- ART4
-
ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 (Dombrock blood group) Identifiers Symbols ART4; CD297; DO; DOK1 External IDs OMIM: 110600 MGI: 1202710 HomoloGene: 10883 GeneCards: ART4 Gene EC number 2.4.2.31 Gene Ontology Molecular function • NAD(P)+-protein-arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity
• transferase activity, transferring glycosyl groupsCellular component • plasma membrane
• membrane
• anchored to membraneBiological process • protein ADP-ribosylation
• arginine metabolic processSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 420 109978 Ensembl ENSG00000111339 ENSMUSG00000030217 UniProt Q93070 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_021071 NM_026639.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_066549 NP_080915.1 Location (UCSC) Chr 12:
14.98 – 15 MbChr 6:
136.8 – 136.81 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ART4 gene.[1][2] ART4 has also been designated as CD297 (cluster of differentiation 297).
This gene encodes a protein that contains a mono-ADP-ribosylation (ART) motif. It is a member of the ADP-ribosyltransferase gene family but enzymatic activity has not been demonstrated experimentally. Antigens of the Dombrock blood group system are located on the gene product, which is glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored to the erythrocyte membrane. Allelic variants, some of which lead to adverse transfusion reactions, are known.[2]
Mouse Mutant Alleles for Art4 Marker Symbol for Mouse Gene. This symbol is assigned to the genomic locus by the MGI Art4 Mutant Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Clones. These are the known targeted mutations for this gene in a mouse. Art4tm1aWTSI(KOMP) Example structure of targeted conditional mutant allele for this gene 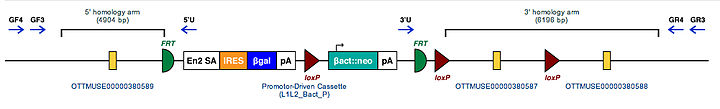
These Mutant ES Cells can be studied directly or used to generate mice with this gene knocked out. Study of these mice can shed light on the function of Art4: see Knockout mouse References
- ^ Koch-Nolte F, Haag F, Braren R, Kuhl M, Hoovers J, Balasubramanian S, Bazan F, Thiele HG (Apr 1997). "Two novel human members of an emerging mammalian gene family related to mono-ADP-ribosylating bacterial toxins". Genomics 39 (3): 370–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.4520. PMID 9119374.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ART4 ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 (Dombrock blood group)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=420.
Further reading
- Reid ME (2003). "The Dombrock blood group system: a review". Transfusion 43 (1): 107–14. doi:10.1046/j.1537-2995.2003.00283.x. PMID 12519438.
- Tippett P (1967). "Genetics of the Dombrock blood group system". J. Med. Genet. 4 (1): 7–11. doi:10.1136/jmg.4.1.7. PMC 1468500. PMID 6034522. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1468500.
- Eiberg H, Mohr J (1996). "Dombrock blood group (DO): assignment to chromosome 12p". Hum. Genet. 98 (5): 518–21. doi:10.1007/s004390050251. PMID 8882867.
- Mauthe J, Coghlan G, Zelinski T (2000). "Confirmation of the assignment of the Dombrock blood group locus (DO) to chromosome 12p: narrowing the boundaries to 12p12.3-p13.2". Vox Sang. 79 (1): 53–6. doi:10.1046/j.1423-0410.2000.7910053.x. PMID 10971215.
- Gubin AN, Njoroge JM, Wojda U et al. (2000). "Identification of the dombrock blood group glycoprotein as a polymorphic member of the ADP-ribosyltransferase gene family". Blood 96 (7): 2621–7. PMID 11001920.
- Wu GG, Jin SZ, Deng ZH, Zhao TM (2002). "Polymerase chain reaction with sequence-specific primers-based genotyping of the human Dombrock blood group DO1 and DO2 alleles and the DO gene frequencies in Chinese blood donors". Vox Sang. 81 (1): 49–51. doi:10.1046/j.1423-0410.2001.00052.x. PMID 11520417.
- Rios M, Hue-Roye K, Øyen R et al. (2002). "Insights into the Holley- and Joseph- phenotypes". Transfusion 42 (1): 52–8. doi:10.1046/j.1537-2995.2002.00004.x. PMID 11896313.
- Rios M, Storry JR, Hue-Roye K et al. (2002). "Two new molecular bases for the Dombrock null phenotype". Br. J. Haematol. 117 (3): 765–7. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2002.03524.x. PMID 12028057.
- Glowacki G, Braren R, Firner K et al. (2003). "The family of toxin-related ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferases in humans and the mouse". Protein Sci. 11 (7): 1657–70. doi:10.1110/ps.0200602. PMC 2373659. PMID 12070318. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2373659.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Grahnert A, Friedrich M, Engeland K, Hauschildt S (2005). "Analysis of mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 gene expression in human monocytes: splicing pattern and potential regulatory elements". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1730 (3): 173–86. doi:10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.08.001. PMID 16140404.
External links
Categories:- Human proteins
- Membrane protein stubs
- Clusters of differentiation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
