- Qatar
-
State of Qatar دولة قطر
Dawlat Qaṭar

Flag Emblem Anthem: السلام الأميري (Arabic)
"As-salām al-amīrī" (transliteration)
Amiri Salute
Capital
(and largest city)Doha
25°18′N 51°31′E / 25.3°N 51.517°EOfficial language(s) Arabic Demonym Qatari Government Absolute monarchy - Emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani - Crown Prince Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani - Prime Minister Hamad bin Jassim bin Jaber Al Thani Legislature Consultative Assembly of Qatar Establishment - Founded by Sheikh Jassim bin Mohammed Al Thani 18 December 1878 - Independence from the Ottoman Empire 1913 - Independence from United Kingdom 3 September 1971 Area - Total 11,437 km2 (164th)
4,416 sq mi- Water (%) negligible Population - 2010 census 1,696,563[1] (148th) - Density 123.2/km2 (123rd)
319.1/sq miGDP (PPP) 2011 estimate - Total $181.912 billion[2] - Per capita $102,891[2] GDP (nominal) 2011 estimate - Total $173.206 billion[2] - Per capita $97,967[2] HDI (2010)  0.803[3] (very high) (38th)
0.803[3] (very high) (38th)Currency Riyal ( QAR)Time zone AST (UTC+3) - Summer (DST) (not observed) (UTC+3) Drives on the Right ISO 3166 code QA Internet TLD .qa, قطر. Calling code 974 Qatar (
 i/ˈkɑːtɑr/ or
i/ˈkɑːtɑr/ or  i/kəˈtɑr/;[4][5] Arabic: قطر [ˈqɑtˤɑr]; local vernacular pronunciation: [ɡɪtˤɑr][6]), also known as the State of Qatar or locally Dawlat Qaṭar, is an Arab emirate, in the Middle East, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeasterly coast of the much larger Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the rest of its territory surrounded by the Persian Gulf. A strait of the Persian Gulf separates Qatar from the nearby island state of Bahrain.
i/kəˈtɑr/;[4][5] Arabic: قطر [ˈqɑtˤɑr]; local vernacular pronunciation: [ɡɪtˤɑr][6]), also known as the State of Qatar or locally Dawlat Qaṭar, is an Arab emirate, in the Middle East, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeasterly coast of the much larger Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the rest of its territory surrounded by the Persian Gulf. A strait of the Persian Gulf separates Qatar from the nearby island state of Bahrain.Qatar has been ruled as an absolute monarchy by the Al Thani family since the mid-19th century. Formerly a British protectorate noted mainly for pearling, it became independent in 1971, and has become one of the region's wealthiest states due to its enormous oil and natural gas revenues. In 1995, Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani became Emir when he seized power from his father, Khalifa bin Hamad Al Thani, in a peaceful coup d'état.[7] The most important positions in Qatar are held by the members of the Al Thani family, or close confidants of the al- Thani family. Beginning in 1992, Qatar has built intimate military ties with the United States, and is now the location of U.S. Central Command’s Forward Headquarters and the Combined Air Operations Center.
Qatar has the world's largest per capita production and proven reserves of both oil and natural gas. In 2010, Qatar had the world's highest GDP per capita, while the economy grew by 19.40%, the fastest in the world. The main drivers for this rapid growth are attributed to ongoing increases in production and exports of liquefied natural gas, oil, petrochemicals and related industries. Qatar has the second-highest human development in the Arab World after the United Arab Emirates. In 2009, Qatar was the United States’ fifth-largest export market in the Middle East, trailing behind the U.A.E., Israel, Saudi Arabia and Egypt. With a small citizen population of less than 300,000 people, Qatar workforce comprises expatriates from other Arab nations (20% of population), the Indian subcontinent (India 20%, Nepal 13%, Pakistan 7%, Sri Lanka 5%), Southeast Asia (Philippines 10%), and other countries (5%)[8]. Qatar has attracted an estimated $100 billion in investment, with approximately $60–70 billion coming from the U.S in the energy sector. It is estimated that Qatar will invest over $120 billion in the energy sector in the next ten years.[9]
Contents
Etymology
The name may derive from "Qatara", believed to refer to the Qatari town of Zubara, an important trading port and town in the region in ancient times.
In Standard Arabic the name is pronounced [ˈqɑtˤɑr], while in the local dialect it is [ˈɡitˤar].[6] In English-language broadcast media within Qatar—for example, television commercials for Qatar Airways and advertisements concerning economic development in Qatar—the name is pronounced "KA-tar" (not "KAT-ar").
History
Main article: History of QatarRecent discoveries on the edge of an island in western Qatar indicate early human presence in pre-historic Qatar.[clarification needed] Discovery of a 6th millennium BC site at Shagra, in southeastern Qatar revealed the key role the sea (the Persian Gulf) played in the lives of Shagra’s inhabitants. Excavations at Al-Khor in northeastern Qatar, Bir Zekrit and Ras Abaruk, and the discovery there of pottery, flint, flint-scraper tools, and painted ceramic vessels indicates Qatar’s connection with the Al-Ubaid civilisation, which flourished in the land between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers in present-day Iraq during the period of 5th–4th millennium BC. There had also been a barter-based trading system between the settlements at Qatar and the Ubaid Mesopotamia, in which the exchanged commodities were mainly pottery and dried fish.[10]
Islam conquered the entire Arabian region during the 7th century in a string of widespread conflicts resulting in the Islamization of the native Arabian pagans. With the spread of Islam in Qatar, the Islamic prophet Muhammad sent his first military envoy, Al Ala Al-Hadrami, to Al-Mundhir Ibn Sawa Al-Tamimi, the ruler of Bahrain (which extended from the coast of Kuwait to the south of Qatar, including Al-Hasa and Bahrain Islands), in the year 628, inviting him to accept Islam as he had invited other kingdoms and empires of his time such as Byzantium and Persia. Mundhir, in response to Muhammad, announced his acceptance of Islam, and all the inhabitants of Qatar became Muslim, heralding the beginning of the Islamic era in Qatar.
In medieval times, Qatar was more often than not independent and a participant in the great Persian Gulf–Indian Ocean commerce. Many races and ideas were introduced into the peninsula from the sailors of Sindh, East Africa, South and Southeast Asia, as well as the Malay archipelago. Today, the traces of these early interactions with the oceanic world of the Indian Ocean survive in the small minorities of races, peoples, languages and religions, such as the presence of Africans and Shihus.
Although the peninsula land mass that makes up Qatar has sustained humans for thousands of years, for the bulk of its history, the arid climate fostered only short-term settlements by nomadic tribes. The Abbasid era (750–1258) saw the rise of several settlements, including Murwab. The Portuguese ruled from 1517 to 1538, when they lost to the Ottomans. For the duration of the 18th and 19th century, Qatar was independent, but in 1876, Shaikh Jassim Bin Muhammad bin Thani invited the Ottomans, who had recently annexed the Ahsa region, to protect Qatar. Qatar thus became a dependency of the Ottoman Empire, although not a part of it. But attempts by the Ottomans to annex Qatar outright soon led to the expulsion of the Ottomans from the Qatar Peninsula. In March 1893, at the Battle of Wajbah (10 miles west of Doha), Shaikh Jassim defeated the Ottomans and banished them for good from Qatar. This date is a landmark in Qatari history, one that marks the emergence of modern Qatar as a nation.
The British initially sought out Qatar and the Persian Gulf as an intermediary vantage point en route to their colonial interests in India; although, the discovery of petroleum and other hydrocarbons in the early 20th century would re-invigorate their interest. During the 19th century, the time of Britain’s formative ventures into the region, the Al Khalifa clan reigned over the northern Qatari peninsula from the nearby island of Bahrain to the west.
Although Qatar had the legal status of a dependency, resentment festered against the Bahraini Al Khalifas along the eastern seaboard of the Qatari peninsula. In 1867, the Al Khalifas launched a successful effort to crush the Qatari rebels, sending a massive naval force to Al Wakrah. However, the Bahraini aggression was in violation of the 1820 Anglo-Bahraini Treaty. The diplomatic response of the British to this violation set into motion the political forces that would eventuate in the founding of the state of Qatar on 18 December 1878 (for this reason, the date of 18 December is celebrated each year as the Qatar National Day). In addition to censuring Bahrain for its breach of agreement, the British Protectorate (per Colonel Lewis Pelly) asked to negotiate with a representative from Qatar.
The request carried with it a tacit recognition of Qatar’s status as distinct from Bahrain. The Qataris chose as their negotiator the entrepreneur and long-time resident of Doha, Muhammed bin Thani. The Al Thanis had taken relatively little part in Persian Gulf politics, but the diplomatic foray ensured their participation in the movement towards independence and their hegemony as the future ruling family, a dynasty that continues to this day. The results of the negotiations left the nation with a new-found sense of political identity, although it did not gain official standing as a British protectorate until 1916.
20th and 21st centuries
The reach of the British Empire diminished after World War II, especially following Indian independence in 1947. Pressure for a British withdrawal from the Arab emirates in the Persian Gulf increased during the 1950s, and the British welcomed Kuwait’s declaration of independence in 1961. When Britain officially announced in 1968 that it would disengage politically (though not economically) from the Persian Gulf in three years’ time, Qatar joined Bahrain and seven other Trucial States in a federation. Regional disputes, however, quickly compelled Qatar to resign and declare independence from the coalition that would evolve into the seven-emirate United Arab Emirates. On 3 September 1971, Qatar became an independent sovereign state.
In 1991, Qatar played a significant role in the Persian Gulf War, particularly during the Battle of Khafji in which Qatari tanks rolled through the streets of the town providing fire support for Saudi Arabian National Guard units which were fighting against units of the Iraqi Army. Qatar also allowed Coalition troops from Canada to use the country as an airbase to launch aircraft on CAP duty.
Since 1995[update], Emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani has ruled Qatar, seizing control of the country from his father Khalifa bin Hamad Al Thani while the latter vacationed in Switzerland. Under Emir Hamad, Qatar has experienced a notable amount of sociopolitical liberalization, including the endorsement of women's suffrage or right to vote, drafting a new constitution, and the launch of Al Jazeera, an outspoken news organization.
The World Factbook states that Qatar has the second-highest GDP per capita in the world, after Liechtenstein.
Qatar served as the headquarters and one of the main launching sites of the US invasion of Iraq[11] in 2003.
In March 2005, a suicide bombing killed a British teacher at the Doha Players Theatre, shocking for a country that had not previously experienced acts of terrorism. The bombing was carried out by Omar Ahmed Abdullah Ali, an Egyptian residing in Qatar, who had suspected ties to Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula.[12][13] According to leaked documents published in The New York Times, Qatar's record of counterterrorism efforts was the "worst in the region" although Qatar had been a generous host to the American military.[14] The cable suggested that Qatar’s security service was "hesitant to act against known terrorists out of concern for appearing to be aligned with the U.S. and provoking reprisals".[14]
In December 2010, Qatar was selected to host the 2022 FIFA World Cup.
National Day
Qatar National Day on December 18 is the day Qatar remembers how their national unity was achieved and how they became a distinct and respected nation out of a society torn apart by conflicting tribal loyalties, devoid of security and order, and overrun by invaders. On that day, the deepest expressions of affection and gratitude are conveyed to the people of Qatar who cooperated in solidarity and vowed sincere allegiance and obedience to Shaikh Jassim bin Mohammed Al Thani, trusting him as a father, brother, leader, and Imam. In him they found a man who had already distinguished himself in his youth as a pious, brave, self-sacrificing, as well as a wise leader. He successfully unified the Qatari Peninsula and safeguarded the interests of its people in the darkest of times ever witnessed by this part of the world.
Geography
Main article: Geography of QatarThe Qatari peninsula juts 100 miles (161 km) north into the Persian Gulf from Saudi Arabia. It lies between latitudes 24° and 27° N, and longitudes 50° and 52° E.
Much of the country consists of a low, barren plain, covered with sand. To the southeast lies the spectacular Khor al Adaid (“Inland Sea”), an area of rolling sand dunes surrounding an inlet of the Persian Gulf. There are mild winters and very hot, humid summers.
The highest point in Qatar is Qurayn Abu al Bawl at 103 metres (338 ft)[15] in the Jebel Dukhan to the west, a range of low limestone outcroppings running north-south from Zikrit through Umm Bab to the southern border. The Jebel Dukhan area also contains Qatar’s main onshore oil deposits, while the natural gas fields lie offshore, to the northwest of the peninsula.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of QatarQatar has an unelected, monarchic, emirate-type government. There are no democratic institutions or elections, and power is assumed on a hereditary basis.[15] Its legal system combines limited aspects of Islamic (or Sharia) and civil law codes in a discretionary system of law totally controlled by the Emir. Although civil codes are being implemented, Islamic law is used in family and personal matters. The country has a parliament called Template:Municipalitial court that composes of ordinary citizens representing every populated area in Qatar. The country has not accepted compulsory International Court of Justice jurisdiction.[15]
Qatari law
When contrasted with other Arab states such as Saudi Arabia, for instance, Qatar has comparatively liberal laws, but is still not as liberal as some other Arab states of the Persian Gulf like United Arab Emirates or Bahrain. Qatar is a civil law jurisdiction. However, Shari'a or Islamic law is applied to aspects of family law, inheritance and certain criminal acts. Women can legally drive in Qatar and there is a strong emphasis in equality and human rights brought by Qatar's National Human Rights Committee. Many cases of ill-treatment of immigrant labour have been observed. Qatar does not maintain wage standards for its immigrant labor and does not permit labour-unions.
The country has undergone a period of liberalization and modernisation during the reign of the current Emir, Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, who came to power in 1995. The laws of Qatar tolerate alcohol to a certain extent. However, the few bars and nightclubs in Qatar operate only in expensive hotels and clubs, with Qatar Distribution Company[16] the only importer and retailer for alcohol in Qatar. Under Qatar's Sharia, it is illegal to show alcohol or be drunk in public.
During the month of Ramadan, eating, drinking, and smoking in public is strictly banned from dawn to sunset. Violating this law can lead to arrest.
In common with other Arab countries of the Persian Gulf, sponsorship laws exist in Qatar. These laws have been widely described as akin to modern-day slavery.[17] The sponsorship system (kafeel or kafala) exists throughout the GCC, apart from Bahrain, and means that a worker (not a tourist) may not enter the country without having a kafeel; cannot leave without the kafeel's permission (an exit permit must first be awarded by the sponsor, or kafeel); and the sponsor has the right to ban the employee from entering Qatar within 2–5 years of his first departure. Various governmental sponsors have recently exercised their right to prevent employees from leaving the country, effectively holding them against their will for no good reason. Some individuals after resigning have not been issued with their exit permits, denying them their basic right to leave the country. Many sponsors do not allow the transfer of one employee to another sponsor. This does not apply to special sponsorship of a Qatar Financial Centre-sponsored worker where it is encouraged and regulated that sponsorship should be uninhibited and assistance should be given to allow for such transfers of sponsorship.
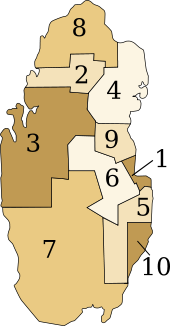
Administrative divisions
Main article: Municipalities of QatarBefore 2004, Qatar was divided into ten municipalities (Arabic: baladiyah), also occasionally or rarely translated as governorates or provinces:
- Ad Doha
- Al Ghuwariyah
- Al Jumaliyah (Al Jumayliyah)[18]
- Al Khawr
- Al Wakrah
- Ar Rayyan
- Jariyan al Batnah
- Ash Shamal
- Umm Salal
- Mesaieed
Since 2004, Qatar has been divided into seven municipalities.[19] A new municipality, Al Daayen, was created under Resolution No. 13,[20] formed from parts of Umm Salal and Al Khawr; at the same time, Al Ghuwariyah was merged with Al Khawr; Al Jumaliyah was merged with Ar Rayyan; and Jarayan al Batnah was split between Ar Rayyan and Al Wakrah.
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of QatarQatar was also an early member of OPEC and a founding member of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). It is a member of the Arab League.
Qatar has bilateral relationships with a variety of foreign powers. It has allowed American forces to use an air base to send supplies to Iraq and Afghanistan.[21] It has also signed a defense cooperation agreement with Saudi Arabia,[22] with whom it shares the largest single non-associated gas field in the world. It was the second nation, the first being France, to have publicly announced its recognition of the Libyan opposition's National Transitional Council as the legitimate government of Libya amidst the 2011 Libyan uprising.[23]
The history of Qatar’s alliances provides insight into the basis of their policy. Between 1760–1971, Qatar sought formal protection from the high transitory powers of the Ottomans, British, Al-Khalifa’s from Bahrain, the Persians, and the Wahhabis from Saudi Arabia.[24] It has undoubtedly been an impuissant nation between influential nations and always feared their sovereignty. It was quickly determined that creating permanent alliances is not in Qatar’s best interest and could not rest its security in the hands of another; the only thing that is permanent is Qatar’s interests. Qatar sought to secure growing threats of geographically being in a volatile region with nuclear threats within close proximity and mistrust by inviting the US to create a full-functioning military base . Sheikh Hamad’s coup in 1995 reinvigorated its foreign policy, allowing it to step out of Saudi Arabia’s shadow and unaligned its policies from them and surprised the region. Speculation of a Saudi Arabian sponsored coup attempt in the late 1990s to reinstate the ousted Emir’s father and border disputes led to obstreperous relations resulting in Riyadh withdrawing diplomatic representation in 2002 to 2007. Launch of Al-Jazeera certainly did not help; it bred mistrust within the region and questioned the motives behind it and Qatar’s road to modernity in relation to the various countries it affected.
Role in international community
Besides causing a stir in the media world, Qatar also made a name for itself in the international arena with its attempt to brand itself as a peaceful neutral world power. It has attempted to achieve that goal by acting as a mediator and promoting peace in the region and beyond.
- Mediation
As of 2011, Qatar has engaged in mediation efforts in Western Sahara, Yemen, Ethiopia-Eritrea conflict, Indonesia, Somalia, and famously in Darfur and Lebanon. In addition, Qatar has involved itself in deep negotiations between the Palestinian authorities, Hamas and Fatah. Qatar’s involvement as a mediator in all of these situations may be vindicated by its lack of ties to any super-national or regional powers, and by the strategy of neutrality it has followed in order to be seen as an unbiased entity in conflicts.
- International Organizations and Conferences
Qatar has continued to take on more roles in the international organizational realm. In 1997 Qatar hosted the Middle East and North African summit, where it invited Israeli representation. In 2001, Qatar took the initiative and held a WTO ministerial meeting to further trade negotiations, commonly known as the ‘Doha Round’. Most notably, Qatar held an elected seat for two years in the United Nations Security Council from 2005 to 2007, maximizing its exposure and solidifying its presence in the international community.
Qatar has hosted academic, religious, political and economic conferences. The 11th annual Doha Forum recently brought in key thinkers, professionals of various backgrounds, and political figures from all over the world to discuss democracy, media\technology, free trade, and water security issues. This year was the first year the forum featured the Middle East Economic Future conference.[25]
Human rights
Main article: Human rights in QatarQatar is a destination for men and women from South Asia and Southeast Asia who migrate willingly, but are subsequently trafficked into involuntary servitude as domestic workers and labourers, and, to a lesser extent, commercial sexual exploitation. The most common offence was forcing workers to accept worse contract terms than those under which they were recruited. Other offences include bonded labour, withholding of pay, restrictions on movement, arbitrary detention, and physical, mental, and sexual abuse.[15]
According to the Trafficking in Persons Report by the US State Department, men and women who are lured into Qatar by promises of high wages are often forced into underpaid labour. The report states that Qatari laws against forced labour are rarely enforced and that labour laws often result in the detention of victims in deportation centres, pending the completion of legal proceedings. The report places Qatar at tier 3, as one of the countries that neither satisfies the minimum standards nor demonstrates significant efforts to come into compliance.[26][27]
The government maintains that it is setting the benchmark when it comes to human rights[28] and treatment of labourers.
Barwa, a Qatari contracting agency, is constructing a residential area for labourers known as Barwa Al Baraha (also called "Worker's City"). The project was launched after a recent scandal in Dubai's labour camps. The project aims to provide a reasonable standard of living as defined by the new Human Rights Legislation.[29] The Barwa Al Baraha will cost around $1.1 billion and will be a completely integrated city in the industrial area in Doha. Along with 4.25 square meters of living space per person, the residential project will provide parks, recreational areas, malls, and shops for labourers. Phase one of the project was set to be completed by the end of 2008, and the project itself is set to be completed by the middle of 2010.[30]
Freedom of religion
The government uses Sunni law as the basis of its criminal and civil regulations. Some religious tolerance is granted. Foreign nationals are free to affiliate with their faiths other than Islam, i.e. Christianity, Hinduism, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Bahái, as long as they are religious in private and do not offend 'public order' or 'morality'.
In March 2008 a Roman Catholic church of “Our Lady of the Rosary” was consecrated in Doha. No missionaries were allowed in the community. The church will have no bells, crosses or other Christian symbols on it and its premises.
Alcohol and other dietary issues
Alcohol consumption is legal in Qatar, with many restrictions. Luxurious hotels and nightclubs are allowed to sell alcohol to its adult non-Muslim customers. Personal consumption or possession of alcohol outside of these premises is illegal, except in a private residence where the non-Muslim adult has obtained a permit through the Qatar Distribution Company. Having alcoholic beverages in public is illegal, unless transferring it to a private residence, hotel or nightclub with a permit. The law punishes drunk driving, offering alcoholic beverages to a minor or a Muslim, and public drinking. It is also illegal, in keeping with Islamic morals, to import pigs or pork products into Qatar and pork products are not sold in Qatar.
Eating and drinking during Ramadan
Eating or drinking in public during daylight hours in the month of Ramadan in Qatar is prohibited.
Capital punishment
Qatar retains the death penalty, mainly for threats against national security.
LGBT rights
Homosexuality and cross-dressing are viewed negatively: social attitudes and public policy disapprove them. Anal sex between adults in Qatar is illegal, and may lead to a sentence of up to five years in prison. Sexual orientation and gender identity are not covered in any civil rights laws and there is no recognition of same-sex marriages, civil unions or domestic partnerships.
Incidents
A Wikileaks report has revealed that letters signed by the deputy prime minister, Abdullah al-Attiyah, and sent to Royal Dutch Shell, ExxonMobil and a number of other major oil companies showed that the Qatar government demanded donations of up to $1.7 billion towards the cost of building a medical centre in 2007.[31]
Economy
Main article: Economy of QatarSee also: List of tallest buildings in Doha, Qatar Qatar's capital, Doha
Qatar's capital, Doha
Qatar has experienced rapid economic growth over the last several years due to high oil prices, and in 2008 posted its eighth consecutive budget surplus. Economic policy is focused on developing Qatar's non-associated natural gas reserves and increasing private and foreign investment in non-energy sectors, but oil and gas still account for more than 50% of GDP; roughly 85% of export earnings, and 70% of government revenues.
Oil and gas have made Qatar one of the highest per-capita income countries, and one of the world's fastest growing. Proved oil reserves of 15 billion barrels should enable continued output at current levels for 37 years. Qatar's proved reserves of natural gas are nearly 26 trillion cubic metres, about 14% of the world total and the third largest in the world.
Before the discovery of oil, the economy of the Qatari region focused on fishing and pearl hunting. After the introduction of the Japanese cultured pearl onto the world market in the 1920s and 1930s, Qatar's pearling industry crashed. However, the discovery of oil, beginning in the 1940s, completely transformed the state's economy. Now, the country has a high standard of living, with many social services offered to its citizens and all the amenities of any modern state. It relies heavily on foreign labour to grow its economy, to the extent that 94% of its labour is carried out by foreigners. Labour laws offer little protection for the foreign labourers mostly coming from developing countries.
Qatar’s national income primarily derives from oil and natural gas exports. The country has oil reserves of 15 billion barrels, while gas reserves in the giant North Field (which straddles the border with Saudi Arabia and is almost as large as the peninsula itself) are estimated to be between 80 trillion cubic feet (2.3×1012 m3) to 800 trillion cubic feet (23×1012 m3) (1 trillion cubic feet of gas is equivalent to about 180 million barrels (29×106 m3) of oil). Qataris’ wealth and standard of living compare well with those of Western European states; Qatar has the highest GDP per capita in the Arab World, according to the International Monetary Fund (2010)[32] and the CIA World Factbook.[33] With no income tax, Qatar (along with Bahrain) is one of the countries with the lowest tax rates in the world.
 West Bay in Doha
West Bay in Doha
While oil and gas will probably remain the backbone of Qatar’s economy for some time to come, the country seeks to stimulate the private sector and develop a “knowledge economy”. In 2004, it established the Qatar Science & Technology Park to attract and serve technology-based companies and entrepreneurs, from overseas and within Qatar. Qatar also established Education City, which consists of international colleges. For the 15th Asian Games in Doha, it established Doha Sports City, consisting of Khalifa stadium, the Aspire Sports Academy, aquatic centres, exhibition centres and many other sports related buildings and centres. Following the success of the Asian Games, Doha kicked off an official bid to host the 2016 Summer Olympics in October 2007.[34] Its bid was finally eliminated from consideration in June 2008. Qatar also plans to build an "entertainment city" in the future.
The Qatari government hopes that large-scale investment in all social and economic sectors will lead to the development of a strong financial market.
The Qatar Financial Centre (QFC) provides financial institutions with world-class services in investment, margin and no-interest loans, and capital support. These platforms are situated in an economy founded on the development of its hydrocarbons resources, specifically its exportation of petroleum. It has been created with a long term perspective to support the development of Qatar and the wider region, develop local and regional markets, and strengthen the links between the energy based economies and global financial markets.
Apart from Qatar itself, which needs to raise capital to finance projects of more than $130 billion, the QFC also provides a conduit for financial institutions to access nearly $1.0 trillion of investments which stretch across the GCC (Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf) as a whole over the next decade. Commercial ties between the United States and Qatar have been expanding at a rapid pace over the last five years, with trade volumes growing by more than 340%, from $738 million in 2003 to $3.2 billion in 2009. Over the same period, U.S. exports increased 580 percent to $2.7 billion, making the United States the largest import partner for Qatar. US companies look to play key role in the $60 billion dollars that Qatar will invest in roads, infrastructure development, housing and real estate, health/medical and sanitation projects in the next decade.
The new town of Lusail, the largest project ever in Qatar, is under construction.
Transportation
Main article: Transport in QatarThe primary means of transportation in Qatar is by road, due to the very cheap price of petroleum. The country as a result has an advanced road system undergoing vast upgrades in response to the country's rapidly rising population, with several highways undergoing upgrades and new expressways within Doha under construction. A large bus network connects Doha with other towns in the country, and is the primary means of public transportation in the city.
The Salwa International Highway currently connects Doha to the border with Saudi Arabia, and a causeway with both road and rail links to Bahrain at Zubarah is due to begin construction shortly. The causeway will become the largest in the world, and will be the second to connect Bahrain to the Arabian Peninsula.
Currently, no rail networks exist in the country. In November 2009, however, the government signed a $26 billion contract with the German company Deutsche Bahn to construct a railway system over the next 20 years. The network will connect the country itself, and will include an international link with neighbouring states as part of a larger rail network being constructed across the countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council. A railway link is also under construction between Qatar and Bahrain as part of the Qatar Bahrain Causeway.
Qatar's main airport is the Doha International Airport, which served almost 15,000,000 passengers in 2007. In comparison, the airport served only 2,000,000 passengers in 1998. As a result of the much larger volumes of passengers flying into and through the country today, the New Doha International Airport is currently under construction, and will replace the existing airport in 2012.
Climate
Main article: Climate of QatarClimate data for Qatar Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 22
(72)23
(73)27
(81)32
(90)38
(100)41
(106)41
(106)41
(106)38
(100)35
(95)29
(84)24
(75)32.6
(90.6)Average low °C (°F) 13
(55)13
(55)17
(63)21
(70)25
(77)27
(81)29
(84)29
(84)26
(79)23
(73)19
(66)15
(59)21.4
(70.6)Precipitation mm (inches) 12.7
(0.5)17.8
(0.701)15.2
(0.598)7.6
(0.299)2.5
(0.098)0
(0)0
(0)0
(0)0
(0)0
(0)2.5
(0.098)12.7
(0.5)71
(2.8)Source: weather.com[35] Environmental issues
In 2005, Qatar had the highest per-capita carbon dioxide emissions, at 55.5 metric tons per person.[36] This is almost double the next highest per-capita emitting country, which is Kuwait at 30.7 metric tons (2005) and they are three times those of the United States. By 2007, Qatar’s emission rate increased to 69 tons per person per year.[37] Qatar had the highest per-capita carbon dioxide emissions for the past 18 years. These emissions are largely due to high rates of energy use in Qatar. Major uses of energy in Qatar include air conditioning, natural gas processing, water desalination and electricity production. Between 1995 and 2011 the electricity generating capacity of Qatar will have increased to six times the previous level. The fact that Qataris do not have to pay for either their water or electricity supplies is thought to contribute to their high rate of energy use. Despite being a desert state they are also one of the highest consumers of water per capita per day, using around 400 litres.[38]
Renee Richer, visiting professor of Biology at Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar[39] lectures:
Social and economic changes are taking place at an alarming rate, putting at risk the natural and cultural resources of Qatar. However, such loss of natural and cultural heritage need not be the case and great economic benefits can be gained from ecologically based development. Qatar is in a unique position, given the financial resources and forward thinking leadership, to move ahead and be amongst the first countries ready to take advantage of the next economic revolution: the green revolution.[40]
Population
Main article: Demographics of QatarYear Population 1908 est. 22,000[41] 1939 est. 28,000[41] late 1960s 70,000[42] 1986 369,079 1997 522,023[43] 2000 744,483 2001 769,152 2002 793,341 2003 817,052 2004 840,290 2005 863,051 2006 885,359 2007 1,207,229 2008 1,524,789[15] 2009 1,309,000[44] 2010 1,696,563 2011 1,692,262 Out of the total population of approximately 1.5 million (May 2008 est.), the make up of ethnic groups is as follows: Qatari (Arab) 20%; other Arab 20%; Indian 20%; Filipino 10%; Nepali 13%; Pakistani 7%; Sri Lankan 5%; other 5%[8]. Arabic, English, Malayalam, Hindi, Urdu are the most widely spoken languages[citation needed].
Culture
See also: Music of QatarQatari culture (music, art, dress, and cuisine) is similar to that of other Arab countries of the Persian Gulf; see Culture of the Arab States of the Persian Gulf. Arab tribes from Saudi Arabia migrated to Qatar and other places in the gulf; therefore, the culture in the Persian Gulf region varies little from country to country.
Qatar explicitly uses Sharia law as the basis of its government, and the vast majority of its citizens follow Hanbali Madhhab. Hanbali (Arabic: حنبلى ) is one of the four schools (Madhhabs) of Fiqh or religious law within Sunni Islam (The other three are Hanafi, Maliki and Shafii). Sunni Muslims believe that all four schools have "correct guidance", and the differences between them lie not in the fundamentals of faith, but in finer judgments and jurisprudence, which are a result of the independent reasoning of the imams and the scholars who followed them. Because their individual methodologies of interpretation and extraction from the primary sources (usul) were different, they came to different judgments on particular matters. Shi'as comprise around 10% of the Muslim population in Qatar.[45]
Alcohol is legal with a permit but it is not permitted to drink it in public.[46]
Religion
Main article: Religion in QatarIslam is the predominant religion. According to the 2004 census, 77.5% of the population are Muslim, 8.5% are Christian and 14% are "Other".[15] About 5% of the Muslims living in Qatar are Shia.[45]
The majority of non-citizens are from South and Southeast Asian and Arab countries working on temporary employment contracts, accompanied by family members in some cases.[citation needed] Non-citizens can be Sunni or Shi'a Muslims, Protestant or Catholic Christians, Hindus, Sikhs, Buddhists, or Bahá'ís.
Religion is not a criterion for citizenship, according to the Nationality Law.
See also: Christianity in QatarThe Christian population consists nearly completely of foreigners. Active churches are Mar Thoma Church from Southern India, Arab Evangelicals from Syria and Palestine, Anglicans,[47] about 50,000 Catholics and Copts from Egypt.[48] No foreign missionary groups operate openly in the country,[49] but the government allows churches to conduct Mass. Since 2008 Christians have been allowed to build churches on ground donated by the government.[50]
Sport
Football is the most popular sport in the country closely followed by cricket. The Qatar Under 20 national football team finished second in the 1981 FIFA World Youth Championship after a 4–0 defeat to Germany in the final.
The Asian Football Confederation's 2011 AFC Asian Cup finals was held in Qatar in January 2011. It was the fifteenth time the tournament has been held, and the second time it has been hosted by Qatar, the other being the 1988 AFC Asian Cup.
Doha, Qatar is also home to Qatar Racing Club a Drag Racing facility. Sheik Khalid bin Hamad Al Thani is very involved in the sport and owner of Al-Anabi Racing.
Khalifa International Tennis Complex in Doha, Qatar hosted the WTA Tour Championships in women's tennis between 2008 and 2010.
On 2 December 2010, Qatar won their bid to host the 2022 FIFA World Cup.[51] Doha is currently bidding to host the 2020 Summer Olympics.[52]
Nasser Al-Attiyah of Qatar won the 2011 Dakar Rally and the Production World Rally Championship in 2006. In addition, he has also won gold medals at the 2002 Asian Games and 2010 Asian Games as part of the Qatari skeet shooting team, as well as a bronze medal in the individual skeet event at the 2010 Games in Guangzhou.
Education
Main article: Education in Qatar Cornell University's Weill Medical College in Qatar
Cornell University's Weill Medical College in Qatar
In recent years Qatar has placed great emphasis on education. Citizens are required to attend government-provided education from kindergarten through high school.[53] Qatar University was founded in 1973. More recently, with the support of the Qatar Foundation, some leading US universities have opened branch campuses in Education City, Qatar although the education courses offered are mostly limited to Bachelors Degree. The Colleges also show very limited faculty compared to parent Universities in United States with low research output. These include
- Carnegie Mellon University
- Georgetown University School of Foreign Service
- Texas A&M University
- Houston Community College System
- Virginia Commonwealth University School of the Arts
- Cornell University’s Weill Cornell Medical College
- Northwestern University
- University College London
In 2008, Qatar established the Qatar Science & Technology Park at Education City to link those universities with industry. Education City is also home to a fully accredited International Baccalaureate school, Qatar Academy. Two Canadian institutions, the College of the North Atlantic and the University of Calgary, also operate campuses in Doha. Other for-profit universities have also established campuses in the city.[54]
In 2009 Qatar Foundation launched a non-profit radio station,QF Radio 93.7 FM [2], which offers a streaming online service providing regular programs about Education, Science, Community Development and the Arts in Qatar, to a global online audience. It also broadcasts to Doha, Qatar on 93.7 FM. The program is produced as 70% in Arabic and 30% in English language.
In 2009, the Qatar Foundation launched the World Innovation Summit for Education – WISE – a global forum that brought together education stakeholders, opinion leaders and decision makers from all over the world to discuss educational issues. The first edition was held in Doha from 16 to 18 November 2009, the second from 7 to 9 December 2010. The third edition will be held from 1 to 3 November 2011.
Moreover, in 2007 the American Brookings Institution announced that it was opening the Brookings Doha Center to undertake research and programming on the socio-economic and geo-political issues facing the region.
In November 2002, the Emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani created the Supreme Education Council.[55] The Council directs and controls education for all ages from the pre-school level through the university level, including the “Education for a New Era”[56] reform initiative.
The Emir’s second wife, Her Highness Sheikha Mozah Bint Nasser Al-Missned, has been instrumental in new education initiatives in Qatar. She chairs the Qatar Foundation, sits on the board of Qatar’s Supreme Education Council, and is a major driving force behind the importation of Western expertise into the education system, particularly at the college level. In addition, The Qatar Foundation has supported the implementation of Arabic language programs in American public schools through the establishment of Qatar Foundation International, a U.S.-based non-profit dedicated to connecting the culture of American and Qatari students.
There are currently a total of 567 schools in operation within Qatar, both in the public and the private sector. A large number of new schools are also under construction, particularly public schools, in order to meet increased demand which arose as a result of the large increase in population that the country has seen of late. The number of universities operating in the country are 9, serving 12,480 students.
Health care
Hamad Medical Corporation (HMC)—affiliated with Cornell University—is the premier non-profit health care provider in Doha, Qatar. Established by the Emiri decree in 1979, HMC manages four highly specialised hospitals and a health care centre: Hamad General Hospital, Rumailah Hospital, Women’s Hospital, Psychiatric Hospital and the Primary Health Care Centres. These hospitals are quite sophisticated by the standards of the region, with most hosting advanced fMRI and other scanning machines. Other private hospitals and polyclinics consist of Sidra Hospital, Al-Ahli Hospital, Doha Clinic, Al-Emadi Hospital, The American Hospital and Tadawi Medical. Qatar has among the highest rates in the world for obesity, diabetes and genetic disorders.[57] On the Qatar border, Saudi Arabia has set up the Salwa General Hospital, which is also serving all Qatari patients in good will of GCC.[citation needed]
Communications
Qatar has a modern telecommunication system centered in Doha. Tropospheric scatter to Bahrain; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia and UAE; submarine cable to Bahrain and UAE; satellite earth stations – two Intelsat (one Atlantic Ocean and one Indian Ocean) and one Arabsat. Callers can call Qatar using submarine cable, satellite, or VoIP (Skype/ Internet calling). However, Qtel has interfered with VoIP systems in the past, and Skype's website has been blocked before. Following complaints from individuals, the website has been unblocked, and Paltalk has previously been blocked.
Qtel’s ISP branch, Internet Qatar, uses SmartFilter to block websites they deem inappropriate to Qatari interests and morality.
In Qatar, ictQATAR (Supreme Council of Information and Communication Technology) is the government agency regulating telecommunication.
Vodafone Qatar, in partnership with the Qatar Foundation, received the second public mobile networks and services license in Qatar on 28 June 2008 and switched on their mobile network on 1 March 2009. They launched 7 July 2009, opening their online store first followed by retail and third party distribution locations throughout Doha. However, this was discontinued in 2010.
Al Jazeera (Arabic: الجزيرة al-ğazīrä [aldʒaˈziːra], “The Island”) is a television network headquartered in Doha, Qatar. Al Jazeera initially launched as an Arabic news and current affairs satellite TV channel of the same name, but has since expanded into a network of several specialty TV channels.
Print media is going through expansion, with over three English dailies and Arabic titles. Qatar Today is the only monthly business magazine in the country. It is published by Oryx Advertising, which is the largest magazine publisher in Qatar. The group also publishes several titles such as Qatar Al Youm, the only monthly business magazine in Qatar in Arabic language, Woman Today, the only magazine for working women, and GLAM,[58] the only fashion magazine. In December 2009 Oryx launched T Qatar: The New York Times Style Magazine,[59] which marks the entry of an international magazine into Qatar.
Doha Stadium Plus is the only dedicated Sports magazine published out of the country. It covers a large variety of sports. It is published by ASPIRE Printing, Publishing and Distribution company. It is published every Wednesday and has been in existence since February, 2006. It brought out a special supplement for the 2010 FIFA World Cup in South Africa as well as the 2011 AFC Asian Cup in Doha, Qatar, in addition to the weekly editions. They relaunched their website on 15 June 2011.
See also
- Outline of Qatar
- Index of Qatar-related articles
- Qatar National Day
- North Dome Gas Field
- Natural gas in Qatar
- Communications in Qatar
- Foreign relations of Qatar
- LGBT rights in Qatar (Gay rights)
- List of cities in Qatar
- List of Qatar-related topics
- Military of Qatar
- Public holidays in Qatar
- The Scout and Guide Association of Qatar
- Al Nuaim
- General Secretariat for Development Planning
- Permanent Population Committee
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "Qatar".
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "Qatar".- ^ "Populations". Qsa.gov.qa. http://www.qsa.gov.qa/QatarCensus/Populations.aspx. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
- ^ a b c d International Monetary Fund, World Economic Outlook Database, September 2011: Report for Selected Countries and Subjects. Data for the year 2011.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2010". United Nations. 2010. http://hdr.undp.org/en/media/HDR_2010_EN_Table1.pdf. Retrieved 5 November 2010.
- ^ "CMU Pronouncing Dictionary". Speech.cs.cmu.edu. http://www.speech.cs.cmu.edu/cgi-bin/cmudict?stress=-s&in=QATAR. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Koerner, Brendan I (3 Dec. 2002). "How Do You Pronounce "Qatar"?". Slate. http://www.slate.com/id/2074824/.[dead link] "The most accurate English estimate is something halfway between 'cutter' and 'gutter.' It's not 'KUH-tar,' the pronunciation that has become the standard among overseas TV and radio newscasters."
- ^ a b Johnstone, T.M. "Ķaṭar." Encyclopaedia of Islam. Edited by: P. Bearman , Th. Bianquis , C.E. Bosworth , E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2008. Brill Online. 4 April 2009 www.brillonline.nl
- ^ "Qatar 1995 Coup". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/publisher,IRBC,,QAT,3ae6ab8824,0.html. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ a b "US State Department Qatar Page". US State Department. http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/5437.htm.
- ^ http://www.buyusa.gov/qatar/en/ccg2010.pdf
- ^ "History of Qatar". Diwan.gov.qa. http://www.diwan.gov.qa/english/qatar/qatar_history.htm. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "Qatar (01/10)". State.gov. http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/5437.htm. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Coman, Julian (21 March 2005). "Egyptian Suicide Bomber Blamed for Attack in Qatar". The Independent.
- ^ "The Advent of Terrorism in Qatar". Forbes. 25 March 2005. http://www.forbes.com/2005/03/25/cz_0325oxan_qatarattack.html.
- ^ a b SCOTT SHANE and ANDREW W. LEHREN (28 November 2010). "Leaked Cables Offer Raw Look at U.S. Diplomacy". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/11/29/world/29cables.html?_r=1. Retrieved 26 December 2010. "... the tiny Persian Gulf state of Qatar, a generous host to the American military for years, was the “worst in the region” in counterterrorism efforts, according to a State Department cable last December. Qatar’s security service was “hesitant to act against known terrorists out of concern for appearing to be aligned with the U.S. and provoking reprisals,” the cable said."
- ^ a b c d e f "Middle East :: Qatar". CIA World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/qa.html. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ^ "Purchasing Alcohol in Qatar". Qatar Visitor. 2 June 2007. http://www.qatarvisitor.com/index.php?cID=414&pID=1053. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (4 June 2008). "Refworld | Trafficking in Persons Report 2008 – Qatar". UNHCR. http://www.unhcr.org/refworld/country,,,,QAT,4562d8cf2,484f9a3732,0.html. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Alternative spelling, travelsradiate.com
- ^ Municipalities of Qatar, Statoids.com
- ^ "AlDaayen Municipality". Baladiya.gov.qa. http://www.baladiya.gov.qa/portal/page?_pageid=135,231041&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL&subTabIndex=5500&branchIndex=0&tabIndex=8000. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Zacharia, Janine (4 March 2008). "For Qatar, relations with West are a balancing act". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/04/world/africa/04iht-letter5.1.10686376.html. Retrieved 30 January 2011.
- ^ "Qatar and Saudi Arabia sign defense agreement". Tehrantimes.com. 25 February 2010. http://www.tehrantimes.com/index_View.asp?code=214868. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
- ^ "Qatar recognises Libyan rebels after oil deal". Al Jazeera English. 28 March 2011. http://english.aljazeera.net/news/middleeast/2011/03/201132814450241767.html. Retrieved 29 March 2011.
- ^ Rahman, Habibur (2005). The Emergence of Qatar. London/New York: Regan Paul.
- ^ "Doha Forum". http://dohaforum.qatar-conferences.org/2011/EN.
- ^ "Country Narratives – Countries Q through Z". Trafficking in Persons Report. Office to Monitor and Combat Trafficking in Persons, United States Department of State. 12 June 2007. http://www.state.gov/g/tip/rls/tiprpt/2007/82807.htm. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "India escapes U.S. list of worst human traffickers". cnn.com (Washington: Cable News Network). 12 June 2007. http://www.cnn.com/2007/US/06/12/human.trafficking/index.html. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "Qatar: National Human Rights Committee report". Qatar National Human Rights Committee. 3 May 2006. http://www.zawya.com/story.cfm/sidZAWYA20060503034405. Retrieved 25 March 2008.. According to zawya.com, the web link “is the unofficial translation by The Peninsula team of the 57-page Arabic text of the report released by the National Human Rights Committee yesterday.”
- ^ "Qatar: National Human Rights Committee Support Expats". The Peninsula via iLoveQatar.net. 18 June 2008. http://www.iloveqatar.net/forum/read.php?28,2540,2540. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
- ^ Bowman, D (2 March 2008). "Qatar to build $1.1bn labourer city". ArabianBusiness.com (Dubai: ITP Digital Publishing). http://www.arabianbusiness.com/512568-qatar-to-build-11bn-labourer-city. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "Wikileaks: Qatar asked Shell and ExxonMobil for donations". The Telegraph. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/newsbysector/energy/oilandgas/8399431/Wikileaks-Qatar-asked-Shell-and-ExxonMobil-for-donations.html. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ World Economic Outlook Database-April 2011, International Monetary Fund. Accessed on 11 April 2011.
- ^ GDP – per capita (PPP), The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency. Accessed on 9 July 2011.
- ^ "Doha 2016 bid brings wind of change". aljazeera.net (Doha: Al Jazeera). 26 October 2007. http://english.aljazeera.net/sport/2007/10/200852610557836483.html. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "Monthly Averages for Doha, Qatar". weather.com. The Weather Channel. http://www.weather.com/outlook/travel/businesstraveler/wxclimatology/monthly/graph/QAXX0003?from=36hr_bottomnav_business. Retrieved 26 October 2009.
- ^ http://cait.wri.org/cait.php?page=yearly
- ^ World Resources Institute (2007). www.wri.org. Retrieved 3 November 2009.
- ^ Qatar to use biofuels? What about the country's energy consumption? Fred Pearce guardian.co.uk Thursday 14 January 2010
- ^ "Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar". http://qatar-weill.cornell.edu/.
- ^ Richer, Renee. "CRIS Lecture Series". CRIS. http://cirs.georgetown.edu/105455.html.
- ^ a b John Lockerbie (6 June 1998). "The population of Qatar". Catnaps.org. http://www.catnaps.org/islamic/population.html. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "Qatar – Country overview, Location and size, Population, Industry, Mining, Manufacturing, Services, Tourism". Nationsencyclopedia.com. http://www.nationsencyclopedia.com/economies/Asia-and-the-Pacific/Qatar.html. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "CGIS Home Page – Main Section". Gisqatar.org.qa. 31 December 1998. http://www.gisqatar.org.qa/alkhabar/Spring99/census.html. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division (2009) (PDF). World Population Prospects, Table A.1. 2008 revision. United Nations.
- ^ a b "Mapping the Global Muslim Population: A Report on the Size and Distribution of the World's Muslim Population". Pew Research Center. 7 October 2009. http://pewforum.org/Muslim/Mapping-the-Global-Muslim-Population%286%29.aspx. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ^ "Buying Alcohol in Qatar". Qatarvisitor.com. 2 June 2007. http://www.qatarvisitor.com/index.php?cID=414&pID=1053. Retrieved 1 May 2011.
- ^ http://www.epiphany-qatar.org/buildingproject.html
- ^ World Christian Encyclopedia, Second edition, Volume 1, Seite 617
- ^ "CIA The World Fact Book". State.gov. 29 June 2006. http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2007/90219.htm. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ [1] Fox News, Friday, 14 March 2008
- ^ Paul Radford (2 Dec 2010). "Russia, Qatar win 2018 and 2022 World Cups". Reuters. http://af.reuters.com/article/sportsNews/idAFJOE6B10FA20101202. Retrieved 2 Dec 2010.
- ^ Six Applicant Cities for the 2020 Olympic Games
- ^ "Qatar constitution". http://english.mofa.gov.qa/details.cfm?id=80.
- ^ "Stenden University Qatar". http://www.stenden.com/en/stenden/Locations/qatar/Pages/default.aspx. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
- ^ "About the SEC". Supreme Education Council. http://www.english.education.gov.qa/section/sec. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ "Education for a New Era". Supreme Education Council. http://www.english.education.gov.qa. Retrieved 25 March 2008.
- ^ Slackman, Michael (26 April 2010). "Privilege Pulls Qatar Toward Unhealthy Choices". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/04/27/world/middleeast/27qatar.html?ref=global-home.
- ^ "Oryx Publishing launches GLAM". Ameinfo.com. 21 November 2007. http://www.ameinfo.com/139704.html. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
- ^ "T Qatar launched". Ameinfo.com. http://www.ameinfo.com/220740.html. Retrieved 2 October 2010.
External links
- Amiri Diwan official government website
- Qatar entry at The World Factbook
- Qatar web resources provided by GovPubs at the University of Colorado–Boulder Libraries
- Qatar at the Open Directory Project
- Qatar travel guide from Wikitravel
- Wikimedia Atlas of Qatar
 Qatari topics
Qatari topicsPolitics Emir · Prime Minister · Parliament · Military · Coat of arms · Human rights · Foreign relations · Crime · House of ThaniGeography Economy Currency · Stock exchange · Agriculture · Natural gas · Energy · Communications · Transport · Airports · Al JazeeraSociety History · Culture · Demographics · Education · Music · Sports · Cuisine · Religion · Flag · Anthem · Public holidays · Rankings · Regional cultureOutline · Index International membership Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) Members Afghanistan · Albania · Algeria · Azerbaijan · Bahrain · Bangladesh · Benin · Burkina Faso · Brunei · Cameroon · Chad · Comoros · Côte d'Ivoire · Djibouti · Egypt · Gabon · Gambia · Guinea · Guinea-Bissau · Guyana · Indonesia · Iran · Iraq · Jordan · Kuwait · Kazakhstan · Kyrgyzstan · Lebanon · Libya · Maldives · Malaysia · Mali · Mauritania · Morocco · Mozambique · Niger · Nigeria · Oman · Pakistan · Palestine · Qatar · Saudi Arabia · Senegal · Sierra Leone · Somalia · Sudan · Suriname · Syria · Tajikistan · Turkey · Tunisia · Togo · Turkmenistan · Uganda · Uzbekistan · United Arab Emirates · YemenObservers Countries and territoriesBosnia and Herzegovina · Central African Republic · Russia · Thailand · Northern Cyprus (as Turkish Cypriot State)Muslim communitiesInternational organizationsMembers of the Arab League Members 
Observers Diplomacy Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) 
Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf Member states 
Monarchies List of current sovereign monarchs · List of current constituent monarchs By continent By country Antigua and Barbuda · Australia · Andorra · The Bahamas · Bahrain · Barbados · Belize · Belgium · Bhutan · Brunei · Cambodia · Canada · Denmark · Grenada · Jamaica · Japan · Jordan · Kuwait · Liechtenstein · Lesotho · Luxembourg · Malaysia · Monaco · Morocco · Netherlands · New Zealand · Norway · Oman · Papua New Guinea · Qatar · Spain · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Saudi Arabia · Solomon Islands · Swaziland · Sweden · Thailand · Tonga · Tuvalu · United Arab Emirates · United Kingdom · Vatican CityBy type Italics indicate Commonwealth realms, which each share the same person as head of state. Semitic-speaking nations FIFA World Cup · Host nations 1954:
 Switzerland
Switzerland
1958: Sweden
Sweden
1962: Chile
Chile
1966: England
England
1970: Mexico
Mexico
1974: West GermanyCategories:
West GermanyCategories:- Qatar
- Arabian Peninsula
- Western Asian countries
- Arabic-speaking countries and territories
- Constitutional monarchies
- Emirates
- Member states of OPEC
- Member states of the Arab League
- Member states of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Middle Eastern countries
- Peninsulas of Asia
- Persian Gulf countries
- States and territories established in 1971
- Western Asia
- Member states of the United Nations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.