- CDH2
-
Cadherin-2 (CDH2), also known as neural cadherin (NCAD) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH2 gene.[1][2] CDH2 has also been designated as CD325 (cluster of differentiation 325).
Contents
Function
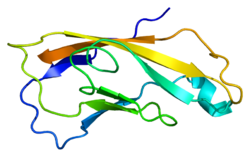
Cadherin 2 a classical cadherin from the cadherin superfamily. Cadherin 2 is a calcium dependent cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein comprising five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail. The protein functions during gastrulation and is required for establishment of left-right asymmetry. At certain central nervous system synapses, presynaptic to postsynaptic adhesion is mediated at least in part by this gene product.[3]
Role in cancer metastasis
N-Cadherin is commonly found in cancer cells and provides a mechanism for transendothelial migration. when a cancer cell adheres to the endothelial cells of a blood vessel it up-regulates the src kinase pathway, which phosphorylates beta-catenins attached to both N-cadherin (this protein) and E-cadherins. This causes the intercellular connection between two adjacent endothelial cells to fail and allows the cancer cell to slip through.[4]
Interactions
CDH2 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin,[5][6] Plakoglobin,[5][7] Catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 1,[5][6] CTNND1,[5][6] LRRC7[8], CDH11[5], and type IIb RPTPs including PTPRM[9][10].
References
- ^ Walsh FS, Barton CH, Putt W, Moore SE, Kelsell D, Spurr N, Goodfellow PN (September 1990). "N-cadherin gene maps to human chromosome 18 and is not linked to the E-cadherin gene". J. Neurochem. 55 (3): 805–12. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04563.x. PMID 2384753.
- ^ Reid RA, Hemperly JJ (October 1990). "Human N-cadherin: nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence". Nucleic Acids Res. 18 (19): 5896–5896. doi:10.1093/nar/18.19.5896. PMC 332345. PMID 2216790. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=332345.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CDH2 cadherin 2, type 1, N-cadherin (neuronal)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1000.
- ^ Ramis-Conde I, Chaplain MA, Anderson AR, Drasdo D (2009). "Multi-scale modelling of cancer cell intravasation: the role of cadherins in metastasis". Phys Biol 6 (1): 016008. doi:10.1088/1478-3975/6/1/016008. PMID 19321920.
- ^ a b c d e Straub, Beate K; Boda Judit, Kuhn Caecilia, Schnoelzer Martina, Korf Ulrike, Kempf Tore, Spring Herbert, Hatzfeld Mechthild, Franke Werner W (Dec. 2003). "A novel cell-cell junction system: the cortex adhaerens mosaic of lens fiber cells". J. Cell. Sci. (England) 116 (Pt 24): 4985–95. doi:10.1242/jcs.00815. ISSN 0021-9533. PMID 14625392.
- ^ a b c Wahl, James K; Kim Young J, Cullen Janet M, Johnson Keith R, Wheelock Margaret J (May. 2003). "N-cadherin-catenin complexes form prior to cleavage of the proregion and transport to the plasma membrane". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (19): 17269–76. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211452200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12604612.
- ^ Sacco, P A; McGranahan T M, Wheelock M J, Johnson K R (Aug. 1995). "Identification of plakoglobin domains required for association with N-cadherin and alpha-catenin". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 270 (34): 20201–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.34.20201. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7650039.
- ^ Izawa, Ichiro; Nishizawa Miwako, Ohtakara Kazuhiro, Inagaki Masaki (Feb. 2002). "Densin-180 interacts with delta-catenin/neural plakophilin-related armadillo repeat protein at synapses". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (7): 5345–50. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110052200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11729199.
- ^ Brady-Kalnay SM, Rimm DL, Tonks NK (1995). "Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPmu associates with cadherins and catenins in vivo.". J Cell Biol 130 (4): 977-86. PMC PMC2199947. PMID 7642713. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=PMC2199947.
- ^ Brady-Kalnay SM, Mourton T, Nixon JP, Pietz GE, Kinch M, Chen H et al. (1998). "Dynamic interaction of PTPmu with multiple cadherins in vivo.". J Cell Biol 141 (1): 287-96. PMC PMC2132733. PMID 9531566. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=PMC2132733.
Further reading
- Doherty P, Smith P, Walsh FS (1997). "Shared cell adhesion molecule (CAM) homology domains point to CAMs signalling via FGF receptors". Perspectives on developmental neurobiology 4 (2–3): 157–68. PMID 9168198.
- Makrigiannakis A, Coukos G, Blaschuk O, Coutifaris C (2000). "Follicular atresia and luteolysis. Evidence of a role for N-cadherin". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 900: 46–55. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06215.x. PMID 10818391.
- Hazan RB et al. (2004). "Cadherin switch in tumor progression". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1014: 155–63. doi:10.1196/annals.1294.016. PMID 15153430.
- Cavallaro U (2005). "N-cadherin as an invasion promoter: a novel target for antitumor therapy?". Current opinion in investigational drugs (London, England : 2000) 5 (12): 1274–8. PMID 15648948.
- Salomon D et al. (1992). "Extrajunctional distribution of N-cadherin in cultured human endothelial cells". J. Cell. Sci. 102 ( Pt 1): 7–17. PMID 1500442.
- Knudsen KA, Wheelock MJ (1992). "Plakoglobin, or an 83-kD homologue distinct from beta-catenin, interacts with E-cadherin and N-cadherin". J. Cell Biol. 118 (3): 671–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.118.3.671. PMC 2289540. PMID 1639850. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2289540.
- Reid RA, Hemperly JJ (1990). "Human N-cadherin: nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence". Nucleic Acids Res. 18 (19): 5896–5896. doi:10.1093/nar/18.19.5896. PMC 332345. PMID 2216790. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=332345.
- Walsh FS et al. (1990). "N-cadherin gene maps to human chromosome 18 and is not linked to the E-cadherin gene". J. Neurochem. 55 (3): 805–12. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04563.x. PMID 2384753.
- Selig S et al. (1995). "Expressed cadherin pseudogenes are localized to the critical region of the spinal muscular atrophy gene". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (9): 3702–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.9.3702. PMC 42029. PMID 7731968. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=42029.
- Wallis J, Fox MF, Walsh FS (1994). "Structure of the human N-cadherin gene: YAC analysis and fine chromosomal mapping to 18q11.2". Genomics 22 (1): 172–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1358. PMID 7959764.
- Andersson AM, Edvardsen K, Skakkebaek NE (1995). "Expression and localization of N- and E-cadherin in the human testis and epididymis". Int. J. Androl. 17 (4): 174–80. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2605.1994.tb01239.x. PMID 7995652.
- Matsuyoshi N, Imamura S (1997). "Multiple cadherins are expressed in human fibroblasts". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235 (2): 355–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6707. PMID 9199196.
- Navarro P, Ruco L, Dejana E (1998). "Differential localization of VE- and N-cadherins in human endothelial cells: VE-cadherin competes with N-cadherin for junctional localization". J. Cell Biol. 140 (6): 1475–84. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.6.1475. PMC 2132661. PMID 9508779. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2132661.
- Gaidar YA, Lepekhin EA, Sheichetova GA, Witt M (1998). "Distribution of N-cadherin and NCAM in neurons and endocrine cells of the human embryonic and fetal gastroenteropancreatic system". Acta Histochem. 100 (1): 83–97. PMID 9542583.
- Kremmidiotis G et al. (1998). "Localization of human cadherin genes to chromosome regions exhibiting cancer-related loss of heterozygosity". Genomics 49 (3): 467–71. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5281. PMID 9615235.
- Lu Q et al. (1999). "delta-catenin, an adhesive junction-associated protein that promotes cell scattering". J. Cell Biol. 144 (3): 519–32. doi:10.1083/jcb.144.3.519. PMC 2132907. PMID 9971746. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2132907.
- Shan WS et al. (2000). "Functional cis-heterodimers of N- and R-cadherins". J. Cell Biol. 148 (3): 579–90. doi:10.1083/jcb.148.3.579. PMC 2174798. PMID 10662782. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2174798.
- Husi H et al. (2000). "Proteomic analysis of NMDA receptor-adhesion protein signaling complexes". Nat. Neurosci. 3 (7): 661–9. doi:10.1038/76615. PMID 10862698.
External links
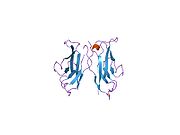
1nch: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF CELL-CELL ADHESION BY CADHERINS1nci: STRUCTURAL BASIS OF CELL-CELL ADHESION BY CADHERINS1ncj: N-CADHERIN, TWO-DOMAIN FRAGMENT1-50 CD1 (a-c, 1A, 1D, 1E) · CD2 · CD3 (γ, δ, ε) · CD4 · CD5 · CD6 · CD7 · CD8 (a) · CD9 · CD10 · CD11 (a, b, c) · CD13 · CD14 · CD15 · CD16 (A, B) · CD18 · CD19 · CD20 · CD21 · CD22 · CD23 · CD24 · CD25 · CD26 · CD27 · CD28 · CD29 · CD30 · CD31 · CD32 (A, B) · CD33 · CD34 · CD35 · CD36 · CD37 · CD38 · CD39 · CD40 · CD41 · CD42 (a, b, c, d) · CD43 · CD44 · CD45 · CD46 · CD47 · CD48 · CD49 (a, b, c, d, e, f) · CD5051-100 CD51 · CD52 · CD53 · CD54 · CD55 · CD56 · CD57 · CD58 · CD59 · CD61 · CD62 (E, L, P) · CD63 · CD64 (A, B, C) · CD66 (a, b, c, d, e, f) · CD68 · CD69 · CD70 · CD71 · CD72 · CD73 · CD74 · CD78 · CD79 (a, b) · CD80 · CD81 · CD82 · CD83 · CD84 · CD85 (a, d, e, h, j, k) · CD86 · CD87 · CD88 · CD89 · CD90 · CD91- CD92 · CD93 · CD94 · CD95 · CD96 · CD97 · CD98 · CD99 · CD100101-150 CD101 · CD102 · CD103 · CD104 · CD105 · CD106 · CD107 (a, b) · CD108 · CD109 · CD110 · CD111 · CD112 · CD113 · CD114 · CD115 · CD116 · CD117 · CD118 · CD119 · CD120 (a, b) · CD121 (a, b) · CD122 · CD123 · CD124 · CD125 · CD126 · CD127 · CD129 · CD130 · CD131 · CD132 · CD133 · CD134 · CD135 · CD136 · CD137 · CD138 · CD140b · CD141 · CD142 · CD143 · CD144 · CD146 · CD147 · CD148 · CD150151-200 CD151 · CD152 · CD153 · CD154 · CD155 · CD156 (a, b, c) · CD157 · CD158 (a, d, e, i, k) · CD159 (a, c) · CD160 · CD161 · CD162 · CD163 · CD164 · CD166 · CD167 (a, b) · CD168 · CD169 · CD170 · CD171 · CD172 (a, b, g) · CD174 · CD177 · CD178 · CD179 (a, b) · CD181 · CD182 · CD183 · CD184 · CD185 · CD186 · CD191 · CD192 · CD193 · CD194 · CD195 · CD196 · CD197 · CDw198 · CDw199 · CD200201-250 CD201 · CD202b · CD204 · CD205 · CD206 · CD207 · CD208 · CD209 · CDw210 (a, b) · CD212 · CD213a (1, 2) · CD217 · CD218 (a, b) · CD220 · CD221 · CD222 · CD223 · CD224 · CD225 · CD226 · CD227 · CD228 · CD229 · CD230 · CD233 · CD234 · CD235 (a, b) · CD236 · CD238 · CD239 · CD240CE · CD240D · CD241 · CD243 · CD244 · CD246 · CD247- CD248 · CD249251-300 CD252 · CD253 · CD254 · CD256 · CD257 · CD258 · CD261 · CD262 · CD264 · CD265 · CD266 · CD267 · CD268 · CD269 · CD271 · CD272 · CD273 · CD274 · CD275 · CD276 · CD278 · CD279 · CD280 · CD281 · CD282 · CD283 · CD284 · CD286 · CD288 · CD289 · CD290 · CD292 · CDw293 · CD294 · CD295 · CD297 · CD298 · CD299301-350 Calcium-independent IgSF CAMLFA-1 (CD11a+CD18) · Integrin alphaXbeta2 (CD11c+CD18) · Macrophage-1 antigen (CD11b+CD18) · VLA-4 (CD49d+CD29) · Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (ITGA2B+ITGB3)Calcium-dependent ClassicalUnconventional/ungroupedOther Lymphocyte homing receptor: CD44 · L-selectin · integrin (VLA-4, LFA-1)
Carcinoembryonic antigen · CD22 · CD24 · CD44 · CD146 · CD164see also cell membrane protein disorders
B memb: cead, trns (1A, 1C, 1F, 2A, 3A1, 3A2-3, 3D), othr - Human proteins
- Membrane protein stubs
- Clusters of differentiation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.