- Voltaic pile
-
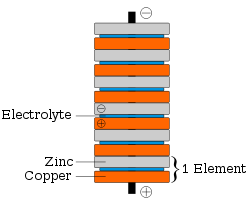
A voltaic pile is a set of individual Galvanic cells placed in series. The voltaic pile, invented by Alessandro Volta in 1800, was the first electric battery. Building on Galvani's 1780s discovery of how a circuit of two metals and a frog's leg can cause the frog's leg to respond, Volta demonstrated in 1791 that when two metals and brine-soaked cloth or cardboard are arranged in a circuit they produce an electric current. In 1800, Volta stacked several pairs of alternating copper (or silver) and zinc discs (electrodes) separated by cloth or cardboard soaked in brine (electrolyte) to increase the electrolyte conductivity.[1] When the top and bottom contacts were connected by a wire, an electric current flowed through the voltaic pile and the connecting wire.
Contents
Electromotive force
The strength of the pile is expressed in terms of its electromotive force, or emf, given in volts. Volta characterized the emf of a pair of metals in terms of the difference in their voltages, which he could measure. His theory of contact tension considered that the emf, which drives the electric current through a circuit containing a voltaic cell, occurs at the contact between the two metals. Sir Humphry Davy and Andrew Crosse were among the first to develop large voltaic piles.[2]
Applications
On March 20, 1800, Volta wrote to the London Royal Society to describe the technique for producing electric current using his pile. On learning of the voltaic pile, William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle used it to discover the electrolysis of water. Humphry Davy showed that the electromotive force, which drives the electric current through a circuit containing a single voltaic cell, was caused by a chemical reaction, not by the voltage difference between the two metals. He also used the voltaic pile to decompose chemicals and to produce new chemicals. William Hyde Wollaston showed that electricity from voltaic piles had identical effects to those of electricity produced by friction. In 1802 Vasily Petrov used voltaic piles in the discovery and research of electric arc effects.
Electrochemistry
Because Volta believed that the emf occurred at the contact between the two metals, Volta's piles had a different design than the modern design illustrated on this page. His piles had one extra disc of copper at the top, in contact with the zinc, and one extra disc of zinc at the bottom, in contact with the copper. Expanding on the work of his mentor Davy, in the early 1830s, Faraday studied voltaic cells in detail. This led to his founding of the area of electrochemistry. The words "electrode" and "electrolyte", used above to describe Volta's work, are due to Faraday.
Dry pile
A number of high-voltage dry piles were invented between the early 19th century and the 1830s in an attempt to determine the source of electricity of the wet voltaic pile, and specifically to support Volta’s hypothesis of contact tension. Indeed, Volta himself experimented with a pile whose cardboard discs had dried out, probably accidentally.
The first to publish was Johann Wilhelm Ritter in 1802, albeit in an obscure journal, but over the next decade, it was announced repeatedly as a new discovery. One form of dry pile is the Zamboni pile. The dry pile was the ancestor of the modern dry cell.
References
- ^ Paul Fleury Mottelay (2008). Bibliographical History of Electricity and Magnetism (Reprint of 1892 ed.). Read Books. p. 247. ISBN 1443728446. http://books.google.com/books?id=9vzti90Q8i0C&pg=PA246&lpg=RA1-PA247.
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica, 1911 edition, Volume V09, Page 185
External links
- Voltaic Pile - Interactive Java Tutorial National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
- "The invention of the Battery". Association for Overseas Technical Scholarship.
- "The Voltaic Pile". Electricity. Kenyon.edu.
- "A Voltaic Pile (c. 1800)". Professor Taylor's Ohm Page Featuring Grade Sheets & Less Important Matters.
- An Encyclopedia Article
- Lewis, Nancy D., "Alesandro Volta The Voltaic Pile".
- Lewis, Nancy D., "Humphry Davy Electrochemistry".
- "Battery Chemistry: Voltaic Pile. How Batteries Work. HowStuffWorks, Inc. 2004.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.