- Greenhouse gas
-
A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect.[1] The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. In the Solar System, the atmospheres of Venus, Mars, and Titan also contain gases that cause greenhouse effects. Greenhouse gases greatly affect the temperature of the Earth; without them, Earth's surface would be on average about 33 °C (59 °F)[note 1] colder than at present.[2][3][4]
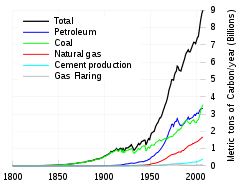
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the burning of fossil fuels has contributed to the increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from 280ppm to 390ppm, despite the uptake of a large portion of the emissions through various natural "sinks" involved in the carbon cycle.[5][6] Carbon dioxide emissions come from combustion of carbonaceous fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas. CO2 is a product of combustion of carbon although burning coal for example, also produces carbon monoxide.[7] Since 2000 fossil fuel related carbon emissions have equaled or exceeded the IPCC's "A2 scenario", except for small dips during two global recessions.[8][9][10] In 2010, global CO2 emissions exceeded the IPCC's worst case scenario,[11] leading to concerns over whether dangerous climate change can be avoided.[12]
Gases in Earth's atmosphere
Greenhouse gases
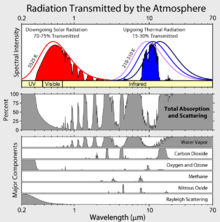 Atmospheric absorption and scattering at different electromagnetic wavelengths. The largest absorption band of carbon dioxide is in the infrared.
Atmospheric absorption and scattering at different electromagnetic wavelengths. The largest absorption band of carbon dioxide is in the infrared.
Greenhouse gases are those that can absorb and emit infrared radiation. [1] In order, the most abundant greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are:
Atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases are determined by the balance between sources (emissions of the gas from human activities and natural systems) and sinks (the removal of the gas from the atmosphere by conversion to a different chemical compound.[13] The proportion of an emission remaining in the atmosphere after a specified time is the "Airborne fraction". More precisely, the annual AF is the ratio of the atmospheric increase in a given year to that year’s total emissions. For CO2 the AF over the last 50 years (1956–2006) has been increasing at 0.25 ± 0.21%/year.[14]
Non-greenhouse gases
Although contributing to many other physical and chemical reactions, the major atmospheric constituents, nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), and argon (Ar), are not greenhouse gases. This is because molecules containing two atoms of the same element such as N2 and O2 and monatomic molecules such as Ar have no net change in their dipole moment when they vibrate and hence are almost totally unaffected by infrared light. Although molecules containing two atoms of different elements such as carbon monoxide (CO) or hydrogen chloride (HCl) absorb IR, these molecules are short-lived in the atmosphere owing to their reactivity and solubility. Because they do not contribute significantly to the greenhouse effect, they are usually omitted when discussing greenhouse gases.
Non-greenhouse gases that have an indirect radiative effect
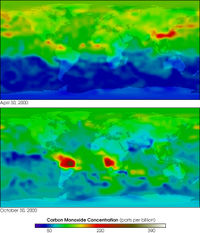
Carbon monoxide has an indirect radiative effect by elevating concentrations of methane and tropospheric ozone through scavenging of atmospheric constituents (e.g., the hydroxyl radical, OH) that would otherwise destroy them. Carbon monoxide is created when carbon-containing fuels are burned incompletely. Through natural processes in the atmosphere, it is eventually oxidized to carbon dioxide. Carbon monoxide has an atmospheric lifetime of only a few months[15] and as a consequence is spatially more variable than longer-lived gases.
Contribution of Clouds to Earth's greenhouse effect
The major non-gas contributor to the Earth's greenhouse effect, clouds, also absorb and emit infrared radiation and thus have an effect on radiative properties of the greenhouse gases. Clouds are water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. [16][17]
Impact of a given gas on climate sensitivity
Each gases' contribution to the greenhouse effect is affected by the characteristics of the gas, its abundance, and any indirect effects it may cause. For example, on a molecule-for-molecule basis the direct radiative effects of methane is about 72 times stronger greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide over a 20 year time frame[18] but it is present in much smaller concentrations so that its total direct radiative effect is smaller. On the other hand, in addition to its direct radiative impact methane has a large indirect radiative effect because it contributes to ozone formation. Shindell et al. (2005)[19] argue that the contribution to climate change from methane is at least double previous estimates as a result of this effect.[20]
When these gases are ranked by their direct contribution to the greenhouse effect, the most important are:[16]
Gas
Formula
Contribution
(%)Water vapor H2O 36 – 72 % Carbon dioxide CO2 9 – 26 % Methane CH4 4 – 9 % Ozone O3 3 – 7 % In addition to the main greenhouse gases listed above, other greenhouse gases include sulfur hexafluoride, hydrofluorocarbons and perfluorocarbons (see IPCC list of greenhouse gases). Some greenhouse gases are not often listed. For example, nitrogen trifluoride has a high global warming potential (GWP) but is only present in very small quantities.[21]
Proportion of direct effects at a given moment
It is not possible to state that a certain gas causes an exact percentage of the greenhouse effect. This is because some of the gases absorb and emit radiation at the same frequencies as others, so that the total greenhouse effect is not simply the sum of the influence of each gas. The higher ends of the ranges quoted are for each gas alone; the lower ends account for overlaps with the other gases.[16][17] In addition, some gases such as methane are known to have large indirect effects that are still being quantified.[22]
Atmospheric lifetime
Aside from water vapor, which has a residence time of about nine days,[23] major greenhouse gases are well-mixed, and take many years to leave the atmosphere.[24] Although it is not easy to know with precision how long it takes greenhouse gases to leave the atmosphere, there are estimates for the principal greenhouse gases. Jacob (1999)[25] defines the lifetime τ of an atmospheric species X in a one-box model as the average time that a molecule of X remains in the box. Mathematically τ can be defined as the ratio of the mass m (in kg) of X in the box to its removal rate, which is the sum of the flow of X out of the box (Fout), chemical loss of X (L), and deposition of X (D) (all in kg/sec):
 .[25] If one stopped pouring any of this gas into the box, then after a time τ, its concentration would be about halved.
.[25] If one stopped pouring any of this gas into the box, then after a time τ, its concentration would be about halved.The atmospheric lifetime of a species therefore measures the time required to restore equilibrium following a sudded increase or decrease in its concentration in the atmosphere. Individual atoms or molecules may be lost or deposited to sinks such as the soil, the oceans and other waters, or vegetation and other biological systems, reducing the excess to background concentrations. The average time taken to achieve this is the mean lifetime.
The atmospheric lifetime of CO2 is estimated of the order of 30-95 years.[26] This figure accounts for CO2 molecules being removed from the atmosphere by mixing into the ocean, photosynthesis, and a few other processes. However, this excludes the balancing fluxes of CO2 into the atmosphere from the geological reservoirs, which have slower characteristic rates.[27]
Global warming potential
The global warming potential (GWP) depends on both the efficiency of the molecule as a greenhouse gas and its atmospheric lifetime. GWP is measured relative to the same mass of CO2 and evaluated for a specific timescale. Thus, if a gas has a high radiative forcing but also a short lifetime, it will have a large GWP on a 20 year scale but a small one on a 100 year scale. Conversely, if a molecule has a longer atmospheric lifetime than CO2 its GWP will increase with the timescale considered.
Carbon dioxide has a variable atmospheric lifetime, and cannot be specified precisely.[28] While more than half of the CO2 emitted is currently removed from the atmosphere within a century, some fraction (about 20%) of emitted CO2 remains in the atmosphere for many thousands of years.[29][30][31] Carbon dioxide is defined to have a GWP of 1 over all time periods.
Methane has an atmospheric lifetime of 12 ± 3 years and a GWP of 72 over 20 years, 25 over 100 years and 7.6 over 500 years. The decrease in GWP at longer times is because methane is degraded to water and CO2 through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
Examples of the atmospheric lifetime and GWP relative to CO2 for several greenhouse gases are given in the following table:[18]
Atmospheric lifetime and GWP relative to CO2 at different time horizon for various greenhouse gases. Gas name Chemical
formulaLifetime
(years)Global warming potential (GWP) for given time horizon 20-yr 100-yr 500-yr Carbon dioxide CO2 See above 1 1 1 Methane CH4 12 72 25 7.6 Nitrous oxide N2O 114 289 298 153 CFC-12 CCl2F2 100 11 000 10 900 5 200 HCFC-22 CHClF2 12 5 160 1 810 549 Tetrafluoromethane CF4 50 000 5 210 7 390 11 200 Hexafluoroethane C2F6 10 000 8 630 12 200 18 200 Sulphur hexafluoride SF6 3 200 16 300 22 800 32 600 Nitrogen trifluoride NF3 740 12 300 17 200 20 700 The use of CFC-12 (except some essential uses) has been phased out due to its ozone depleting properties.[32] The phasing-out of less active HCFC-compounds will be completed in 2030.[33]
Natural and anthropogenic sources
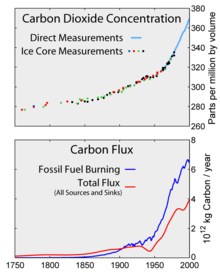 Top: Increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels as measured in the atmosphere and reflected in ice cores. Bottom: The amount of net carbon increase in the atmosphere, compared to carbon emissions from burning fossil fuel.
Top: Increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels as measured in the atmosphere and reflected in ice cores. Bottom: The amount of net carbon increase in the atmosphere, compared to carbon emissions from burning fossil fuel.
Aside from purely human-produced synthetic halocarbons, most greenhouse gases have both natural and human-caused sources. During the pre-industrial Holocene, concentrations of existing gases were roughly constant. In the industrial era, human activities have added greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, mainly through the burning of fossil fuels and clearing of forests.[34][35]
The 2007 Fourth Assessment Report compiled by the IPCC (AR4) noted that "changes in atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and aerosols, land cover and solar radiation alter the energy balance of the climate system", and concluded that "increases in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations is very likely to have caused most of the increases in global average temperatures since the mid-20th century".[36] In AR4, "most of" is defined as more than 50%.
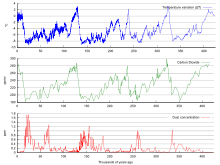
Gas Preindustrial level Current level Increase since 1750 Radiative forcing (W/m2) Carbon dioxide 280 ppm 388 ppm 108 ppm 1.46 Methane 700 ppb 1745 ppb 1045 ppb 0.48 Nitrous oxide 270 ppb 314 ppb 44 ppb 0.15 CFC-12 0 533 ppt 533 ppt 0.17 Ice cores provide evidence for variation in greenhouse gas concentrations over the past 800,000 years. Both CO2 and CH4 vary between glacial and interglacial phases, and concentrations of these gases correlate strongly with temperature. Direct data does not exist for periods earlier than those represented in the ice core record, a record which indicates CO2 mole fractions staying within a range of between 180ppm and 280ppm throughout the last 800,000 years, until the increase of the last 250 years. However, various proxies and modeling suggests larger variations in past epochs; 500 million years ago CO2 levels were likely 10 times higher than now.[37] Indeed higher CO2 concentrations are thought to have prevailed throughout most of the Phanerozoic eon, with concentrations four to six times current concentrations during the Mesozoic era, and ten to fifteen times current concentrations during the early Palaeozoic era until the middle of the Devonian period, about 400 Ma.[38][39][40] The spread of land plants is thought to have reduced CO2 concentrations during the late Devonian, and plant activities as both sources and sinks of CO2 have since been important in providing stabilising feedbacks.[41] Earlier still, a 200-million year period of intermittent, widespread glaciation extending close to the equator (Snowball Earth) appears to have been ended suddenly, about 550 Ma, by a colossal volcanic outgassing which raised the CO2 concentration of the atmosphere abruptly to 12%, about 350 times modern levels, causing extreme greenhouse conditions and carbonate deposition as limestone at the rate of about 1 mm per day.[42] This episode marked the close of the Precambrian eon, and was succeeded by the generally warmer conditions of the Phanerozoic, during which multicellular animal and plant life evolved. No volcanic carbon dioxide emission of comparable scale has occurred since. In the modern era, emissions to the atmosphere from volcanoes are only about 1% of emissions from human sources.[42][43]
Anthropogenic greenhouse gases
Since about 1750 human activity has increased the concentration of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Measured atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide are currently 100 ppm higher than pre-industrial levels.[44] Natural sources of carbon dioxide are more than 20 times greater than sources due to human activity,[45] but over periods longer than a few years natural sources are closely balanced by natural sinks, mainly photosynthesis of carbon compounds by plants and marine plankton. As a result of this balance, the atmospheric mole fraction of carbon dioxide remained between 260 and 280 parts per million for the 10,000 years between the end of the last glacial maximum and the start of the industrial era.[46]
It is likely that anthropogenic warming, such as that due to elevated greenhouse gas levels, has had a discernible influence on many physical and biological systems. Warming is projected to affect various issues such as freshwater resources, industry, food and health.[47]
The main sources of greenhouse gases due to human activity are:
- burning of fossil fuels and deforestation leading to higher carbon dioxide concentrations in the air. Land use change (mainly deforestation in the tropics) account for up to one third of total anthropogenic CO2 emissions.[46]
- livestock enteric fermentation and manure management,[48] paddy rice farming, land use and wetland changes, pipeline losses, and covered vented landfill emissions leading to higher methane atmospheric concentrations. Many of the newer style fully vented septic systems that enhance and target the fermentation process also are sources of atmospheric methane.
- use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in refrigeration systems, and use of CFCs and halons in fire suppression systems and manufacturing processes.
- agricultural activities, including the use of fertilizers, that lead to higher nitrous oxide (N2O) concentrations.
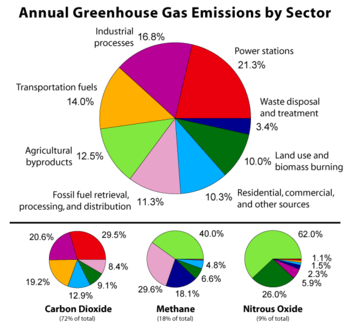
The seven sources of CO2 from fossil fuel combustion are (with percentage contributions for 2000–2004):[49]
Seven main fossil fuel
combustion sourcesContribution
(%)Liquid fuels (e.g., gasoline, fuel oil) 36 % Solid fuels (e.g., coal) 35 % Gaseous fuels (e.g., natural gas) 20 % Cement production 3 % Flaring gas industrially and at wells < 1 % Non-fuel hydrocarbons < 1 % "International bunker fuels" of transport
not included in national inventories4 % The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) ranks the major greenhouse gas contributing end-user sectors in the following order: industrial, transportation, residential, commercial and agricultural.[50] Major sources of an individual's greenhouse gas include home heating and cooling, electricity consumption, and transportation. Corresponding conservation measures are improving home building insulation, installing geothermal heat pumps and compact fluorescent lamps, and choosing energy-efficient vehicles.
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and three groups of fluorinated gases (sulfur hexafluoride, HFCs, and PFCs) are the major greenhouse gases and the subject of the Kyoto Protocol, which came into force in 2005.[51]
Although CFCs are greenhouse gases, they are regulated by the Montreal Protocol, which was motivated by CFCs' contribution to ozone depletion rather than by their contribution to global warming. Note that ozone depletion has only a minor role in greenhouse warming though the two processes often are confused in the media.
On December 7, 2009, the US Environmental Protection Agency released its final findings on greenhouse gases, declaring that "greenhouse gases (GHGs) threaten the public health and welfare of the American people". The finding applied to the same "six key well-mixed greenhouse gases" named in the Kyoto Protocol: carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride.[52][53]
Role of water vapor
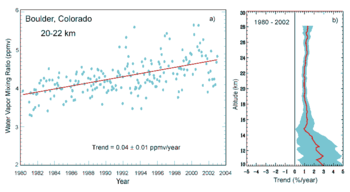
Water vapor accounts for the largest percentage of the greenhouse effect, between 36% and 66% for clear sky conditions and between 66% and 85% when including clouds.[17] Water vapor concentrations fluctuate regionally, but human activity does not significantly affect water vapor concentrations except at local scales, such as near irrigated fields. The atmospheric concentration of vapor is highly variable, from less than 0.01% in extremely cold regions up to 20% in warm, humid regions.[54]
The average residence time of a water molecule in the atmosphere is only about nine days, compared to years or centuries for other greenhouse gases such as CH4 and CO2. Thus, water vapor responds to and amplifies effects of the other greenhouse gases. The Clausius-Clapeyron relation establishes that air can hold more water vapor per unit volume when it warms. This and other basic principles indicate that warming associated with increased concentrations of the other greenhouse gases also will increase the concentration of water vapor. Because water vapor is a greenhouse gas, this results in further warming and so is a "positive feedback" that amplifies the original warming. Eventually other earth processes offset these positive feedbacks, stabilizing the global temperature at a new equilibrium and preventing the loss of earth's water through a Venus-like runaway greenhouse effect.[55]
Atmospheric concentration
Measurements from Antarctic ice cores show that before industrial emissions started atmospheric CO2 mole fractions were about 280 parts per million (ppm), and stayed between 260 and 280 during the preceding ten thousand years.[56] Carbon dioxide mole fractions in the atmosphere have gone up by approximately 35 percent since the 1900s, rising from 280 parts per million by volume to 387 parts per million in 2009. One study using evidence from stomata of fossilized leaves suggests greater variability, with carbon dioxide mole fractions above 300 ppm during the period seven to ten thousand years ago,[57] though others have argued that these findings more likely reflect calibration or contamination problems rather than actual CO2 variability.[58][59] Because of the way air is trapped in ice (pores in the ice close off slowly to form bubbles deep within the firn) and the time period represented in each ice sample analyzed, these figures represent averages of atmospheric concentrations of up to a few centuries rather than annual or decadal levels.
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the concentrations of most of the greenhouse gases have increased. For example, the mole fraction of carbon dioxide has increased from 280ppm by about 36% to 380 ppm, or 100 ppm over modern pre-industrial levels. The first 50 ppm increase took place in about 200 years, from the start of the Industrial Revolution to around 1973; however the next 50 ppm increase took place in about 33 years, from 1973 to 2006.[60]
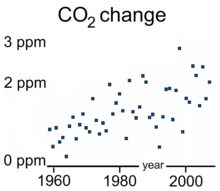
Recent data also shows that the concentration is increasing at a higher rate. In the 1960s, the average annual increase was only 37% of what it was in 2000 through 2007.[61]
The other greenhouse gases produced from human activity show similar increases in both amount and rate of increase. Many observations are available online in a variety of Atmospheric Chemistry Observational Databases.
Relevant to radiative forcing Gas Current (1998)
Amount by volumeIncrease
(absolute, ppm)
over pre-industrial (1750)Increase
(relative, %)
over pre-industrial (1750)Radiative
forcing
(W/m2)Carbon dioxide 365 ppm
(383 ppm, 2007.01)87 ppm
(105 ppm, 2007.01)31 %
(38 %, 2007.01)1.46
(~1.53, 2007.01)Methane 1745 ppb 1045 ppb 150 % 0.48 Nitrous oxide 314 ppb 44 ppb 16 % 0.15 Relevant to both radiative forcing and ozone depletion; all of the following have no natural sources and hence zero amounts pre-industrial Gas Current (1998)
Amount by volumeRadiative forcing
(W/m2)CFC-11 268 ppt 0.07 CFC-12 533 ppt 0.17 CFC-113 84 ppt 0.03 Carbon tetrachloride 102 ppt 0.01 HCFC-22 69 ppt 0.03 (Source: IPCC radiative forcing report 1994 updated (to 1998) by IPCC TAR table 6.1[62][63] ).
Greenhouse gas emissions ("sources")
Main articles: List of countries by carbon dioxide emissions, List of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita, List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions, and List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capitaAt present, the two primary sources of CO2 emissions are from burning coal used for electricity generation and petroleum used for motor transport.
Regional and national attribution of emissions
See also: Kyoto Protocol and government actionThere are several different ways of measuring GHG emissions (see World Bank (2010, p. 362) for a table of national emissions data).[64]
Some variables that have been reported[65] include:
- Definition of measurement boundaries. Emissions can be attributed geographically, to the area where they were emitted (the territory principle) or by the activity principle to the territory that caused the emissions to be produced. These two principles would result in different totals when measuring for example the importation of electricity from one country to another or the emissions at an international airport.
- The time horizon of different GHGs. Contribution of a given GHG is reported as a CO2 equivalent; the calculation to determine this takes into account how long that gas remains in the atmosphere. This is not always known accurately and calculations must be regularly updated to take into account new information.
- What sectors are included in the calculation (e.g. energy industries, industrical processes, agriculture etc.). There is often a conflict between transparency and availability of data.
- The measurement protocol itself. This may be via direct measurement or estimation; the four main methods are the emission factor-based method, the mass balance method, the predictive emissions monitoring system and the continuing emissions monitoring systems. The methods differ in accuracy, but also in cost and usability.
The different measures are sometimes used by different countries in asserting various policy/ethical positions to do with climate change (Banuri et al., 1996, p. 94).[66] This use of different measures leads to a lack of comparability, which is problematic when monitoring progress towards targets. There are arguments for the adoption of a common measurement tool, or at least the development of communication between different tools.[65]
Emissions may be measured over long time periods. This measurement type is called historical or cumulative emissions. Cumulative emissions give some indication of who is responsible for the build-up in the atmospheric concentration of GHGs (IEA, 2007, p. 199).[67]
The national accounts balance would be positively related to carbon emissions. The national accounts balance shows the difference between exports and imports. For many richer nations, such as the United States, the accounts balance is negative because more goods are imported than they are exported. This is mostly due to the fact that it is cheaper to produce goods outside of developed countries, leading the economies of developed countries to become increasingly dependent on services and not goods. We believed that a positive accounts balance would means that more production was occurring in a country, so more factories working would increase carbon emission levels.(Holtz-Eakin, 1995, pp.;85;101).[68]
Emissions may also be measured across shorter time periods. Emissions changes may, for example, be measured against a base year of 1990. 1990 was used in the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) as the base year for emissions, and is also used in the Kyoto Protocol (some gases are also measured from the year 1995) (Grubb, 2003, pp. 146, 149).[69] A country's emissions may also be reported as a proportion of global emissions for a particular year.
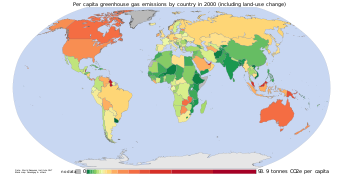
Another measurement is of per capita emissions. This divides a country's total annual emissions by its mid-year population (World Bank, 2010, p. 370). Per capita emissions may be based on historical or annual emissions (Banuri et al., 1996, pp. 106–107).
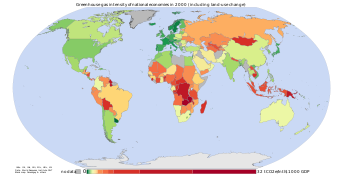
Greenhouse gas intensity and land-use change
The figure opposite is based on data from the World Resources Institute, and shows a measurement of GHG emissions for the year 2000 according to greenhouse gas intensity and land-use change. Herzog et al. (2006, p. 3) defined greenhouse gas intensity as GHG emissions divided by economic output.[70] GHG intensities are subject to uncertainty over whether they are calculated using market exchange rates (MER) or purchasing power parity (PPP) (Banuri et al., 1996, p. 96).[66] Calculations based on MER suggest large differences in intensities between developed and developing countries, whereas calculations based on PPP show smaller differences.
Land-use change, e.g., the clearing of forests for agricultural use, can affect the concentration of GHGs in the atmosphere by altering how much carbon flows out of the atmosphere into carbon sinks.[71] Accounting for land-use change can be understood as an attempt to measure “net” emissions, i.e., gross emissions from all GHG sources minus the removal of emissions from the atmosphere by carbon sinks (Banuri et al., 1996, pp. 92–93).
There are substantial uncertainties in the measurement of net carbon emissions.[72] Additionally, there is controversy over how carbon sinks should be allocated between different regions and over time (Banuri et al., 1996, p. 93). For instance, concentrating on more recent changes in carbon sinks is likely to favour those regions that have deforested earlier, e.g., Europe.
Cumulative and historical emissions
Top-5 historic CO2 contributors by region over the years 1800 to 1988 (in %) Region Industrial
CO2Total
CO2OECD North America 33.2 29.7 OECD Europe 26.1 16.6 Former USSR 14.1 12.5 China 5.5 6.0 Eastern Europe 5.5 4.8 The table above to the left is based on Banuri et al. (1996, p. 94).[66] Overall, developed countries accounted for 83.8% of industrial CO2 emissions over this time period, and 67.8% of total CO2 emissions. Developing countries accounted for industrial CO2 emissions of 16.2% over this time period, and 32.2% of total CO2 emissions. The estimate of total CO2 emissions includes biotic carbon emissions, mainly from deforestation. Banuri et al. (1996, p. 94) calculated per capita cumulative emissions based on then-current population. The ratio in per capita emissions between industrialized countries and developing countries was estimated to be more than 10 to 1.
Including biotic emissions brings about the same controversy mentioned earlier regarding carbon sinks and land-use change (Banuri et al., 1996, pp. 93–94). The actual calculation of net emissions is very complex, and is affected by how carbon sinks are allocated between regions (an equity consideration), and the dynamics of the climate system.
The International Energy Agency (IEA, 2007, p. 201) compared cumulative energy-related CO2 emissions for several countries and regions.[67] Over the time period 1900-2005, the US accounted for 30% of total cumulative emissions; the EU, 23%; China, 8%; Japan, 4%; and India, 2%. The rest of the world accounted for 33% of global, cumulative, energy-related CO2 emissions.
Changes since a particular base year
In total, Annex I Parties managed a cut of 3.3% in GHG emissions between 1990 and 2004 (UNFCCC, 2007, p. 11).[73] Annex I Parties are those countries listed in Annex I of the UNFCCC, and are the industrialized countries. For non-Annex I Parties, emissions in several large developing countries and fast growing economies (China, India, Thailand, Indonesia, Egypt, and Iran) GHG emissions have increased rapidly over this period (PBL, 2009).[74]
The sharp acceleration in CO2 emissions since 2000 to more than a 3% increase per year (more than 2 ppm per year) from 1.1% per year during the 1990s is attributable to the lapse of formerly declining trends in carbon intensity of both developing and developed nations. China was responsible for most of global growth in emissions during this period. Localised plummeting emissions associated with the collapse of the Soviet Union have been followed by slow emissions growth in this region due to more efficient energy use, made necessary by the increasing proportion of it that is exported.[49] In comparison, methane has not increased appreciably, and N2O by 0.25% y−1.
Annual and per capita emissions
At the present time, total annual emissions of GHGs are rising (Rogner et al., 2007).[75] Between the period 1970 to 2004, emissions increased at an average rate of 1.6% per year, with CO2 emissions from the use of fossil fuels growing at a rate of 1.9% per year.
Today, the stock of carbon in the atmosphere increases by more than 3 million tonnes per annum (0.04%) compared with the existing stock.[clarification needed] This increase is the result of human activities by burning fossil fuels, deforestation and forest degradation in tropical and boreal regions.[76]
Per capita emissions in the industrialized countries are typically as much as ten times the average in developing countries (Grubb, 2003, p. 144).[69] Due to China's fast economic development, its per capita emissions are quickly approaching the levels of those in the Annex I group of the Kyoto Protocol (PBL, 2009).[77] Other countries with fast growing emissions are South Korea, Iran, and Australia. On the other hand, per capita emissions of the EU-15 and the USA are gradually decreasing over time. Emissions in Russia and the Ukraine have decreased fastest since 1990 due to economic restructuring in these countries (Carbon Trust, 2009, p. 24).[78]
Energy statistics for fast growing economies are less accurate than those for the industrialized countries. For China's annual emissions in 2008, PBL (2008) estimated an uncertainty range of about 10%.
Top emitters
In 2005, the world's top-20 emitters comprised 80% of total GHG emissions (PBL, 2010. See notes for the following table).[79] Tabulated below are the top-5 emitters for the year 2005 (MNP, 2007).[80] The second column is the country's or region's share of the global total of annual emissions. The third column is the country's or region's average annual per capita emissions, in tonnes of GHG per head of population:
Top-5 emitters for the year 2005 Country or region % of global total
annual emissionsTonnes of GHG
per capitaChinab 17 % 5.8 United Statesa 16 % 24.1 European Union-27a 11 % 10.6 Indonesiac 6 % 12.9 India 5 % 2.1 Table footnotes:
- These values are for the GHG emissions from fossil fuel use and cement production. Calculations are for carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and gases containing fluorine (the F-gases HFCs, PFCs and SF6).
- These estimates are subject to large uncertainties regarding CO2 emissions from deforestation; and the per country emissions of other GHGs (e.g., methane). There are also other large uncertainties which mean that small differences between countries are not significant. CO2 emissions from the decay of remaining biomass after biomass burning/deforestation are not included.
- a Industrialised countries: official country data reported to UNFCCC.
- b Excluding underground fires.
- c Including an estimate of 2000 million tonnes CO2 from peat fires and decomposition of peat soils after draining. However, the uncertainty range is very large.
Embedded emissions
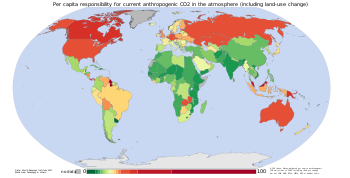
One way of attributing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is to measure the embedded emissions (also referred to as "embodied emissions") of goods that are being consumed. Emissions are usually measured according to production, rather than consumption (Helm et al., 2007, p. 3).[81] Under a production-based accounting of emissions, embedded emissions on imported goods are attributed to the exporting, rather than the importing, country. Under a consumption-based accounting of emissions, embedded emissions on imported goods are attributed to the importing country, rather than the exporting, country.
Davis and Caldeira (2010, p. 4) found that a substantial proportion of CO2 emissions are traded internationally.[82] The net effect of trade was to export emissions from China and other emerging markets to consumers in the US, Japan, and Western Europe. Based on annual emissions data from the year 2004, and on a per-capita consumption basis, the top-5 emitting countries were found to be (in tCO2 per person, per year): Luxembourg (34.7), the US (22.0), Singapore (20.2), Australia (16.7), and Canada (16.6) (Davis and Caldeira, 2010, p. 5).
Effect of policy
Rogner et al. (2007) assessed the effectiveness of policies to reduce emissions (mitigation of climate change).[75] They concluded that mitigation policies undertaken by UNFCCC Parties were inadequate to reverse the trend of increasing GHG emissions. The impacts of population growth, economic development, technological investment, and consumption had overwhelmed improvements in energy intensities and efforts to decarbonize (energy intensity is a country's total primary energy supply (TPES) per unit of GDP (Rogner et al., 2007).[83] TPES is a measure of commercial energy consumption (World Bank, 2010, p. 371)).[64]
Projections
Based on then-current energy policies, Rogner et al. (2007) projected that energy-related CO2 emissions in 2030 would be 40-110% higher than in 2000.[75] Two-thirds of this increase was projected to come from non-Annex I countries. Per capita emissions in Annex I countries were still projected to remain substantially higher than per capita emissions in non-Annex I countries. Projections consistently showed a 25-90% increase in the Kyoto gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, sulphur hexafluoride) compared to 2000.
IEA (2007, p. 199) estimated future cumulative energy-related CO2 emissions for several countries.[67] Their reference scenario projected cumulative energy-related CO2 emissions between the years 1900 and 2030. In this scenario, China’s share of cumulative emissions rises to 16%, approaching that of the United States (25%) and the European Union (18%). India’s cumulative emissions (4%) approach those of Japan (4%).
Relative CO2 emission from various fuels
One liter of gasoline, when used as a fuel, produces 2.32 kg (1.3 cubic meters) of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. One US gallon produces 19.4 lb (172.65 cubic feet)[84][85][86]
Mass of carbon dioxide emitted per quantity of energy for various fuels[87] Fuel name CO2
emitted
(lbs/106 Btu)CO2
emitted
(g/106 J)Natural gas 117 50.30 Liquefied petroleum gas 139 59.76 Propane 139 59.76 Aviation gasoline 153 65.78 Automobile gasoline 156 67.07 Kerosene 159 68.36 Fuel oil 161 69.22 Tires/tire derived fuel 189 81.26 Wood and wood waste 195 83.83 Coal (bituminous) 205 88.13 Coal (subbituminous) 213 91.57 Coal (lignite) 215 92.43 Petroleum coke 225 96.73 Coal (anthracite) 227 97.59 Removal from the atmosphere ("sinks")
Natural processes
Greenhouse gases can be removed from the atmosphere by various processes, as a consequence of:
- a physical change (condensation and precipitation remove water vapor from the atmosphere).
- a chemical reaction within the atmosphere. For example, methane is oxidized by reaction with naturally occurring hydroxyl radical, OH· and degraded to CO2 and water vapor (CO2 from the oxidation of methane is not included in the methane Global warming potential). Other chemical reactions include solution and solid phase chemistry occurring in atmospheric aerosols.
- a physical exchange between the atmosphere and the other compartments of the planet. An example is the mixing of atmospheric gases into the oceans.
- a chemical change at the interface between the atmosphere and the other compartments of the planet. This is the case for CO2, which is reduced by photosynthesis of plants, and which, after dissolving in the oceans, reacts to form carbonic acid and bicarbonate and carbonate ions (see ocean acidification).
- a photochemical change. Halocarbons are dissociated by UV light releasing Cl· and F· as free radicals in the stratosphere with harmful effects on ozone (halocarbons are generally too stable to disappear by chemical reaction in the atmosphere).
Negative emissions
See also: Bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, Carbon dioxide air capture, Geoengineering, and Greenhouse gas remediationThere are a number of technologies that remove emissions of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. Most widely analysed are those which remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, either to geologic formations such as bio-energy with carbon capture and storage[88][89][90] and carbon dioxide air capture,[90] or to the soil as in the case with biochar.[90] It has been pointed out by the IPCC, that many long-term climate scenario models require large scale manmade negative emissions in order to avoid serious climate change.[91]
History of scientific research
Late 19th century scientists experimentally discovered that N2 and O2 do not absorb infrared radiation (called, at that time, "dark radiation") while, on the contrary, water, both as true vapour and condensed in the form of microscopic droplets suspended in clouds, as well as CO2 and other poly-atomic gaseous molecules, do absorb infrared radiation. It was recognized in the early 20th century that the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere caused the Earth's overall temperature to be higher than it would be without them. During the late 20th century, a scientific consensus evolved that increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are causing a substantial rise in global temperatures and changes to other parts of the climate system, with consequences for the environment and for human health.[92]
See also
- Attribution of recent climate change
- Carbon credit
- Carbon Disclosure Project
- Carbon emissions reporting
- Carbon neutrality
- Carbon offset
- Clean Air Act
- Infrared window Atmospheric window
- Integrated Carbon Observation System
- Eddy covariance (also known as eddy correlation and eddy flux)
- Effects of global warming
- Emission standard
- Environmental impact of aviation
- European Climate Change Programme
- Externality
- Global Atmosphere Watch
- Greenhouse debt
- Hydrogen economy
- List of countries by electricity production from renewable sources
- List of international environmental agreements
- Low-carbon economy
- Low-carbon fuel standard
- Mobile source air pollution
- North American Carbon Program
- Physical properties of greenhouse gases
- Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative
- Regulation of greenhouse gases under the Clean Air Act
- Sustainability measurement
- World energy consumption
- Zero-emissions vehicle
Notes
- ^ Note that the greenhouse effect produces a temperature increase of about 33 °C (59 °F) with respect to black body predictions and not a surface temperature of 33 °C (91 °F) which is 32 °F higher. The average surface temperature is about 14 °C (57 °F).
References
- ^ a b "IPCC AR4 SYR Appendix Glossary" (PDF). http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/syr/ar4_syr_appendix.pdf. Retrieved 14 December 2008.
- ^ Karl TR, Trenberth KE (2003). "Modern Global Climate Change". Science 302 (5651): 1719–23. Bibcode 2003Sci...302.1719K. doi:10.1126/science.1090228. PMID 14657489. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/302/5651/1719.
- ^ Le Treut H, Somerville R, Cubasch U, Ding Y, Mauritzen C, Mokssit A, Peterson T and Prather M (2007) (PDF). Historical Overview of Climate Change Science In: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M and Miller HL, editors). Cambridge University Press. http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/wg1/ar4-wg1-chapter1.pdf. Retrieved 14 December 2008.
- ^ "NASA Science Mission Directorate article on the water cycle". Nasascience.nasa.gov. http://nasascience.nasa.gov/earth-science/oceanography/ocean-earth-system/ocean-water-cycle. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Global Change Questions". Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center. http://cdiac.ornl.gov/pns/faq.html.
- ^ ESRL Web Team (2008-01-14). "Trends in Carbon Dioxide". Esrl.noaa.gov. http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ Lindeburgh, Michael R., (2006). Mechanical Engineering Reference Manual for the PE Exam. Professional Publications, Inc., Belmont, CA. ISBN 978-1-59126-049-3.
- ^ "Special Report on Emissions Scenarios: (Data) IPCC SRES Emissions Scenarios - Version 1.1 (July, 2000)". IPCC. http://sres.ciesin.org/data/Version1.1/table/A2_ASF/A2_ASF_World.html. Retrieved 6-25-2011.
- ^ CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion 2010 - Highlights 2010 ed.. International Energy Agency. http://www.iea.org/co2highlights/CO2highlights.pdf.
- ^ Harvey, Fiona (5-29-1011). "Worst ever carbon emissions leave climate on the brink". Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2011/may/29/carbon-emissions-nuclearpower. Retrieved 6-25-2011.
- ^ Boden T, Blasing T (2011). Record High 2010 Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Fossil-Fuel Combustion and Cement Manufacture. US DOE (ORNL), Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC). 3 Nov. 2011.
- ^ Agence France-Press. 2011, Nov. 5. |Biggest spike ever in global warming gases: U.S.
- ^ IPCC (2007). "Chapter 7: Couplings Between Changes in the Climate System and Biogeochemistry" (PDF). IPCC WG1 AR4 Report. IPCC. p. FAQ 7.1; report page 512; pdf page 14. http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/wg1/ar4-wg1-chapter7.pdf. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ Canadell, J.G.; Le Quere, C.; Raupach, M.R.; Field, C.B.; Buitenhuis, E.T.; Ciais, P.; Conway, T.J.; Gillett, N.P.; Houghton, R.A.; Marland, G. (2007). "Contributions to accelerating atmospheric CO2 growth from economic activity, carbon intensity, and efficiency of natural sinks". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (47): 18866–18870. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702737104. PMID 17962418.
- ^ Impact of Emissions, Chemistry, and Climate on Atmospheric Carbon Monoxide: 100-year Predictions from a Global Chemistry-Climate ModelPDF (115 KB)
- ^ a b c Kiehl, J. T.; Kevin E. Trenberth (1997). "Earth's Annual Global Mean Energy Budget" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 78 (2): 197–208. Bibcode 1997BAMS...78..197K. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<0197:EAGMEB>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1520-0477. Archived from the original on 30 March 2006. http://web.archive.org/web/20060330013311/http://www.atmo.arizona.edu/students/courselinks/spring04/atmo451b/pdf/RadiationBudget.pdf. Retrieved 1 May 2006.
- ^ a b c "Water vapour: feedback or forcing?". RealClimate. 6 April 2005. http://www.realclimate.org/index.php?p=142. Retrieved 1 May 2006.
- ^ a b IPCC Fourth Assessment Report, Table 2.14, Chap. 2, p. 212
- ^ Shindell, Drew T. (2005). "An emissions-based view of climate forcing by methane and tropospheric ozone". Geophysical Research Letters 32 (4): L04803. Bibcode 2005GeoRL..3204803S. doi:10.1029/2004GL021900. http://www.nasa.gov/vision/earth/lookingatearth/methane.html.
- ^ "Methane's Impacts on Climate Change May Be Twice Previous Estimates". Nasa.gov. 2007-11-30. http://www.nasa.gov/vision/earth/lookingatearth/methane.html. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ Prather, Michael J.; J Hsu (2008). "NF3, the greenhouse gas missing from Kyoto". Geophysical Research Letters 35 (12): L12810. Bibcode 2008GeoRL..3512810P. doi:10.1029/2008GL034542.
- ^ Isaksen, Ivar S. A.; Michael Gauss, Gunnar Myhre, Katey M. Walter Anthony, and Carolyn Ruppel (20 April 2011). "Strong atmospheric chemistry feedback to climate warming from Arctic methane emissions". Global Biogeochemical Cycles 25 (2). Bibcode 2011GBioC..25B2002I. doi:10.1029/2010GB003845. http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/2011Q2/558/IsaksenGB2011.pdf. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
- ^ "AGU Water Vapor in the Climate System". Eso.org. 1995-04-27. http://www.eso.org/gen-fac/pubs/astclim/espas/pwv/mockler.html. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ Betts (2001). "6.3 Well-mixed Greenhouse Gases". Chapter 6 Radiative Forcing of Climate Change. Working Group I: The Scientific Basis IPCC Third Assessment Report - Climate Change 2001. UNEP/GRID-Arendal - Publications. http://www.grida.no/publications/other/ipcc%5Ftar/?src=/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/218.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ a b Jacob, Daniel (1999). Introduction to Atmospheric Chemistry. Princeton University Press. pp. 25–26. ISBN 0-691-00185-5. http://www-as.harvard.edu/people/faculty/djj/book/.
- ^ Jacobson, MZ (2005). "Correction to "Control of fossil-fuel particulate black carbon and organic matter, possibly the most effective method of slowing global warming."". J. Geophys. Res. 110: pp. D14105. doi:10.1029/2005JD005888. http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2005/2005JD005888.shtml.
- ^ Archer, David (2009). "Atmospheric Lifetime of Fossil Fuel Carbon Dioxide". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 37: pp. 117–134. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100206. http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100206.
- ^ edited by Susan Solomon ... (2007). "Frequently Asked Question 7.1 "Are the Increases in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide and Other Greenhouse Gases During the Industrial Era Caused by Human Activities?"". In Solomon, Kristen; Qin, Dahe; Manning, Martin et al.. IPCC, 2007: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge Press. ISBN 978-0521-88009-1. http://www.gcrio.org/ipcc/ar4/wg1/faq/ar4wg1faq-7-1.pdf. Retrieved 24 July 2007.
- ^ Meehl, G.A. (2007). "Frequently Asked Question 10.3: If Emissions of Greenhouse Gases are Reduced, How Quickly do Their Concentrations in the Atmosphere Decrease?". In S. Solomon, et al., (eds.). Chapter 10: Global Climate Projections. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press (CUP), Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.: Print version:CUP. This version: IPCC website. http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg1/en/faq-10-3.html. Retrieved 2011-06-01.
- ^ See also: Archer, David (2005). "Fate of fossil fuel CO2 in geologic time" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research 110 (C9): C09S05.1–C09S05.6. Bibcode 2005JGRC..11009S05A. doi:10.1029/2004JC002625. http://geosci.uchicago.edu/~archer/reprints/archer.2005.fate_co2.pdf. Retrieved 27 July 2007.
- ^ See also: Caldeira, Ken; Wickett, Michael E. (2005). "Ocean model predictions of chemistry changes from carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere and ocean" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research 110 (C9): C09S04.1–12. Bibcode 2005JGRC..11009S04C. doi:10.1029/2004JC002671. Archived from the original on 10 August 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070810202611/http://www.ipsl.jussieu.fr/~jomce/acidification/paper/Caldeira_Wickett_2005_JGR.pdf. Retrieved 27 July 2007.
- ^ Use of ozone depleting substances in laboratories. TemaNord 2003:516
- ^ Montreal Protocol
- ^ {{cite web|url= http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/wg1/ar4-wg1-chapter1.pdf%7Cformat=PDF%7Ctitle= Chapter 1 Historical Overview of Climate Change Science - FAQ 1.3 Figure 1 description page 116|work=Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change|accessdate=25 April 2008|date=5 February 2007|publisher=Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
- ^ "Chapter 3, IPCC Special Report on Emissions Scenarios, 2000". Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2000. http://www.grida.no/Climate/ipcc/emission/049.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "AR4 SYR SPM page 5" (PDF). http://www.ipcc.ch/pdf/assessment-report/ar4/syr/ar4_syr_spm.pdf. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ Image:Phanerozoic Carbon Dioxide.png
- ^ Berner, Robert A. (1994). "GEOCARB II: a revised model of atmospheric CO2 over Phanerozoic time". American Journal of Science 294: 56–91. doi:10.2475/ajs.294.1.56. ISSN 0002-9599. http://earth.geology.yale.edu/~ajs/1994/01.1994.02Berner.pdf.
- ^ Royer, DL; RA Berner and DJ Beerling (2001). "Phanerozoic atmospheric CO2 change: evaluating geochemical and paleobiological approaches". Earth-Science Reviews 54 (4): 349–92. Bibcode 2001ESRv...54..349R. doi:10.1016/S0012-8252(00)00042-8.
- ^ Berner, Robert A.; Kothavala, Zavareth (2001). "GEOCARB III: a revised model of atmospheric CO2 over Phanerozoic time". American Journal of Science 301 (2): 182–204. doi:10.2475/ajs.301.2.182. http://www.geology.yale.edu/~ajs/2001/Feb/qn020100182.pdf.
- ^ Beerling, DJ; Berner, RA (2005). "Feedbacks and the co-evolution of plants and atmospheric CO2". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (5): 1302–5. Bibcode 2005PNAS..102.1302B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408724102. PMC 547859. PMID 15668402. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=547859.
- ^ a b Hoffmann, PF; AJ Kaufman, GP Halverson, DP Schrag (1998). "A neoproterozoic snowball earth". Science 281 (5381): 1342–6. Bibcode 1998Sci...281.1342H. doi:10.1126/science.281.5381.1342. PMID 9721097. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/281/5381/1342.
- ^ Gerlach, TM (1991). "Present-day CO2 emissions from volcanoes". Transactions of the American Geophysical Union 72 (23): 249–55. Bibcode 1991EOSTr..72..249.. doi:10.1029/90EO10192.
- ^ "Climate Change 2001: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis: figure 6-6". http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/fig6-6.htm. Retrieved 1 May 2006.
- ^ "The present carbon cycle - Climate Change". Grida.no. http://www.grida.no/climate/vital/13.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ a b IPCC; Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M. Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.) (2007). [PDF 7.83 MB "Chapter 7. Couplings Between Changes in the Climate System and Biogeochemistry"]. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88009-1. PDF 7.83 MB. Retrieved 13 May 2008.
- ^ AR4 WG2 SPM pp. 9,11
- ^ H. Steinfeld, P. Gerber, T. Wassenaar, V. Castel, M. Rosales, C. de Haan (2006) Livestock’s long shadow. Environmental issues and options. FAO Livestock, Environment and Development (LEAD) Initiative.
- ^ a b Raupach, M.R. et al. (2007). "Global and regional drivers of accelerating CO2 emissions". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (24): 10288–93. Bibcode 2007PNAS..10410288R. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700609104. PMC 1876160. PMID 17519334. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/reprint/0700609104v1.pdf.
- ^ "U.S. Greenhouse Gas Inventory - U.S. Greenhouse Gas Inventory Reports|Climate Change - Greenhouse Gas Emissions|U.S. EPA". Epa.gov. 2006-06-28. http://epa.gov/climatechange/emissions/usinventoryreport.html. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ Lerner & K. Lee Lerner, Brenda Wilmoth (2006). "Environmental issues: essential primary sources". Thomson Gale. http://catalog.loc.gov/cgi-bin/Pwebrecon.cgi?v3=1&DB=local&CMD=010a+2006000857&CNT=10+records+per+page. Retrieved 11 September 2006.
- ^ "EPA: Greenhouse Gases Threaten Public Health and the Environment / Science overwhelmingly shows greenhouse gas concentrations at unprecedented levels due to human activity" (Press release). United States Environmental Protection Agency. 7 December 2009. http://yosemite.epa.gov/opa/admpress.nsf/d0cf6618525a9efb85257359003fb69d/08d11a451131bca585257685005bf252!OpenDocument. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ^ "Endangerment and Cause or Contribute Findings for Greenhouse Gases under the Clean Air Act". Climate Change - Regulatory Initiatives. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 7 December 2009. http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/endangerment.html. Retrieved 10 December 2009.
- ^ Evans, Kimberly Masters (2005). "The greenhouse effect and climate change". The environment: a revolution in attitudes. Detroit: Thomson Gale. ISBN 0-7876-9082-1.
- ^ Held, I. M.; Soden, B. J. (2000). "Water Vapor Feedback and Global Warming1". Annual Review of Energy and the Environment 25: 441–475. doi:10.1146/annurev.energy.25.1.441.
- ^ Flückiger, Jacqueline (2002). "High-resolution Holocene N2O ice core record and its relationship with CH4 and CO2". Global Biogeochemical Cycles 16: 1010. Bibcode 2002GBioC..16a..10F. doi:10.1029/2001GB001417.
- ^ Friederike Wagner, Bent Aaby and Henk Visscher (2002). "Rapid atmospheric CO2 changes associated with the 8,200-years-B.P. cooling event". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (19): 12011–4. Bibcode 2002PNAS...9912011W. doi:10.1073/pnas.182420699. PMC 129389. PMID 12202744. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=129389.
- ^ Andreas Indermühle, Bernhard Stauffer, Thomas F. Stocker (1999). "Early Holocene Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations". Science 286 (5446): 1815. doi:10.1126/science.286.5446.1815a. "Early Holocene Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations". Science. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/286/5446/1815a. Retrieved 26 May 2005.
- ^ H.J. Smith, M Wahlen and D. Mastroianni (1997). "The CO2 concentration of air trapped in GISP2 ice from the Last Glacial Maximum-Holocene transition". Geophysical Research Letters 24 (1): 1–4. Bibcode 1997GeoRL..24....1S. doi:10.1029/96GL03700.
- ^ "Monthly Average Carbon Dioxide Concentration, Mauna Loa Observatory" (PDF). Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center. 2005. http://cdiac.ornl.gov/trends/co2/graphics/mlo145e_thrudc04.pdf. Retrieved 14 December 2008.
- ^ Dr. Pieter Tans (3 May 2008) "Annual CO2 mole fraction increase (ppm)" for 1959–2007 National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Earth System Research Laboratory, Global Monitoring Division (additional details; see also K.A. Masarie, P.P. Tans (1995). "Extension and integration of atmospheric carbon dioxide data into a globally consistent measurement record". J. Geophys. Research 100: 11593–610. Bibcode 1995JGR...10011593M. doi:10.1029/95JD00859.
- ^ "Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis". Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/221.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ Blasing, TJ (February 2011). "Recent Greenhouse Gas Concentrations". Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center. http://cdiac.esd.ornl.gov/pns/current_ghg.html. Retrieved 2011-05-12.
- ^ a b World Bank (2010). World Development Report 2010: Development and Climate Change. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank, 1818 H Street NW, Washington DC 20433. doi:10.1596/978-0-8213-7987-5. ISBN 9780821379875. http://go.worldbank.org/BKLQ9DSDU0. Retrieved 2010-04-06.
- ^ a b "Bader, N. and R. Bleichwitz (2009) "Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The Challenge of Comparability". ''S.A.P.I.EN.S.'' '''2''' (3)". Sapiens.revues.org. http://sapiens.revues.org/index854.html. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ a b c Banuri, T. (1996) (PDF). Equity and Social Considerations. In: Climate Change 1995: Economic and Social Dimensions of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (J.P. Bruce et al. Eds.). This version: Printed by Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. PDF version: IPCC website. doi:10.2277/0521568544. ISBN 9780521568548. http://www.ipcc.ch/ipccreports/sar/wg_III/ipcc_sar_wg_III_full_report.pdf.
- ^ a b c IEA (2007). World Energy Outlook 2007 Edition- China and India Insights. International Energy Agency (IEA), Head of Communication and Information Office, 9 rue de la Fédération, 75739 Paris Cedex 15, France. p. 600. ISBN 9789264027305. http://www.iea.org/publications/free_new_Desc.asp?PUBS_ID=1927. Retrieved 2010-05-04.
- ^ Holtz-Eakin, D. (1995). "Stoking the Fires? CO2 Emissions and Economic Growth". Journal of Public Economics 57 (1): 85–101. doi:10.1016/0047-2727(94)01449-X. http://www.nber.org. Retrieved 2011-20-04.
- ^ a b Grubb, M. (July–September 2003). "The Economics of the Kyoto Protocol". World Economics 4 (3): 143–189. http://www.econ.cam.ac.uk/rstaff/grubb/publications/J36.pdf. Retrieved 2010-03-25.
- ^ Herzog, T. (November 2006). Yamashita, M.B.. ed (PDF). Target: intensity - an analysis of greenhouse gas intensity targets. World Resources Institute. ISBN 1569736383. http://pdf.wri.org/target_intensity.pdf. Retrieved 2011-04-11.
- ^ IPCC (2007). "Annex I: Glossary J-P". In B. Metz, O.R. Davidson, P.R. Bosch, R. Dave, L.A. Meyer. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA. This version: IPCC website. ISBN 9780521880114. http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg3/en/annex1sglossary-j-p.html. Retrieved 2011-04-11.
- ^ Markandya, A. (2001). "7.3.5 Cost Implications of Alternative GHG Emission Reduction Options and Carbon Sinks". In B. Metz et al.. Costing Methodologies. Climate Change 2001: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: GRID-Arendal website. doi:10.2277/0521015022. ISBN 9780521015028. http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg3/293.htm. Retrieved 2011-04-11.
- ^ UNFCCC (19 November 2007). "Compilation and synthesis of fourth national communications. Executive summary. Note by the secretariat. Document code: FCCC/SBI/2007/INF.6". United Nations Office at Geneva, Switzerland. http://unfccc.int/documentation/documents/advanced_search/items/3594.php?rec=j&priref=600004368#beg. Retrieved 2010-05-17.
- ^ PBL (October 16, 2009). "Industrialised countries will collectively meet 2010 Kyoto target". Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL) website. http://www.pbl.nl/en/dossiers/COP13Bali/moreinfo/Industrialised-countries-will-collectively-meet-2010-Kyoto-target.html. Retrieved 2010-04-03.
- ^ a b c Rogner, H.-H., D. Zhou, R. Bradley. P. Crabbé, O. Edenhofer, B.Hare, L. Kuijpers, M. Yamaguchi (2007). "Executive Summary". In B. Metz, O.R. Davidson, P.R. Bosch, R. Dave, L.A. Meyer. Introduction. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA. This version: IPCC website. ISBN 9780521880114. http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg3/en/ch1s1-es.html. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ Târziu DR, Păcurar VD (February 2011). "Forest, climate and energy". Revista pădurilor 125 (1): 34–40. http://www.revistapadurilor.ro/index.php?section=Article&ID=16720. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ PBL (25 June 2009). "Global CO2 emissions: annual increase halves in 2008". Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL) website. http://www.pbl.nl/en/publications/2009/Global-CO2-emissions-annual-increase-halves-in-2008.html. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ Carbon Trust (March 2009). "Global Carbon Mechanisms: Emerging lessons and implications (CTC748)". Carbon Trust website. http://www.carbontrust.co.uk/Publications/pages/publicationdetail.aspx?id=CTC748&respos=2&q=global+carbon+market&o=Rank&od=asc&pn=0&ps=10. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ^ PBL (24 February 2010). "Dossier Climate Change: FAQs. Question 10: Which are the top-20 CO2 or GHG emitting countries?". Netherlands Environment Agency website. http://www.pbl.nl/en/dossiers/Climatechange/FAQs/index.html?vraag=10&title=Which%20are%20the%20top-20%20CO2%20or%20GHG%20emitting%20countries%3F#10. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ^ MNP (2007). "Greenhouse gas emissions of countries in 2005 and ranking of their per capita emissions. Table 2.a. Top-20 countries of greenhouse emissions in 2006 from fossil fuels and cement production". Netherlands Environment Agency website. http://www.pbl.nl/images/Top20-CO2andGHG-countries-in2006-2005(GB)_tcm61-36276.xls. Retrieved 2010-05-01.[dead link]
- ^ Helm, D., et al. (10 December 2007). "Too Good To Be True? The UK's Climate Change Record" (PDF). Website of Dieter Helm, a professor at the University of Oxford and a Fellow of New College, Oxford. http://www.dieterhelm.co.uk/sites/default/files/Carbon_record_2007_0.pdf. Retrieved 2011-04-18.
- ^ Davis, S.K. and K. Caldeira (8 March 2010). "Consumption-based Accounting of CO2 Emissions". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107 (12): 5687. Bibcode 2010PNAS..107.5687D. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906974107. http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2010/02/23/0906974107.abstract. Retrieved 2011-04-18.
- ^ Rogner, H.-H., D. Zhou, R. Bradley. P. Crabbé, O. Edenhofer, B.Hare, L. Kuijpers, M. Yamaguchi (2007). 1.3.1.2 Intensities. In (book chapter): Introduction. In: Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (B. Metz, O.R. Davidson, P.R. Bosch, R. Dave, L.A. Meyer (eds)). Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA. This version: IPCC website. ISBN 9780521880114. http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/ar4/wg3/en/ch1s1-3-1-2.html. Retrieved 2010-05-05.
- ^ "Greenhouse Gas Emissions from a Typical Passenger Vehicle, US Environment Protection Agency". Epa.gov. http://www.epa.gov/oms/climate/420f05004.htm#step1. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ Engber, Daniel (2006-11-01). "How Gasoline Becomes CO2, Slate Magazine". Slate.com. http://www.slate.com/id/2152685/. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ "Volume calculation for carbon dioxide". Icbe.com. http://www.icbe.com/carbondatabase/CO2volumecalculation.asp. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ "Voluntary Reporting of Greenhouse Gases Program". Energy Information Administration. http://www.eia.doe.gov/oiaf/1605/coefficients.html. Retrieved 21 August 2009.
- ^ Obersteiner M, Azar C, Kauppi P et al. (October 2001). "Managing climate risk". Science 294 (5543): 786–7. doi:10.1126/science.294.5543.786b. PMID 11681318.
- ^ Azar, C., Lindgren, K., Larson, E.D. and Möllersten, K. (2006). "Carbon capture and storage from fossil fuels and biomass – Costs and potential role in stabilising the atmosphere". Climatic Change 74: 47–79. doi:10.1007/s10584-005-3484-7. http://www.environmental-expert.com/Files%5C6063%5Carticles%5C6220%5Cw30h4274h130580u.pdf.
- ^ a b c "Geoengineering the climate: science, governance and uncertainty". The Royal Society. 2009. http://royalsociety.org/displaypagedoc.asp?id=35151. Retrieved 12 September 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Fischer, B.S., N. Nakicenovic, K. Alfsen, J. Corfee Morlot, F. de la Chesnaye, J.-Ch. Hourcade, K. Jiang, M. Kainuma, E. La Rovere, A. Matysek, A. Rana, K. Riahi, R. Richels, S. Rose, D. van Vuuren, R. Warren, (2007)“Issues related to mitigation in the long term context”, In Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Inter-governmental Panel on Climate Change [B. Metz, O.R. Davidson, P.R. Bosch, R. Dave, L.A. Meyer (eds)], Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- ^ "Global Warming Opposing Viewpoints Paper". OPPapers. http://www.oppapers.com/essays/Global-Warming-Opposing-Viewpoints-Paper/733173?topic. Retrieved 12 September 2011.
External links
- Greenhouse gas at the Open Directory Project
- The NOAA Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI)
- Atmospheric spectra of GHGs and other trace gases
- How Much Greenhouse Gas Does the United States Emit?
- Grist article on convenient summary from various sources incl IPCC of greenhouse gas emissions * *
- Convenient summary of Greenhouse gas emissions
- Greenhouse Gases
- Greenhouse Gases Sources, Levels, Study results — University of Michigan; eia.doe.gov findings
- Carbon dioxide emissions
- Carbon Emissions World Map in 2009 Mark McCormick and Paul Scruton, The Guardian February 2011
- International Energy Annual: Reserves
- International Energy Annual 2003: Carbon Dioxide Emissions
- International Energy Annual 2003: Notes and Sources for Table H.1co2 (Metric tons of carbon dioxide can be converted to metric tons of carbon equivalent by multiplying by 12/44)
- Textbook on Eddy Covariance Measurements of Gas Emissions
- Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide (NOAA)
- NOAA Paleoclimatology Program — Vostok Ice Core
- NOAA CMDL CCGG — Interactive Atmospheric Data Visualization NOAA CO2 data
- Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Centre FAQ Includes links to Carbon Dioxide statistics
- Little Green Data Book 2007, World Bank. Lists CO2 statistics by country, including per capita and by country income class.
- Database of carbon emissions of power plants
- NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory
- The Carbon Bag: the carbon dioxide emission of a typical British home
- Methane emissions
- BBC News — Thawing Siberian bogs are releasing more methane
- Textbook on Eddy Covariance Measurements of Gas Emissions
Categories:- Climate change
- Climate forcing agents
- Greenhouse gases
- Millennium Development Goals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.