gironde) • Périgueux (Dordogne) • Mont-de-Marsan (Landes) • Agen (Lot-et-Garonne) • Pau (Pyrénées-Atlantiques)Regions of France - Alsace
- Aquitaine
- Auvergne
- Burgundy
- Brittany
- Centre
- Champagne-Ardenne
- Corsica
- Franche-Comté
- Île-de-France
- Languedoc-Roussillon
- Limousin
- Lorraine
- Midi-Pyrénées
- Nord-Pas-de-Calais
- Lower Normandy
- Upper Normandy
- Pays de la Loire
- Picardy
- Poitou-Charentes
- Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur
- Rhône-Alpes
- Overseas regions:
- French Guiana
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Mayotte
- Réunion

 Historical Provinces of France
Historical Provinces of FranceProvinces Alsace • Angoumois • Anjou • Artois • Aunis • Auvergne • Basse-Navarre • Béarn • Beaujolais • Berry • Bourbonnais • Brittany • Burgundy • Champagne • Corsica • Dauphiné • Flanders and Hainaut • Foix • Forez • Franche-Comté • Gascony • Guyenne • Île-de-France • Languedoc • Limousin • Lorraine • Lyonnais • Maine • Marche • Montbéliard • Mulhouse • Nice • Nivernais • Normandy • Orléanais • Perche • Picardy • Poitou • Provence • Roussillon • Saintonge • Savoy • Touraine • Trois-Évêchés • Venaissin Categories:
Categories:- Former provinces of France
- Aquitaine
- Regions of France
- NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.