- Outline of energy
-
See also: Index of energy articles
In physics, energy (from the Greek ἐνέργεια – energeia, "activity, operation", from ἐνεργός – energos, "active, working"[1]) is a scalar physical quantity that describes the amount of work that can be performed by a force. Energy is an attribute of objects and systems that is subject to a conservation law. Several different forms of energy exist to explain all known natural phenomena. These forms include (but are not limited to) kinetic, potential, thermal, gravitational, sound, light, elastic, and electromagnetic energy. The forms of energy are often named after a related force.
Any form of energy can be transformed into another form, but the total energy always remains the same. This principle, the conservation of energy, was first postulated in the early 19th century, and applies to any isolated system. According to Noether's theorem, the conservation of energy is a consequence of the fact that the laws of physics do not change over time.[2]
Although the total energy of a system does not change with time, its value may depend on the frame of reference. For example, a seated passenger in a moving airplane has zero kinetic energy relative to the airplane, but non-zero kinetic energy relative to the Earth.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to energy:
Essence of energy
- Main article: Energy
- Mass–energy equivalence (E=mc2)
Forms of energy
- Potential energy
- Gravitational potential energy
- Elastic potential energy
- Nuclear potential energy
- Kinetic energy
- Thermal energy
- Electric energy
- Magnetic energy
- Electromagnetic fields
- Chemical energy
- Nuclear binding energy
- Surface energy
Energy units (terms)
See Units of energy
- Barrel of oil equivalent
- British thermal unit
- Calorie
- Current solar income – the amount of solar energy that falls as sunlight
- Electronvolt – (symbol: eV) is the amount of energy gained by a single unbound electron when it falls through an electrostatic potential difference of one volt
- Planck energy, 1.22 × 1019 GeV (billion electron volts)
- Enthalpy
- Erg – (symbol "erg") unit of energy and mechanical work in the centimetre-gram-second (CGS) system of units
- EU energy label
- Fill factor – defined as the ratio of the maximum power (Vmp x Jmp) divided by the short-circuit current (Isc) and open-circuit voltage (Voc) in light current density – voltage (J-V) characteristics of solar cells.
- Foot-pound – (symbol ft·lbf or ft·lbf) is an Imperial and U.S. customary unit of mechanical work, or energy, although in scientific fields one commonly uses the equivalent metric unit of the joule (J). There are approximately 1.356 J/(ft·lbf).
- Gigaton – Metric Unit of mass, equal to 1,000,000,000 (1 billion) metric tons, 1,000,000,000,000 (1 trillion) kilograms
- Any of various units of energy, such as gigatons of TNT equivalent, gigatons of coal equivalent, gigatons petroleum equivalent.
- Gray (unit) – (symbol: Gy), is the SI unit of energy for the absorbed dose of radiation. One gray is the absorption of one joule of radiation energy by one kilogram of matter. One gray equals 100 rad, an older unit.
- Heat
- Joule – (symbol J, also called newton meter, watt second, or coulomb volt)
- Kilowatt-hour – (symbol: kW·h) corresponds to one kilowatt (kW) of power being used over a period of one hour.
- Mass-energy equivalence – where mass has an energy equivalence, and energy has a mass equivalence
- Megawatt
- Net energy gain
- Power factor – of an AC electric power system is defined as the ratio of the real power to the apparent power.
- Therm – (symbol thm) a non-SI unit of heat energy. It is approximately the heat equivalent of burning 100 cubic feet of natural gas. In the US gas industry it is defined as exactly 100,000 BTU59°F or 105.4804 megajoules.
- Ton of oil equivalent
- TPE – Ton Petroleum Equivalent, 45.217 GJ, see ton of oil equivalent
History of energy
- Main article: History of energy
Energy infrastructure
See especially Category:Electric power and Category:Fuels for a large number of conventional energy related topics.
- Energy storage
- Electricity generation
- Electricity retailing
- Grid energy storage
- Liquified natural gas
- Microwave power transmission
- Power plant
- Power supply
- Power transmission
- Underground power station
Energy applications
- Biofuel
- Distributed generation
- Electric vehicle
- Hybrid vehicle
- Hydrogen vehicle
- Passive solar building design
- Steam engine
Physics of energy
- Energy
- Activation energy explains the differences in the speeds of various chemical reactions
- Alternative Energy Index
- Bioenergetics
- Chemical energetics
- Energy in physical cosmology
- Energy in Earth science that is responsible for the macroscopic transformations on the planet Earth
- Electricity
- Exergy
- Green energy
- Orders of magnitude (energy) – list describes various energy levels between 10−31 joules and 1070 joules
- Thermodynamics
- Perpetual motion
- Heat
- History of energy
- Energy forms, the forms in which energy can be defined
- Energy transformation, relating to energy's changes from one form to another.
- Energy (signal processing), the inner product of a signal in the time domain
- Energy density spectrum, relating to the distribution of signal energy over frequencies.
- Potential energy, the form of energy that is due to position of an object
- Kinetic energy, the form of energy as a consequence of the motion of an object or its constituents
- Mechanical energy, the potential energy and kinetic energy present in the components of a mechanical system.
- Binding energy, a concept explaining how the constituents of atoms or molecules are bound together
- Bond energy, a measure of the strength of a chemical bond
- Nuclear energy, energy that is the consequence of decomposition or combination of atomic nuclei
- Osmotic power,or salinity gradient power and blue energy, is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water
- Gibbs free energy, a related concept in chemical thermodynamics that incorporates entropy considerations too
- Helmholtz free energy, a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" work obtainable from a closed thermodynamic system at a constant temperature, useful for studying explosive chemical reactions
- Elastic energy, which causes or is released by the elastic distortion of a solid or a fluid
- Ionization energy – the (IE) of an atom is the energy required to strip it of an electron.
- Interaction energy, the contribution to the total energy that is a result of interaction between the objects being considered
- Internal energy – (abbreviated E or U) the total kinetic energy due to the motion of molecules (translational, rotational, vibrational) and the total potential energy associated with the vibrational and electric energy of atoms within molecules.
- Negative energy
- Energy conversion – process of converting energy from one form to another
- Dark energy, used to explain some cosmological phenomena
- Energy quality, empirical experience of the characteristics of different energy forms as they flow and transform
- Energy density, amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume, or per unit mass
- Energy flow, flow of energy in an ecosystem through food chains
- Energetics, the scientific study of energy flows under transformation
- Stress-energy tensor, the density and flux of energy and momentum in space-time; the source of the gravitational field in general relativity
- Food energy, energy in food that is available
- Primary energy – Energy contained in raw fuels and any other forms of energy received by a system as input to the system.
- Radiant energy – energy that is transported by waves
- Rotational energy – An object's rotational energy or angular kinetic energy is part of its total kinetic energy
- Solar radiation – radiant energy emitted by the sun, particularly electromagnetic energy
- Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form of hydropower that converts the energy of tides into useful forms of power - mainly electricity, dynamic tidal power,tidal lagoons,Tidal barrage
- Wave power is the transport of energy by ocean surface waves, and the capture of that energy to do useful work — for example, electricity generation, water desalination, or the pumping of water (into reservoirs). Machinery able to exploit wave power is generally known as a wave energy converter (WEC).
- Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air in motion;Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships
Allegorical, esoteric, and pseudoscientific
- Energy (esotericism), invoked by spiritualists for alternative modes of healing the human body as well as a spirit that permeates all of reality.
- Orgone, Wilhelm Reich discovered this energy and tried to use it to cure various physical ailments and control the weather.
- Qi a concept from Oriental medicine that is sometimes translated as "energy" in the West.
- Vitalism, often referred to as "energy"
- Cold fusion, nuclear fusion at conditions close to room temperature.
- Bubble fusion, also known as Sonofusion, energy from acoustic collapse of bubbles.
- Water-fuelled car, powering a car using water as fuel.
Energy industry
Main article: Energy industry- World energy resources and consumption
- List of energy resources, substances like fuels, petroleum products and electricity
- Energy crisis, the need to conserve energy resources
- Energy development, development of energy resources
- Embodied energy, the sum total of energy expended to deliver a good or service as it travels through the economy
- Energy conservation, tips for conserving energy resources
- Energy economics, as the foundation of other relationships
- Energy policy, government policies and plans for energy supply
- Energy storage, methods commonly used to store energy resources for later use
- Biosphere
- Ecological energetics
- Ecology
- Energy balance
- Earth Day
- U4energy, a pan European school challenge on energy education launched in September 2010. U4energy is an initiative funded under the IEE programme to improve energy consumption in schools and their local communities.
- Energy development – Ongoing effort to provide abundant and accessible energy, through knowledge, skills and constructions.
- Energy speculation
- Free energy suppression
- Future energy development – Provides a general overview of future energy development.
- History of perpetual motion machines
- Hubbert peak theory, also known as peak oil – the theory that world oil production will peak (or has peaked), and will then rapidly decline, with a corresponding rapid increase in prices.
- Primary production
- Power harvesting
- Renewable energy development
Energy politics
Energy Issues
- 2000 Watt society
- Environmental concerns with electricity generation
- Fuel poverty
- Greasestock, American showcase of vehicles and technologies powered by alternative energy
- Low-carbon economy
- Peak Oil
- Soft energy path – an energy use and development strategy delineated and promoted by some energy experts and activists
- Strategic Petroleum Reserve
Energy Policies and Use – National and International
International
- Energy policy – Introductory article
- Energy and Environmental Security Initiative (EESI)
Regional and national
Main page: Energy policy by country- Energy law – overview of many energy laws from various countries and states
- Energy Tax Act – United States energy-related legislation. See also : Category:United States federal energy legislation
- United Kingdom:
Energy economics
Main article: Energy economicsEnergy companies
- Exxon Mobil
- Enercon GmbH – Company based in Germany that operates in the wind turbine industry. One of the biggest producers in the world.
- Saudi Aramco
- Sasol
- United States Enrichment Corporation – contracts with the United States Department of Energy to produce enriched uranium.
Non-profit organizations
Industry associations
- OPEC – Organization of Petroleum-exporting Countries
- IEA – International Energy Agency
- CAPP – Canadian Association of Petroleum Producers
- World LP Gas Association – WLPGA
Energy technology inventors
- Alessandro Volta
- Charles Kettering
- Farrington Daniels – solar energy
- Georges Leclanché – battery
- John Frederic Daniell – Daniell cell
- Rudolf Diesel – compression ignition internal combustion engine
- Georges Imbert – wood gas
- Leonardo da Vinci
- Moritz von Jacobi
- Nikolaus Otto – internal combustion engine
- Robert Stirling – Stirling engine (external combustion)
- Nikola Tesla
- James Watt – steam engine with separate condensor
- List of books about energy issues
- List of energy abbreviations
- List of large wind farms
- List of notable renewable energy organizations
- List of photovoltaics companies
- List of renewable energy topics by country
- List of solar thermal power stations
- list of wave topics
- List of wind turbine manufacturers
See also
- Energy (disambiguation)
- List of environment topics
References
- ^ Harper, Douglas. "Energy". Online Etymology Dictionary. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=energy. Retrieved May 1, 2007.
- ^ Lofts, G; O'Keeffe D; et al (2004). "11 — Mechanical Interactions". Jacaranda Physics 1 (2 ed.). Milton, Queensland, Australia: John Willey & Sons Australia Ltd.. pp. 286. ISBN 0 7016 3777 3.
External links
Bioenergy Biofuels Algae fuel · Bagasse · Babassu oil · Biobutanol · Biodiesel · Biogas · Biogasoline · Cellulosic ethanol · Corn stover · Ethanol fuel · Methanol fuel · Stover · Straw · Vegetable oil
Energy from foodstock Non-food energy crops Arundo · Big bluestem · Camelina · Chinese tallow · Duckweed · Jatropha curcas · Millettia pinnata · Miscanthus giganteus · Switchgrass · Wood fuelTechnology Concepts Cellulosic ethanol commercialization · Energy content of biofuel · Energy crop · Energy forestry · EROEI · Food vs. fuel · Sustainable biofuelElectricity generation Concepts Availability factor · Baseload · Black start · Capacity factor · Demand factor · Demand management · EROEI · Grid storage · Intermittency · Load following · Nameplate capacity · Peak demand · Repowering · Spark spreadSources Technology Distribution Policies Carbon offset · Coal phase out · Ecotax · Energy subsidies · Feed-in tariff · Net metering · Pigovian tax · Renewable Energy Certificates · Renewable energy payments · Renewable energy policyCategories: Electric power distribution · Electricity economics · Power station technology · Portals: Energy · Sustainable developmentGalvanic cells Non-rechargeable:
primary cellsAlkaline battery · Aluminium battery · Bunsen cell · Chromic acid cell · Clark cell · Daniell cell · Dry cell · Grove cell · Leclanché cell · Lithium battery · Mercury battery · Nickel oxyhydroxide battery · Silicon–air battery · Silver-oxide battery · Weston cell · Zamboni pile · Zinc–air battery · Zinc–carbon battery · Zinc–chloride battery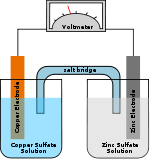
Rechargeable:
secondary cellsAutomotive battery · Lead–acid battery · Lead–acid battery (gel) · Lithium–air battery · Lithium-ion battery · Beltway battery · Lithium-ion polymer battery · Lithium iron phosphate battery · Lithium–sulfur battery · Lithium–titanate battery · Nickel–cadmium battery · Nickel–hydrogen battery · Nickel–iron battery · Nickel–lithium battery · Nickel–metal hydride battery · Low self-discharge NiMH battery · Nickel–zinc battery · Potassium-ion battery · Rechargeable alkaline battery · Sodium-ion battery · Sodium–sulfur battery · Vanadium redox battery · Zinc–bromine battery · Zinc–cerium batteryKinds of cells Battery (including Wet cell · Dry cell) · Concentration cell · Flow battery · Fuel cell · Trough battery · Voltaic pileParts of cells Geothermal power Geothermal power Geothermal energy • Geothermal electricity • Geothermal heating • Geothermal gradient
By country Armenia • Australia • Canada • Chile • China • Denmark • El Salvador • Germany • Iceland • Indonesia • Japan • Kenya • Lithuania • Mexico • New Zealand • Portugal • Philippines • Romania • Russia • Turkey • United Kingdom • United States • West IndiesTechnologies Aquaculture • Desalination • Geothermal heat pump • District heating • Binary Cycle • EGS • Heat pumpEnergy Concepts Global warming and climate change Temperatures Causes Anthropogenic - Attribution of recent climate change
- Aviation
- Biofuel
- Black carbon
- Carbon dioxide
- Earth's energy budget
- Earth's radiation balance
- Fossil fuel
- Global dimming
- Global warming potential
- Greenhouse effect
- (Infrared window)
- Greenhouse gases
- (Halocarbons)
- Land use and forestry
- Radiative forcing
- Tropospheric ozone
- Urban heat island
Natural Models History - History of climate change science
- Atmospheric thermodynamics
- Svante Arrhenius
- Charles David Keeling
- James Hansen
Opinion and climate change - Scientific opinion on climate change
- Scientists opposing the mainstream assessment
- Media coverage of climate change
- Public opinion on climate change
- (Popular culture)
- Environmental ethics
- Individual countries
- (China
- United States
- Russia
- Japan
- Australia
- Sweden
- Belgium
- Finland
- New Zealand
- Tuvalu
- Scotland)
Politics Potential effects and issues General - Abrupt climate change
- Arctic dipole
- Arctic haze
- Arctic methane release
- Climate change and agriculture
- Climate change and ecosystems
- Drought
- Economics of global warming
- Effects on humans
- Effects on marine mammals
- Fisheries and climate change
- Forest dieback
- Glacier retreat
- Iris hypothesis
- Mass extinction
- Migration and refugees
- Ozone depletion
- Ocean acidification
- Ocean anoxia
- Plant biodiversity
- Physical effects
- Polar stratospheric cloud
- Poverty
- Regime shift
- Runaway climate change
- Sea level rise
- Season creep
- Shutdown of thermohaline circulation
By country - Australia
- India
- (South Asia)
- United States
Mitigation Kyoto Protocol Governmental Emissions reduction - Coal phase out
- Emissions trading
- Carbon tax
- Carbon offset
- Carbon credit
Carbon-free energy Other - Geoengineering
- Carbon dioxide removal
- Carbon sink
- Individual and political action on climate change
- Climate change mitigation scenarios
- Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation
Proposed adaptations Strategies Programmes Modernizing the Electrical grid Proposals EU: SuperSmart Grid · Smartgrids Technology Platform · USA: Unified Smart Grid · Pickens plan super grid · Electranet
Efficient energy use Challenge: Intermittency Sources: Ocean · Solar · Wind · Micro hydro · Solutions: Super grid · Grid storage · Vehicle-to-grid · Distributed generationOther technologies/
concepts:HVDC bulk transmission · FACTS · Power line communication · Phasor measurement unit · Load following · Load control · Peak demandPolicies Related Issues Energy security · Climate change · United States energy independence · Peak oil · Energy crisis · Renewable energy commercialization · Rural electrificationOcean energy Wave power Australia • New Zealand
Tidal power Osmotic power Other Marine current power • Offshore construction • Ocean thermal energy conversion • Pelamis wave energy converter • • SDE Sea Waves Power Plant • Wind power (offshore) • Wave farmPeak Oil Core issues 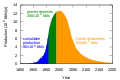
Results/responses Hirsch report · Oil Depletion Protocol · Price of petroleum · 2000s energy crisis · Energy crisis · Export Land Model · Food vs fuel · Oil reserves · Pickens Plan · Swing producer · Transition TownsPeople Books Films A Crude Awakening · Collapse · The End of Suburbia · Oil Factor · PetroApocalypse Now? · How Cuba Survived Peak Oil · What a Way to GoOrganizations Other "peaks" Petroleum industry Companies Major petroleum
companiesADNOC · China National Offshore Oil Corporation · CNPC · Iraq National Oil Company · Kuwait Petroleum Corporation · NIOC · Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation · Oil and Natural Gas Corporation · Orlen · Pertamina · Petrobras · Petronas · PDVSA · Qatar Petroleum · Rosneft · Saudi Aramco · SonatrachOther
integratedBG Group · Eni · Gazprom (Gazprom Neft) · Lukoil · Nippon Oil · Occidental Petroleum · OMV · PetroChina · Reliance Petroleum · Repsol YPF · Sinopec · Statoil · Suncor Energy · Surgutneftegas · TNK-BPMajor services
companiesAMEC · Baker Hughes · CGGVeritas · CH2M HILL · China Oilfield Services · Ensco · GE Oil & Gas · Halliburton · Petrofac · Saipem · Schlumberger · Transocean · Weatherford International · Wood GroupData Consumption · Production · Reserves · Imports · Exports · Price of petroleum · Price of gasoline and dieselExploration and
productionCore sampling · Geophysics · Petroleum engineering (Reservoir simulation · Seismic to simulation) · Petroleum geology · Petrophysics · Integrated asset modelling · Reflection seismology (Seismic inversion) · Seismic sourceAgreements (Concessions · Production sharing agreements) · Artificial lift (Pumpjack · Submersible pump (ESP) · Gas lift) · Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) (Steam injection · Gas reinjection) · Petroleum product · Pipeline transport · Refining · Water injection · Well intervention · Upstream · Midstream · Downstream · XTHistory 1967 Oil Embargo · 1973 oil crisis · 1979 energy crisis · 1980s oil glut · 2000s energy crisis · Founders of the petroleum industry · History of petroleum · Nationalization of oil supplies · Seven Sisters · Standard Oil · Oil market timelinesProvinces and fields Research and
developmentDeep Sea Drilling Program · Energy Biosciences Institute · French Institute of Petroleum · Beijing Institute of Petrochemical Technology · IHS · Integrated Ocean Drilling Program · Kola Superdeep Borehole · Project Mohole · TaskForceMajellaOther Acronymns · Big Oil · Drill, baby, drill · OPEC · Peak oil (Mitigation · Timing) · Shale gas · Society of Petroleum Engineers · Swing producer · Unconventional oil (Heavy crude oil · Oil sands · Oil shale)Solar energy Concepts Solar power Photovoltaic effect · Solar cell · Polymer solar cell · Nanocrystal solar cell · Photovoltaic module (solar panel) · Photovoltaic array (photovoltaic systems and power stations)Experimental
& proposedSolar updraft tower · Solar-pumped laser · Thermoelectric generator · Solar chemical and artificial photosynthesis · Space-based solar power · Solar sail · Magnetic sail · Solar thermal rocketAustralia · Canada · China · Germany · India · Israel · Japan · Portugal · Spain · United Kingdom · United StatesDistribution
& usesStorageAdoptionApplicationsSee also Wind power Wind power Environmental effects · History · Vehicles · Offshore wind power · Wind turbine · Windmill · Kitegen
Wind power by country Wind turbines Aerodynamics · Airborne · Darrieus · Design · Floating · Savonius · Quietrevolution · Small · Unconventional · Vertical axis · Devices in useWind power industry Wind farms Concepts Betz' law · Capacity factor · EROEI · Grid energy storage · HVDC · Intermittency · Net energy gain · Storage · Subsidies · Wind power forecasting · Wind profile power law · Wind resource assessmentOutlines - General reference
- Culture and the arts
- Geography and places
- Health and fitness
- History and events
- Mathematics and logic
- Natural and physical sciences
- People and self
- Philosophy and thinking
- Religion and belief systems
- Society and social sciences
- Technology and applied sciences
Categories:- Outlines
- Energy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

